java8新特性(九):CompletableFuture多线程并发异步编程
首先因为现在的应用越来越复杂,越来越多模块多系统之间相互依赖,一个操作可能需要使用多个模块或者多个系统提供的多个服务来完成一个功能,如果每个服务顺序的执行,可能需要消耗很多时间,或者前端用户需要得到及时响应,不需要等待所有服务完成便可以返回部分结果,而且现在的计算机处理器性能越来越强大,多核处理器越来越普遍,核心数也越来越多,使用多线程可以更加充分利用硬件的资源,不论是什么原因异步编程应运而生。
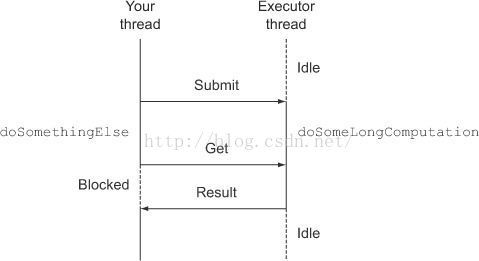
先看一下使用JDK5的Future接口简单的实现异步编程
代码
//创建ExecutorService,并且通过它向线程池提交任务
ExecutorService executorService = Executors. newCachedThreadPool();
//向线程池提交任务
Future future = executorService.submit( new Callable() {
@Override
public Double call() throws Exception {
return doSomeLongTime();
}
});
//当前线程继续做其他事情
doSomeElse();
//获取异步操作的结果
try {
double result = ( double)future.get( 1,TimeUnit. SECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
//线程被中断
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
//线程抛出异常
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
//线程超时
e.printStackTrace();
}
ExecutorService executorService = Executors. newCachedThreadPool();
//向线程池提交任务
Future future = executorService.submit( new Callable
@Override
public Double call() throws Exception {
return doSomeLongTime();
}
});
//当前线程继续做其他事情
doSomeElse();
//获取异步操作的结果
try {
double result = ( double)future.get( 1,TimeUnit. SECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
//线程被中断
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
//线程抛出异常
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
//线程超时
e.printStackTrace();
}
示意图
既然要讲CompletableFuture那么明显Future接口肯定有很多局限性, 我们需要更多的特性:
1. 将两个异步计算的结果组合成一个结果,并且这两个异步计算时相互独立的在不同到线程中,并且第二个计算依赖第一个计算。
2. 等待所有异步任务的完成。
3. 等待所有异步任务中任意一个完成并且获得计算结果。
4.编程式的完成异步任务。(手动提供一个结果)
5.异步任务完成响应事件。
CompletableFuture实现异步编程:
public class Shop {
private String name;
private Random random = new Random();
public Shop(String name) {
this. name = name;
}
//直接获取价格
public double getPrice(String product){
return calculatePrice(product);
}
//模拟延迟
public static void delay(){
try {
Thread. sleep( 1000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//模拟获取价格的服务
private double calculatePrice(String product){
delay();
return random.nextDouble() * product.charAt( 0) + product.charAt( 1);
}
//异步获取价格
public Future getPriceAsync(String product){
CompletableFuture future =
new CompletableFuture<>();
new Thread(() -> {
double price = calculatePrice(product);
future.complete(price);
}).start();
return future;
}
}
private String name;
private Random random = new Random();
public Shop(String name) {
this. name = name;
}
//直接获取价格
public double getPrice(String product){
return calculatePrice(product);
}
//模拟延迟
public static void delay(){
try {
Thread. sleep( 1000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//模拟获取价格的服务
private double calculatePrice(String product){
delay();
return random.nextDouble() * product.charAt( 0) + product.charAt( 1);
}
//异步获取价格
public Future
CompletableFuture
new Thread(() -> {
double price = calculatePrice(product);
future.complete(price);
}).start();
return future;
}
}
调用异步接口:
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args){
Shop shop =
new Shop(
"BestShop");
long start = System.
currentTimeMillis();
Future future = shop.getPriceAsync(
"My Favorite");
long invocationTime = System. currentTimeMillis() - start;
System. out.println( "调用接口时间:" + invocationTime + "毫秒");
doSomethingElse();
try {
double price = future.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
long retrievalTime = System. currentTimeMillis() - start;
System. out.println( "返回价格消耗时间:" + retrievalTime + "毫秒");
}
public static void doSomethingElse(){
System. out.println( "做其他的事情。。。");
}
}
Future
long invocationTime = System. currentTimeMillis() - start;
System. out.println( "调用接口时间:" + invocationTime + "毫秒");
doSomethingElse();
try {
double price = future.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
long retrievalTime = System. currentTimeMillis() - start;
System. out.println( "返回价格消耗时间:" + retrievalTime + "毫秒");
}
public static void doSomethingElse(){
System. out.println( "做其他的事情。。。");
}
}
打印结果:
调用接口时间:127毫秒
做其他的事情。。。
返回价格消耗时间:1127毫秒
并行操作 Streams 和CompletableFutures 比较
1. 如果有大量计算的操作而没有I/O 操作(包括连接互联网),那么使用异步的
Streams 可以得到最好的性能。
2. 相反如果有很多io操作, 使用
CompletableFutures可以得到更好的编弹性。
parallelStream的并行操作:
public static void main(String[] args){
long start = System. currentTimeMillis();
System. out.println( findPrice( "java8实战"));
long duration = System. currentTimeMillis() - start;
System. out.println( "总消耗时间:" + duration + "毫秒");
}
public static List findPrice(String product){
List shops = Arrays.
