使用IDEA详解Spring中依赖注入的类型
使用IDEA详解Spring中依赖注入的类型(上)
在Spring中实现IoC容器的方法是依赖注入,依赖注入的作用是在使用Spring框架创建对象时动态地将其所依赖的对象(例如属性值)注入Bean组件中。
Spring框架的依赖注入通常有两种实现方式,一种是使用构造方法注入,另一种是使用属性的setter方法注入。
使用构造方法注入
Spring框架可以采用Java反射机制,通过构造方法完成依赖注入。
创建项目及导入Maven模块过程请看《使用IDEA开发Spring入门程序》,在这就不赘述了。在这继续前面的项目,按照下面的步骤补充:
创建entity包,创建Person类
package entity;
public class Person {
private String name;
private String sex;
public Person() {
System.out.println("无参构造调用了...");
}
public Person(String name, String sex) {
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
}
复制代码构造方法注入方式一
编写配置文件
在src根目录下创建Spring配置文件applicationContext.xml。在配置文件中首先将entity.Person类托管给Spring,让Spring创建其对象,同时给构造方法传递实参。
配置文件的具体代码如下:
复制代码在测试类TestDemo中测试
package test;
import dao.TestDao;
import entity.Person;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResource;
public class TestDemo {
@Test
public void test4(){
//初始化spring容器ApplicationContext,加载配置文件
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//通过容器获取test实例
Person person2 =(Person) applicationContext.getBean("person2");
System.out.println("姓名:"+person2.getName()+";"+"性别:"+person2.getSex());
}
}
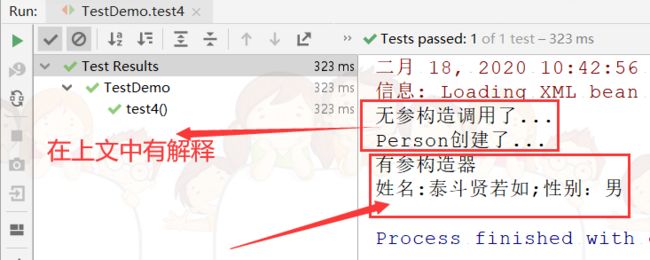
复制代码测试结果
构造方法注入方式二
编写配置文件
复制代码在测试类TestDemo中测试
package test;
import dao.TestDao;
import entity.Person;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResource;
public class TestDemo {
@Test
public void test5(){
//初始化spring容器ApplicationContext,加载配置文件
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//通过容器获取test实例
Person person3 =(Person) applicationContext.getBean("person3");
System.out.println("姓名:"+person3.getName()+";"+"性别:"+person3.getSex());
}
}
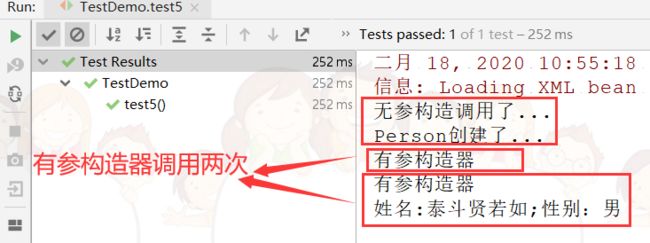
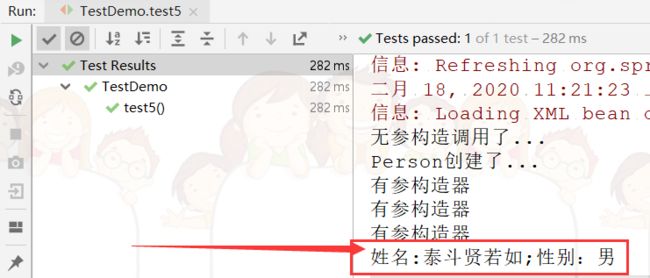
复制代码测试结果
需要注意的是,如果使用这种方法,要严格按照构造器参数的位置赋值,如果不这样赋值,当然也不会报错,但会造成赋值错乱,比如会把姓名赋值成性别,这当然是我们不愿意看到的,如果你非不按要求赋值(有点极端,皮一下),有种方法可以避免你赋值错乱,请看下面代码:
编写配置文件
复制代码在测试类TestDemo中测试
package test;
import dao.TestDao;
import entity.Person;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResource;
public class TestDemo {
@Test
public void test5(){
//初始化spring容器ApplicationContext,加载配置文件
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//通过容器获取test实例
Person person4 =(Person) applicationContext.getBean("person4");
System.out.println("姓名:"+person4.getName()+";"+"性别:"+person4.getSex());
}
}
复制代码测试结果
不要以为这样就完了,我在想,如果出现重载的情况,该如何办?且看我向下分解:
将entity包下的Person类修改如下
package entity;
public class Person {
private String name;
private String sex;
private Integer age;
private String email;
public Person() {
System.out.println("无参构造调用了...");
System.out.println("Person创建了...");
}
public Person(String name, String sex) {
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
System.out.println("有参构造器");
}
public Person(String name, String sex, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
}
public Person(String name, String sex, String email) {
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.email = email;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
}
复制代码编写配置文件
复制代码在测试类TestDemo中测试
package test;
import dao.TestDao;
import entity.Person;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResource;
public class TestDemo {
@Test
public void test6(){
//初始化spring容器ApplicationContext,加载配置文件
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//通过容器获取test实例
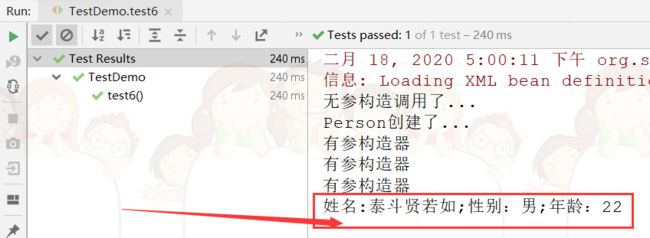
Person person5 =(Person) applicationContext.getBean("person5");
System.out.println("姓名:"+person5.getName()+";"+"性别:"+person5.getSex()+";"+"年龄:"+person5.getAge());
}
}
复制代码测试结果
不过话又说过来了,明明name能搞定的事情弄这么复杂干嘛,所以常用的还是方式一
使用属性的setter方法注入
这部分放到下一篇讲解吧,篇幅有点多了,请持续关注!
公众号
能欣赏我的文章的话,可以顺便关注一下公众号,彼此欣赏,何必孤独: