2与27日 双目视觉系统,相机标定,矫正,匹配(特征,稠密),特征提取的方法,得到视差图
双目立体视觉系统
CVST提供了双目立体视觉处理、校正、仿真的函数,这极大的提高了我们对双目立体视觉系统研究的效率。本节将介绍双目立体视觉系统的基本结构及相较于单目视觉系统的优势等。
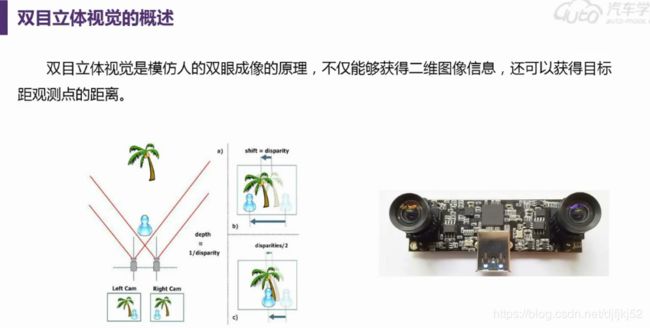
双目系统可以获得景深信息
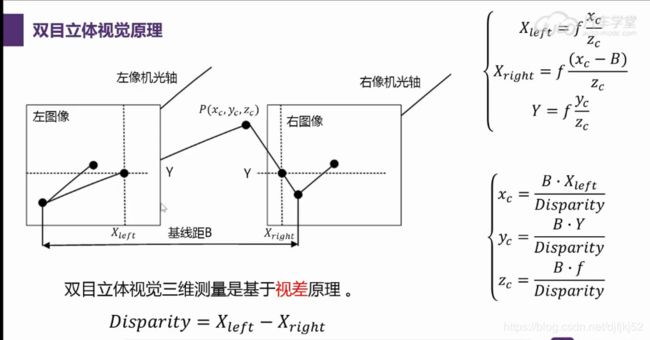
原理
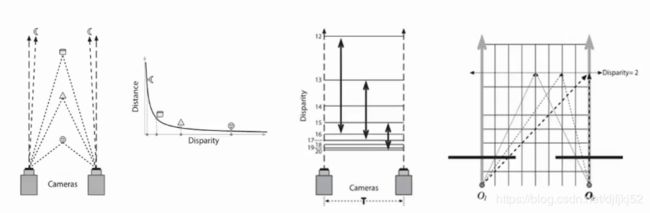
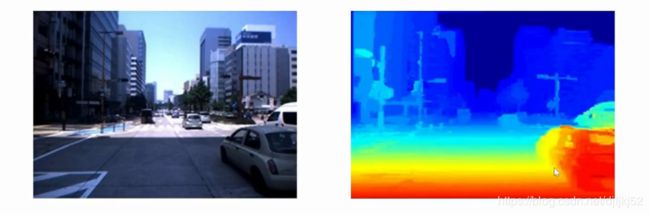
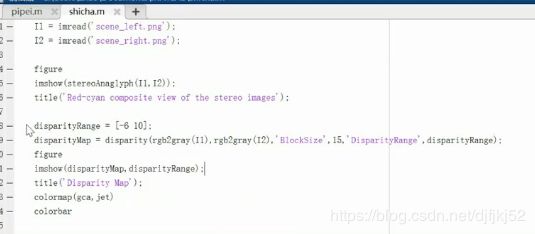
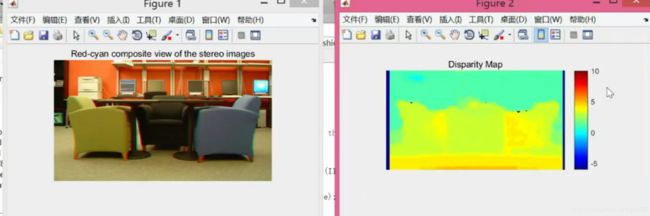
视差图
编程
处理流程
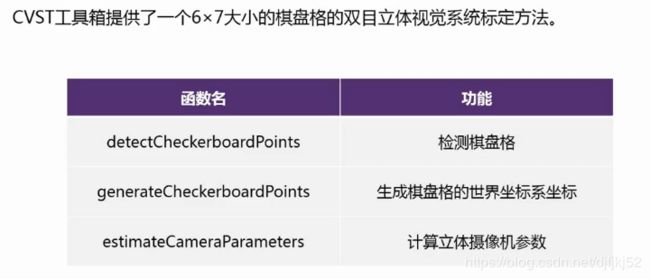
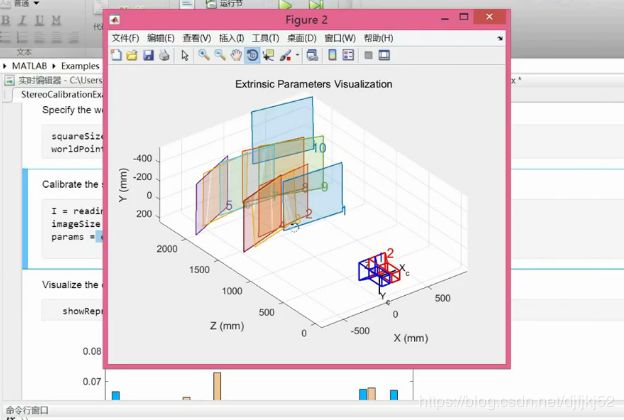
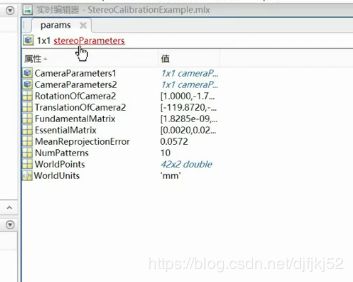
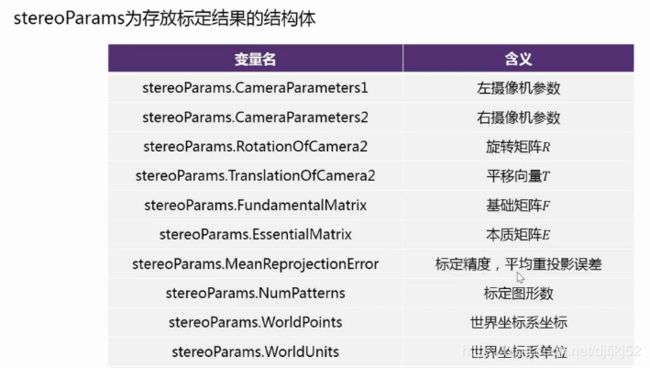
相机标定——target:得到内参,外参,畸变参数
标定流程
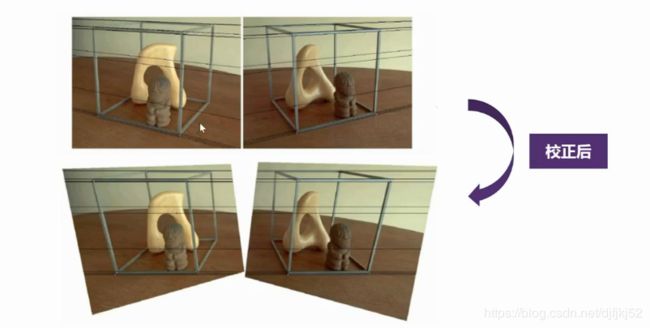
图像校正——target:输入两幅图像,相机参数,输出矫正后的图像
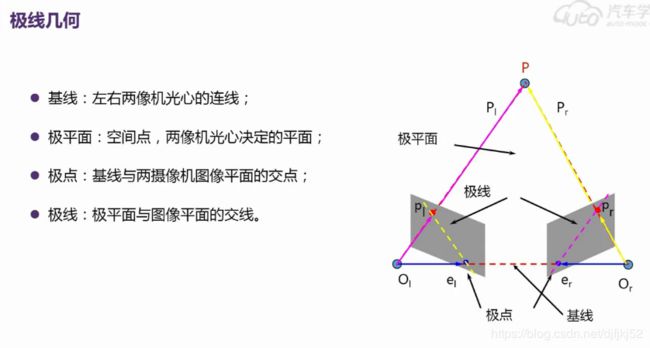
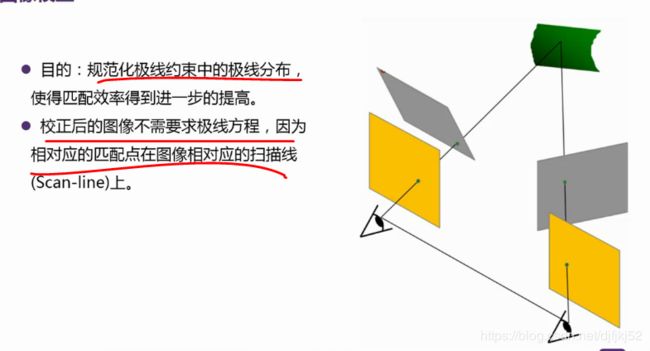
极线几何的相关概念:
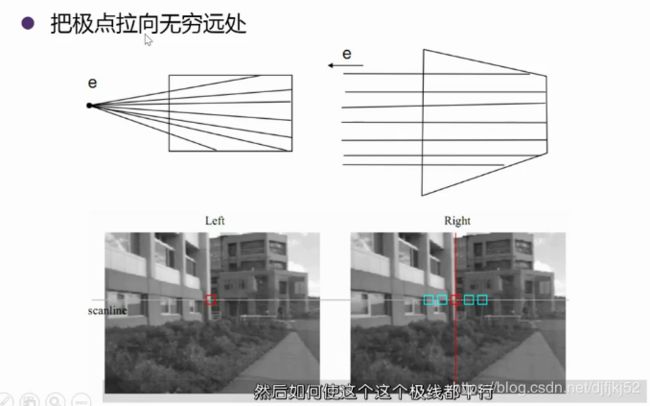
