Java8 File / FileSystem(一) 源码解析
目录
1、separator / pathSeparatorChar
2、构造方法
3、isAbsolute / getAbsolutePath / getCanonicalPath
4、exists / isDirectory / isFile / isHidden / lastModified / length
5、createNewFile / createTempFile / delete / deleteOnExit
6、mkdir / mkdirs
7、list / listFiles / listRoots
File表示文件系统中的一个文件,提供了文件操作的相关API,其底层实现都是通过FileSystem实现的。FileSystem表示底层操作系统的一个文件系统,windows下的实现是WinNTFileSystem,类Unix系统下的实现是UnixFileSystem,我们重点关注后者的实现细节。
1、separator / pathSeparatorChar
这两个是File类的public static属性,分别表示路径分隔符和多个路径字符串的分隔符,其定义如下:
//路径分隔符,对应系统属性file.separator
public static final String separator = "" + separatorChar;
public static final char separatorChar = fs.getSeparator();
//多个路径字符串的分隔符,对应系统属性path.separator
public static final String pathSeparator = "" + pathSeparatorChar;
public static final char pathSeparatorChar = fs.getPathSeparator();
//fs表示文件系统的实现
private static final FileSystem fs = DefaultFileSystem.getFileSystem();
//slash和colon都是UnixFileSystem的私有属性,在构造方法中完成初始化
public char getSeparator() {
return slash;
}
public char getPathSeparator() {
return colon;
}
public UnixFileSystem() {
//读取对应的系统属性
slash = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new GetPropertyAction("file.separator")).charAt(0);
colon = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new GetPropertyAction("path.separator")).charAt(0);
javaHome = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new GetPropertyAction("java.home"));
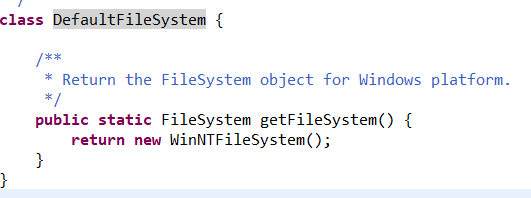
}window下DefaultFileSystem的实现如下:
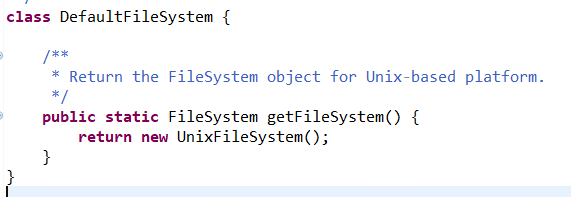
类Unix下DefaultFileSystem的实现如下,其源码在jdk\src\solaris\classes\java\io目录下:
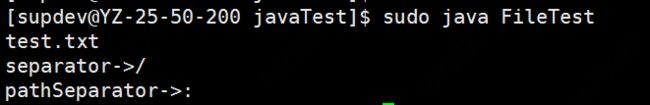
测试用例如下:
import java.io.File;
public class FileTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//windows下文件路径
// File file=new File("D:\\export\\data\\test.txt");
//Linux下的文件路径
File file=new File("/export/data/test.txt");
System.out.println(file.getName());
System.out.println("separator->"+File.separator);
System.out.println("pathSeparator->"+File.pathSeparator);
}
window下输出如下:
Linux下输出如下:
2、构造方法
public File(String pathname) {
if (pathname == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
//将文件路径转换成正常格式
this.path = fs.normalize(pathname);
//获取路径前缀的长度,Linux下如果以/开始则prefixLength是1,否则是0,
//windows下需要计算包含前面盘符在内的前缀的长度
this.prefixLength = fs.prefixLength(this.path);
}
public File(String parent, String child) {
if (child == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if (parent != null) {
if (parent.equals("")) {
//父路径为空,则使用默认的父路径,Linux下是/
//resolve返回该父路径下某个子路径的真实路径
this.path = fs.resolve(fs.getDefaultParent(),
fs.normalize(child));
} else {
this.path = fs.resolve(fs.normalize(parent),
fs.normalize(child));
}
} else {
this.path = fs.normalize(child);
}
this.prefixLength = fs.prefixLength(this.path);
}
public File(File parent, String child) {
if (child == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if (parent != null) {
//逻辑同上
if (parent.path.equals("")) {
this.path = fs.resolve(fs.getDefaultParent(),
fs.normalize(child));
} else {
this.path = fs.resolve(parent.path,
fs.normalize(child));
}
} else {
this.path = fs.normalize(child);
}
this.prefixLength = fs.prefixLength(this.path);
}
