欢迎加群:1012878218,一起学习、交流强化学习,里面会有关于深度学习、机器学习、强化学习的各种资料 。
主要采用了OpenCV3.1.0分别基于Surf-SITF-ORB实现了简单的图像拼接与融合。
要说明的是,OpenCV3.1.0的版本中,这些特征都放在了OpenCV的未发行扩展版本contrib中,所以在这之前要先安装对应于OpenCV版本的contrib。经过一天的折腾,最终笔者参考下面的这个链接,安装成功了。https://blog.csdn.net/lyl771857509/article/details/79070799
使用的配置为OpenCV3.1.0+Cmake3.6.2+OpenCV contrib3.1.0。
输入图片为:
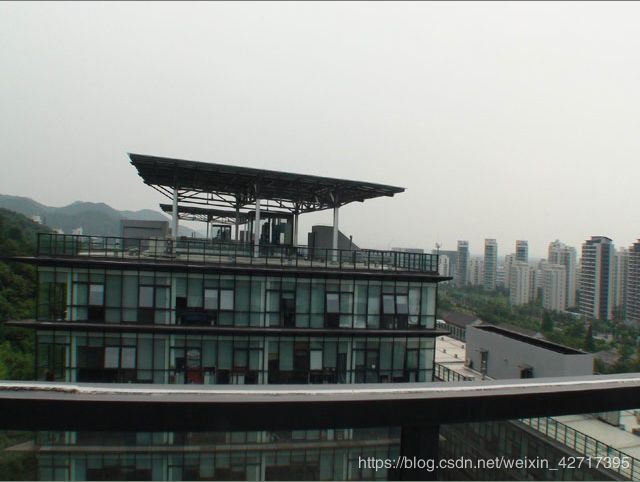
1.jpg
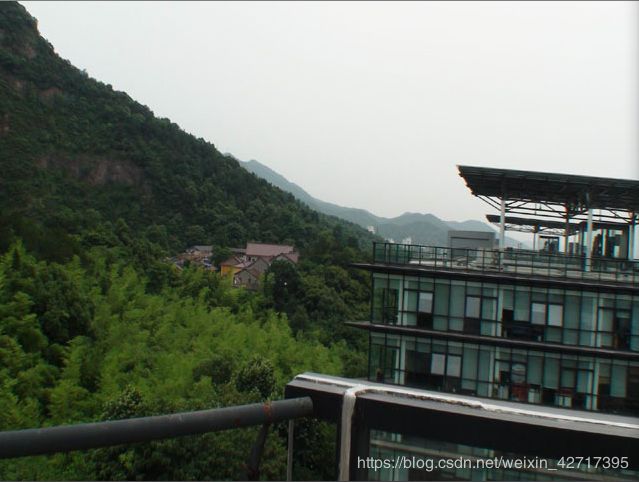

2.jpg

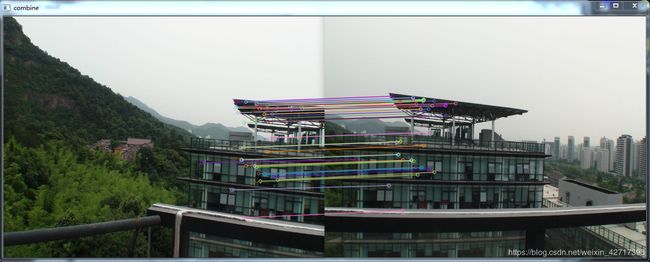
SURF:
#include
#include
#include "opencv2/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/core/utility.hpp"
#include "opencv2/core/ocl.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp"
#include"opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp"
#include"opencv2/ml.hpp"
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
using namespace cv::xfeatures2d;
using namespace cv::ml;
void OptimizeSeam(Mat& img1, Mat& trans, Mat& dst);
typedef struct
{
Point2f left_top;
Point2f left_bottom;
Point2f right_top;
Point2f right_bottom;
}four_corners_t;
four_corners_t corners;
void CalcCorners(const Mat& H, const Mat& src)
{
double v2[] = { 0, 0, 1 };//左上角
double v1[3];//变换后的坐标值
Mat V2 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v2); //列向量
Mat V1 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v1); //列向量
V1 = H * V2;
//左上角(0,0,1)
cout << "V2: " << V2 << endl;
cout << "V1: " << V1 << endl;
corners.left_top.x = v1[0] / v1[2];
corners.left_top.y = v1[1] / v1[2];
//左下角(0,src.rows,1)
v2[0] = 0;
v2[1] = src.rows;
v2[2] = 1;
V2 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v2); //列向量
V1 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v1); //列向量
V1 = H * V2;
corners.left_bottom.x = v1[0] / v1[2];
corners.left_bottom.y = v1[1] / v1[2];
//右上角(src.cols,0,1)
v2[0] = src.cols;
v2[1] = 0;
v2[2] = 1;
V2 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v2); //列向量
V1 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v1); //列向量
V1 = H * V2;
corners.right_top.x = v1[0] / v1[2];
corners.right_top.y = v1[1] / v1[2];
//右下角(src.cols,src.rows,1)
v2[0] = src.cols;
v2[1] = src.rows;
v2[2] = 1;
V2 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v2); //列向量
V1 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v1); //列向量
V1 = H * V2;
corners.right_bottom.x = v1[0] / v1[2];
corners.right_bottom.y = v1[1] / v1[2];
}
int main()
{
Mat a = imread("2.jpg", 1);//右图
Mat b = imread("1.jpg", 1);//左图
Ptr surf; //创建方式和OpenCV2中的不一样,并且要加上命名空间xfreatures2d
//否则即使配置好了还是显示SURF为未声明的标识符
surf = SURF::create(800);
BFMatcher matcher; //实例化一个暴力匹配器
Mat c, d;
vector key1, key2;
vector matches; //DMatch是用来描述匹配好的一对特征点的类,包含这两个点之间的相关信息
//比如左图有个特征m,它和右图的特征点n最匹配,这个DMatch就记录它俩最匹配,并且还记录m和n的
//特征向量的距离和其他信息,这个距离在后面用来做筛选
surf->detectAndCompute(a, Mat(), key1, c);//输入图像,输入掩码,输入特征点,输出Mat,存放所有特征点的描述向量
surf->detectAndCompute(b, Mat(), key2, d);//这个Mat行数为特征点的个数,列数为每个特征向量的尺寸,SURF是64(维)
matcher.match(d, c, matches); //匹配,数据来源是特征向量,结果存放在DMatch类型里面
//sort函数对数据进行升序排列
sort(matches.begin(), matches.end()); //筛选匹配点,根据match里面特征对的距离从小到大排序
vector good_matches;
