Arduino 编程相关 使用EEPROM 断电数据不消失
很多时候,我们会在运行某个功能的时候要记录数据,
例如
我要做个人流量计算器,如果长时间运行又或者换电池等情况,会把珍贵的数据丢失。
所以现在我们用Arduino的EEPROM来及时存储数据,以便以后调用。
注意
EEPROM的刷写次数是有限的,并且一个地址只能存储数值0-255,其实实用性真的不太大
Arduino EEPROM 的设计寿命是 100,000 write/erase cycles (10万次写入/清除)
(10万次也不少,但如果经常需要修改数据,可以选择使用SD卡的方式)
Arduino Uno SD卡模块 (一)获取SDcard的信息
Arduino Uno SD卡模块 (二)读取文件
Arduino Uno SD卡模块 (三)创建文件并写入
Arduino Uno SD卡模块 (四)删除文件
程序
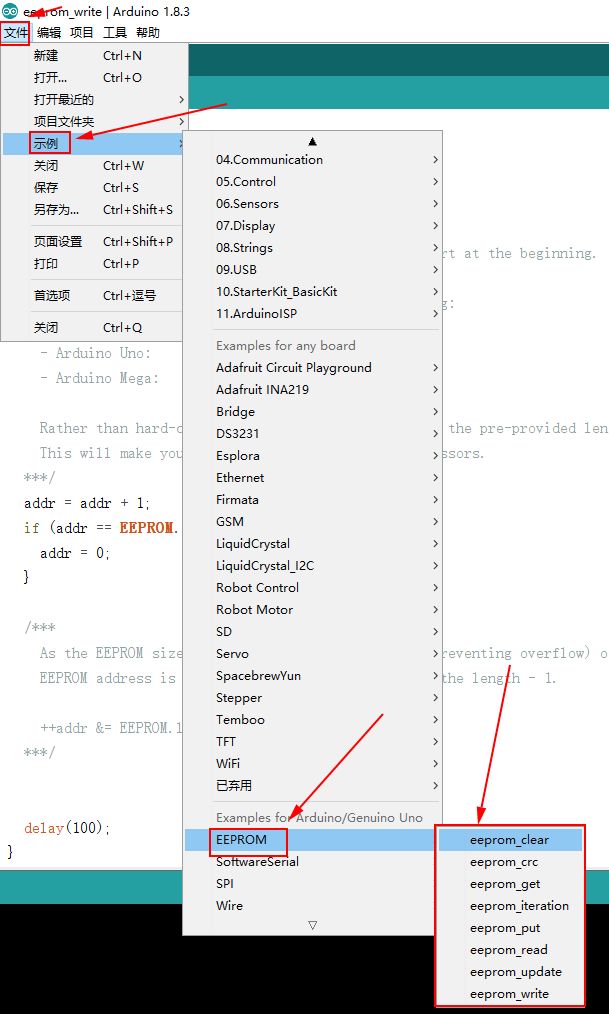
EEPROM官方库里有一些例子,按下图依次打开可以找到。
可以从例程名字大概可以猜到
eeprom_read eeprom读取
eeprom_write eeprom写入
eeprom_clear eeprom清除
还有其他,里面程序有大概说明,如eeprom_crc,打开有注释,大意是检查数据修改是否已修改和是否有损坏。
我先来看看写入的程序
/*
* EEPROM Write
* EEPROM 写入
* Stores values read from analog input 0 into the EEPROM.
* 读取模拟输入IO口0的数据写入EEPROM
* These values will stay in the EEPROM when the board is
* 这些数据会保留在EEPROM
* turned off and may be retrieved later by another sketch.
* 关闭此程序,将用另一程序读取
*/
#include
/** the current address in the EEPROM (i.e. which byte we're going to write to next) **/
/** EEPROM中的当前地址(即我们要写入下一个字节)**/
int addr = 0;
void setup() {
/** Empty setup. **/
}
void loop() {
/***
Need to divide by 4 because analog inputs range from
0 to 1023 and each byte of the EEPROM can only hold a
value from 0 to 255.
需要除以4,因为模拟输入范围从
0到1023,EEPROM的每个字节只能保持
一个值从0到255。
***/
int val = analogRead(0) / 4;
/***
Write the value to the appropriate byte of the EEPROM.
these values will remain there when the board is
turned off.
将值写入EEPROM的相应字节。
这些数据将在板子里留下
关掉程序。
***/
EEPROM.write(addr, val); //在地址addr写入val数据
/***
Advance to the next address, when at the end restart at the beginning.