public File(URI uri) {
//检查uri是否符合file类uri 规范
if (!uri.isAbsolute())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("URI is not absolute");
if (uri.isOpaque())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("URI is not hierarchical");
String scheme = uri.getScheme();
if ((scheme == null) || !scheme.equalsIgnoreCase("file"))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("URI scheme is not \"file\"");
if (uri.getAuthority() != null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("URI has an authority component");
if (uri.getFragment() != null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("URI has a fragment component");
if (uri.getQuery() != null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("URI has a query component");
String p = uri.getPath();
if (p.equals(""))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("URI path component is empty");
//计算路径
p = fs.fromURIPath(p);
if (File.separatorChar != '/')
p = p.replace('/', File.separatorChar);
this.path = fs.normalize(p);
this.prefixLength = fs.prefixLength(this.path);
}
//去掉路径中多余的/
public String normalize(String pathname) {
int n = pathname.length();
char prevChar = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
char c = pathname.charAt(i);
if ((prevChar == '/') && (c == '/'))
//如果是连续两个//
return normalize(pathname, n, i - 1);
prevChar = c;
}
//如果最后一个字符是/
if (prevChar == '/') return normalize(pathname, n, n - 1);
return pathname;
}
//计算路径中前缀字符串的长度
public int prefixLength(String pathname) {
if (pathname.length() == 0) return 0;
//如果以/开头则返回1,否则返回0
return (pathname.charAt(0) == '/') ? 1 : 0;
}
//计算某个父路径下子路径的完整路径
public String resolve(String parent, String child) {
//child是空,则直接返回parent
if (child.equals("")) return parent;
if (child.charAt(0) == '/') {
//parent是/
if (parent.equals("/")) return child;
return parent + child;
}
if (parent.equals("/")) return parent + child;
return parent + '/' + child;
}
//去掉路径中多余的/
private String normalize(String pathname, int len, int off) {
if (len == 0) return pathname;
int n = len;
//倒着遍历,找到第一个不是/的字符
while ((n > 0) && (pathname.charAt(n - 1) == '/')) n--;
if (n == 0) return "/";
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(pathname.length());
//截取0到off之间的字符串
if (off > 0) sb.append(pathname.substring(0, off));
char prevChar = 0;
//遍历off到n之间的字符
for (int i = off; i < n; i++) {
char c = pathname.charAt(i);
//如果是连续多个/则跳过后面的/
if ((prevChar == '/') && (c == '/')) continue;
sb.append(c);
prevChar = c;
}
return sb.toString();
}
public String fromURIPath(String path) {
String p = path;
//去掉末尾多余的/
if (p.endsWith("/") && (p.length() > 1)) {
// "/foo/" --> "/foo", but "/" --> "/"
p = p.substring(0, p.length() - 1);
}
return p;
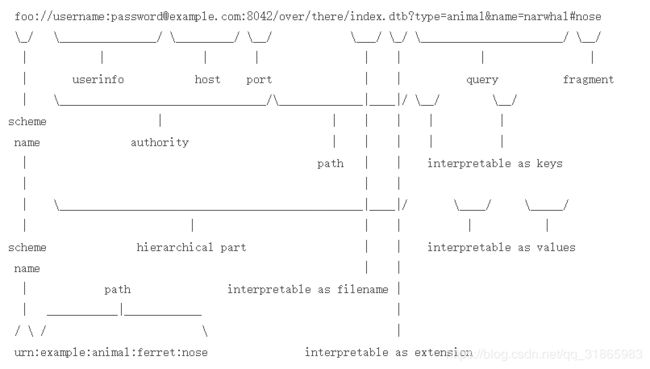
}其中涉及URI的校验,需要理解URI的格式规范,如下图:
测试用例如下:
import java.io.File;
import java.net.URI;
public class FileTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file=new File("//export//data///test.txt/");
System.out.println("exist->"+file.exists()+",path->"+file.getPath());
file=new File("//export/data","/test.txt/");
System.out.println("exist->"+file.exists()+",path->"+file.getPath());
file=new File(new File("//export/data///"),"test.txt/");