int ptsPairs = std::min(50, (int)(matches.size() * 0.15));
cout << ptsPairs << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < ptsPairs; i++)
{
good_matches.push_back(matches[i]);//距离最小的50个压入新的DMatch
}
Mat outimg; //drawMatches这个函数直接画出摆在一起的图
drawMatches(b, key2, a, key1, good_matches, outimg, Scalar::all(-1), Scalar::all(-1), vector(), DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS); //绘制匹配点
imshow("combine", outimg);
//计算图像配准点
vector imagePoints1, imagePoints2;
for (int i = 0; i(i); //获取第i行的首地址
uchar* t = trans.ptr(i);
uchar* d = dst.ptr(i);
for (int j = start; j < cols; j++)
{
//如果遇到图像trans中无像素的黑点,则完全拷贝img1中的数据
if (t[j * 3] == 0 && t[j * 3 + 1] == 0 && t[j * 3 + 2] == 0)
{
alpha = 1;
}
else
{
//img1中像素的权重,与当前处理点距重叠区域左边界的距离成正比,实验证明,这种方法确实好
alpha = (processWidth - (j - start)) / processWidth;
}
d[j * 3] = p[j * 3] * alpha + t[j * 3] * (1 - alpha);
d[j * 3 + 1] = p[j * 3 + 1] * alpha + t[j * 3 + 1] * (1 - alpha);
d[j * 3 + 2] = p[j * 3 + 2] * alpha + t[j * 3 + 2] * (1 - alpha);
}
}
}



ORB:
#include
#include
#include "opencv2/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/core/utility.hpp"
#include "opencv2/core/ocl.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp"
#include"opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp"
#include"opencv2/ml.hpp"
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
using namespace cv::xfeatures2d;
using namespace cv::ml;
void OptimizeSeam(Mat& img1, Mat& trans, Mat& dst);
typedef struct
{
Point2f left_top;
Point2f left_bottom;
Point2f right_top;
Point2f right_bottom;
}four_corners_t;
four_corners_t corners;
void CalcCorners(const Mat& H, const Mat& src)
{
double v2[] = { 0, 0, 1 };//左上角
double v1[3];//变换后的坐标值
Mat V2 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v2); //列向量
Mat V1 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v1); //列向量
V1 = H * V2;
//左上角(0,0,1)
cout << "V2: " << V2 << endl;
cout << "V1: " << V1 << endl;
corners.left_top.x = v1[0] / v1[2];
corners.left_top.y = v1[1] / v1[2];
//左下角(0,src.rows,1)
v2[0] = 0;
v2[1] = src.rows;
v2[2] = 1;
V2 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v2); //列向量
V1 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v1); //列向量
V1 = H * V2;
corners.left_bottom.x = v1[0] / v1[2];
corners.left_bottom.y = v1[1] / v1[2];
//右上角(src.cols,0,1)
v2[0] = src.cols;
v2[1] = 0;
v2[2] = 1;
V2 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v2); //列向量
V1 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v1); //列向量
V1 = H * V2;
corners.right_top.x = v1[0] / v1[2];
corners.right_top.y = v1[1] / v1[2];
//右下角(src.cols,src.rows,1)
v2[0] = src.cols;
v2[1] = src.rows;
v2[2] = 1;
V2 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v2); //列向量
V1 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v1); //列向量
V1 = H * V2;
corners.right_bottom.x = v1[0] / v1[2];
corners.right_bottom.y = v1[1] / v1[2];
}
int main()
{
Mat a = imread("2.jpg", 1);//右图
Mat b = imread("1.jpg", 1);//左图
Ptr orb; //创建方式和OpenCV2中的不一样,并且要加上命名空间xfreatures2d
//否则即使配置好了还是显示SURF为未声明的标识符
orb = ORB::create(800);