矫正:让极线平行
立体匹配
特征匹配
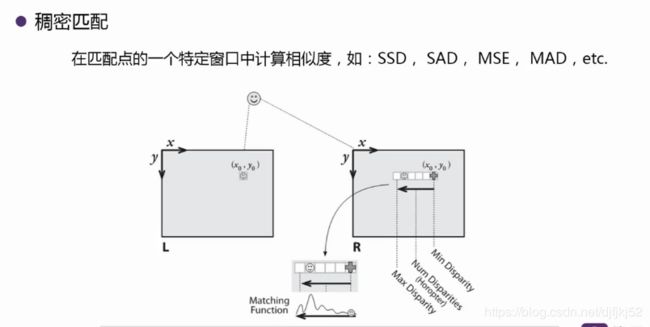
稠密匹配
| a | b |
|---|---|
| Matching cost computation; | |
| Cost aggregation: connects the matching cost within a certain neighborhood; | |
| Disparity computation: selects the disparity with the lowest matching cost; | |
| Disparity refinement: removing peaks, interpolating gaps or increasing the accuracy by sub-pixel interpolation. |
中心思想及要求
idea: 使用MI (Mutual Information) 来进行单像素匹配 + 多个一维平滑约束(来拟二维约束)来进行“全局”优化。
前提: 已知立体像对间的对极几何关系。
计算视差
MATLAB图像处理-特征提取-形状特征 方法小结
https://blog.csdn.net/wenyusuran/article/details/41724801?locationNum=6
matlab 中的extractFeatures函数:Extract interest point descriptors
[features,validPoints] = extractFeatures(I,points)%);%这里的points就是detectSURFFeatures函数的返回值, I 就是输入的灰度图像
