Linux驱动开发—— input子系统
我们平时使用的按键、鼠标、键盘、触摸屏等都属于输入(input)设备, Linux 内核专门有一个叫做 input子系统的框架来处理输入事件。输入设备本质上还是字符设备,只是在此基础上套上了 input 框架,用户只需要负责上报输入事件,比如按键值、坐标等信息, input 核心层负责处理这些事件。input输入子系统分为3层:上层(input事件驱动层)、中层(input核心层)、下层(input设备驱动层),如下图所示:
图中Drivers对应的就是下层input设备驱动层,对应各种各样不同的输入设备,Input Core对应的就是中层input核心层,Handlers对应的就是上层input事件驱动层,最右边代表的是用户空间。这三个层的分工如下:
input设备驱动层:输入设备的具体驱动程序,比如按键驱动程序,向内核报告输入内容。
input核心层:承上启下,为input设备驱动层提供输入设备注册和操作接口。通知input事件驱动层对输入事件进行处理。
input事件驱动层:主要和用户空间进行交互。
input子系统解决了不同的输入类设备的输入事件与应用层之间的数据传输,使得应用层能够获取到各种不同输入设备的输入事件,input输入子系统能够囊括所有的不同种类的输入设备,在应用层都能够感知到所有发生的输入事件。
相关源码分析:
input输入子系统中的所有源码都放在 drivers\input 这个目录中,input.c文件是核心层的源代码文件。在input目录中还可以看到一些文件夹,例如gameport、joystick、keyboard、misc、mouse等等。
这些文件夹里面存放的是属于这类input输入设备的设备驱动源代码,可以理解为input输入子系统的下层(input设备驱动层)。
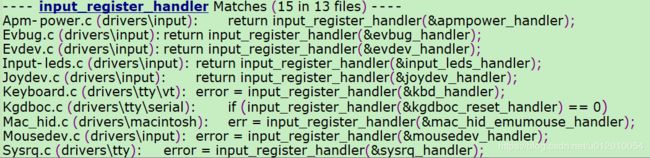
input目录下的evdev.c、joydev.c、mousedev.c等分别对应上层(input事件驱动层)的各个不同的handler的源代码:
一、input核心层
input核心层会向Linux内核注册一个字符设备,input.c就是input输入子系统的核心层,位于drivers/input目录下。
相关数据结构:
struct class input_class = {
.name = "input",
.devnode = input_devnode,
}; * struct input_dev - represents an input device
* @name: name of the device
* @phys: physical path to the device in the system hierarchy
* @uniq: unique identification code for the device (if device has it)
* @id: id of the device (struct input_id)
* @propbit: bitmap of device properties and quirks
* @evbit: bitmap of types of events supported by the device (EV_KEY,
* EV_REL, etc.)
* @keybit: bitmap of keys/buttons this device has
* @relbit: bitmap of relative axes for the device
* @absbit: bitmap of absolute axes for the device
* @mscbit: bitmap of miscellaneous events supported by the device
* @ledbit: bitmap of leds present on the device
* @sndbit: bitmap of sound effects supported by the device
* @ffbit: bitmap of force feedback effects supported by the device
* @swbit: bitmap of switches present on the device
* @hint_events_per_packet: average number of events generated by the
* device in a packet (between EV_SYN/SYN_REPORT events). Used by
* event handlers to estimate size of the buffer needed to hold
* events.
* @keycodemax: size of keycode table
* @keycodesize: size of elements in keycode table
* @keycode: map of scancodes to keycodes for this device
* @getkeycode: optional legacy method to retrieve current keymap.
* @setkeycode: optional method to alter current keymap, used to implement
* sparse keymaps. If not supplied default mechanism will be used.
* The method is being called while holding event_lock and thus must
* not sleep
* @ff: force feedback structure associated with the device if device
* supports force feedback effects
* @repeat_key: stores key code of the last key pressed; used to implement
* software autorepeat
* @timer: timer for software autorepeat
* @rep: current values for autorepeat parameters (delay, rate)
* @mt: pointer to multitouch state
* @absinfo: array of &struct input_absinfo elements holding information
* about absolute axes (current value, min, max, flat, fuzz,
* resolution)
* @key: reflects current state of device's keys/buttons
* @led: reflects current state of device's LEDs
* @snd: reflects current state of sound effects
* @sw: reflects current state of device's switches
* @open: this method is called when the very first user calls
* input_open_device(). The driver must prepare the device
* to start generating events (start polling thread,
* request an IRQ, submit URB, etc.)
* @close: this method is called when the very last user calls
* input_close_device().
