新特性:Andorid-foreground 解析
Andorid-foreground 解析
foreground 前景色
foreground 也就是前景色,它与background相对应,顾名思义,它指定的drawable是在view视图的上方绘制的。
开发实例
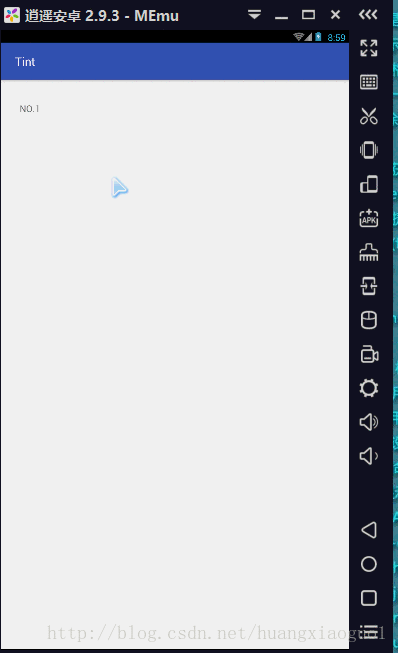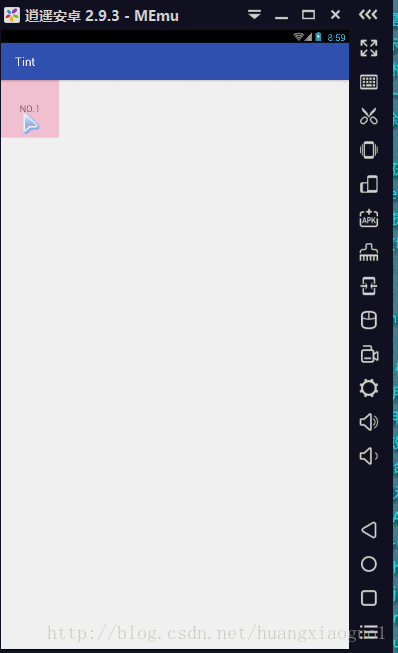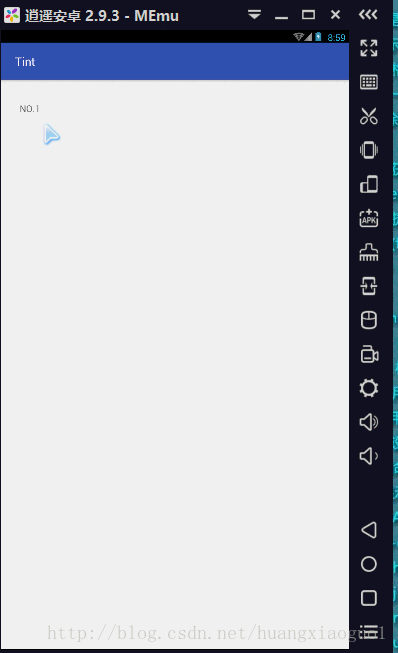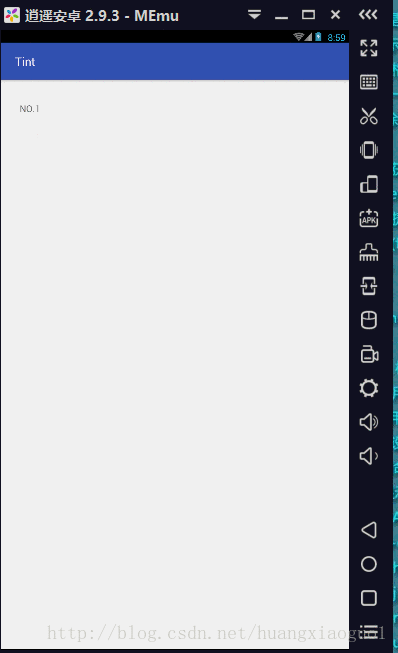
1.实现遮罩层:
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/id_frameLayout"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:foreground="#aaff0000"
android:foregroundTintMode="src_in"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/id_text"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:text="NO.1"
android:gravity="center_horizontal|center_vertical"
/>
FrameLayout>实现效果
2.实现点击效果
属性能设置为drawable,我们自然就想到了也可以使用 selector drawable,在点击时套上drawable来实现类似点击效果的功能
xml代码:
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/id_frameLayout"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/transparent"
android:foreground="@drawable/selector_foreground"
android:foregroundTintMode="src_in"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/id_text"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:text="NO.1"
android:gravity="center_horizontal|center_vertical"
/>
FrameLayout>drawable:
<selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:enterFadeDuration="@android:integer/config_shortAnimTime"
android:exitFadeDuration="@android:integer/config_mediumAnimTime"
>
<item android:state_pressed="true">
<shape
android:shape="rectangle">
<solid android:color="#15000000"/>
shape>
item>
<item android:drawable="@android:color/transparent">
item>
selector>当然别忘记了在代码中给 frameLayout 设置点击事件
实现效果:
缺陷
Android在所有布局的基类 View 类中 就定义了 Foreground 这个属性,但是测试发现 运行时,只有FrameLayout布局上设置该属性才会生效。观察View的代码发现这样一段。它只针对是FrameLayout的实例做获取该styleable的操作。
case R.styleable.View_foreground:
if (targetSdkVersion >= VERSION_CODES.M || this instanceof FrameLayout) {
setForeground(a.getDrawable(attr));
}
break;
case R.styleable.View_foregroundGravity:
if (targetSdkVersion >= VERSION_CODES.M || this instanceof FrameLayout) {
setForegroundGravity(a.getInt(attr, Gravity.NO_GRAVITY));
}
break;解决方案
模拟,FrameLayout的相关实现为TextView添加foreGround的代码功能
public class ForegroundTextView extends TextView {
// UI
private Drawable foreground;
// Controller/logic fields
private final Rect rectPadding = new Rect();
private boolean foregroundPadding = false;
private boolean foregroundBoundsChanged = false;
private boolean backgroundAsForeground = false;
// Constructors
public ForegroundTextView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public ForegroundTextView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public ForegroundTextView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
final TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.ForegroundLayout, defStyle, 0);
final Drawable d = a.getDrawable(R.styleable.ForegroundLayout_foreground);
foregroundPadding = a.getBoolean(R.styleable.ForegroundLayout_foregroundInsidePadding, false);