[features,validPoints] = extractFeatures(I,points,Name,Value)
用这个函数来提取选中的特征点:
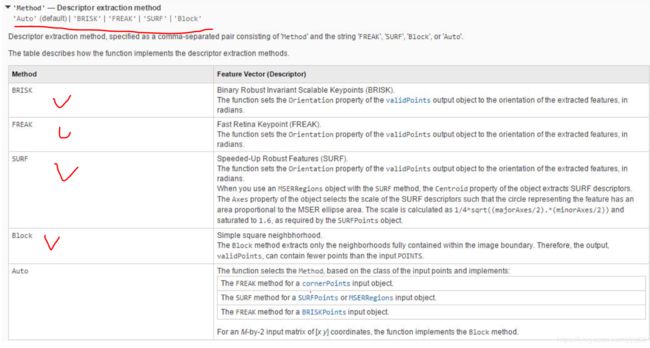
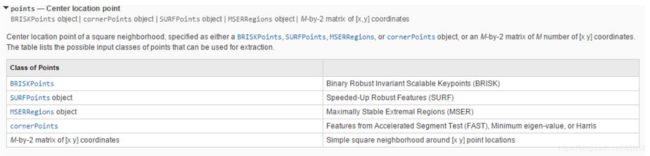
这里的特征点只能是用这几种方法提取出的特征点:
detectSURFFeatures
points = detectSURFFeatures(I) %I是输入的灰度图像,返回值是一个 SURFPoints类,这个SURFPoints类包含了一些从这个灰度图像中提取的一些特征
points = detectSURFFeatures(I,Name,Value)
SURFPoints 这个类型
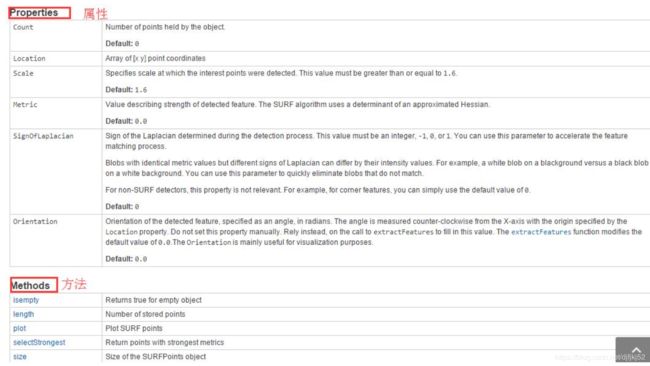
属性
- cout : 计算这个物体所拥有点的数量
- Location:定位这个点
- scale:确定这个兴趣点的取值范围
- length:长度
角点
角点所在的领域通常也是图像中稳定的,信息丰富的区域,这些领域看能具有某些特性如旋转不变性,尺度不变性,仿射不变性和光照亮度不变性。
%Read the image.
I = imread('cameraman.tif');
Find and extract corner features.
%corners = detectHarrisFeatures(I);
[features, valid_corners] = extractFeatures(I, corners);
%Display image.
figure; imshow(I); hold on
plot(valid_corners);
SURF特征
SURF特征提取检测
