mysql 聚合函数比较函数字符串函数...大全
文章目录
- 聚合函数
- AVG()
- SUM()
- STDEV(),STDDEV_POP()
- VARIANCE(),VAR_POP(),VARP_SAM()
- 比较函数
- coalesce
- 字符串函数
- concat
- concat_ws
- group_concat
- 控制流函数跟表达 control flow and expression
- CASE
- 1. simple case
- 2. searched case
- IF
- IFNULL
- NULLIF
- 问题
聚合函数
函数名(数据)
也可以 函数名(distinct 数据);
AVG()
返回组中数据中非null值的平均值;
SUM()
返回组中数据的总和
STDEV(),STDDEV_POP()
返回总体标准差
STDDEV_SAMP() 返回样本标准差
VARIANCE(),VAR_POP(),VARP_SAM()
前两个返回总体方差,后面一个返回样本方差;
比较函数
coalesce
coalesce(val1,val2,val3,...valn)
如果coalesce只有两个输入参数的话,则跟ifnull作用一样;
例子
数据:
CREATE TABLE articles (
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
title VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
excerpt TEXT,
body TEXT NOT NULL,
published_at DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
updated_at DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
INSERT INTO articles(title,excerpt,body)
VALUES('MySQL COALESCE Tutorial','This tutorial is about MySQL COALESCE function', 'all about COALESCE function'),
('MySQL 8.0 New Features',null, 'The following is a list of new features in MySQL 8.0');
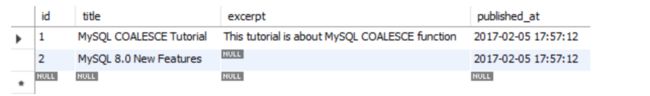
SELECT
id, title, excerpt, published_at
FROM
articles;
excerpt行存在null值,对body字段从左开始截取150个字符作为excerpt null值的替代;
SELECT
id, title, COALESCE(excerpt, LEFT(body, 150)), published_at
FROM
articles;
SELECT
id,
title,
(CASE
WHEN excerpt IS NULL THEN LEFT(body, 150)
ELSE excerpt
END) AS excerpt,
published_at
FROM
articles;
select coalesce(1,2,3); # 返回第一个非null值
select greatest(1,2,3); #返回最大值
select least(1,2,3); #返回最小值
select isnull(0); # is null 1 otherwise 0;
字符串函数
concat
-
语法及使用特点:
CONCAT(str1,str2,…)
返回结果为连接参数产生的字符串。如有任何一个参数为NULL ,则返回值为 NULL。可以有一个或多个参数。 -
例子
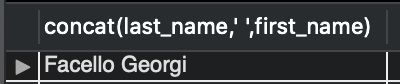
select concat(last_name,' ',first_name) from Name limit 1;
select concat(last_name,' ',first_name,null) from Name limit 1;
return null;
concat_ws
CONCAT_WS(separator,str1,str2,…)
CONCAT_WS() 代表 CONCAT With Separator ,是CONCAT()的特殊形式。
select concat_ws(last_name,' ',first_name,null) from Name limit 2;

忽略null,如果拼接字符串中存在空格字符串也忽略。如果空格字符串是separator位置的话,则以该字符串为分隔符;
select concat_ws(' ',last_name,first_name,null) from Name limit 2;
group_concat
- 用法一
group_concat(column1,column2,…) from table_name;
则将表中所有列的值都拼接起来成一个字符串,每个元组以,隔开; seperator = ,是default。
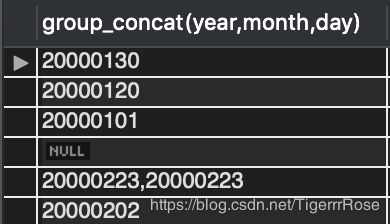
select group_concat(year,month,day) from t1;
‘20000101,20000120,20000130,20000202,20000223,20000223’
如果加group by的话,则每个group的元组都拼接起来,最终成为k个group的字符串; 可加order by进行排序 或者 distinct去重。
select group_concat(year,month,day) from t1 group by year,month,day order by month,day desc;
select group_concat(year,month,day) from t1 group by year,month order by month desc;
select group_concat(distinct year,month,day) from t1 group by year,month order by month desc;
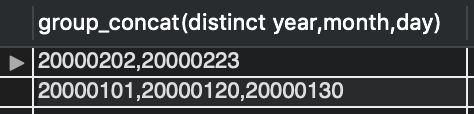
2. 用法二
GROUP_CONCAT(
DISTINCT expression
ORDER BY expression
SEPARATOR sep
);
例子:
CREATE TABLE t (
v CHAR
);
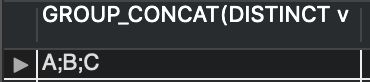
INSERT INTO t(v) VALUES('A'),('B'),('C'),('B');
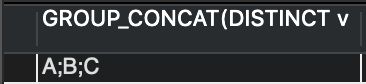
SELECT
GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT v
ORDER BY v ASC
SEPARATOR ';')
FROM
t;
SELECT
GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT v
# ORDER BY v desc
SEPARATOR ';')
FROM
t
order by v desc;
系统默认最大字符串长度1024, 超过这个长度的字符串就被截断;
可以通过
set session group_concat_max_len = 18446744073709551615;
来设置:
group_concat()将不同行的结果拼接起来;
而concat_ws()将不同列的结果拼接起来;
Note that GROUP_CONCAT() function concatenates string values in different rows while the CONCAT_WS() or CONCAT()function concatenates two or more string values in different columns.