System.out.println("exist->"+file.exists()+",path->"+file.getPath());
//冒号后面不能带两个//,会被认为是URI中带有登录用户名等权限信息,校验失败
file=new File(URI.create("file:/export///data//test.txt//"));
System.out.println("exist->"+file.exists()+",path->"+file.getPath());
}
}
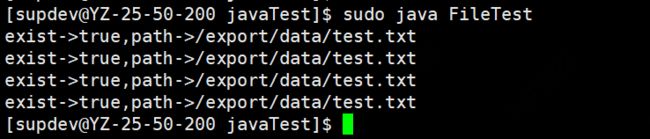
输出如下:
3、isAbsolute / getAbsolutePath / getCanonicalPath
isAbsolute判断当前文件的路径是否绝对路径,getAbsolutePath获取绝对路径,如果不是绝对路径则获取在user.dir下的绝对路径;getCanonicalPath 获取当前文件路径的规范化标准化的路径,会替换掉路径中包含的./ 和 ../,其实现如下:
//是否绝对路径
public boolean isAbsolute() {
return fs.isAbsolute(this);
}
//获取当前文件的绝对路径
public String getAbsolutePath() {
return fs.resolve(this);
}
//获取当前文件路径的规范路径,会处理掉路径中的./或者../
public String getCanonicalPath() throws IOException {
if (isInvalid()) {
throw new IOException("Invalid file path");
}
return fs.canonicalize(fs.resolve(this));
}
final boolean isInvalid() {
if (status == null) {
//如果路径中包含空字符则认为是无效路径
status = (this.path.indexOf('\u0000') < 0) ? PathStatus.CHECKED
: PathStatus.INVALID;
}
return status == PathStatus.INVALID;
}
//UnixFileSystem的实现
//是否绝对路径
public boolean isAbsolute(File f) {
return (f.getPrefixLength() != 0);
}
//获取绝对路径
public String resolve(File f) {
if (isAbsolute(f)) return f.getPath();
//如果不是绝对路径,则获取在user.dir下的绝对路径
return resolve(System.getProperty("user.dir"), f.getPath());
}
public String canonicalize(String path) throws IOException {
//父类FileSystem的静态属性,默认为true,通过属性sun.io.useCanonCaches配置
if (!useCanonCaches) {
//是本地方法
return canonicalize0(path);
} else {
//cache是ExpiringCache实例,一个支持缓存key自动过期的Map
String res = cache.get(path);
if (res == null) {
String dir = null;
String resDir = null;
//父类FileSystem的静态属性,默认为true,通过属性sun.io.useCanonPrefixCache配置
if (useCanonPrefixCache) {
// Note that this can cause symlinks that should
// be resolved to a destination directory to be
// resolved to the directory they're contained in
dir = parentOrNull(path);
if (dir != null) {
//javaHomePrefixCache也是ExpiringCache实例
resDir = javaHomePrefixCache.get(dir);
if (resDir != null) {
// Hit only in prefix cache; full path is canonical
String filename = path.substring(1 + dir.length());
res = resDir + slash + filename;
//将解析结果添加到缓存中
cache.put(dir + slash + filename, res);
}
}
}
if (res == null) {
res = canonicalize0(path);
cache.put(path, res);
//javaHome是系统属性java.home的值
if (useCanonPrefixCache &&
dir != null && dir.startsWith(javaHome)) {
resDir = parentOrNull(res);
// Note that we don't allow a resolved symlink
// to elsewhere in java.home to pollute the
// prefix cache (java.home prefix cache could
// just as easily be a set at this point)
if (resDir != null && resDir.equals(dir)) {
File f = new File(res);
if (f.exists() && !f.isDirectory()) {
javaHomePrefixCache.put(dir, resDir);
}
}
}
}//第二个res等于null
}//第一个res等于null
return res;
}
}
//获取path的父路径,尽可能避免canonicalize0方法中抛出异常
static String parentOrNull(String path) {
if (path == null) return null;
char sep = File.separatorChar;
int last = path.length() - 1;
int idx = last;
//连续的.字符的个数
int adjacentDots = 0;
//不是.和分隔符的字符的个数
int nonDotCount = 0;
//从最后一个字符开始往前遍历
while (idx > 0) {
char c = path.charAt(idx);
if (c == '.') {
if (++adjacentDots >= 2) {
//路径中包含..
return null;
}
} else if (c == sep) {
if (adjacentDots == 1 && nonDotCount == 0) {
//路径中包含/.