SURF将DoH中的高斯二阶微分模板进行了近似简化,使得模板对图像的滤波只需要进行几个简单的加减法运算,并且,这种预算与滤波模板的尺寸无关,从而极大地提高了尺度不变特征的检测速度。https://blog.csdn.net/PaTricKHzp/article/details/68944072
points = detectSURFFeatures(I);%I是输入的灰度图像,返回值是一个 SURFPoints类,这个SURFPoints类包含了一些从这个灰度图像中提取的一些特征
I = imread('cameraman.tif');
%Find and extract features.
points = detectSURFFeatures(I);%I是输入的灰度图像,返回值是一个 SURFPoints类,这个SURFPoints类包含了一些从这个灰度图像中提取的一些特征
[features, valid_points] = extractFeatures(I, points);
%Display and plot ten strongest SURF features.
figure; imshow(I); hold on;
plot(valid_points.selectStrongest(10),'showOrientation',true);
提一下:基于SURF特征的目标检测流程
载入图像
分别检测SURF特征点
分别提取SURF描述子,即特征向量
用两个特征相互匹配
利用匹配结果计算两者之间的transform关系tform
根据obj位置与变换关系tform,在scene图上框出obj
Extract MSERFeatures from an Image,MSER提取特征
I = imread('cameraman.tif');
%Find features using MSER with SURF feature descriptor.