backgroundAsForeground = a.getBoolean(R.styleable.ForegroundLayout_backgroundAsForeground, false);
// Apply foreground padding for ninepatches automatically
if (!foregroundPadding && getBackground() instanceof NinePatchDrawable) {
final NinePatchDrawable npd = (NinePatchDrawable) getBackground();
if (npd != null && npd.getPadding(rectPadding)) {
foregroundPadding = true;
}
}
final Drawable b = getBackground();
if (backgroundAsForeground && b != null) {
setForeground(b);
} else if (d != null) {
setForeground(d);
}
a.recycle();
}
/**
* Supply a Drawable that is to be rendered on top of all of the child views in the layout.
*
* @param drawable The Drawable to be drawn on top of the children.
*/
public void setForeground(Drawable drawable) {
if (foreground != drawable) {
if (foreground != null) {
foreground.setCallback(null);
unscheduleDrawable(foreground);
}
foreground = drawable;
if (drawable != null) {
setWillNotDraw(false);
drawable.setCallback(this);
if (drawable.isStateful()) {
drawable.setState(getDrawableState());
}
} else {
setWillNotDraw(true);
}
requestLayout();
invalidate();
}
}
/**
* Returns the drawable used as the foreground of this layout. The foreground drawable,
* if non-null, is always drawn on top of the children.
*
* @return A Drawable or null if no foreground was set.
*/
public Drawable getForeground() {
return foreground;
}
@Override
protected void drawableStateChanged() {
super.drawableStateChanged();
if (foreground != null && foreground.isStateful()) {
foreground.setState(getDrawableState());
}
}
@Override
protected boolean verifyDrawable(Drawable who) {
return super.verifyDrawable(who) || (who == foreground);
}
@Override
public void jumpDrawablesToCurrentState() {
super.jumpDrawablesToCurrentState();
if (foreground != null) {
foreground.jumpToCurrentState();
}
}
@Override protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
foregroundBoundsChanged = true;
}
@Override
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
super.draw(canvas);
if (foreground != null) {
final Drawable foreground = this.foreground;
if (foregroundBoundsChanged) {
foregroundBoundsChanged = false;
final int w = getRight() - getLeft();
final int h = getBottom() - getTop();
if (foregroundPadding) {
foreground.setBounds(rectPadding.left, rectPadding.top, w - rectPadding.right, h - rectPadding.bottom);
} else {
foreground.setBounds(0, 0, w, h);
}
}
foreground.draw(canvas);
}
}
@TargetApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) @Override public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent e) {
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
if (e.getActionMasked() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
if (foreground != null) {
foreground.setHotspot(e.getX(), e.getY());
}
}
}
return super.onTouchEvent(e);
}
}原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/zhuoxiuwu/article/details/50976145