asList(
new Shop(
"sunjin.org"),
new Shop( "加瓦匠"),
new Shop( "京东商城"),
new Shop( "天猫商城"));
return shops.parallelStream()
.map(shop -> String. format( "%s 的价格是 %.2f", shop.getName(),shop.getPrice(product)))
.collect(Collectors. toList());
}
long start = System. currentTimeMillis();
System. out.println( findPrice( "java8实战"));
long duration = System. currentTimeMillis() - start;
System. out.println( "总消耗时间:" + duration + "毫秒");
}
public static List
List
new Shop( "加瓦匠"),
new Shop( "京东商城"),
new Shop( "天猫商城"));
return shops.parallelStream()
.map(shop -> String. format( "%s 的价格是 %.2f", shop.getName(),shop.getPrice(product)))
.collect(Collectors. toList());
}
执行结果:
[sunjin.org 的价格是 177.48, 加瓦匠 的价格是 189.90, 京东商城 的价格是 155.85, 天猫商城 的价格是 163.67]
总消耗时间:1207毫秒
CompletableFuture的并行操作
public static List findPrice2(String product){
List> priceFuture =
shops.stream()
.map(shop -> CompletableFuture. supplyAsync( // 使用异步的方式计算每种商品的价格
() -> shop.getName() + " 的价格是 " + shop.getPrice(product)))
.collect( toList());
return priceFuture.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join) //join 操作等待所有异步操作的结果
.collect( toList());
}
List
.map(shop -> CompletableFuture. supplyAsync( // 使用异步的方式计算每种商品的价格
() -> shop.getName() + " 的价格是 " + shop.getPrice(product)))
.collect( toList());
return priceFuture.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join) //join 操作等待所有异步操作的结果
.collect( toList());
}
long start = System.
currentTimeMillis();
System. out.println( findPrice2( "java8实战"));
long duration = System. currentTimeMillis() - start;
System. out.println( findPrice2( "java8实战"));
long duration = System. currentTimeMillis() - start;
System.out.println("总消耗时间:" + duration + "毫秒");
执行结果:
[sunjin.org 的价格是 163.26300732704362, 加瓦匠 的价格是 172.3990021133357, 京东商城 的价格是 143.43284048828846, 天猫商城 的价格是 139.768245677111]
总消耗时间:2235毫秒
很明显这个操作比parallelStream慢了一倍
多个任务的流水线操作
获取价格字符串
public String getPrice2(String product){
double price = calculatePrice(product);
Discount.Code code = Discount.Code. values()[ random.nextInt(Discount.Code. values(). length)];
return String. format( "s%:%.2f:%s", name, price, code);
double price = calculatePrice(product);
Discount.Code code = Discount.Code. values()[ random.nextInt(Discount.Code. values(). length)];
return String. format( "s%:%.2f:%s", name, price, code);
}
解析价格字符串的报价类
public class Quote {
private final String shopName;
private final double price;
private final Discount.Code code;
public Quote(String shopName, double price, Discount.Code code) {
this. shopName = shopName;
this. price = price;
this. code = code;
}
public String getShopName() {
return shopName;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public Discount.Code getCode() {
return code;
}
public static Quote parse(String s){
String[] arr = s.split( ":");
return new Quote(arr[ 0], Double. valueOf(arr[ 1]), Discount.Code. valueOf(arr[ 2]));
}
private final String shopName;
private final double price;
private final Discount.Code code;
public Quote(String shopName, double price, Discount.Code code) {
this. shopName = shopName;
this. price = price;
this. code = code;
}
public String getShopName() {
return shopName;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public Discount.Code getCode() {
return code;
}
public static Quote parse(String s){
String[] arr = s.split( ":");
return new Quote(arr[ 0], Double. valueOf(arr[ 1]), Discount.Code. valueOf(arr[ 2]));
}
}
折扣类型,包含枚举类型 和应用报价的方法。
public class Discount {