return null;
}
if (idx == 0 ||
idx >= last - 1 ||
path.charAt(idx - 1) == sep) {
//第一个字符或者倒数的两个字符包含/,或者连续两个//
return null;
}
return path.substring(0, idx);
} else {
//不是.和分隔符,计数加1
++nonDotCount;
adjacentDots = 0;
}
//遍历下一个字符
--idx;
}
return null;
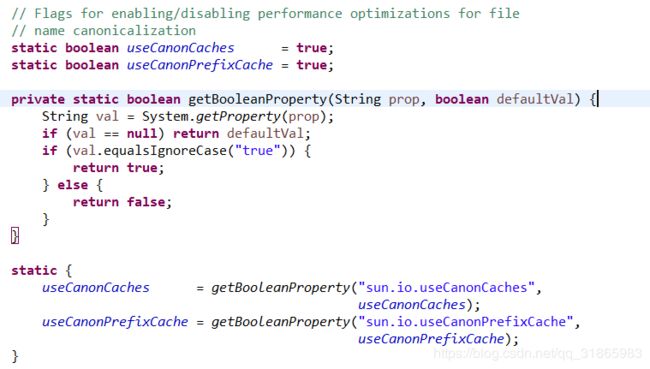
}其中父类FileSystem的useCanonCaches和useCanonPrefixCache属性定义如下:
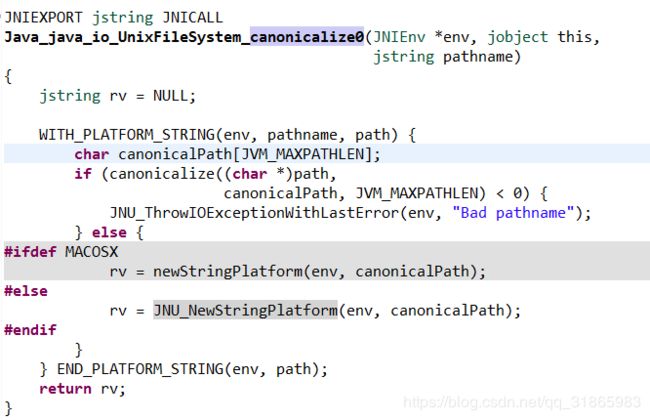
canonicalize0本地方法的实现在jdk\src\solaris\native\java\io\UnixFileSystem_md.c中,如下图:
canonicalize C方法的实现在同目录下的canonicalize_md.c中,可以自行参考,其中的核心就是对路径做规范化标准化处理的C realpath函数。测试用例如下:
@Test
public void test() throws Exception {
//绝对路径
File file=new File("D:\\code\\test.txt");
System.out.println("isAbsolute:"+file.isAbsolute());
System.out.println("getAbsolutePath:"+file.getAbsolutePath());
}
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception {
//相对路径
File file=new File("../test.txt");
System.out.println("isAbsolute:"+file.isAbsolute());
System.out.println("getAbsolutePath:"+file.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("user.dir:"+System.getProperty("user.dir"));
System.out.println("getCanonicalPath:"+file.getCanonicalPath());
}
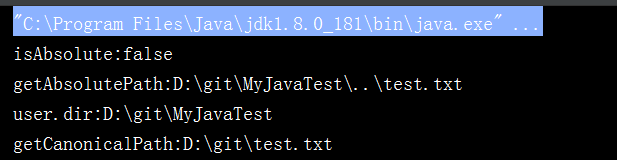
其中第二个测试用例输出如下:
4、exists / isDirectory / isFile / isHidden / lastModified / length
这几个方法都是获取文件属性,判断文件是否存在,文件类型,是否隐藏,最后一次修改时间和文件的大小,其实现如下:
public boolean exists() {
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkRead(path);
}
if (isInvalid()) {
return false;
}
return ((fs.getBooleanAttributes(this) & FileSystem.BA_EXISTS) != 0);
}
public boolean isDirectory() {
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkRead(path);
}
if (isInvalid()) {
return false;
}
return ((fs.getBooleanAttributes(this) & FileSystem.BA_DIRECTORY)
!= 0);
}
public boolean isFile() {
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkRead(path);
}
if (isInvalid()) {
return false;
}
return ((fs.getBooleanAttributes(this) & FileSystem.BA_REGULAR) != 0);
}
public boolean isHidden() {
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkRead(path);
}
if (isInvalid()) {
return false;
}
return ((fs.getBooleanAttributes(this) & FileSystem.BA_HIDDEN) != 0);
}
public long lastModified() {
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkRead(path);
}
if (isInvalid()) {
return 0L;
}
//本地方法实现
return fs.getLastModifiedTime(this);
}
//获取文件的字节数,如果不存在则返回0
public long length() {
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkRead(path);
}
if (isInvalid()) {
return 0L;
}
//本地方法实现
return fs.getLength(this);
}
//UnixFileSystem的实现
public int getBooleanAttributes(File f) {
//本地方法实现
int rv = getBooleanAttributes0(f);
String name = f.getName();
// 以. 开头的文件认为是隐藏文件
boolean hidden = (name.length() > 0) && (name.charAt(0) == '.');
return rv | (hidden ? BA_HIDDEN : 0);
}
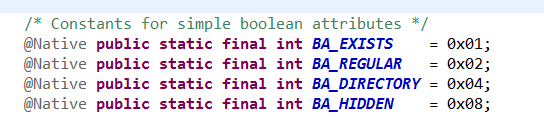
其中涉及的FileSystem的几个常量的定义如下:
其中涉及的本地方法的实现都在UnixFileSystem_md.c中,其核心是获取文件属性的stat64函数,如下:
JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL
Java_java_io_UnixFileSystem_getBooleanAttributes0(JNIEnv *env, jobject this,
jobject file)
{
jint rv = 0;
WITH_FIELD_PLATFORM_STRING(env, file, ids.path, path) {
int mode;