BFMatcher matcher; //实例化一个暴力匹配器
Mat c, d;
vector key1, key2;
vector matches; //DMatch是用来描述匹配好的一对特征点的类,包含这两个点之间的相关信息
//比如左图有个特征m,它和右图的特征点n最匹配,这个DMatch就记录它俩最匹配,并且还记录m和n的
//特征向量的距离和其他信息,这个距离在后面用来做筛选
orb->detectAndCompute(a, Mat(), key1, c);//输入图像,输入掩码,输入特征点,输出Mat,存放所有特征点的描述向量
orb->detectAndCompute(b, Mat(), key2, d);//这个Mat行数为特征点的个数,列数为每个特征向量的尺寸,SURF是64(维)
matcher.match(d, c, matches); //匹配,数据来源是特征向量,结果存放在DMatch类型里面
//sort函数对数据进行升序排列
sort(matches.begin(), matches.end()); //筛选匹配点,根据match里面特征对的距离从小到大排序
vector good_matches;
int ptsPairs = std::min(50, (int)(matches.size() * 0.15));
cout << ptsPairs << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < ptsPairs; i++)
{
good_matches.push_back(matches[i]);//距离最小的50个压入新的DMatch
}
Mat outimg; //drawMatches这个函数直接画出摆在一起的图
drawMatches(b, key2, a, key1, good_matches, outimg, Scalar::all(-1), Scalar::all(-1), vector(), DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS); //绘制匹配点
imshow("combine", outimg);
//计算图像配准点
vector imagePoints1, imagePoints2;
for (int i = 0; i(i); //获取第i行的首地址
uchar* t = trans.ptr(i);
uchar* d = dst.ptr(i);
for (int j = start; j < cols; j++)
{
//如果遇到图像trans中无像素的黑点,则完全拷贝img1中的数据
if (t[j * 3] == 0 && t[j * 3 + 1] == 0 && t[j * 3 + 2] == 0)
{
alpha = 1;
}
else
{
//img1中像素的权重,与当前处理点距重叠区域左边界的距离成正比,实验证明,这种方法确实好
alpha = (processWidth - (j - start)) / processWidth;
}
d[j * 3] = p[j * 3] * alpha + t[j * 3] * (1 - alpha);
d[j * 3 + 1] = p[j * 3 + 1] * alpha + t[j * 3 + 1] * (1 - alpha);
d[j * 3 + 2] = p[j * 3 + 2] * alpha + t[j * 3 + 2] * (1 - alpha);
}
}
}
SIFT:
#include
#include
#include "opencv2/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/core/utility.hpp"
#include "opencv2/core/ocl.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp"
#include"opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp"
#include"opencv2/ml.hpp"
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
using namespace cv::xfeatures2d;
using namespace cv::ml;
void OptimizeSeam(Mat& img1, Mat& trans, Mat& dst);
typedef struct
{
Point2f left_top;
Point2f left_bottom;
Point2f right_top;
Point2f right_bottom;
}four_corners_t;
four_corners_t corners;
void CalcCorners(const Mat& H, const Mat& src)
{
double v2[] = { 0, 0, 1 };//左上角
double v1[3];//变换后的坐标值
Mat V2 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v2); //列向量
Mat V1 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v1); //列向量
V1 = H * V2;
//左上角(0,0,1)
cout << "V2: " << V2 << endl;
cout << "V1: " << V1 << endl;
corners.left_top.x = v1[0] / v1[2];
corners.left_top.y = v1[1] / v1[2];
//左下角(0,src.rows,1)
v2[0] = 0;
v2[1] = src.rows;
v2[2] = 1;
V2 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v2); //列向量
V1 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v1); //列向量
V1 = H * V2;
corners.left_bottom.x = v1[0] / v1[2];
corners.left_bottom.y = v1[1] / v1[2];
//右上角(src.cols,0,1)
v2[0] = src.cols;
v2[1] = 0;
v2[2] = 1;
V2 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v2); //列向量
V1 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v1); //列向量
V1 = H * V2;
corners.right_top.x = v1[0] / v1[2];
