解决:Android中常见的热门标签的流式布局flowlayout不能wrap_content
最近在项目中药使用流式布局,但是在网上找的都不能满足要求,这篇博客内容只支持match_parent,我改后的代码可以支持wrap_content,原文也仅仅是少加一行高度而已。。新博客希望大家多多评论。。原文链接
一:概述:
1.流式布局的特点以及应用场景
特点:当上面一行的空间不够容纳新的TextView时候,
才开辟下一行的空间
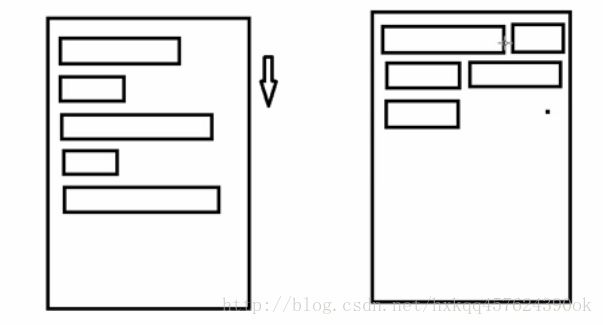
场景:主要用于关键词搜索或者热门标签等场景
2.自定义ViewGroup,重点重写下面两个方法
1、onMeasure:测量子view的宽高,设置自己的宽和高
2、onLayout:设置子view的位置
onMeasure:根据子view的布局文件中属性,来为子view设置测量模式和测量值
测量=测量模式+测量值;
测量模式有3种:
EXACTLY:表示设置了精确的值,一般当childView设置其宽、高为精确值、match_parent时,ViewGroup会将其设置为EXACTLY;
AT_MOST:表示子布局被限制在一个最大值内,一般当childView设置其宽、高为wrap_content时,ViewGroup会将其设置为AT_MOST;
UNSPECIFIED:表示子布局想要多大就多大,一般出现在AadapterView的item的heightMode中、ScrollView的childView的heightMode中;此种模式比较少见。
3.LayoutParams
ViewGroup LayoutParams :每个 ViewGroup 对应一个 LayoutParams; 即 ViewGroup -> LayoutParams
getLayoutParams 不知道转为哪个对应的LayoutParams ,其实很简单,就是如下:
子View.getLayoutParams 得到的LayoutParams对应的就是 子View所在的父控件的LayoutParams;
例如,LinearLayout 里面的子view.getLayoutParams ->LinearLayout.LayoutParams
所以 咱们的FlowLayout 也需要一个LayoutParams,由于上面的效果图是子View的 margin,
所以应该使用MarginLayoutParams。即FlowLayout->MarginLayoutParams
4.最后来看看实现的最终效果图:
二:代码
- 自定义热门标签的ViewGroup实现
根据上面的技术分析,自定义类继承于ViewGroup,并重写 onMeasure和onLayout等方法。具体实现代码如下:
我主要改了原文中onMeasure中的一些代码,让它可以包裹内容
1,自定义flowlayout代码
package com.yaofangwang.flowlayout;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class FlowGroupView extends ViewGroup {
/**
* 储存所有的view 按行记录
*/
private List> mAllViews = new ArrayList>();
/**
* 记录每一行的高度
*/
private List mLineHeight = new ArrayList();
private String TAG = "TAG";
public FlowGroupView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs,
int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
public FlowGroupView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public FlowGroupView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// 置空 view 容器 和 lineHeight 容器 重新赋值
//因为OnMeasure方法会走两次,第一次是实例化这个对象的时候高度和宽度都是0
//之后走了OnSizeChange()方法后 又走了一次OnMeasure,所以要把第一次加进去的数据清空。
mAllViews.clear();
mLineHeight.clear();
//得到上级容器为其推荐的宽高和计算模式
int specWidthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int specHeighMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int specWidthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int specHeighSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
// 计算出所有的 child 的 宽和高
// measureChildren(specWidthSize, specHeighSize);
// 记录如果是 warp_content 是设置的宽和高
int width = 0;
int height = 0;
// 得到子view的个数
int cCount = getChildCount();
/**
* 记录每一行的宽度,width不断取最大宽度
*/
int lineWidth = 0;
/**
* 每一行的高度,累加至height
*/
int lineHeight = 0;
// 存储每一行所有的childView
List lineViews = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < cCount; i++) {
// 得到每个子View
View child = getChildAt(i);
// 测量每个子View的宽高
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 当前子view的lp
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
// 子view的宽和高
int cWidth = 0;
int cheight = 0;
// 当前子 view 实际占的宽
cWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
// 当前子View 实际占的高
cheight = child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
lineHeight=cheight;
// 需要换行
if(lineWidth + cWidth > specWidthSize){
width = Math.max(lineWidth, cWidth);// 取最大值
lineWidth = cWidth; // 开启新行的时候重新累加width
// 开启新行时累加 height
// lineHeight = cheight; // 记录下一行的高度
mAllViews.add(lineViews);
mLineHeight.add(cheight);
lineViews = new ArrayList<>();
// 换行的时候把该 view 放进 集合里
lineViews.add(child);// 这个 view(child) 是下一行的第一个view
height += cheight; //每个View高度是一样的,直接累加
Log.e("需要换行", "hight--" + height);
Log.e("onMeasure", "AllViews.size() -- > " + mAllViews.size());
}else {
// 不需要换行
lineWidth += cWidth;//
Log.e("不需要换行","hight--"+height);
// 不需要换行时 把子View add 进集合
lineViews.add(child);
}
if(i == cCount-1){
// 如果是最后一个view