* @flush: purges the device. Most commonly used to get rid of force
* feedback effects loaded into the device when disconnecting
* from it
* @event: event handler for events sent _to_ the device, like EV_LED
* or EV_SND. The device is expected to carry out the requested
* action (turn on a LED, play sound, etc.) The call is protected
* by @event_lock and must not sleep
* @grab: input handle that currently has the device grabbed (via
* EVIOCGRAB ioctl). When a handle grabs a device it becomes sole
* recipient for all input events coming from the device
* @event_lock: this spinlock is is taken when input core receives
* and processes a new event for the device (in input_event()).
* Code that accesses and/or modifies parameters of a device
* (such as keymap or absmin, absmax, absfuzz, etc.) after device
* has been registered with input core must take this lock.
* @mutex: serializes calls to open(), close() and flush() methods
* @users: stores number of users (input handlers) that opened this
* device. It is used by input_open_device() and input_close_device()
* to make sure that dev->open() is only called when the first
* user opens device and dev->close() is called when the very
* last user closes the device
* @going_away: marks devices that are in a middle of unregistering and
* causes input_open_device*() fail with -ENODEV.
* @dev: driver model's view of this device
* @h_list: list of input handles associated with the device. When
* accessing the list dev->mutex must be held
* @node: used to place the device onto input_dev_list
* @num_vals: number of values queued in the current frame
* @max_vals: maximum number of values queued in a frame
* @vals: array of values queued in the current frame
* @devres_managed: indicates that devices is managed with devres framework
* and needs not be explicitly unregistered or freed.
*/
struct input_dev {
const char *name; //input设备的名字
const char *phys;
const char *uniq;
struct input_id id;
/*
这些是用来表示该input设备能够上报的事件类型有哪些
用位的方式来表示
*/
unsigned long propbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(INPUT_PROP_CNT)];
//事件类型的定义在input-event-codes.h (include\uapi\linux)
unsigned long evbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(EV_CNT)]; //evbit 表示输入事件类型
unsigned long keybit[BITS_TO_LONGS(KEY_CNT)];
unsigned long relbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(REL_CNT)];
unsigned long absbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(ABS_CNT)];
unsigned long mscbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(MSC_CNT)];
unsigned long ledbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(LED_CNT)];
unsigned long sndbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(SND_CNT)];
unsigned long ffbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(FF_CNT)];
unsigned long swbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(SW_CNT)];
unsigned int hint_events_per_packet;
unsigned int keycodemax;
unsigned int keycodesize;
void *keycode;
int (*setkeycode)(struct input_dev *dev,
const struct input_keymap_entry *ke,
unsigned int *old_keycode);
int (*getkeycode)(struct input_dev *dev,
struct input_keymap_entry *ke);
struct ff_device *ff;
unsigned int repeat_key;
struct timer_list timer;
int rep[REP_CNT];
struct input_mt *mt;
struct input_absinfo *absinfo;
unsigned long key[BITS_TO_LONGS(KEY_CNT)];
unsigned long led[BITS_TO_LONGS(LED_CNT)];
unsigned long snd[BITS_TO_LONGS(SND_CNT)];
unsigned long sw[BITS_TO_LONGS(SW_CNT)];
int (*open)(struct input_dev *dev);
void (*close)(struct input_dev *dev);
int (*flush)(struct input_dev *dev, struct file *file);
int (*event)(struct input_dev *dev, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value); //上报事件函数
struct input_handle __rcu *grab;
spinlock_t event_lock;
struct mutex mutex;
unsigned int users;
bool going_away;
struct device dev; //内置的device结构体变量
struct list_head h_list; //用来挂接input_dev 设备连接的所有handle 的一个链表头
struct list_head node; //作为链表节点挂接到 input_dev_list 链表上 (input_dev_list链表是input核心层维护的一个用来挂接所有input设备的一个链表头)
unsigned int num_vals;
unsigned int max_vals;
struct input_value *vals;
bool devres_managed;
};/**
* struct input_handler - implements one of interfaces for input devices
* @private: driver-specific data
* @event: event handler. This method is being called by input core with
* interrupts disabled and dev->event_lock spinlock held and so
* it may not sleep
* @events: event sequence handler. This method is being called by
* input core with interrupts disabled and dev->event_lock
* spinlock held and so it may not sleep
* @filter: similar to @event; separates normal event handlers from
* "filters".
