wav头文件解析
文章目录
- 什么是wav格式
- 文件构成
- 文件头(也叫头文件)
- 文件实体:
- wav头文件
- 写头文件 方法一
- 需要注意的是大端存储以及小端存储.
- 从源码中可以看到
- 写头文件 方法二
什么是wav格式
网上介绍wav 格式的文章已经很多了 为什么还要写这个文章
- 练手 发帖子比较少,找到适合自己写作风格的方式 写帖子 为以后做准备
- 整理自己的知识库, 这个知识点之前习得的过程比较零散.整理一下,心里有个底,思路上可以完善的将各个零散的点合并起来,便于记忆
- 好记性不如烂笔头
- 帮助后来者理解该知识点,每个知识点,每个人理解的方式过程不一样,没准有那么一类人,就喜欢我的心路风格呢
.WAV 格式文件 为微软公司(Microsoft)开发的一种声音文件格式.
WAV是最接近无损的音乐格式,所以文件大小相对也比较大.
那么为什么 wav格式是如何存储的呢
文件构成
文件头(也叫头文件)
作用: 告诉播放器(为什么是告诉播放器,而不是告诉 word打开,应为.wav后缀的文件默认是用播放器打开的,你要强制用word去打开,我也没办法),这个文件 中的数据 如何使用, 用什么样的方法 才能正确的进行播放.
就像迷宫门口的建筑图纸,还是带gps定位的那种,可以指引需要的人穿过 整个座迷宫,还顺便知道了迷宫的构造
文件实体:
作用: 具体播放的内容 就是迷宫本身
当播放器 拿着迷宫门口的建筑图纸后,获取迷宫中的信息,那是分分钟的事.
wav头文件
头文件 听起来高大上,说白了依然是二进制流.(废话,所有数据都可以搞成二进制流) 其本质是按照一定格式规范 写的一个固定 说明书,
就像图书,有个目录,有序,有引言.
wav头文件有44个字节
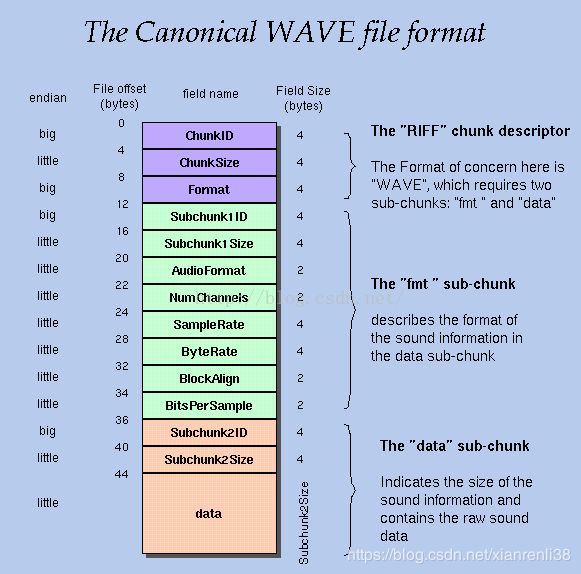
如图[1][1]:图片来自http://soundfile.sapp.org/doc/WaveFormat/
写头文件 方法一
需要注意的是大端存储以及小端存储.
这个涉及到cpu的规则,我不太了解.
在实际应用这个知识点时,
涉及到 RandomAccessFile 的write 方法
具体去看api了
从源码中可以看到
写头文件时,writeInt,writeShort,会将其中的序列翻过来,变为大端
/**
* Writes an {@code int} to the file as four bytes, high byte first.
* The write starts at the current position of the file pointer.
*
* @param v an {@code int} to be written.
* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs.
