卷积和快速傅里叶变换(FFT)的实现
卷积运算
卷积可以说是图像处理中最基本的操作。线性滤波通过不同的卷积核,可以产生很多不同的效果。假如有一个要处理的二维图像,通过二维的滤波矩阵(卷积核),对于图像的每一个像素点,计算它的领域像素和滤波器矩阵的对应元素的乘积,然后累加,作为该像素位置的值。关于图像卷积和滤波的一些知识点可以参考这篇博客。
下面是通过python模拟实现的图像卷积操作,模拟了sobel算子,prewitt算子和拉普拉斯算子。python的np包中有convolve函数可以直接调用,scipy中也有scipy.signal.convolve函数可以直接调用。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pylab
import cv2
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import os
def conv(image, kernel):
height, width = image.shape # 获取图像的维度
h, w = kernel.shape # 卷积核的维度
# 经过卷积操作后得到的新的图像的尺寸
new_h = height - h + 1
new_w = width - w + 1
# 对新的图像矩阵进行初始化
new_image = np.zeros((new_h, new_w), dtype=np.float)
# 进行卷积操作,矩阵对应元素值相乘
for i in range(new_w):
for j in range(new_h):
new_image[i, j] = np.sum(image[i:i+h, j:j+w] * kernel) # 矩阵元素相乘累加
# 去掉矩阵乘法后的小于0的和大于255的原值,重置为0和255
# 用clip函数处理矩阵的元素,使元素值处于(0,255)之间
new_image = new_image.clip(0, 255)
# 将新图像各元素的值四舍五入,然后转成8位无符号整型
new_image = np.rint(new_image).astype('uint8')
return new_image
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 读取图像信息,并转换为numpy下的数组
image = Image.open("图片.jpg", 'r')
output_path = "./outputPic/"
if not os.path.exists(output_path):
os.mkdir(output_path)
a = np.array(image)
# sobel 算子
sobel_x = np.array(([-1, 0, 1],
[-2, 0, 2],
[-1, 0, 1]))
sobel_y = np.array(([-1, -2, -1],
[0, 0, 0],
[1, 2, 1]))
sobel = np.array(([-1, -1, 0],
[-1, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1]))
# prewitt各个方向上的算子
prewitt_x = np.array(([-1, 0, 1],
[-1, 0, 1],
[-1, 0, 1]))
prewitt_y = np.array(([-1, -1, -1],
[0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1]))
prewitt = np.array(([-2, -1, 0],
[-1, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 2]))
# 拉普拉斯算子
laplacian = np.array(([0, -1, 0],
[-1, 4, -1],
[0, -1, 0]))
laplacian_2 = np.array(([-1, -1, -1],
[-1, 8, -1],
[-1, -1, -1]))
kernel_list = ("sobel_x", "sobel_y", "sobel", "prewitt_x", "prewitt_y", "prewitt", "laplacian", "laplacian_2")
print("Gridient detection\n")
for w in kernel_list:
print("starting %s....." % w)
print("kernel:\n")
print("R\n")
R = conv(a[:, :, 0], eval(w))
print("G\n")
G = conv(a[:, :, 1], eval(w))
print("B\n")
B = conv(a[:, :, 2], eval(w))
I = np.stack((R, G, B), axis=2) # 合并三个通道的结果
Image.fromarray(I).save("%s//bigger-%s.jpg" % (output_path, w))
快速傅里叶变换(FFT)
通过上面的方法实现卷积操作之后,发现可以通过快速傅里叶变换提升卷积运算的效率。python提供了很多标准工具和封装来计算它。NumPy 和 SciPy 都有经过充分测试的封装好的FFT库,分别位于子模块 numpy.fft 和 scipy.fftpack 。有关FFT算法的原理和推导可以参见参考链接的博客。
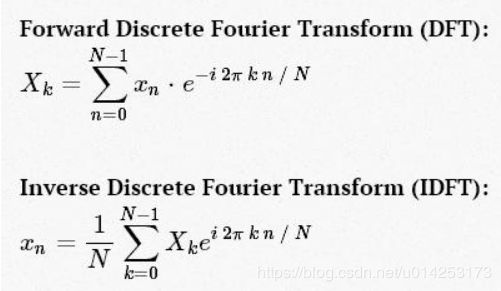
离散傅里叶变换
xn 到 Xk 的转化就是空域到频域的转换,转化为点值表示法。
def DFT_slow(x):
# Compute the discrete Fourier Transform of the 1D array x
x = np.asarray(x, dtype=float) # 转化为ndarray
N = x.shape[0] # 维度
n = np.arange(N) # 0~N组成一个一维向量
k = n.reshape((N, 1)) # 转换为一个N维向量
M = np.exp(-2j * np.pi * k * n / N) # 离散傅里叶公式 -2j复数表示
return np.dot(M, x)
快速傅里叶变换
离散傅里叶变换具有对称性,利用这种对称性,可以推出递归的快速傅里叶算法。
def FFT(x):
# A recursive implementation of the 1D Cooley-Tukey FFT
x = np.asarray(x, dtype=float) # 浅拷贝