* @match: called after comparing device's id with handler's id_table
* to perform fine-grained matching between device and handler
* @connect: called when attaching a handler to an input device
* @disconnect: disconnects a handler from input device
* @start: starts handler for given handle. This function is called by
* input core right after connect() method and also when a process
* that "grabbed" a device releases it
* @legacy_minors: set to %true by drivers using legacy minor ranges
* @minor: beginning of range of 32 legacy minors for devices this driver
* can provide
* @name: name of the handler, to be shown in /proc/bus/input/handlers
* @id_table: pointer to a table of input_device_ids this driver can
* handle
* @h_list: list of input handles associated with the handler
* @node: for placing the driver onto input_handler_list
*
* Input handlers attach to input devices and create input handles. There
* are likely several handlers attached to any given input device at the
* same time. All of them will get their copy of input event generated by
* the device.
*
* The very same structure is used to implement input filters. Input core
* allows filters to run first and will not pass event to regular handlers
* if any of the filters indicate that the event should be filtered (by
* returning %true from their filter() method).
*
* Note that input core serializes calls to connect() and disconnect()
* methods.
*/
struct input_handler {
void *private;
void (*event)(struct input_handle *handle, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value); //用于向上层上报输入事件的函数
void (*events)(struct input_handle *handle,
const struct input_value *vals, unsigned int count);
bool (*filter)(struct input_handle *handle, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value);
bool (*match)(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev); //match 函数用来匹配handler与input_dev设备
int (*connect)(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev, const struct input_device_id *id);
void (*disconnect)(struct input_handle *handle);
void (*start)(struct input_handle *handle);
bool legacy_minors;
int minor;
const char *name;
const struct input_device_id *id_table;
struct list_head h_list; //用来挂接handler上连接的所有handle的一个链表头
struct list_head node; //作为一个链表节点挂接到input_handler_list链表上
};/**
* struct input_handle - links input device with an input handler
* @private: handler-specific data
* @open: counter showing whether the handle is 'open', i.e. should deliver
* events from its device
* @name: name given to the handle by handler that created it
* @dev: input device the handle is attached to
* @handler: handler that works with the device through this handle
* @d_node: used to put the handle on device's list of attached handles
* @h_node: used to put the handle on handler's list of handles from which
* it gets events
*/
struct input_handle {
void *private;
int open; //用来做打开计数
const char *name;
struct input_dev *dev; //用来指向该handle绑定的input_dev结构体
struct input_handler *handler; //用来指向该handle绑定的handler结构体
struct list_head d_node; //作为一个链表节点挂接到与他绑定的input_dev->hlist链表上
struct list_head h_node; //作为一个链表节点挂接到与他绑定的handler->hlist链表上
};/*
* Event types
*/
#define EV_SYN 0x00 //同步事件
#define EV_KEY 0x01 //按键事件
#define EV_REL 0x02 //相对坐标事件
#define EV_ABS 0x03 //绝对坐标事件
#define EV_MSC 0x04 //杂项(其他)事件
#define EV_SW 0x05 //开关事件
#define EV_LED 0x11 //LED
#define EV_SND 0x12 //sound(声音)
#define EV_REP 0x14 //重复事件
#define EV_FF 0x15 //压力事件
#define EV_PWR 0x16 //电源事件
#define EV_FF_STATUS 0x17 //压力状态事件
#define EV_MAX 0x1f
#define EV_CNT (EV_MAX+1)
input核心层为上下两层提供了如下几个比较重要的函数:
1. input设备驱动层:
1.1 input_allocate_device
/**
* input_allocate_device - allocate memory for new input device
*
* Returns prepared struct input_dev or %NULL.
*
* NOTE: Use input_free_device() to free devices that have not been
* registered; input_unregister_device() should be used for already
* registered devices.
*/
struct input_dev *input_allocate_device(void)
{
static atomic_t input_no = ATOMIC_INIT(-1);
struct input_dev *dev;
dev = kzalloc(sizeof(struct input_dev), GFP_KERNEL); //申请分配内存
if (dev) {
dev->dev.type = &input_dev_type; //确定input设备的设备类型
dev->dev.class = &input_class; //确定input设备所属的设备类
device_initialize(&dev->dev);
mutex_init(&dev->mutex);
spin_lock_init(&dev->event_lock);
init_timer(&dev->timer);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->h_list); //input_dev->h_list 链表初始化
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->node); //input_dev->node 链表初始化
dev_set_name(&dev->dev, "input%lu",
(unsigned long)atomic_inc_return(&input_no));
__module_get(THIS_MODULE);
}
return dev;
}1.2 input_register_device
/**
* input_register_device - register device with input core
* @dev: device to be registered
*
* This function registers device with input core. The device must be
* allocated with input_allocate_device() and all it's capabilities
* set up before registering.
* If function fails the device must be freed with input_free_device().