public enum Code{
NONE( 0), SILVER( 5), GOLD( 10), PLATINUM( 15), DIAMOND( 20);
private final int percentage;
Code( int percentage){
this. percentage = percentage;
}
}
public static String applyDiscount(Quote quote){
return quote.getShopName() + " price is " + Discount. apply(quote.getPrice(),quote.getCode());
}
public static double apply( double price, Code code){
delay();
return price * ( 100 - code. percentage) / 100 ;
}
public static void delay(){
try {
Thread. sleep( 1000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public enum Code{
NONE( 0), SILVER( 5), GOLD( 10), PLATINUM( 15), DIAMOND( 20);
private final int percentage;
Code( int percentage){
this. percentage = percentage;
}
}
public static String applyDiscount(Quote quote){
return quote.getShopName() + " price is " + Discount. apply(quote.getPrice(),quote.getCode());
}
public static double apply( double price, Code code){
delay();
return price * ( 100 - code. percentage) / 100 ;
}
public static void delay(){
try {
Thread. sleep( 1000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static List findPrice3(String product){
return shops.stream()
.map(shop -> shop.getPrice2(product)) //获取原始报价
.map(Quote:: parse) //解析报价字符串
.map(Discount:: applyDiscount) //调用折扣服务应用报价折扣
.collect( toList());
return shops.stream()
.map(shop -> shop.getPrice2(product)) //获取原始报价
.map(Quote:: parse) //解析报价字符串
.map(Discount:: applyDiscount) //调用折扣服务应用报价折扣
.collect( toList());
}
getPrice 请求耗时1秒, applyDiscount请求耗时1秒, 这是同步方法调用, 由于Stream中间操作的延迟性, 应用
五个商店,
这个方法整体将会耗时10秒。
使用CompletableFuture
s异步操作
public static List findPrice4(String product){
List> priceFuture =
shops.stream()
.map(shop -> CompletableFuture. supplyAsync( // 异步获取价格
() -> shop.getPrice2(product), executor))
.map(future -> future.thenApply(Quote:: parse)) // 获取到价格后对价格解析
.map(future -> future.thenCompose(quote -> CompletableFuture. supplyAsync( // 另一个异步任务构造异步应用报价
() -> Discount. applyDiscount(quote), executor)))
.collect( toList());
return priceFuture.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join) //join 操作和get操作有相同的含义,等待所有异步操作的结果。
.collect( toList());
}
List
.map(shop -> CompletableFuture. supplyAsync( // 异步获取价格
() -> shop.getPrice2(product), executor))
.map(future -> future.thenApply(Quote:: parse)) // 获取到价格后对价格解析
.map(future -> future.thenCompose(quote -> CompletableFuture. supplyAsync( // 另一个异步任务构造异步应用报价
() -> Discount. applyDiscount(quote), executor)))
.collect( toList());
return priceFuture.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join) //join 操作和get操作有相同的含义,等待所有异步操作的结果。
.collect( toList());
}
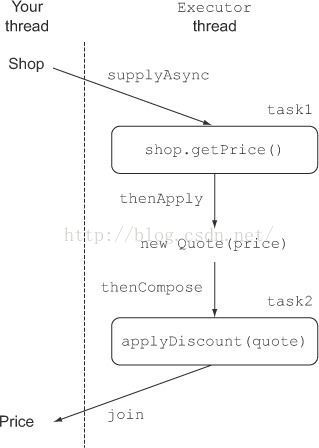
这是用
CompletableFuture 的实现, 是异步的调用,但是
Stream中间操作的延迟性依然存在, 仍然应用五个商店,
获取报价 解析报价 应用报价 这三个操作是顺序的,但是5个商店的任务是并行的,所以整个耗时2秒。
构造同步操作和异步任务示意图
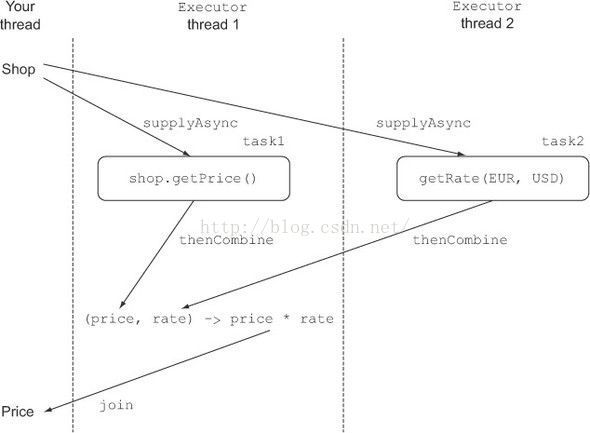
如果两个异步操作是相互独立的
List> priceFuture =
shops.stream()
.map(shop -> CompletableFuture. supplyAsync( // 异步获取价格
() -> shop.getPrice(product), executor))
.map(future -> future.thenCombine(CompletableFuture. supplyAsync( // 异步获取折扣率
() -> Discount. getRate(), executor)
, (price, rate) -> price * rate)) // 将两个异步任务的结果合并
.map(shop -> CompletableFuture. supplyAsync( // 异步获取价格
() -> shop.getPrice(product), executor))
.map(future -> future.thenCombine(CompletableFuture. supplyAsync( // 异步获取折扣率
() -> Discount. getRate(), executor)
, (price, rate) -> price * rate)) // 将两个异步任务的结果合并
.collect(toList());
将两个独立的
CompletableFuture
s组合,因为操作是并行的,任务也是并行的,所以最终5个商店10个操作将在1秒左右执行结束。