if (statMode(path, &mode)) { //返回true表示文件存在
int fmt = mode & S_IFMT;
//stat的结果转换
rv = (jint) (java_io_FileSystem_BA_EXISTS
| ((fmt == S_IFREG) ? java_io_FileSystem_BA_REGULAR : 0) //如果是文件
| ((fmt == S_IFDIR) ? java_io_FileSystem_BA_DIRECTORY : 0)); //如果是文件夹
}
} END_PLATFORM_STRING(env, path);
return rv;
}
JNIEXPORT jlong JNICALL
Java_java_io_UnixFileSystem_getLastModifiedTime(JNIEnv *env, jobject this,
jobject file)
{
jlong rv = 0;
WITH_FIELD_PLATFORM_STRING(env, file, ids.path, path) {
struct stat64 sb;
if (stat64(path, &sb) == 0) {
rv = 1000 * (jlong)sb.st_mtime;
}
} END_PLATFORM_STRING(env, path);
return rv;
}
JNIEXPORT jlong JNICALL
Java_java_io_UnixFileSystem_getLength(JNIEnv *env, jobject this,
jobject file)
{
jlong rv = 0;
WITH_FIELD_PLATFORM_STRING(env, file, ids.path, path) {
struct stat64 sb;
if (stat64(path, &sb) == 0) {
rv = sb.st_size;
}
} END_PLATFORM_STRING(env, path);
return rv;
}
static jboolean
statMode(const char *path, int *mode)
{
struct stat64 sb;
//stat64是标准C函数,用于获取文件属性,ls命令的底层实现就是该函数
if (stat64(path, &sb) == 0) {
*mode = sb.st_mode;
return JNI_TRUE;
}
return JNI_FALSE;
}5、createNewFile / createTempFile / delete / deleteOnExit
createNewFile会创建一个新文件,如果当前File对象对应的文件不存在的话,如果存在则返回false。createTempFile会创建一个在指定目录下的临时文件,临时文件的文件名是通过prefix、随机数、suffix生成,返回的File对应的文件肯定是原来不存在的,注意createTempFile本身并不删除临时文件,需要程序显示调用delete方法删除或者放在操作系统临时目录下,由操作系统负责删除。delete和deleteOnExit都是用于删除文件,区别在于前者是立即删除,后者是在JVM退出时通过回调钩子方法执行的删除,实际的删除动作还是delete方法完成的。
//如果目标路径的文件不存在则创建一个新的
public boolean createNewFile() throws IOException {
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) security.checkWrite(path);
if (isInvalid()) {
throw new IOException("Invalid file path");
}
//是一个本地方法
return fs.createFileExclusively(path);
}
//在指定目录下创建一个临时文件,文件名由prefix 和 suffix指定,不宜过长,如果超长会被自动截断
//如果suffix为null,则默认为.tmp,如果directory为null,则默认在系统的临时目录下创建文件,Unix下是/tmp或者/var/tmp
public static File createTempFile(String prefix, String suffix,
File directory)
throws IOException
{
if (prefix.length() < 3) //前缀不小于3
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Prefix string too short");
if (suffix == null)
suffix = ".tmp"; //后缀默认为.tmp
//文件路径默认为系统的临时文件夹目录
File tmpdir = (directory != null) ? directory
: TempDirectory.location();
SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
File f;
do {
//生成一个随机文件名的File对象,此时未实际创建文件
f = TempDirectory.generateFile(prefix, suffix, tmpdir);
if (sm != null) {
try {
//检查访问权限
sm.checkWrite(f.getPath());
} catch (SecurityException se) {
// don't reveal temporary directory location
if (directory == null)
throw new SecurityException("Unable to create temporary file");
throw se;
}
}
//检查文件是否存在,如果存在则继续生成一个新文件名的文件
} while ((fs.getBooleanAttributes(f) & FileSystem.BA_EXISTS) != 0);
if (!fs.createFileExclusively(f.getPath())) //如果创建文件失败,则抛出异常
throw new IOException("Unable to create temporary file");
return f;
}
public static File createTempFile(String prefix, String suffix)
throws IOException
{
return createTempFile(prefix, suffix, null);
}
public boolean delete() {
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkDelete(path);
}
if (isInvalid()) {
return false;
}
return fs.delete(this);