* Once device has been successfully registered it can be unregistered
* with input_unregister_device(); input_free_device() should not be
* called in this case.
*
* Note that this function is also used to register managed input devices
* (ones allocated with devm_input_allocate_device()). Such managed input
* devices need not be explicitly unregistered or freed, their tear down
* is controlled by the devres infrastructure. It is also worth noting
* that tear down of managed input devices is internally a 2-step process:
* registered managed input device is first unregistered, but stays in
* memory and can still handle input_event() calls (although events will
* not be delivered anywhere). The freeing of managed input device will
* happen later, when devres stack is unwound to the point where device
* allocation was made.
*/
int input_register_device(struct input_dev *dev)
{
struct input_devres *devres = NULL;
struct input_handler *handler; //定义一个 input_handler 结构体指针
unsigned int packet_size;
const char *path;
int error;
if (dev->devres_managed) {
devres = devres_alloc(devm_input_device_unregister,
sizeof(struct input_devres), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!devres)
return -ENOMEM;
devres->input = dev;
}
/* Every input device generates EV_SYN/SYN_REPORT events. */
__set_bit(EV_SYN, dev->evbit);
/* KEY_RESERVED is not supposed to be transmitted to userspace. */
__clear_bit(KEY_RESERVED, dev->keybit);
/* Make sure that bitmasks not mentioned in dev->evbit are clean. */
input_cleanse_bitmasks(dev);
packet_size = input_estimate_events_per_packet(dev);
if (dev->hint_events_per_packet < packet_size)
dev->hint_events_per_packet = packet_size;
dev->max_vals = dev->hint_events_per_packet + 2;
dev->vals = kcalloc(dev->max_vals, sizeof(*dev->vals), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!dev->vals) {
error = -ENOMEM;
goto err_devres_free;
}
/*
* If delay and period are pre-set by the driver, then autorepeating
* is handled by the driver itself and we don't do it in input.c.
*/
if (!dev->rep[REP_DELAY] && !dev->rep[REP_PERIOD])
input_enable_softrepeat(dev, 250, 33);
if (!dev->getkeycode)
dev->getkeycode = input_default_getkeycode;
if (!dev->setkeycode)
dev->setkeycode = input_default_setkeycode;
error = device_add(&dev->dev) //添加设备, 例如: /sys/devices/virtual/input/input0
if (error)
goto err_free_vals;
path = kobject_get_path(&dev->dev.kobj, GFP_KERNEL); //获取input设备对象所在的路径/sys/devices/virtual/input/input_xxx
pr_info("%s as %s\n",
dev->name ? dev->name : "Unspecified device",
path ? path : "N/A");
kfree(path);
error = mutex_lock_interruptible(&input_mutex);
if (error)
goto err_device_del;
list_add_tail(&dev->node, &input_dev_list); //链表挂接: 将input_dev->node作为节点挂接到input_dev_list链表上
list_for_each_entry(handler, &input_handler_list, node) //遍历input_handler_list 链表上的所有handler
input_attach_handler(dev, handler); //将handler与input设备进行匹配:根据input_handler的id_table判断能否支持这个input_dev
input_wakeup_procfs_readers(); //更新proc文件系统
mutex_unlock(&input_mutex);
if (dev->devres_managed) {
dev_dbg(dev->dev.parent, "%s: registering %s with devres.\n",
__func__, dev_name(&dev->dev));
devres_add(dev->dev.parent, devres);
}
return 0;
err_device_del:
device_del(&dev->dev);
err_free_vals:
kfree(dev->vals);
dev->vals = NULL;
err_devres_free:
devres_free(devres);
return error;
}1.3 input_attach_handler
static int input_attach_handler(struct input_dev *dev, struct input_handler *handler)
{
const struct input_device_id *id; //定义一个input_device_id 的指针
int error;
id = input_match_device(handler, dev); //通过这个函数进行handler与input设备的匹配工作
if (!id)
return -ENODEV;
error = handler->connect(handler, dev, id); //匹配成功则调用handler中的connect函数进行连接
if (error && error != -ENODEV)
pr_err("failed to attach handler %s to device %s, error: %d\n",
handler->name, kobject_name(&dev->dev.kobj), error);
return error;
}2. input事件驱动层:
2.1 input_register_handler
/**
* input_register_handler - register a new input handler
* @handler: handler to be registered
*
* This function registers a new input handler (interface) for input
* devices in the system and attaches it to all input devices that
* are compatible with the handler.
*/
int input_register_handler(struct input_handler *handler) //向核心层注册handler
{
struct input_dev *dev;
int error;
error = mutex_lock_interruptible(&input_mutex);
if (error)
return error;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&handler->h_list); //初始化handler->h_list 链表
list_add_tail(&handler->node, &input_handler_list); //将handler 通过handler -> node节点 挂接到input_handler_list 链表上
list_for_each_entry(dev, &input_dev_list, node) //遍历 input_dev_list 链表下挂接的所有的 input_dev 设备
input_attach_handler(dev, handler); //将handler与input设备进行匹配:根据input_handler的id_table判断能否支持这个input_dev
input_wakeup_procfs_readers(); //更新proc 文件系统
mutex_unlock(&input_mutex);
return 0;
}2.2 input_register_handle
/**
* input_register_handle - register a new input handle
* @handle: handle to register
*
* This function puts a new input handle onto device's
* and handler's lists so that events can flow through
* it once it is opened using input_open_device().
*
* This function is supposed to be called from handler's
* connect() method.
*/
int input_register_handle(struct input_handle *handle)
{
struct input_handler *handler = handle->handler; //evdev->handle->handler
struct input_dev *dev = handle->dev; //evdev->handle->dev
int error;
/*
* We take dev->mutex here to prevent race with
* input_release_device().
*/
error = mutex_lock_interruptible(&dev->mutex);
if (error)
return error;
/*
* Filters go to the head of the list, normal handlers
* to the tail.
*/
if (handler->filter)
list_add_rcu(&handle->d_node, &dev->h_list);
else
list_add_tail_rcu(&handle->d_node, &dev->h_list); //把d_node(device node)添加到input_handler的h_list
mutex_unlock(&dev->mutex);
/*
* Since we are supposed to be called from ->connect()
* which is mutually exclusive with ->disconnect()
* we can't be racing with input_unregister_handle()
* and so separate lock is not needed here.
*/
list_add_tail_rcu(&handle->h_node, &handler->h_list); //把h_node(handler node)添加到input_dev的h_list
if (handler->start)
handler->start(handle);
return 0;
}input核心层的初始化函数:
static int __init input_init(void)
{
int err;
err = class_register(&input_class); //注册一个 input 类,/sys/class/input
if (err) {
pr_err("unable to register input_dev class\n");
return err;
}
err = input_proc_init(); //proc文件系统相关的初始化
if (err)
goto fail1;
err = register_chrdev_region(MKDEV(INPUT_MAJOR, 0), //INPUT_MAJOR = 13,输入子系统的主设备号
INPUT_MAX_CHAR_DEVICES, "input"); //INPUT_MAX_CHAR_DEVICES = 1024
if (err) {
pr_err("unable to register char major %d", INPUT_MAJOR);
goto fail2;
}
return 0;
fail2: input_proc_exit();
fail1: class_unregister(&input_class);
return err;
}该函数完成了:1.注册input类(实际就是在/sys/class目录下建立一个input目录)
2.input的proc文件系统初始化
3.动态注册设备号
input子系统的所有设备主设备号都为 13,在使用input子系统处理输入设备的时候就不需要去注册字符设备了,我们只需要向系统注册一个input_device即可。
二、input设备驱动层和input事件驱动层
上下两层涉及的文件比较多(各种设备驱动以及对应的事件驱动handler),这里通过分析一个实际的例子来描述:
设备驱动层:gpio_keys.c (drivers\input\keyboard)
static int gpio_keys_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
struct input_dev *input;
input = devm_input_allocate_device(dev);
input = input_allocate_device();
error = input_register_device(input);
struct input_handler *handler; //定义一个 input_handler 结构体指针
list_add_tail(&dev->node, &input_dev_list); //链表挂接: 将input_dev->node作为节点挂接到input_dev_list链表上
list_for_each_entry(handler, &input_handler_list, node) //遍历input_handler_list链表上的所有handler
input_attach_handler(dev, handler); //将handler与input设备进行匹配:根据input_handler的id_table判断能否支持这个input_dev
const struct input_device_id *id;
id = input_match_device(handler, dev); //通过这个函数进行handler与input设备的匹配工作
error = handler->connect(handler, dev, id); //匹配成功则调用handler中的connect函数进行连接
事件驱动层:evdev.c (drivers\input)
static const struct input_device_id evdev_ids[] = {
{ .driver_info = 1 }, /* Matches all devices */
{ }, /* Terminating zero entry */
};
