利用分治法解决凸包问题
凸包的意思就是包含所有给定点的凸多边形。
输入一组已经制定x,y坐标的点。输出是这组点的凸包。
例子:
Input : points[] = {(0, 0), (0, 4), (-4, 0), (5, 0), (0, -6), (1, 0)};
Output : (-4, 0), (5, 0), (0, -6), (0, 4)预备知识:
两个凸多边形之间的切线。
算法:
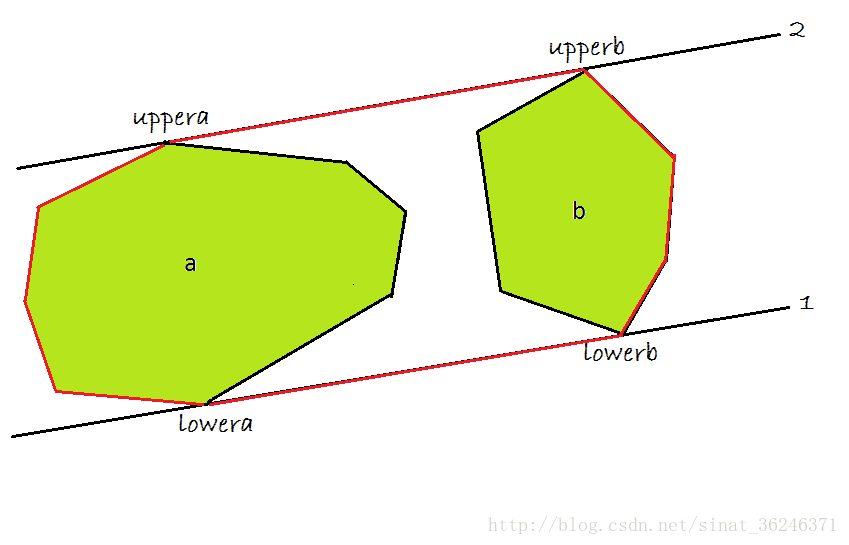
已知一个点集合,我们已经知道了它们的凸包。假设我们已经知道了左半部分和右半部分的凸包,那么现在的问题就变成了合并这两个凸包,并且确定整个集合的凸包。
这一步可以通过找到左右两个凸包的上下切线来搞定。这就是两个凸多边形之间的切线。
设左边的凸包为a,右边的凸包为b。于是下面的切线和上面的切线分别为1和2,如图所示。
然后红线画出了最后的凸包。
现在问题还没完全解决,我们如何才能找到左右整个的凸包呢?这里递归在图中出现了,我们可以把集合中的点分区,直到每个集合中的点的数目都非常小,例如5个点,然后我们就可以通过暴力法找到这个集合的凸包了。对于整个集合的点,在合并的过程中就可以得到整个凸包。
注意:
我们已经用暴力算法来得到小集合的点的凸包了,这一步的时间复杂度是 O(n3) 。但是有些人建议这么做,一个3个或者更少的点集的凸包就是整个点集。这个一般来说没问题,但是当我们要合并一个两个点的左凸包和3个点的右凸包的时候,在一些特殊情况下程序就会陷入无限的循环。所以为了解决这个问题,我们可以在 O(n3) 的时间内直接找到5个或者更少点的凸包,这个做法虽然数字大了点,但是不影响算法的整体时间复杂度。
// A divide and conquer program to find convex
// hull of a given set of points.