}
public void deleteOnExit() {
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkDelete(path);
}
if (isInvalid()) {
return;
}
//在JVM退出时执行删除
DeleteOnExitHook.add(path);
}
//File的静态内部类
private static class TempDirectory {
private TempDirectory() { }
//获取临时文件夹路径
private static final File tmpdir = new File(AccessController
.doPrivileged(new GetPropertyAction("java.io.tmpdir")));
//返回系统临时文件夹路径
static File location() {
return tmpdir;
}
//使用SecureRandom而非Random生成随机数,可避免因为种子问题导致生成的随机数序列一致的问题
private static final SecureRandom random = new SecureRandom();
//在指定目录下生成一个临时文件
static File generateFile(String prefix, String suffix, File dir)
throws IOException
{
long n = random.nextLong();
if (n == Long.MIN_VALUE) {
n = 0; // corner case
} else {
n = Math.abs(n);
}
//获取前缀,这里通过File的构造方法去掉了prefix中可能的多余的/
prefix = (new File(prefix)).getName();
//生成随机的文件名
String name = prefix + Long.toString(n) + suffix;
File f = new File(dir, name);
//如果name中包含多余的字符或者是非法路径则抛出异常
if (!name.equals(f.getName()) || f.isInvalid()) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null)
throw new IOException("Unable to create temporary file");
else
throw new IOException("Unable to create temporary file, " + f);
}
return f;
}
}
//UnixFileSystem实现
public boolean delete(File f) {
//清空路径解析的缓存
cache.clear();
javaHomePrefixCache.clear();
//本地方法实现
return delete0(f);
}其中涉及的本地方法的实现都在UnixFileSystem_md.c中,其核心是负责打开和创建文件的open64函数和删除文件的remove函数,如下:
JNIEXPORT jboolean JNICALL
Java_java_io_UnixFileSystem_createFileExclusively(JNIEnv *env, jclass cls,
jstring pathname)
{
jboolean rv = JNI_FALSE;
WITH_PLATFORM_STRING(env, pathname, path) {
FD fd;
/* The root directory always exists */
if (strcmp (path, "/")) {
//O_CREAT下如果文件不存在则创建
fd = handleOpen(path, O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_EXCL, 0666);
if (fd < 0) {
if (errno != EEXIST) //如果不是因为文件已存在导致的失败,则抛出异常
JNU_ThrowIOExceptionWithLastError(env, path);
} else {
if (close(fd) == -1) //关闭fd失败,抛出异常
JNU_ThrowIOExceptionWithLastError(env, path);
rv = JNI_TRUE;
}
}
} END_PLATFORM_STRING(env, path);
return rv;
}
JNIEXPORT jboolean JNICALL
Java_java_io_UnixFileSystem_delete0(JNIEnv *env, jobject this,
jobject file)
{
jboolean rv = JNI_FALSE;
WITH_FIELD_PLATFORM_STRING(env, file, ids.path, path) {
//remove是C函数,用于移除文件
if (remove(path) == 0) {//移除成功,返回true
rv = JNI_TRUE;
}
} END_PLATFORM_STRING(env, path);
return rv;
}
FD
handleOpen(const char *path, int oflag, int mode) {
FD fd;
//open64是一个C函数,用于打开文件,根据oflag不同会有不同的行为
RESTARTABLE(open64(path, oflag, mode), fd);
if (fd != -1) {
//open64执行成功
struct stat64 buf64;
int result;
//fstat64是C函数,获取文件属性
RESTARTABLE(fstat64(fd, &buf64), result);
if (result != -1) {
if (S_ISDIR(buf64.st_mode)) {
//如果目录文件存在且是文件夹
close(fd);
errno = EISDIR;
fd = -1;
}
} else {
//执行fstat64异常
close(fd);
fd = -1;
}
}
return fd;
}测试用例如下:
@Test
public void test3() throws Exception {
File file=new File("D:\\code\\test2.txt");
System.out.println("exist->"+file.exists());
System.out.println("createNewFile->"+file.createNewFile());
System.out.println("exist after create->"+file.exists());
System.out.println("createNewFile two->"+file.createNewFile());