*/
public final void writeInt(int v) throws IOException {
write((v >>> 24) & 0xFF);
write((v >>> 16) & 0xFF);
write((v >>> 8) & 0xFF);
write((v >>> 0) & 0xFF);
//written += 4;
}
而我们需要的顺序是
write((v >>> 0) & 0xFF);
write((v >>> 8) & 0xFF);
write((v >>> 16) & 0xFF);
write((v >>> 24) & 0xFF);
因此在使用RandomAccessFile .writeInt,和writeByet时需要手动想将其倒序,然后调用api,就负负得正了
开始写录音文件前调用
/**
* @param weikuan 位宽
* @param nChannels 通道数
* @param sampleRate 采样率
* @throws IOException
*/
private void writeHead(short weikuan, short nChannels, int sampleRate) throws IOException {
RandomAccessFile rand;
int byteofSeconds = weikuan * nChannels * sampleRate/8;
rand = randomAccessFile;
//设置文件大小为0, 防止未知情况导致 该文件已经存在
rand.setLength(0);
//初始化wav文件的头文件
/* RIFF header */
rand.writeBytes("RIFF"); // riff id
rand.writeInt(0); // riff chunk size *PLACEHOLDER*
rand.writeBytes("WAVE"); // wave type
/* fmt chunk */
rand.writeBytes("fmt "); // fmt id
rand.writeInt(Integer.reverseBytes(16)); // fmt chunk size
rand.writeShort(Short.reverseBytes((short) 1)); // AudioFormat,1 for PCM
rand.writeShort(Short.reverseBytes(nChannels));// Number of channels, 1 for mono, 2 for stereo
rand.writeInt(Integer.reverseBytes(sampleRate)); // Sample rate 采样率
rand.writeInt(Integer.reverseBytes(byteofSeconds));//Byte rate,波形数据传输速率(每秒平均字节数)
// SampleRate*NumberOfChannels*BitsPerSample/8
//每次采样大小 单位byte
rand.writeShort(Short.reverseBytes((short) (nChannels * weikuan / 8))); // Block align,
// NumberOfChannels*BitsPerSample/8
rand.writeShort(Short.reverseBytes(weikuan)); // Bits per sample
/* data chunk */
rand.writeBytes("data"); // data id
rand.writeInt(0); // data chunk size *PLACEHOLDER*
}
录完音后,补充 头文件中的内容
private void writeInsertHead() throws IOException {
RandomAccessFile rand = randomAccessFile;
rand.seek(4); // riff chunk size
// rand.writeInt(Integer.reverseBytes((int) (rand.length() - 8)));
rand.writeInt(Integer.reverseBytes((int) (dataSize + 36)));
rand.seek(40); // data chunk size
// rand.writeInt(Integer.reverseBytes((int) (rand.length() - 44)));
rand.writeInt(Integer.reverseBytes((int) (dataSize)));
onSuccess(rand.length());
}
写头文件 方法二
当然 如果搞不清上面的这个问题. 写头文件也可以直接使用writebyte,在录音结束时,返回到开口预留的44个字节中 从seek(0)开始,一次写入 44个字节的数组,就可以避开这个问题.
/**
* @param totalAudioLen 音频数据总大小
* @param sampleRate 采样率
* @param byteRate 位元(组)率(每秒的数据量 单位 字节/秒) 采样率(44100之类的) * 通道数(1,或者2)*每次采样得到的样本位数(16或者8) / 8;
* @param nChannels 声道数量
* @param weikuan 位宽
* @throws IOException
*/
private void writeHead(int totalAudioLen, int sampleRate, int byteRate, int nChannels, int weikuan) throws
IOException {
RandomAccessFile rand = randomAccessFile;
long totalDataLen = totalAudioLen + 36;
//长度
print(rand.readInt());
rand.seek(0);
byte[] header = new byte[44];
header[0] = 'R'; // RIFF/WAVE header
header[1] = 'I';
header[2] = 'F';
header[3] = 'F';
header[4] = (byte) (totalDataLen & 0xff);
header[5] = (byte) ((totalDataLen >> 8) & 0xff);
header[6] = (byte) ((totalDataLen >> 16) & 0xff);
header[7] = (byte) ((totalDataLen >> 24) & 0xff);
header[8] = 'W';
header[9] = 'A';
header[10] = 'V';
header[11] = 'E';
header[12] = 'f'; // 'fmt ' chunk
header[13] = 'm';
header[14] = 't';
header[15] = ' ';
header[16] = 16; // 4 bytes: size of 'fmt ' chunk
header[17] = 0;
header[18] = 0;
header[19] = 0;
header[20] = 1; // format = 1
header[21] = 0;
header[22] = (byte) (nChannels & 0xff);
header[23] = (byte) ((nChannels >> 8) & 0xff);
header[24] = (byte) (sampleRate & 0xff);//采样率
header[25] = (byte) ((sampleRate >> 8) & 0xff);
header[26] = (byte) ((sampleRate >> 16) & 0xff);
header[27] = (byte) ((sampleRate >> 24) & 0xff);
header[28] = (byte) (byteRate & 0xff);//取八位
header[29] = (byte) ((byteRate >> 8) & 0xff);
header[30] = (byte) ((byteRate >> 16) & 0xff);
header[31] = (byte) ((byteRate >> 24) & 0xff);
int b = weikuan * nChannels / 8;//每次采样的大小
header[32] = (byte) (b & 0xff); // block align
header[33] = (byte) ((b >> 8) & 0xff);
header[34] = (byte) (weikuan & 0xff);//位宽
header[35] = (byte) ((weikuan >> 8) & 0xff);
header[36] = 'd';//data
header[37] = 'a';
header[38] = 't';
header[39] = 'a';
header[40] = (byte) (totalAudioLen & 0xff);
header[41] = (byte) ((totalAudioLen >> 8) & 0xff);
header[42] = (byte) ((totalAudioLen >> 16) & 0xff);
header[43] = (byte) ((totalAudioLen >> 24) & 0xff);
rand.write(header, 0, header.length);
本文参考了
http://soundfile.sapp.org/doc/WaveFormat/
https://www.cnblogs.com/wangguchangqing/p/5957531.html
https://www.jianshu.com/p/90c77197f1d4