AutoLayoutActivity
AutoLayoutActivity
public class AutoLayoutActivity extends FragmentActivity {
private static final String LAYOUT_LINEARLAYOUT = "LinearLayout";
private static final String LAYOUT_FRAMELAYOUT = "FrameLayout";
private static final String LAYOUT_RELATIVELAYOUT = "RelativeLayout";
@Override
public View onCreateView(String name, Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
View view = null;
if (name.equals(LAYOUT_FRAMELAYOUT)) {
view = new AutoFrameLayout(context, attrs);
}
if (name.equals(LAYOUT_LINEARLAYOUT)) {
view = new AutoLinearLayout(context, attrs);
}
if (name.equals(LAYOUT_RELATIVELAYOUT)) {
view = new AutoRelativeLayout(context, attrs);
}
if (view != null) return view;
return super.onCreateView(name, context, attrs);
}
}
我们可以发现,只是做了name的判断,
如果是属性中的3中Layout, 会自动替换成 对应的AutoXXXLayout
如果不是,直接调用父类的 View onCreateView(String name, Context context, AttributeSet attrs) 即可
LinearLayout -> AutoLinearLayout
RelativeLayout -> AutoRelativeLayout
FrameLayout -> AutoFrameLayout
AutoLinearLayout
我们来看一看对应的源码
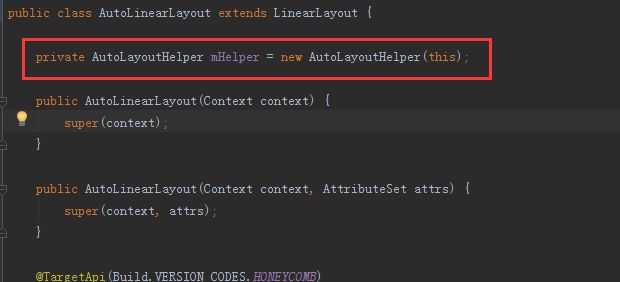
public class AutoLinearLayout extends LinearLayout {
private AutoLayoutHelper mHelper = new AutoLayoutHelper(this);
public AutoLinearLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public AutoLinearLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
@TargetApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB)
public AutoLinearLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@TargetApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP)
public AutoLinearLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
}
@Override
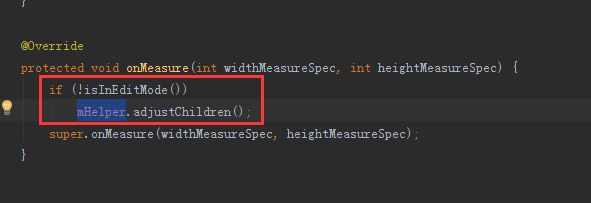
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
if (!isInEditMode())
mHelper.adjustChildren();
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
super.onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
}
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new AutoLinearLayout.LayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
public static class LayoutParams extends LinearLayout.LayoutParams
implements AutoLayoutHelper.AutoLayoutParams {
private AutoLayoutInfo mAutoLayoutInfo;
public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(c, attrs);
mAutoLayoutInfo = AutoLayoutHelper.getAutoLayoutInfo(c, attrs);
}
@Override
public AutoLayoutInfo getAutoLayoutInfo() {
return mAutoLayoutInfo;
}
public LayoutParams(int width, int height) {
super(width, height);
}
public LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams source) {
super(source);
}
public LayoutParams(MarginLayoutParams source) {
super(source);
}
}
}
我们可以发现,类中只关联了一个 AutoLayoutHelper类
重写onMeasure方法
这里同样会调用关联AutoLayoutHelper的对象
这里,在调用 父类
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec)之前
会去调用 关联AutoLayoutHelper的 mHelper.adjustChildren();
这里有 isInEditMode() 判断
是为了判断 是否在例如 可视化编辑器 中打开
这样可以避免不必要的报错
可以参考:
http://blog.csdn.net/lamp_zy/article/details/9405925
重写generateLayoutParams方法
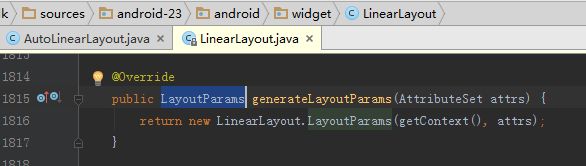
我们先来看一下, 父类 LinearLayout中, generateLayoutParams方法的实现
父类 LinearLayout中, generateLayoutParams方法的实现为:
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
再看一下这个return new 的 LinearLayout.LayoutParams 静态内部类
(自己理解静态内部类,一般内部类 就是和本来关系比较密切,在其他地方不需要调用,非静态内部类可以调用外部类的属性和方法, 比较方便。 静态内部类相对于非静态内部类,独立性较强)
public static class LayoutParams extends ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams {
/**
* Indicates how much of the extra space in the LinearLayout will be
* allocated to the view associated with these LayoutParams. Specify
* 0 if the view should not be stretched. Otherwise the extra pixels
* will be pro-rated among all views whose weight is greater than 0.
*/
@ViewDebug.ExportedProperty(category = "layout")
public float weight;
/**
* Gravity for the view associated with these LayoutParams.