N = x.shape[0]
if N % 2 > 0:
raise ValueError("size of x must be a power of 2")
elif N <= 32:
return DFT_slow(x)
else:
X_even = FFT(x[::2]) # 从0开始,2为间隔
X_odd = FFT(x[1::2]) # 从1开始,2为间隔
factor = np.exp(-2j * np.pi * np.arange(N) / N)
'''
使用/会出现下面的错误,改为// 向下取整
TypeError: slice indices must be integers or None or have an __index__ method
'''
return np.concatenate([X_even + factor[:N // 2] * X_odd,
X_even + factor[N // 2:] * X_odd])
向量化的FFT
使用numpy进行矩阵向量化。
def FFT_vectorized(x):
# A vectorized, non-recurisive version of the Cooley_Tukey FFT
x = np.asarray(x, dtype=float)
N = x.shape[0]
if np.log2(N) % 1 > 0:
raise ValueError("size of x must be a power of 2")
# N_min here is equivalent to the stopping condition above,
# and should be a power of 2
N_min = min(N, 32)
# Perform an O[N^2] DFT on all length-N_min sub-problems at once
n = np.arange(N_min)
k = n[:, None]
M = np.exp(-2j * np.pi * n * k / N_min)
X = np.dot(M, x.reshape((N_min, -1)))
# build-up each level of the recursive calculation all at once
while X.shape[0] < N:
X_even = X[:, :X.shape[1] // 2]
X_odd = X[:, X.shape[1] // 2:]
factor = np.exp(-1j * np.pi * np.arange(X.shape[0]) / X.shape[0])[:, None]
X = np.vstack([X_even + factor * X_odd,
X_even - factor * X_odd])
return X.ravel() # 降维
用快速傅里叶变换实现卷积
根据卷积定理,时域上卷积运算对应于频域上的傅里叶变换的乘积。
def fft_convolve(a, b):
n = len(a) + len(b) -1
N = 2 ** (int(np.log2(n))+1)
A = np.fft.fft(a, N)
B = np.fft.fft(b, N)
return np.fft.ifft(A*B)[:n]
c++实现的递归版
void FFT(Complex* a,int len){
if(len==1) return;
Complex* a0=new Complex[len/2];
Complex* a1=new Complex[len/2];
for(int i=0;ic++实现的非递归版
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
// 复数
struct complex
{
double r,i;
complex(double _r = 0.0, double _i = 0.0)
{
r = _r;
i = _i;
}
complex operator +(const complex &b)
{
return complex(r + b.r, i + b.i);
}
complex operator -(const complex &b)
{
return complex(r - b.r, i - b.i);
}
complex operator *(const complex &b)
{
return complex(r*b.r - i*b.i, r*b.i + i*b.r);
}
};
// 雷德算法 -- 倒位序
void Rader(complex F[], int len)
{
int j = len >> 1;
for(int i=1; i> 1;
while(j >= k)
{
j -= k;
k >>= 1;
}
if(j < k)
j += k;
}
}
void FFT(complex F[], int len, int on)
{
Rader(F, len);
for(int h=2; h<=len; h<<=1) //计算长度为h的DFT
{
complex wn(cos(-on*2*PI/h), sin(-on*2*PI/h)); //单位复根e^(2*PI/m),用欧拉公式展开
for(int j=0; j 参考链接:
http://blog.jobbole.com/58246/ (快速傅里叶变换)
https://blog.csdn.net/acdreamers/article/details/39005227 (快速傅里叶变换)
http://blog.miskcoo.com/2015/04/polynomial-multiplication-and-fast-fourier-transform#i-15 (快速傅里叶变换)
https://blog.csdn.net/WADuan2/article/details/79529900 (快速傅里叶变换)
https://blog.csdn.net/oliverkingli/article/details/79243731 (图像卷积)
https://blog.csdn.net/zlh_hhhh/article/details/75604333 (快速傅里叶变换)
https://www.cnblogs.com/youmuchen/p/6724780.html (图像卷积)
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_154d272c90102x98p.html (雷德算法)
https://www.cnblogs.com/Sakits/p/8405098.html (快速傅里叶变换)