控制流函数跟表达 control flow and expression
允许在sql查询中加入 if-then-else等逻辑判断;
CASE
– return the corresponding result in THEN branch if the condition in the WHEN branch is satisfied, otherwise, return the result in the ELSE branch.
1. simple case
CASE value
WHEN value1 THEN result1
WHEN value2 THEN result2
…
[ELSE else_result]
END
不可以用null作为判断语句,因为null=null 返回false;
例子:
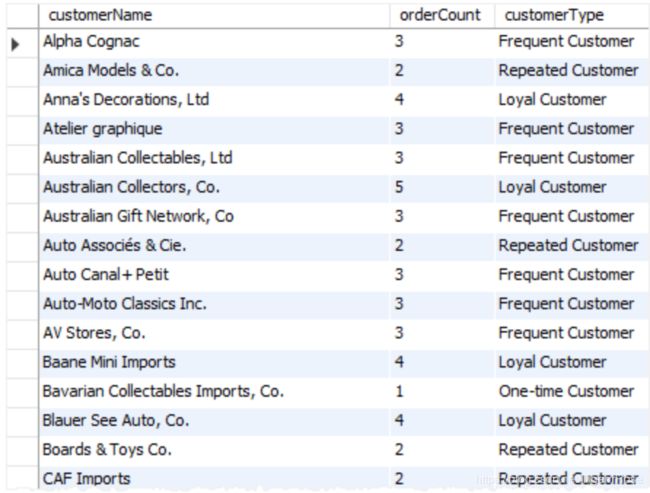
要返回顾客名跟下单数,并新建一列为顾客贴上标签,下单数=1的话为 one-time Customer, 2为 repeated ccustomer,3为 frequent customer, 其他为loyal customer;
select
customerName,
orderCount,
CASE orderCount
when 1 then 'one time'
when 2 then 'repeated'
when 3 then 'frequent'
else 'loyal'
end customerType
FROM
(select customerName, count(*) orderCount from customers
join orders using (customerNumber)
group by customerName
order by customerName) D;
做法二 用with table_name as (xxxx) 创建临时表
WITH cte AS (
SELECT
customerName,
COUNT(*) orderCount
FROM
orders
INNER JOIN customers
USING (customerNumber)
GROUP BY customerName
)
SELECT
customerName,
orderCount,
CASE orderCount
WHEN 1 THEN 'One-time Customer'
WHEN 2 THEN 'Repeated Customer'
WHEN 3 THEN 'Frequent Customer'
ELSE 'Loyal Customer'
end customerType
FROM
cte
ORDER BY customerName;
2. searched case
CASE
WHEN expression1 THEN result1
WHEN expression2 THEN result2
…
[ELSE else_result]
END
例子1:嵌套在order里面 sort
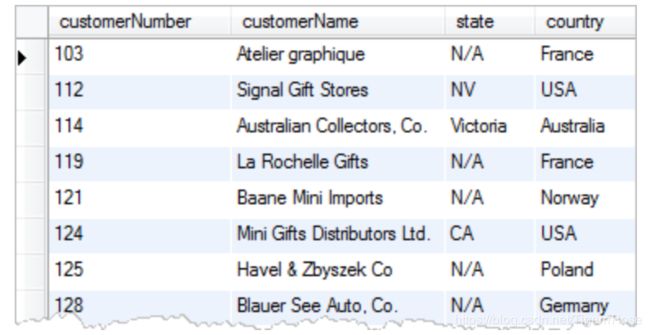
结果是选出顾客名,洲,国家,并按所在的洲排序,如果洲是null的话则按照国家排序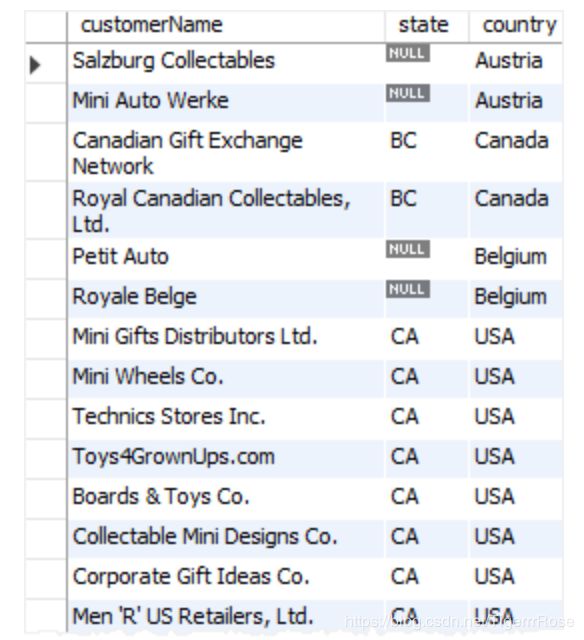
SELECT
customerName,
state,
country
FROM
customers
ORDER BY (
CASE
WHEN state IS NULL
THEN country
ELSE state
END);
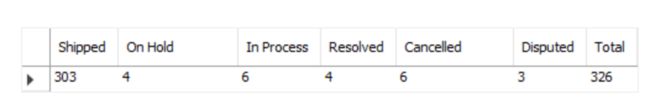
SELECT
SUM(CASE
WHEN status = 'Shipped' THEN 1
ELSE 0
END) AS 'Shipped',
SUM(CASE
WHEN status = 'On Hold' THEN 1
ELSE 0
END) AS 'On Hold',
SUM(CASE
WHEN status = 'In Process' THEN 1
ELSE 0
END) AS 'In Process',
SUM(CASE
WHEN status = 'Resolved' THEN 1
ELSE 0
END) AS 'Resolved',
SUM(CASE
WHEN status = 'Cancelled' THEN 1
ELSE 0
END) AS 'Cancelled',
SUM(CASE
WHEN status = 'Disputed' THEN 1
ELSE 0
END) AS 'Disputed',
COUNT(*) AS Total
FROM
orders;
该题也可以用if解决,或者 countif 解决, countif 中不计null
SELECT
sum(if(status='Shipped',1,0)) as 'Shipped',
sum(if(status='On Hold',1,0)) as 'On Hold',
sum(if(status='In Process',1,0)) as 'In Process',
sum(if(status='Resolved',1,0)) as 'Resolved',
sum(if(status='Cancelled',1,0)) as 'Cancelled',
