Java基础-零拷贝技术应用案例
作者:尹正杰
版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任。
零拷贝技术在Hadoop生态圈中很多组件得到应用,典型的比如kafka组件,它就很成功的应用了零拷贝技术,那么究竟什么是零拷贝技术呢?以及零拷贝技术和传统的拷贝技术有什么差异呢?还有零拷贝有什么缺陷呢?接下来,本篇博客会跟你一起验证这些问题!
一.传统拷贝
1>.Java中的传统拷贝
答:正常拷贝先将文件从磁盘交换到系统(内核)空间,再从内核空间交换到user空间,再从user空间交换到内核空间,最后从内核空间交换到目的缓冲区.。接下里我画一张草图来进行解析说明,如下:
2>.传统拷贝案例展示
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E5%BA%93%E4%BB%8E%E5%85%A5%E9%97%A8%E5%88%B0%E7%B2%BE%E9%80%9A/ 4 EMAIL:[email protected] 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.zeroCopy; 7 8 import java.io.File; 9 import java.io.FileInputStream; 10 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 11 import java.io.RandomAccessFile; 12 import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; 13 14 public class Test2 { 15 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 16 File input = new File("D:\\BigData\\JavaSE\\yinzhengjieData\\yinzhengjieJava.rar"); 17 File tcOutput = new File("D:\\BigData\\JavaSE\\yinzhengjieData\\yinzhengjieJava2.rar"); 18 19 traditionalCopy(input,tcOutput); 20 } 21 22 23 public static void traditionalCopy(File input,File output) throws Exception{ 24 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); 25 RandomAccessFile rafRead = new RandomAccessFile(input,"rw"); 26 RandomAccessFile rafWrite = new RandomAccessFile(output,"rw"); 27 byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; 28 int len ; 29 while ((len = rafRead.read(buf)) != -1 ){ 30 rafWrite.write(buf,0,len); 31 } 32 rafRead.close(); 33 rafWrite.close(); 34 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); 35 System.out.println("traditionalCopy 用时为:" + (end - start)); 36 } 37 } 38 39 40 /* 41 traditionalCopy 用时为:5399 42 */
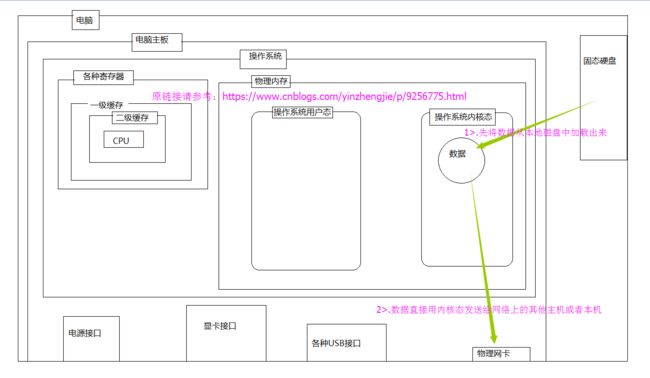
二.零拷贝
1>.什么是零拷贝
答:零拷贝是直接从磁盘交换到内核空间,从内核空间直接输出到目的缓冲区。接下里我画一张草图来进行解析说明,如下:
2>.零拷贝案例展示
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E5%BA%93%E4%BB%8E%E5%85%A5%E9%97%A8%E5%88%B0%E7%B2%BE%E9%80%9A/ 4 EMAIL:[email protected] 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.zeroCopy; 7 8 import java.io.File; 9 import java.io.FileInputStream; 10 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 11 import java.io.RandomAccessFile; 12 import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; 13 14 public class Test2 { 15 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 16 File input = new File("D:\\BigData\\JavaSE\\yinzhengjieData\\yinzhengjieJava.rar"); 17 File zcOutput = new File("D:\\BigData\\JavaSE\\yinzhengjieData\\yinzhengjieJava3.rar"); 18 19 ZeroCopy(input,zcOutput); 20 } 21 22 public static void ZeroCopy(File input,File output) throws Exception { 23 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); 24 //文件输出 25 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(input); 26 //源文件通道 27 FileChannel srcFC = fis.getChannel(); 28 //输出流 29 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(output); 30 //输出文件通道 31 FileChannel destFC = fos.getChannel(); 32 srcFC.transferTo(0 , input.length() , destFC) ; 33 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); 34 System.out.println("ZeroCopy 用时为:" + (end - start)); 35 } 36 } 37 38 39 /* 40 ZeroCopy 用时为:588 41 */