*
* @see android.view.Gravity
*/
@ViewDebug.ExportedProperty(category = "layout", mapping = {
@ViewDebug.IntToString(from = -1, to = "NONE"),
@ViewDebug.IntToString(from = Gravity.NO_GRAVITY, to = "NONE"),
@ViewDebug.IntToString(from = Gravity.TOP, to = "TOP"),
@ViewDebug.IntToString(from = Gravity.BOTTOM, to = "BOTTOM"),
@ViewDebug.IntToString(from = Gravity.LEFT, to = "LEFT"),
@ViewDebug.IntToString(from = Gravity.RIGHT, to = "RIGHT"),
@ViewDebug.IntToString(from = Gravity.START, to = "START"),
@ViewDebug.IntToString(from = Gravity.END, to = "END"),
@ViewDebug.IntToString(from = Gravity.CENTER_VERTICAL, to = "CENTER_VERTICAL"),
@ViewDebug.IntToString(from = Gravity.FILL_VERTICAL, to = "FILL_VERTICAL"),
@ViewDebug.IntToString(from = Gravity.CENTER_HORIZONTAL, to = "CENTER_HORIZONTAL"),
@ViewDebug.IntToString(from = Gravity.FILL_HORIZONTAL, to = "FILL_HORIZONTAL"),
@ViewDebug.IntToString(from = Gravity.CENTER, to = "CENTER"),
@ViewDebug.IntToString(from = Gravity.FILL, to = "FILL")
})
public int gravity = -1;
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(c, attrs);
TypedArray a =
c.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, com.android.internal.R.styleable.LinearLayout_Layout);
weight = a.getFloat(com.android.internal.R.styleable.LinearLayout_Layout_layout_weight, 0);
gravity = a.getInt(com.android.internal.R.styleable.LinearLayout_Layout_layout_gravity, -1);
a.recycle();
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
public LayoutParams(int width, int height) {
super(width, height);
weight = 0;
}
/**
* Creates a new set of layout parameters with the specified width, height
* and weight.
*
* @param width the width, either {@link #MATCH_PARENT},
* {@link #WRAP_CONTENT} or a fixed size in pixels
* @param height the height, either {@link #MATCH_PARENT},
* {@link #WRAP_CONTENT} or a fixed size in pixels
* @param weight the weight
*/
public LayoutParams(int width, int height, float weight) {
super(width, height);
this.weight = weight;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
public LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) {
super(p);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
public LayoutParams(ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams source) {
super(source);
}
/**
* Copy constructor. Clones the width, height, margin values, weight,
* and gravity of the source.
*
* @param source The layout params to copy from.
*/
public LayoutParams(LayoutParams source) {
super(source);
this.weight = source.weight;
this.gravity = source.gravity;
}
@Override
public String debug(String output) {
return output + "LinearLayout.LayoutParams={width=" + sizeToString(width) +
", height=" + sizeToString(height) + " weight=" + weight + "}";
}
/** @hide */
@Override
protected void encodeProperties(@NonNull ViewHierarchyEncoder encoder) {
super.encodeProperties(encoder);
encoder.addProperty("layout:weight", weight);
encoder.addProperty("layout:gravity", gravity);
}
}
LinearLayout.LayoutParams类中,注解较多,并且是不常用的注解
再加上也是 继承 ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams 对应的内部静态类
自己也不花时间研究,不和大家扯淡了
让我们回到 鸿洋大神 的 AutoLinearLayout的
静态内部类AutoLinearLayout.LayoutParams
public static class LayoutParams extends LinearLayout.LayoutParams
implements AutoLayoutHelper.AutoLayoutParams
{
private AutoLayoutInfo mAutoLayoutInfo;
public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs)
{
super(c, attrs);
mAutoLayoutInfo = AutoLayoutHelper.getAutoLayoutInfo(c, attrs);
}
@Override
public AutoLayoutInfo getAutoLayoutInfo()
{
return mAutoLayoutInfo;
}
public LayoutParams(int width, int height)
{
super(width, height);
}
public LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams source)
{
super(source);
}
public LayoutParams(MarginLayoutParams source)
{
super(source);
}
}
这里我们发现, 这个类除了上面说到的 extends LinearLayout.LayoutParams,
还 implements AutoLayoutHelper.AutoLayoutParams。
而对应的实现, 也只是在LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs)构造中
给 属性private AutoLayoutInfo mAutoLayoutInfo;
传递了一下AutoLayoutHelper的实现
再通过接口实现,返回对象
可以发现,绕了一圈, 最后只是把具体的实现传递给父类的逻辑中
(自己对这些Override的方法也不太熟悉, 为什么要Override这几个方法,而不从别的方法下手,自己以后再做考虑)
后面我们再说明下,是怎么通过AutoLayoutHelper把 传递值 和 计算 联系起来的
AutoRelativeLayout 和 AutoFrameLayout
这里AutoRelativeLayout 和 AutoFrameLayout都类似,
都只是通过 关联和依赖 AutoLayoutHelper ,
Override对应的
onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) 和 generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs)
通过静态内部类 的接口, 传递 AutoLayoutHelper的实现
返回 AutoLayoutInfo 对象
AutoLayoutInfo类
我们看看 AutoLayoutInfo 类
public class AutoLayoutInfo {
private List autoAttrs = new ArrayList<>();
public void addAttr(AutoAttr autoAttr) {
autoAttrs.add(autoAttr);
}
public void fillAttrs(View view) {
for (AutoAttr autoAttr : autoAttrs) {
autoAttr.apply(view);
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "AutoLayoutInfo{" +
"autoAttrs=" + autoAttrs +
'}';
}
}
我们可以发现,其实也只是一个简单的容器类
通过 addAttr(AutoAttr autoAttr) 给ArrayList容器add添加对象
通过 fillAttrs(View view) 去让容器中AutoAttr和依赖的view关系
后续
具体类之间的关系,我们后面再慢慢分析
下一篇我们可以了解鸿洋AutoLayout代码分析(四):剩下的类