static struct input_handler evdev_handler = {
.event = evdev_event,
.events = evdev_events,
.connect = evdev_connect,
.disconnect = evdev_disconnect,
.legacy_minors = true,
.minor = EVDEV_MINOR_BASE, //次设备号起始为64
.name = "evdev",
.id_table = evdev_ids, //input_attach_handler里会用到
};
evdev_init(void)
input_register_handler(&evdev_handler);
list_add_tail(&handler->node, &input_handler_list); //将handler通过handler->node节点挂接到input_handler_list链表上
list_for_each_entry(dev, &input_dev_list, node) //遍历input_dev_list链表下挂接的所有的input_dev设备
input_attach_handler(dev, handler); //然后进行匹配
const struct input_device_id *id;
id = input_match_device(handler, dev); //通过这个函数进行handler与input设备的匹配工作
error = handler->connect(handler, dev, id); //匹配成功则调用handler中的connect函数进行连接static const struct input_device_id *input_match_device(struct input_handler *handler,
struct input_dev *dev)
{
const struct input_device_id *id;
for (id = handler->id_table; id->flags || id->driver_info; id++) {
if (id->flags & INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_BUS)
if (id->bustype != dev->id.bustype)
continue;
if (id->flags & INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_VENDOR)
if (id->vendor != dev->id.vendor)
continue;
if (id->flags & INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_PRODUCT)
if (id->product != dev->id.product)
continue;
if (id->flags & INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_VERSION)
if (id->version != dev->id.version)
continue;
if (!bitmap_subset(id->evbit, dev->evbit, EV_MAX))
continue;
if (!bitmap_subset(id->keybit, dev->keybit, KEY_MAX))
continue;
if (!bitmap_subset(id->relbit, dev->relbit, REL_MAX))
continue;
if (!bitmap_subset(id->absbit, dev->absbit, ABS_MAX))
continue;
if (!bitmap_subset(id->mscbit, dev->mscbit, MSC_MAX))
continue;
if (!bitmap_subset(id->ledbit, dev->ledbit, LED_MAX))
continue;
if (!bitmap_subset(id->sndbit, dev->sndbit, SND_MAX))
continue;
if (!bitmap_subset(id->ffbit, dev->ffbit, FF_MAX))
continue;
if (!bitmap_subset(id->swbit, dev->swbit, SW_MAX))
continue;
//执行这里的判断
if (!handler->match || handler->match(handler, dev)) //如果数组中的某个匹配成功了就返回他的地址
return id;
}
return NULL;
gpio_keys.c和evdev.c 分别在初始化函数里面调用input_attach_handler函数遍历input_handler_list里的handler和input_dev_list里的input_dev进行匹配,成功匹配返回对应的id,然后调用evdev的connect函数:
/*
* Create new evdev device. Note that input core serializes calls
* to connect and disconnect.
*/
static int evdev_connect(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev,
const struct input_device_id *id)
{
struct evdev *evdev; //定义一个evdev 指针
int minor;
int dev_no;
int error;
minor = input_get_new_minor(EVDEV_MINOR_BASE, EVDEV_MINORS, true); //申请一个次设备号
if (minor < 0) {
error = minor;
pr_err("failed to reserve new minor: %d\n", error);
return error;
}
evdev = kzalloc(sizeof(struct evdev), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!evdev) {
error = -ENOMEM;
goto err_free_minor;
}
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&evdev->client_list); //初始化evdev->client_list 链表
spin_lock_init(&evdev->client_lock);
mutex_init(&evdev->mutex);
init_waitqueue_head(&evdev->wait);
evdev->exist = true;
dev_no = minor;
/* Normalize device number if it falls into legacy range */
if (dev_no < EVDEV_MINOR_BASE + EVDEV_MINORS)
dev_no -= EVDEV_MINOR_BASE;
dev_set_name(&evdev->dev, "event%d", dev_no); //设置input设备的名字
evdev->handle.dev = input_get_device(dev); //将我们传进来的input_dev 指针存放在evdev->handle.dev 中
evdev->handle.name = dev_name(&evdev->dev); //设置evdev -> dev 对象的名字,并且把名字赋值给evdev->handle.name
evdev->handle.handler = handler; //将我们传进来的handler 指针存放在handle.handler 中
evdev->handle.private = evdev; //把evdev 作为handle 的私有数据
evdev->dev.devt = MKDEV(INPUT_MAJOR, minor); //设置evdev->device 设备的设备号
evdev->dev.class = &input_class; //将input_class 作为evdev->device 的设备类
evdev->dev.parent = &dev->dev; //将input_dev->device 作为evdev->device 的父设备
evdev->dev.release = evdev_free;
device_initialize(&evdev->dev); //设备初始化
error = input_register_handle(&evdev->handle); //注册handle
if (error)
goto err_free_evdev;
cdev_init(&evdev->cdev, &evdev_fops); //应用层调用open函数,就会对应到evdev_fops的open(evdev_open),最后是对应到驱动程序的open(input_dev->open)
evdev->cdev.kobj.parent = &evdev->dev.kobj;
error = cdev_add(&evdev->cdev, evdev->dev.devt, 1); //注册字符设备驱动 主设备号13
if (error)
goto err_unregister_handle;
/*
/sys/devices/virtual/input/input0 这个设备是在注册input_dev时创建的,而input0/event0
就是在handler和input_dev匹配成功之后创建的,也会在/dev/目录下创建设备
节点。
*/
error = device_add(&evdev->dev); //添加设备到系统 /sys/devices/virtual/input/input0/event0 event0就是表示建立的设备文件
if (error)
goto err_cleanup_evdev;
return 0;
err_cleanup_evdev:
evdev_cleanup(evdev);
err_unregister_handle:
input_unregister_handle(&evdev->handle);
err_free_evdev:
put_device(&evdev->dev);
err_free_minor:
input_free_minor(minor);
return error;
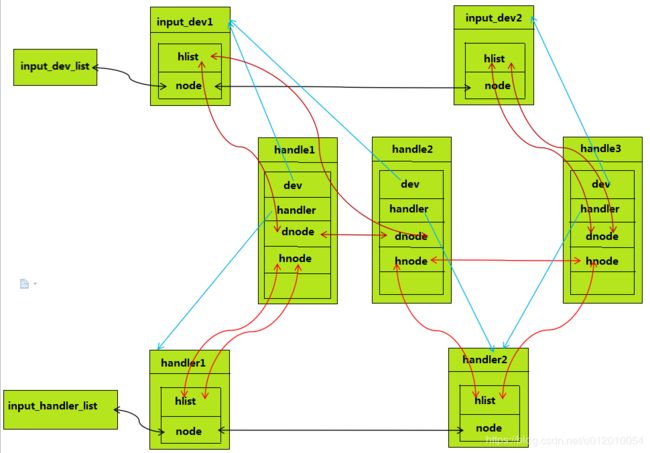
}这个connect函数我们重点留意一下里面调用的input_register_handle函数,它将handle放到input_dev的h_list和input_handler的h_list,这样通过dev或者handler就可以找到 handle,通过handle 也可以找到dev和handler,这样他们三个就都关联起来了。相互关系可以参考一下下面的图片:
/**
* input_register_handle - register a new input handle
* @handle: handle to register
*
* This function puts a new input handle onto device's
* and handler's lists so that events can flow through
* it once it is opened using input_open_device().
*
* This function is supposed to be called from handler's
* connect() method.
*/
int input_register_handle(struct input_handle *handle)
{
struct input_handler *handler = handle->handler; //evdev->handle->handler
struct input_dev *dev = handle->dev; //evdev->handle->dev
int error;
/*
* We take dev->mutex here to prevent race with
* input_release_device().
*/
error = mutex_lock_interruptible(&dev->mutex);
if (error)
return error;
/*
* Filters go to the head of the list, normal handlers
* to the tail.
*/
if (handler->filter)
list_add_rcu(&handle->d_node, &dev->h_list);
else
list_add_tail_rcu(&handle->d_node, &dev->h_list); //把d_node(device node)添加到input_handler的h_list
mutex_unlock(&dev->mutex);
/*
* Since we are supposed to be called from ->connect()
* which is mutually exclusive with ->disconnect()
* we can't be racing with input_unregister_handle()
* and so separate lock is not needed here.
*/
list_add_tail_rcu(&handle->h_node, &handler->h_list); //把h_node(handler node)添加到input_dev的h_list
if (handler->start)
handler->start(handle);
return 0;
}三、input子系统事件传递过程
当输入设备有输入时,比如说按键按下,会进入到驱动的中断函数中:
static irqreturn_t gpio_keys_irq_isr(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
struct gpio_button_data *bdata = dev_id;
const struct gpio_keys_button *button = bdata->button;
struct input_dev *input = bdata->input;
unsigned long flags;
BUG_ON(irq != bdata->irq);
spin_lock_irqsave(&bdata->lock, flags);
if (!bdata->key_pressed) {
if (bdata->button->wakeup)
pm_wakeup_event(bdata->input->dev.parent, 0);
input_event(input, EV_KEY, button->code, 1);
input_sync(input);
if (!bdata->release_delay) {
input_event(input, EV_KEY, button->code, 0);
input_sync(input);
goto out;
}
bdata->key_pressed = true;
}
if (bdata->release_delay)
mod_timer(&bdata->release_timer,
jiffies + msecs_to_jiffies(bdata->release_delay));
out:
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&bdata->lock, flags);
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}中断函数调用了 input_event来报告事件:事件类型、按键键值、按键的状态(松开或者按下)
/**
* input_event() - report new input event
* @dev: device that generated the event
* @type: type of the event
* @code: event code
* @value: value of the event
*
* This function should be used by drivers implementing various input
* devices to report input events. See also input_inject_event().
*
* NOTE: input_event() may be safely used right after input device was
* allocated with input_allocate_device(), even before it is registered
* with input_register_device(), but the event will not reach any of the
* input handlers. Such early invocation of input_event() may be used
* to 'seed' initial state of a switch or initial position of absolute
* axis, etc.
*/
void input_event(struct input_dev *dev,
unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value)
{
unsigned long flags;
if (is_event_supported(type, dev->evbit, EV_MAX)) {
spin_lock_irqsave(&dev->event_lock, flags);
input_handle_event(dev, type, code, value); //上报数据
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&dev->event_lock, flags);
}
}input_event函数进一步调用input_handle_event函数来上报数据
static void input_handle_event(struct input_dev *dev,
unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value)
{
int disposition;
disposition = input_get_disposition(dev, type, code, &value); //获取事件的处理方式
if ((disposition & INPUT_PASS_TO_DEVICE) && dev->event)
dev->event(dev, type, code, value);
if (!dev->vals)
return;
if (disposition & INPUT_PASS_TO_HANDLERS) {
struct input_value *v;
if (disposition & INPUT_SLOT) {
v = &dev->vals[dev->num_vals++];
v->type = EV_ABS;
v->code = ABS_MT_SLOT;
v->value = dev->mt->slot;
}
v = &dev->vals[dev->num_vals++];
v->type = type; //设置dev->vals->type = type
v->code = code; //设置dev->vals->code = code
v->value = value; //设置dev->vals->value = value
}
if (disposition & INPUT_FLUSH) {
if (dev->num_vals >= 2)
input_pass_values(dev, dev->vals, dev->num_vals);
dev->num_vals = 0;
} else if (dev->num_vals >= dev->max_vals - 2) {
dev->vals[dev->num_vals++] = input_value_sync;
input_pass_values(dev, dev->vals, dev->num_vals); //最后通过调用handler对应的event函数来传递数据到用户空间
dev->num_vals = 0;
}
通过input_get_disposition函数来获取事件的处理方式,gpio_keys驱动的disposition是INPUT_PASS_TO_HANDLERS,然后设置好dev->vals结构体,通过它进一步传递数据:input_pass_values(dev, dev->vals, dev->num_vals)。
input_pass_values(dev, dev->vals, dev->num_vals);
count = input_to_handler(handle, vals, count);
if (handler->events) //在这里对应到了handler的event函数
handler->events(handle, vals, count);
else if (handler->event)
for (v = vals; v != vals + count; v++)
handler->event(handle, v->type, v->code, v->value);最后在input_pass_values函数中对应上了相应的事件处理器。
evdev_event
evdev_events(handle, vals, 1);
list_for_each_entry_rcu(client, &evdev->client_list, node) //遍历client链表,调用evdev_pass_values函数
evdev_pass_values(client, vals, count, ev_time);
struct input_event event;
event.type = v->type;
event.code = v->code;
event.value = v->value;
__pass_event(client, &event);
client->buffer[client->head++] = *event; //将事件赋值给客户端的input_event 数组
struct evdev_client {
unsigned int head;
unsigned int tail;
unsigned int packet_head; /* [future] position of the first element of next packet */
spinlock_t buffer_lock; /* protects access to buffer, head and tail */
struct fasync_struct *fasync;
struct evdev *evdev;
struct list_head node; //作为一个链表节点挂接到相应的evdev->client_list 链表上
unsigned int clk_type;
bool revoked;
unsigned long *evmasks[EV_CNT];
unsigned int bufsize;
struct input_event buffer[]; //用来存放input_dev事件的缓冲区
};evdev_pass_values函数最终将事件传递给了客户端client结构体中的input_event数组中,只需将这个input_event数组复制给用户空间,进程就能收到输入设备的信息了。
应用层要读取输入信息:
app: read->.....->evdev_read
evdev_read
struct input_event event;
evdev_fetch_next_event(client, &event)
if (have_event) {
event = client->buffer[client->tail++];
client->tail &= client->bufsize - 1;
}
input_event_to_user(buffer + read, &event)
copy_to_user(buffer, event, sizeof(struct input_event)) //通过该函数传递到用户空间