regions = detectMSERFeatures(I);
[features, valid_points] = extractFeatures(I,regions,'Upright',true);
%Display SURF features corresponding to the MSER ellipse centers.
figure; imshow(I); hold on;
plot(valid_points,'showOrientation',true);
matchFeatures
indexPairs = matchFeatures(features1,features2);
[indexPairs,matchmetric] = matchFeatures(features1,features2);
[indexPairs,matchmetric] = matchFeatures(features1,features2,Name,Value);123
indexPairs 是返回的两幅图像匹配的指标%这个地方可以将他的返回值进行截图
features1就是上面extractFeatures函数的返回值中validpoints,然后只用输入想要配对的两张图片就可以了
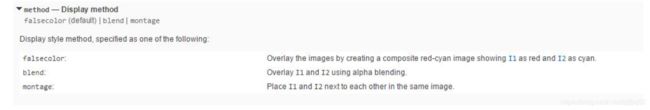
showMatchedFeatures
showMatchedFeatures(I1,I2,matchedPoints1,matchedPoints2)
showMatchedFeatures(I1,I2,matchedPoints1,matchedPoints2,method)
% I1 和 I2就是需要匹配的两个函数
clc
%读取图像
I1= imread('D:\matlab 2015b\workspace\source\1.jpg');
I1=imresize(I1,0.6); %imresize 将原来的图像缩小原来的一般
I1=rgb2gray(I1); %把RGB图像变成灰度图像
figure
imshow(I1)
I2= imread('D:\matlab 2015b\workspace\source\2.jpg');
I2=imresize(I2,0.6);
I2=rgb2gray(I2);
figure
imshow(I2)
%寻找特征点
points1 = detectSURFFeatures(I1); %读取特征点
points2 = detectSURFFeatures(I2);
%Extract the features.计算描述向量
[f1, vpts1] = extractFeatures(I1, points1);
[f2, vpts2] = extractFeatures(I2, points2);
%Retrieve the locations of matched points. The SURF feature vectors are already normalized.
%进行匹配
indexPairs = matchFeatures(f1, f2, 'Prenormalized', true) ;
matched_pts1 = vpts1(indexPairs(:, 1)); %这个地方应该是对他进行取值吧 这个应该是啊吧他们做成一个数组
matched_pts2 = vpts2(indexPairs(:, 2));
%显示匹配
figure('name','匹配后的图像'); showMatchedFeatures(I1,I2,matched_pts1,matched_pts2,'montage'); %总共找了39个特征点
legend('matched points 1','matched points 2');
目标识取
%step1:读取图片
%读取object图片
boxImage = imread('stapleRemover.jpg');
%读取场景图片
sceneImage = imread('clutteredDesk.jpg');
%step2:检测特征点
boxPoints = detectSURFFeatures(boxImage);
scenePoints = detectSURFFeatures(sceneImage);
% figure; imshow(boxImage);
% title('Box Image中最强的100个feature points');
% hold on;
% plot(boxPoints.selectStrongest(100));
%step3 extract feature descriptors 提取出特征的描述子
%使用extractFeatures(),具体的feature类型是通过boxPoints位置的参数指定的,这里是SURF
%烂设计,为什么extractFeatures输入了boxPoints后,还要返回boxPoints?
[boxFeatures, boxPoints] = extractFeatures(boxImage, boxPoints);
[sceneFeatures, scenePoints] = extractFeatures(sceneImage, scenePoints);
%step4 find putative point matches
%Match the features using their descriptors.
boxPairs = matchFeatures(boxFeatures, sceneFeatures);
%Display putatively matched features.
matchedBoxPoints = boxPoints(boxPairs(:,1), :);
matchedScenePoints = scenePoints(boxPairs(:,2),:);
figure;
showMatchedFeatures(boxImage, sceneImage, matchedBoxPoints, matchedScenePoints, 'montage');
title('Putatively Matched Points (Including Outliers)');
%step5 locate the Object in the Scene Using Putative Matches
[tform, inlierBoxPoints, inlierScenePoints] = ...