sum(if(status='Disputed',1,0)) as 'Disputed',
count(*) as total
FROM orders;
SELECT
COUNT(IF(status = 'Cancelled', 1, NULL)) Cancelled,
COUNT(IF(status = 'Disputed', 1, NULL)) Disputed,
COUNT(IF(status = 'In Process', 1, NULL)) 'In Process',
COUNT(IF(status = 'On Hold', 1, NULL)) 'On Hold',
COUNT(IF(status = 'Resolved', 1, NULL)) 'Resolved',
COUNT(IF(status = 'Shipped', 1, NULL)) 'Shipped'
FROM
orders;
ps 附更
Note that MySQL has a CASE statement that you can use only in stored programs such as stored procedures, stored functions, events and triggers, which is not the CASE expression covered in this tutorial.
IF
IF(expr,if_true_expr,if_false_expr)
SELECT IF(1 = 2,'true','false'); -- false
SELECT IF(1 = 1,' true','false'); -- true
select customername,customerNumber,if(state is null,'N/A',state) state,country
from customers;
IFNULL
IFNULL(expression_1,expression_2);
如果expression1是null的话,返回expression2,否则的话返回expression1;
空字符串不等于null!!!
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS contacts (
contactid INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
contactname VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
bizphone VARCHAR(15),
homephone VARCHAR(15)
);
INSERT INTO contacts(contactname,bizphone,homephone)
VALUES('John Doe','(541) 754-3009',NULL),
('Cindy Smith',NULL,'(541) 754-3110'),
('Sue Greenspan','(541) 754-3010','(541) 754-3011'),
('Lily Bush',NULL,'(541) 754-3111');
select * from contacts;

homephone bizphone 均存在null值,如果bizphone是null的话用homophone 替代,如果homophone是null的话用bizphone替代;
select contactName,ifnull(bizphone,homephone),ifnull(homephone,bizphone)
from contacts;
– return the first argument if it is not NULL , otherwise returns the second argument.
NULLIF
NULLIF(expression_1,expression_2);
如果expression1跟expression2相等的话,返回null,
否则返回 expression1。
跟searched case 语句类似
CASE WHEN expression_1 = expression_2
THEN NULL
ELSE
expression_1
END;
用法1 防止被除数是0
SELECT 1/NULLIF(0,0); -- return NULL
在新版的sql中已经默认把除数0改为null;
问题
CREATE TABLE special_isnull (
start_date DATE NOT NULL
);
INSERT INTO special_isnull(start_date)
VALUES('2000-01-01'),
('0000-00-00');
INSERT INTO special_isnull(start_date)
VALUES('2000-01-01'),
('0000-00-00');
对null的行都选出来,
SELECT
*
FROM
special_isnull
WHERE isnull(start_date);
按理应该返回空表
但返回了
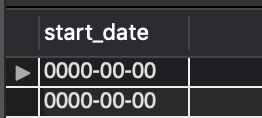
试了一下 select isnull(‘0000-00-00’);
但返回了0 说明该值不是null,但为啥会被选出来呢?