width = Math.max(lineWidth, cWidth);
height += cheight;
Log.e("最后一个view","hight--"+height);
}
}
// 循环结束后 把最后一行内容add进集合中
mLineHeight.add(lineHeight); // 记录最后一行
mAllViews.add(lineViews);
// MeasureSpec.EXACTLY 表示设置了精确的值
// 如果 mode 是 MeasureSpec.EXACTLY 时候,则不是 warp_content 用计算来的值,否则则用上级布局分给它的值
setMeasuredDimension(
specWidthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? specWidthSize : width,
specHeighMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? specHeighSize : height
);
Log.e("onMeasure", "mAllViews.size() -- > " + mAllViews.size() + " mLineHeight.size() -- > " + mLineHeight.size() + "Height -- > "+height);
}
/**
* 所有childView的位置的布局
*/
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
// 当前行的最大高度
int lineHeight = 0;
// 存储每一行所有的childView
List lineViews = new ArrayList();
int left = 0;
int top = 0;
// 得到总行数
int lineNums = mAllViews.size();
for (int i = 0; i < lineNums; i++)
{
// 每一行的所有的views
lineViews = mAllViews.get(i);
// 当前行的最大高度
lineHeight = mLineHeight.get(i);
Log.e("onLayout" , "第" + i + "行 :" + lineViews.size()+"-------lineHeight"+ lineHeight);
// 遍历当前行所有的View
for (int j = 0; j < lineViews.size(); j++)
{
View child = lineViews.get(j);
if (child.getVisibility() == View.GONE)
{
continue;
}
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
//计算childView的left,top,right,bottom
int lc = left + lp.leftMargin;
int tc = top + lp.topMargin;
int rc =lc + child.getMeasuredWidth();
int bc = tc + child.getMeasuredHeight();
child.layout(lc, tc, rc, bc);
left += child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.rightMargin + lp.leftMargin;
}
left = 0;
top += lineHeight;
}
Log.v("onLayout", "onLayout mAllViews.size() -- > " + mAllViews.size() + " mLineHeight.size() -- > "+ mLineHeight.size());
}
/**
* 这个一定要设置,否则会包强转错误
* 设置它支持 marginLayoutParams
*/
@Override
public ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(),attrs);
}
} 2,布局文件
"http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/layout"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<com.yaofangwang.flowlayout.FlowGroupView
android:id="@+id/flowgroupview"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
com.yaofangwang.flowlayout.FlowGroupView>
3,TextView的样式文件:
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" >
<solid android:color="#666666" />
<corners android:radius="10dp" />
<padding
android:left="5dp"
android:right="5dp"
android:top="5dp"
android:bottom="5dp"
/>
shape> 4,使用该布局的类
ArrayList names = new ArrayList();
FlowGroupView view;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
setData();
view = (FlowGroupView) findViewById(R.id.flowgroupview);
for (int i = 0; i < names.size(); i++) {
addTextView(names.get(i));
}
}
/**
* 动态添加布局
* @param str
*/
private void addTextView(String str) {
TextView child = new TextView(this);
ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams params = new ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams(ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
params.setMargins(15, 15, 15, 15);
child.setLayoutParams(params);
child.setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.shape_textback);
child.setText(str);
child.setTextColor(Color.WHITE);
initEvents(child);//监听
view.addView(child);
}
/**
* 为每个view 添加点击事件
*/
private void initEvents(final TextView tv){
tv.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, tv.getText().toString(), 0).show();
}
});
}
private void setData(){
names.add("降龙十八掌");
names.add("黯然销魂掌");
names.add("左右互搏术");
names.add("七十二路空明拳");
names.add("小无相功");
names.add("拈花指");
names.add("打狗棍法");
names.add("蛤蟆功");
names.add("九阴白骨爪");
names.add("一招半式闯江湖");
names.add("醉拳");
names.add("龙蛇虎豹");
names.add("葵花宝典");
names.add("吸星大法");
names.add("如来神掌警示牌");
}