Larger AVR processors have larger EEPROM sizes, E.g:
- Arduno Duemilanove: 512b EEPROM storage.
- Arduino Uno: 1kb EEPROM storage.
- Arduino Mega: 4kb EEPROM storage.
Rather than hard-coding the length, you should use the pre-provided length function.
This will make your code portable to all AVR processors.
提前到下一个地址,最后再重新由地址0开始继续写入数据。
较大的AVR处理器具有较大的EEPROM大小,例如:
- Arduno Duemilanove:512b EEPROM存储。
- Arduino Uno:1kb EEPROM存储。
- Arduino Mega:4kb EEPROM存储。
可以使用固定值长度,但你必须使用对应的长度。
这将使您的代码可移植到所有AVR处理器。
***/
addr = addr + 1; //地址addr+1
if (addr == EEPROM.length()) {//如果地址addr 等于EEPROM的大小,则
addr = 0; //addr重置为0
}
/***
As the EEPROM sizes are powers of two, wrapping (preventing overflow) of an
EEPROM address is also doable by a bitwise and of the length - 1.
由于EEPROM大小为2的幂,EEPROM地址的包装(防止溢出)也可以通过按位和长度为1来执行。
++addr &= EEPROM.length() - 1;
***/
delay(100);
} 在看看读取的程序
/*
* EEPROM Read
*
* Reads the value of each byte of the EEPROM and prints it
* to the computer.
* This example code is in the public domain.
*/
#include //加载EEOROM库
// start reading from the first byte (address 0) of the EEPROM
int address = 0; //定义地址address
byte value;
void setup() {
// initialize serial and wait for port to open:
// 初始化串行等待端口打开:
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial) {
; // wait for serial port to connect. Needed for native USB port only
//等待串口连接。 仅适用于本机USB端口
}
}
void loop() {
// read a byte from the current address of the EEPROM
//从EEPROM的当前地址读取一个字节
value = EEPROM.read(address);
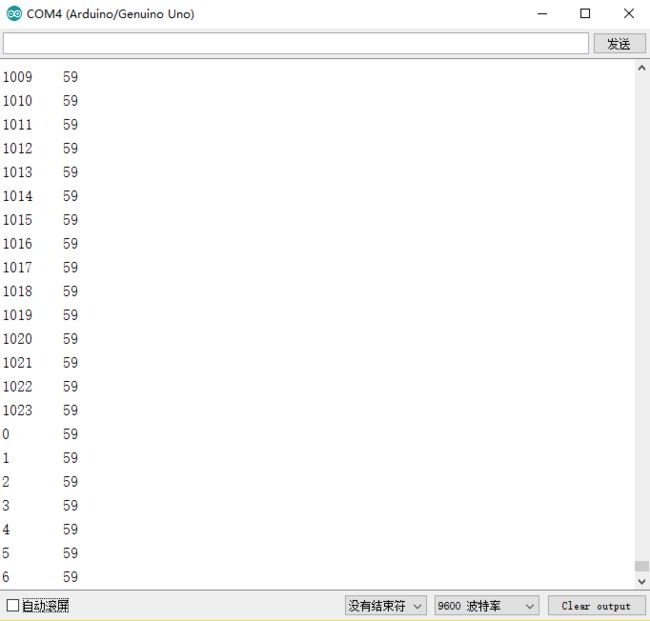
//在串口输出当前地址的序列,和对应的1字节数据
Serial.print(address);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(value, DEC);
Serial.println();
/***
Advance to the next address, when at the end restart at the beginning.
Larger AVR processors have larger EEPROM sizes, E.g:
- Arduno Duemilanove: 512b EEPROM storage.
- Arduino Uno: 1kb EEPROM storage.
- Arduino Mega: 4kb EEPROM storage.
Rather than hard-coding the length, you should use the pre-provided length function.
This will make your code portable to all AVR processors.
***/
//地址+1,读取到最后的地址时,又把地址重置为0重新读取一遍
address = address + 1;
if (address == EEPROM.length()) {
address = 0;
}
/***
As the EEPROM sizes are powers of two, wrapping (preventing overflow) of an
EEPROM address is also doable by a bitwise and of the length - 1.
++address &= EEPROM.length() - 1;
***/
delay(500);
} 
以上是写与读,比较常用的。清除就不再列举了,自己可以看看例子。
清楚的大概思路和写的一样,遍历每一个地址,把数值改成0,就是clear了。
程序思路讲解
1
#include
2
int addr = 0; //定义需要读取或者写入的地址
之后可以利用以下函数去进行相关处理
read()
write()
update()
get()
put()
EEPROM[]
相关资料:https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/EEPROM