corners.right_top.y = v1[1] / v1[2];
//右下角(src.cols,src.rows,1)
v2[0] = src.cols;
v2[1] = src.rows;
v2[2] = 1;
V2 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v2); //列向量
V1 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v1); //列向量
V1 = H * V2;
corners.right_bottom.x = v1[0] / v1[2];
corners.right_bottom.y = v1[1] / v1[2];
}
int main()
{
Mat a = imread("2.jpg", 1);//右图
Mat b = imread("1.jpg", 1);//左图
Ptr sift; //创建方式和OpenCV2中的不一样,并且要加上命名空间xfreatures2d
//否则即使配置好了还是显示SURF为未声明的标识符
sift = SIFT::create(800);
BFMatcher matcher; //实例化一个暴力匹配器
Mat c, d;
vector key1, key2;
vector matches; //DMatch是用来描述匹配好的一对特征点的类,包含这两个点之间的相关信息
//比如左图有个特征m,它和右图的特征点n最匹配,这个DMatch就记录它俩最匹配,并且还记录m和n的
//特征向量的距离和其他信息,这个距离在后面用来做筛选
sift->detectAndCompute(a, Mat(), key1, c);//输入图像,输入掩码,输入特征点,输出Mat,存放所有特征点的描述向量
sift->detectAndCompute(b, Mat(), key2, d);//这个Mat行数为特征点的个数,列数为每个特征向量的尺寸,SURF是64(维)
matcher.match(d, c, matches); //匹配,数据来源是特征向量,结果存放在DMatch类型里面
//sort函数对数据进行升序排列
sort(matches.begin(), matches.end()); //筛选匹配点,根据match里面特征对的距离从小到大排序
vector good_matches;
int ptsPairs = std::min(50, (int)(matches.size() * 0.15));
cout << ptsPairs << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < ptsPairs; i++)
{
good_matches.push_back(matches[i]);//距离最小的50个压入新的DMatch
}
Mat outimg; //drawMatches这个函数直接画出摆在一起的图
drawMatches(b, key2, a, key1, good_matches, outimg, Scalar::all(-1), Scalar::all(-1), vector(), DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS); //绘制匹配点
imshow("combine", outimg);
//计算图像配准点
vector imagePoints1, imagePoints2;
for (int i = 0; i(i); //获取第i行的首地址
uchar* t = trans.ptr(i);
uchar* d = dst.ptr(i);
for (int j = start; j < cols; j++)
{
//如果遇到图像trans中无像素的黑点,则完全拷贝img1中的数据
if (t[j * 3] == 0 && t[j * 3 + 1] == 0 && t[j * 3 + 2] == 0)
{
alpha = 1;
}
else
{
//img1中像素的权重,与当前处理点距重叠区域左边界的距离成正比,实验证明,这种方法确实好
alpha = (processWidth - (j - start)) / processWidth;
}
d[j * 3] = p[j * 3] * alpha + t[j * 3] * (1 - alpha);
d[j * 3 + 1] = p[j * 3 + 1] * alpha + t[j * 3 + 1] * (1 - alpha);
d[j * 3 + 2] = p[j * 3 + 2] * alpha + t[j * 3 + 2] * (1 - alpha);
}
}
}
stitch:
#include
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
//#include "opencv2/nonfree/nonfree.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/stitching.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
bool try_use_gpu = false;
vector imgs;
string result_name = "result.jpg";
int main()
{
Mat img1 = imread("1.jpg");
Mat img2 = imread("2.jpg");
if (img1.empty() || img2.empty())
{
cout << "con't open image" << endl;
return -1;
}
imgs.push_back(img1);
imgs.push_back(img2);
imshow("p1", img1);
imshow("p2", img2);
waitKey();
Mat pano;
Stitcher stitcher = Stitcher::createDefault(try_use_gpu); //使用stitch函数进行拼接
Stitcher::Status status = stitcher.stitch(imgs, pano);
if (status != Stitcher::OK)
{
cout << "Can't stitch images, error code = " << status << endl;
return -1;
}
namedWindow(result_name);
imshow(result_name, pano);
imwrite("stitch_output.jpg", pano);
waitKey();
return 0;
}
不使用OpenCV,直接实现的Surf特征提取:
#include
#include
#include
#include