estimateGeometricTransform(matchedBoxPoints, matchedScenePoints, 'affine');
figure;
showMatchedFeatures(boxImage, sceneImage, inlierBoxPoints, ...
inlierScenePoints, 'montage');
title('Matched Points (Inliers Only)');
%Get the bounding polygon of the reference image.
boxPolygon = [1, 1;... % top-left
size(boxImage,2), 1; ... % top-right
size(boxImage, 2), size(boxImage, 1); ... % bottom-right
1, size(boxImage, 1); ... % bottom-left
1, 1]; % top-left again to close the polygon
% transform the polygon into the coordinate system of the target image
%将多边形变换到目标图片上,变换的结果表示了物体的位置
newBoxPolygon = transformPointsForward(tform, boxPolygon);
%display the detected object 显示被检测到的物体
figure; imshow(sceneImage);
hold on;
line(newBoxPolygon(:, 1), newBoxPolygon(:, 2), 'Color', 'y');
title('Detected Box');
各种方法
https://blog.csdn.net/wenyusuran/article/details/41724801?locationNum=6
(一)特点:
各种基于形状特征的检索方法都可以比较有效地利用图像中感兴趣的目标来进行检索,但它们也有一些共同的问题,包括:①目前基于形状的检索方法还缺乏比较完善的数学模型;②如果目标有变形时检索结果往往不太可靠;③许多形状特征仅描述了目标局部的性质,要全面描述目标常对计算时间和存储量有较高的要求;④许多形状特征所反映的目标形状信息与人的直观感觉不完全一致,或者说,特征空间的相似性与人视觉系统感受到的相似性有差别。另外,从 2-D 图像中表现的 3-D 物体实际上只是物体在空间某一平面的投影,从 2-D 图像中反映出来的形状常不是 3-D 物体真实的形状,由于视点的变化,可能会产生各种失真。
(二)常用的特征提取与匹配方法
基于小波和相对矩的形状特征提取与匹配
该方法先用小波变换模极大值得到多尺度边缘图像,然后计算每一尺度的 7个不变矩,再转化为 10 个相对矩,将所有尺度上的相对矩作为图像特征向量,从而统一了区域和封闭、不封闭结构
几种典型的形状特征描述方法
通常情况下,形状特征有两类表示方法,一类是轮廓特征,另一类是区域特征。图像的轮廓特征主要针对物体的外边界,而图像的区域特征则关系到整个形状区域。
几种典型的形状特征描述方法:
(1)边界特征法该方法通过对边界特征的描述来获取图像的形状参数。其中Hough 变换检测平行直线方法和边界方向直方图方法是经典方法。Hough 变换是利用图像全局特性而将边缘像素连接起来组成区域封闭边界的一种方法,其基本思想是点—线的对偶性;边界方向直方图法首先微分图像求得图像边缘,然后,做出关于边缘大小和方向的直方图,通常的方法是构造图像灰度梯度方向矩阵。
(2)傅里叶形状描述符法
傅里叶形状描述符(Fourier shape descriptors)基本思想是用物体边界的傅里叶变换作为形状描述,利用区域边界的封闭性和周期性,将二维问题转化为一维问题。
由边界点导出三种形状表达,分别是曲率函数、质心距离、复坐标函数。
(3)几何参数法
形状的表达和匹配采用更为简单的区域特征描述方法,例如采用有关形状定量测度(如矩、面积、周长等)的形状参数法(shape factor)。在 QBIC 系统中,便是利用圆度、偏心率、主轴方向和代数不变矩等几何参数,进行基于形状特征的图像检索。
需要说明的是,形状参数的提取,必须以图像处理及图像分割为前提,参数的准确性必然受到分割效果的影响,对分割效果很差的图像,形状参数甚至无法提取。
(4)形状不变矩法
利用目标所占区域的矩作为形状描述参数。
(5)其它方法
近年来,在形状的表示和匹配方面的工作还包括有限元法(Finite Element Method 或 FEM)、旋转函数(Turning Function)和小波描述符(Wavelet Descriptor)等方法。