#include int , int>> merger(vectorint , int> > a,
vectorint , int> > b) {
// n1 -> number of points in polygon a
// n2 -> number of points in polygon b
int n1 = a.size(), n2 = b.size();
int ia = 0, ib = 0;
for (int i = 1; iif (a[i].first > a[ia].first)
ia = i;
// ib -> leftmost point of b
for (int i = 1; iif (b[i].first < b[ib].first)
ib = i;
// finding the upper tangent
int inda = ia, indb = ib;
bool done = 0;
while (!done) {
done = 1;
while (orientation(b[indb], a[inda], a[(inda + 1) % n1]) >= 0)
inda = (inda + 1) % n1;
while (orientation(a[inda], b[indb], b[(n2 + indb - 1) % n2]) <= 0) {
indb = (n2 + indb - 1) % n2;
done = 0;
}
}
int uppera = inda, upperb = indb;
inda = ia, indb = ib;
done = 0;
int g = 0;
while (!done)//finding the lower tangent
{
done = 1;
while (orientation(a[inda], b[indb], b[(indb + 1) % n2]) >= 0)
indb = (indb + 1) % n2;
while (orientation(b[indb], a[inda], a[(n1 + inda - 1) % n1]) <= 0) {
inda = (n1 + inda - 1) % n1;
done = 0;
}
}
int lowera = inda, lowerb = indb;
vectorint , int>> ret;
//ret contains the convex hull after merging the two convex hulls
//with the points sorted in anti-clockwise order
int ind = uppera;
ret.push_back(a[uppera]);
while (ind != lowera) {
ind = (ind + 1) % n1;
ret.push_back(a[ind]);
}
ind = lowerb;
ret.push_back(b[lowerb]);
while (ind != upperb) {
ind = (ind + 1) % n2;
ret.push_back(b[ind]);
}
return ret;
}
// Brute force algorithm to find convex hull for a set
// of less than 6 points
vectorint , int>> bruteHull(vectorint , int>> a) {
// Take any pair of points from the set and check
// whether it is the edge of the convex hull or not.
// if all the remaining points are on the same side
// of the line then the line is the edge of convex
// hull otherwise not
setint , int> > s;
for (int i = 0; ifor (int j = i + 1; jint x1 = a[i].first, x2 = a[j].first;
int y1 = a[i].second, y2 = a[j].second;
int a1 = y1 - y2;
int b1 = x2 - x1;
int c1 = x1*y2 - y1*x2;
int pos = 0, neg = 0;
for (int k = 0; kif (a1*a[k].first + b1*a[k].second + c1 <= 0)
neg++;
if (a1*a[k].first + b1*a[k].second + c1 >= 0)
pos++;
}
if (pos == a.size() || neg == a.size()) {
s.insert(a[i]);
s.insert(a[j]);
}
}
}
vectorint , int>>ret;
for (auto e : s)
ret.push_back(e);
// Sorting the points in the anti-clockwise order
mid = { 0, 0 };
int n = ret.size();
for (int i = 0; ifor (int i = 0; ireturn ret;
}
// Returns the convex hull for the given set of points
vectorint , int>> divide(vectorint , int>> a) {
// If the number of points is less than 6 then the
// function uses the brute algorithm to find the
// convex hull
if (a.size() <= 5)
return bruteHull(a);
// left contains the left half points
// right contains the right half points
vectorint , int>>left, right;
for (int i = 0; i2; i++)
left.push_back(a[i]);
for (int i = a.size() / 2; i// convex hull for the left and right sets
vectorint , int>>left_hull = divide(left);
vectorint , int>>right_hull = divide(right);
// merging the convex hulls
return merger(left_hull, right_hull);
}
// Driver code
int main() {
vectorint , int> > a;
a.push_back(make_pair(0, 0));
a.push_back(make_pair(1, -4));
a.push_back(make_pair(-1, -5));
a.push_back(make_pair(-5, -3));
a.push_back(make_pair(-3, -1));
a.push_back(make_pair(-1, -3));
a.push_back(make_pair(-2, -2));
a.push_back(make_pair(-1, -1));
a.push_back(make_pair(-2, -1));
a.push_back(make_pair(-1, 1));
int n = a.size();
// sorting the set of points according
// to the x-coordinate
sort(a.begin(), a.end());
vectorint , int> >ans = divide(a);
cout << "convex hull:\n";
for (auto e : ans)
cout << e.first << " "
<< e.second << endl;
return 0;
} 输出:
Convex Hull:
-5 -3
-1 -5
1 -4
0 0
-1 1时间复杂度:
因为我们要把点集分成两个相等的部分,所以合并左右凸包的时间复杂度是 O(n) ,所以上述算法时间复杂度是 O(nlogn) 。
相关文章:
Convex Hull | Set 1 (Jarvis’s Algorithm or Wrapping)
Convex Hull | Set 2 (Graham Scan)
Quickhull Algorithm for Convex Hull