System.out.println("delete ->"+file.delete());
System.out.println("delete two->"+file.delete());
}
@Test
public void test4() throws Exception {
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) {
//后缀默认是.tmp,文件路径默认是系统的临时目录
File file = File.createTempFile("tst", null);
System.out.println("exists->" + file.exists() + ",path->" + file.getPath());
}
}
6、mkdir / mkdirs
mkdir用于创建一个文件夹,mkdirs用于创建从父目录到当前目录的多个文件夹,如果创建失败则返回false,如果创建成功或者本身已经存在则返回true,其实现如下:
//创建文件夹,如果创建失败则返回false
public boolean mkdir() {
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkWrite(path);
}
if (isInvalid()) {
return false;
}
//本地方法实现
return fs.createDirectory(this);
}
//创建多个文件夹,如果创建失败则返回false
public boolean mkdirs() {
if (exists()) { //文件已存在
return false;
}
if (mkdir()) { //直接创建文件夹失败
return true;
}
File canonFile = null;
try {
//获取标准化路径对应的文件
canonFile = getCanonicalFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
return false;
}
//获取父文件夹对应的File
File parent = canonFile.getParentFile();
//parent不为空,则调用其mkdirs,此处实际是一个递归
return (parent != null && (parent.mkdirs() || parent.exists()) &&
canonFile.mkdir());
}
public File getCanonicalFile() throws IOException {
String canonPath = getCanonicalPath();
return new File(canonPath, fs.prefixLength(canonPath));
}其中createDirectory本地方法的实现在UnixFileSystem_md.c中,其核心是mkdir函数,如下:
JNIEXPORT jboolean JNICALL
Java_java_io_UnixFileSystem_createDirectory(JNIEnv *env, jobject this,
jobject file)
{
jboolean rv = JNI_FALSE;
WITH_FIELD_PLATFORM_STRING(env, file, ids.path, path) {
//0777表示创建的文件是所有用户都可读可写可执行的
if (mkdir(path, 0777) == 0) {
rv = JNI_TRUE;
}
} END_PLATFORM_STRING(env, path);
return rv;
}7、list / listFiles / listRoots
list和listFiles都是获取当前File下的子文件或者子目录,区别在于前者返回文件名,后者返回文件名对应的File对象,可以添加FilenameFilter 或者FileFilter 实现过滤掉不满足条件的文件。listRoots返回根目录对应的File,Unix下返回 / 对应的File对象,Windows下返回所有磁盘分区对应的File对象。
public String[] list() {
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkRead(path);
}
if (isInvalid()) { //路径无效,返回null
return null;
}
//本地方法
return fs.list(this);
}
public String[] list(FilenameFilter filter) {
String names[] = list();
if ((names == null) || (filter == null)) {
return names;
}
List v = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0 ; i < names.length ; i++) {
//执行过滤逻辑
if (filter.accept(this, names[i])) {
v.add(names[i]);
}
}
return v.toArray(new String[v.size()]);
}
public File[] listFiles() {
String[] ss = list();
if (ss == null) return null;
int n = ss.length;
File[] fs = new File[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
//将list方法文件的文件名转换成File对象
fs[i] = new File(ss[i], this);
}
return fs;
}
public File[] listFiles(FilenameFilter filter) {
String ss[] = list();
if (ss == null) return null;
ArrayList files = new ArrayList<>();
for (String s : ss)
//执行过滤逻辑,将文件名转换成File对象
if ((filter == null) || filter.accept(this, s))
files.add(new File(s, this));
return files.toArray(new File[files.size()]);
}
public File[] listFiles(FileFilter filter) {
String ss[] = list();
if (ss == null) return null;
ArrayList files = new ArrayList<>();
for (String s : ss) {
File f = new File(s, this);
//执行过滤逻辑,将文件名转换成File对象