三.测试零拷贝方式和常规拷贝方式性能对比
测试零拷贝和传统拷贝的性能我们只需要加一个计时功能即可,具体实现代码如下:
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E5%BA%93%E4%BB%8E%E5%85%A5%E9%97%A8%E5%88%B0%E7%B2%BE%E9%80%9A/ 4 EMAIL:[email protected] 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.zeroCopy; 7 8 import java.io.File; 9 import java.io.FileInputStream; 10 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 11 import java.io.RandomAccessFile; 12 import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; 13 14 public class Test2 { 15 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 16 File input = new File("D:\\BigData\\JavaSE\\yinzhengjieData\\yinzhengjieJava.rar"); 17 File tcOutput = new File("D:\\BigData\\JavaSE\\yinzhengjieData\\yinzhengjieJava2.rar"); 18 File zcOutput = new File("D:\\BigData\\JavaSE\\yinzhengjieData\\yinzhengjieJava3.rar"); 19 20 traditionalCopy(input,tcOutput); 21 ZeroCopy(input,zcOutput); 22 } 23 24 25 public static void traditionalCopy(File input,File output) throws Exception{ 26 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); 27 RandomAccessFile rafRead = new RandomAccessFile(input,"rw"); 28 RandomAccessFile rafWrite = new RandomAccessFile(output,"rw"); 29 byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; 30 int len ; 31 while ((len = rafRead.read(buf)) != -1 ){ 32 rafWrite.write(buf,0,len); 33 } 34 rafRead.close(); 35 rafWrite.close(); 36 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); 37 System.out.println("traditionalCopy 用时为:" + (end - start)); 38 } 39 40 41 public static void ZeroCopy(File input,File output) throws Exception { 42 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); 43 //文件输出 44 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(input); 45 //源文件通道 46 FileChannel srcFC = fis.getChannel(); 47 //输出流 48 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(output); 49 //输出文件通道 50 FileChannel destFC = fos.getChannel(); 51 srcFC.transferTo(0 , input.length() , destFC) ; 52 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); 53 System.out.println("ZeroCopy 用时为:" + (end - start)); 54 } 55 } 56 57 58 /* 59 traditionalCopy 用时为:5286 60 ZeroCopy 用时为:1986 61 */
执行以上代码后,需要去响应目录检查是否拷贝成功,验证结果如下:
四.零拷贝细节
1>.Linux中的零拷贝
零拷贝技术的发展很多样化,现有的零拷贝技术种类也非常多,而当前并没有一个适合于所有场景的零拷贝技术的出现。对于 Linux 来说,现存的零拷贝技术也比较多,这些零拷贝技术大部分存在于不同的 Linux 内核版本,有些旧的技术在不同的 Linux 内核版本间得到了很大的发展或者已经渐渐被新的技术所代替。Linux 中的零拷贝技术主要有下面这几种:
直接 I/O:
对于这种数据传输方式来说,应用程序可以直接访问硬件存储,操作系统内核只是辅助数据传输:这类零拷贝技术针对的是操作系统内核并不需要对数据进行直接处理的情况,数据可以在应用程序地址空间的缓冲区和磁盘之间直接进行传输,完全不需要 Linux 操作系统内核提供的页缓存的支持。 在数据传输的过程中,避免数据在操作系统内核地址空间的缓冲区和用户应用程序地址空间的缓冲区之间进行拷贝。
有的时候,应用程序在数据进行传输的过程中不需要对数据进行访问,那么,将数据从 Linux 的页缓存拷贝到用户进程的缓冲区中就可以完全避免,传输的数据在页缓存中就可以得到处理。在某些特殊的情况下,这种零拷贝技术可以获得较好的性能。Linux 中提供类似的系统调用主要有 mmap(),sendfile() 以及 splice()。 对数据在 Linux 的页缓存和用户进程的缓冲区之间的传输过程进行优化。
该零拷贝技术侧重于灵活地处理数据在用户进程的缓冲区和操作系统的页缓存之间的拷贝操作。这种方法延续了传统的通信方式,但是更加灵活。在 Linux 中,该方法主要利用了写时复制技术。
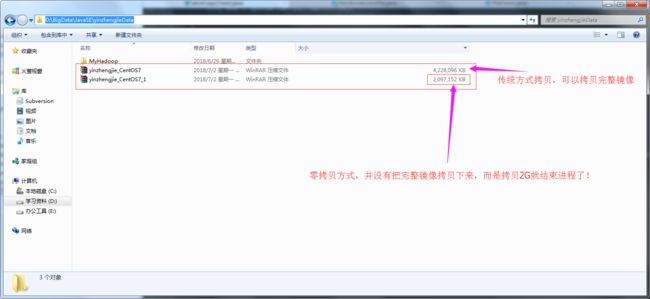
2>.零拷贝缺陷
零拷贝也有自己的缺陷,当它拷贝的文件大于2G时,就无法完整实现拷贝过程!比如你拷贝一个4G文件左右,它最终的结果是只能拷贝2G大小的文件。我测试使用CentOS官方镜像进行拷贝!测试代码如下:
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E5%BA%93%E4%BB%8E%E5%85%A5%E9%97%A8%E5%88%B0%E7%B2%BE%E9%80%9A/ 4 EMAIL:[email protected] 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.zeroCopy; 7 8 import java.io.File; 9 import java.io.FileInputStream; 10 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 11 import java.io.RandomAccessFile; 12 import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; 13 14 public class Test2 { 15 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 16 RandomAccessFileTest(); 17 ZeroCopy(); 18 } 19 20 21 public static void RandomAccessFileTest() throws Exception{ 22 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); 23 File input = new File("D:\\VMwareworkStation\\ISO\\CentOS-7-x86_64-DVD-1511.iso"); 24 File output = new File("D:\\BigData\\JavaSE\\yinzhengjieData\\yinzhengjie_CentOS7.iso"); 25 RandomAccessFile rafRead = new RandomAccessFile(input,"rw"); 26 RandomAccessFile rafWrite = new RandomAccessFile(output,"rw"); 27 28 byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; 29 30 int len ; 31 while ((len = rafRead.read(buf)) != -1 ){ 32 rafWrite.write(buf,0,len); 33 } 34 35 rafRead.close(); 36 rafWrite.close(); 37 38 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); 39 System.out.println("RandomAccessFile 用时为:" + (end - start)); 40 } 41 42 43 public static void ZeroCopy() throws Exception { 44 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); 45 46 File input = new File("D:\\VMwareworkStation\\ISO\\CentOS-7-x86_64-DVD-1511.iso") ; 47 //文件输出 48 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(input); 49 //源文件通道 50 FileChannel srcFC = fis.getChannel(); 51 //输出流 52 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\BigData\\JavaSE\\yinzhengjieData\\yinzhengjie_CentOS7_1.iso"); 53 //输出文件通道 54 FileChannel destFC = fos.getChannel(); 55 srcFC.transferTo(0 , input.length() , destFC) ; 56 System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - start); 57 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); 58 System.out.println("ZeroCopy 用时为:" + (end - start)); 59 } 60 } 61 62 63 /* 64 RandomAccessFile 用时为:46436 65 ZeroCopy 用时为:1275 66 67 */
以上代码执行结果如下:(数据并没有完整拷贝!!!)