if ((filter == null) || filter.accept(f))
files.add(f);
}
return files.toArray(new File[files.size()]);
}
public static File[] listRoots() {
return fs.listRoots();
}
//UnixFileSystem的实现
public File[] listRoots() {
try {
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkRead("/");
}
return new File[] { new File("/") };
} catch (SecurityException x) {
return new File[0];
}
}
其中list本地方法的实现在 UnixFileSystem_md.c中,其核心是打开目录文件的opendir函数,负责逐一读取目录下子目录或者子文件的readdir64_r函数以及关闭目录对象Dir的closedir函数,如下:
JNIEXPORT jobjectArray JNICALL
Java_java_io_UnixFileSystem_list(JNIEnv *env, jobject this,
jobject file)
{
DIR *dir = NULL;
struct dirent64 *ptr;
struct dirent64 *result;
int len, maxlen;
jobjectArray rv, old;
jclass str_class;
//获取String对应的Class
str_class = JNU_ClassString(env);
CHECK_NULL_RETURN(str_class, NULL);
WITH_FIELD_PLATFORM_STRING(env, file, ids.path, path) {
//opendir是C函数,打开某个文件目录
dir = opendir(path);
} END_PLATFORM_STRING(env, path);
//目录不存在,返回null
if (dir == NULL) return NULL;
//创建一个dirent64数组
ptr = malloc(sizeof(struct dirent64) + (PATH_MAX + 1));
if (ptr == NULL) {
//内存不足,抛出异常
JNU_ThrowOutOfMemoryError(env, "heap allocation failed");
//closedir是C函数,关闭目录
closedir(dir);
return NULL;
}
/* Allocate an initial String array */
len = 0;
maxlen = 16;
//创建一个初始长度为16的String数组
rv = (*env)->NewObjectArray(env, maxlen, str_class, NULL);
//创建失败,跳转到goto
if (rv == NULL) goto error;
/* Scan the directory */
//readdir64_r是C函数,用于读取下一个目录,读取的结果放到ptr数组中
while ((readdir64_r(dir, ptr, &result) == 0) && (result != NULL)) {
jstring name;
if (!strcmp(ptr->d_name, ".") || !strcmp(ptr->d_name, "..")) //跳过. 和 ..
continue;
if (len == maxlen) {
//数组满了,执行扩容
old = rv;
//创建一个扩容一倍的数组
rv = (*env)->NewObjectArray(env, maxlen <<= 1, str_class, NULL);
if (rv == NULL) goto error;
//数组拷贝
if (JNU_CopyObjectArray(env, rv, old, len) < 0) goto error;
//删除本地引用old
(*env)->DeleteLocalRef(env, old);
}
//创建Java字符串,d_name表示文件名
name = JNU_NewStringPlatform(env, ptr->d_name);
if (name == NULL) goto error;
//保存到Java数组中,len加1,并删除本地引用
(*env)->SetObjectArrayElement(env, rv, len++, name);
(*env)->DeleteLocalRef(env, name);
}
//关闭目录,释放内存
closedir(dir);
free(ptr);
/* 根据实际的结果大小,重新创建一个String数组 */
old = rv;
rv = (*env)->NewObjectArray(env, len, str_class, NULL);
if (rv == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
//数组拷贝
if (JNU_CopyObjectArray(env, rv, old, len) < 0) {
return NULL;
}
return rv;
error:
closedir(dir);
free(ptr);
return NULL;
}测试用例如下:
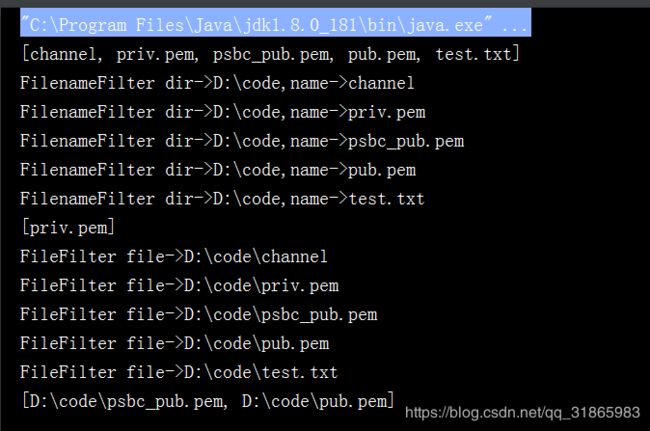
@Test
public void test5() throws Exception {
File file=new File("D:\\code");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(file.list()));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(file.list(new FilenameFilter() {
@Override
public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
System.out.println("FilenameFilter dir->"+dir+",name->"+name);
return name.contains("priv");
}
})));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(file.listFiles(new FileFilter() {
@Override
public boolean accept(File pathname) {
System.out.println("FileFilter file->"+pathname.getPath());
return pathname.getPath().contains("pub");
}
})));
}结果如下: