【数据结构】文件压缩项目
项目名称:文件压缩
开发环境:vs2010
运用到的数据结构:
1、heap堆
2、huffmantree哈夫曼树
3、Huffmancode哈夫曼编码
4、面向对象C++编程语言
思路:
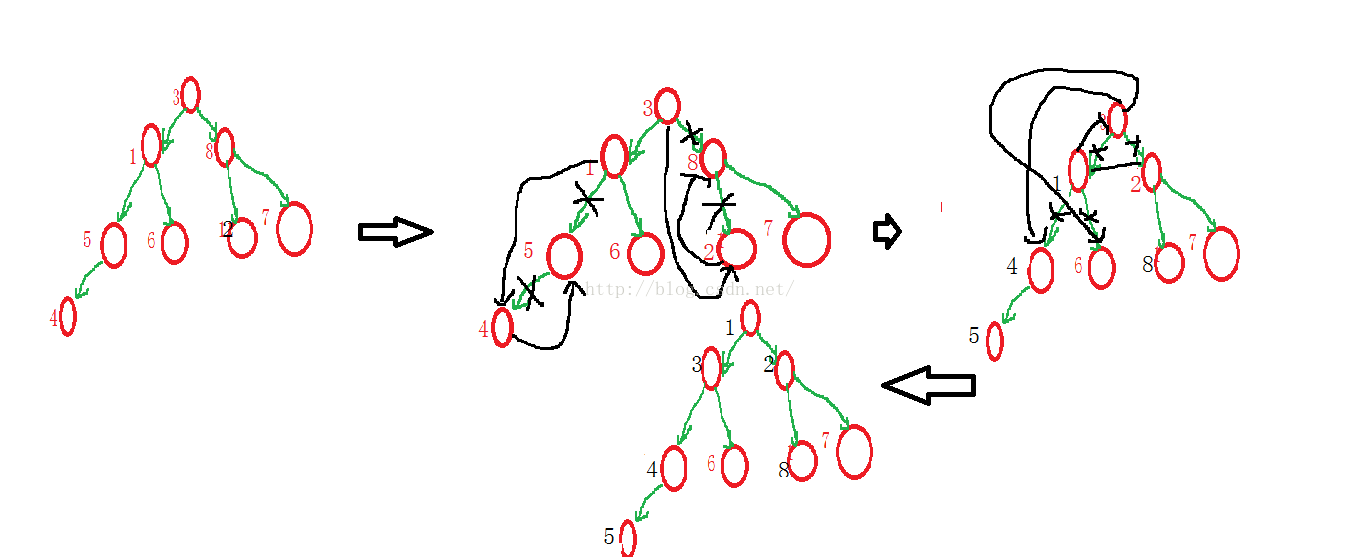
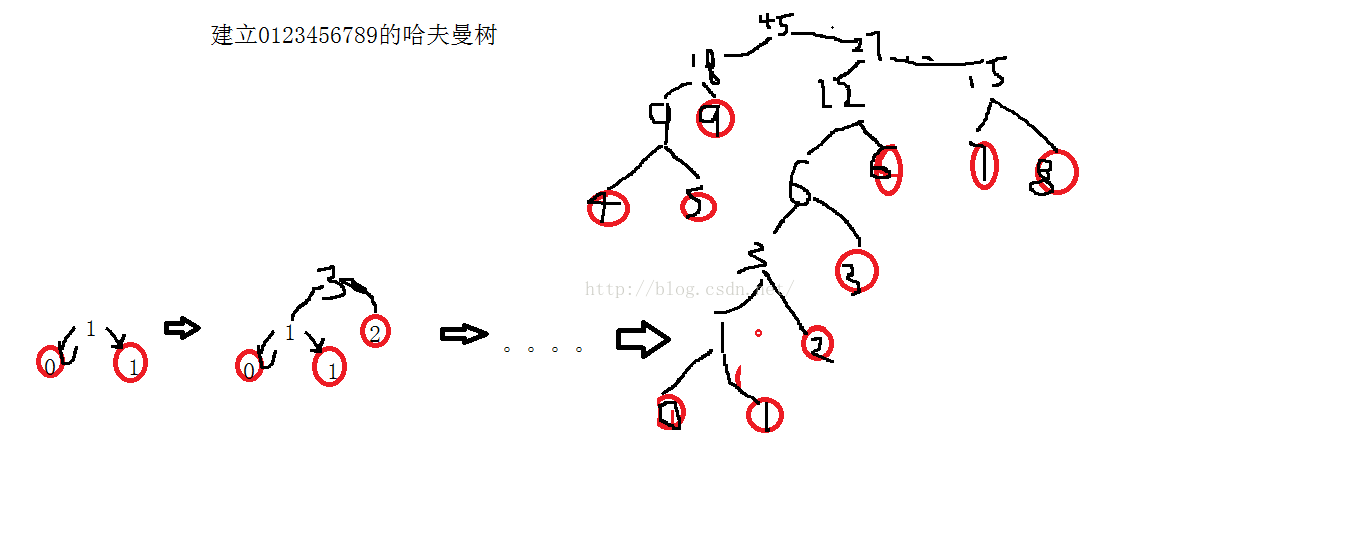
1、利用小堆建立哈弗曼树
2、利用哈弗曼树产生哈夫曼编码
3、利用哈夫曼编码对文件进行压缩,产生压缩文件**.compress文件,以及**.config配置文件方便解码
4、利用配置文件获取到文件中每个字符出现的次数
5、利用配置文件用小堆再次建立哈弗曼树
6、利用配置文件建立的哈弗曼树进行解码生成解压后的文件**.uncompress
建立大小堆博文连接在下面
http://blog.csdn.net/shangguan_1234/article/details/52791719
堆结构的二叉树存储是
最大堆:每个父节点的都大于孩子节点。
最小堆:每个父节点的都小于孩子节点。
这里举小堆的例子
将每个子孩子与父节点的值进行比较,如果比父节点小则父节点下移,较小的子孩子上移
#pragma once
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// 小堆
template
struct Less
{
bool operator() (const T& l, const T& r)
{
return l < r;
}
};
//大堆
template
struct Greater
{
bool operator() (const T& l, const T& r)
{
return l > r;
}
};
template>
class Heap
{
public:
Heap()
{}
Heap(const T* a, size_t size)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
_infosays.push_back(a[i]);
}
// 建堆
for (int i = (_infosays.size() - 2) / 2; i >= 0; --i)
{
AdjustDown(i);
}
}
void Push(const T& x)
{
_infosays.push_back(x);
AdjustUp(_infosays.size() - 1);
}
void Pop()
{
assert(_infosays.size() > 0);
swap(_infosays[0], _infosays[_infosays.size() - 1]);
_infosays.pop_back();
AdjustDown(0);
}
const T& Top()
{
//assert(_infosays.size() > 0);
if (!Empty())
{
return _infosays[0];
}
}
bool Empty()
{
return _infosays.empty();
}
int Size()
{
return _infosays.size();
}
void AdjustDown(int root)
{
size_t child = root * 2 + 1;
Compare com;
while (child < _infosays.size())
{
if (child + 1<_infosays.size() &&
com(_infosays[child + 1], _infosays[child]))
{
++child;
}
if (com(_infosays[child], _infosays[root]))
{
swap(_infosays[child], _infosays[root]);
root = child;
child = 2 * root + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void AdjustUp(int child)
{
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (Compare()(_infosays[child], _infosays[parent]))
{
swap(_infosays[parent], _infosays[child]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void Print()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _infosays.size(); ++i)
{
cout << _infosays[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
public:
vector _infosays;
};
利用堆建立哈夫曼树
Huffm an树,又称为最优二叉树,是加权路径长度最短的二叉树。
【贪心算法】是指在问题求解时,总是做出当前看起来最好的选择。也就是说贪心算法做出的不是整体最优的的选择,而是某种意义上的
局部最优解。贪心算法不是对所有的问题都能得到整体最优解。
使用贪心算法构建Huffman树
#pragma once
#include "Heap.h"
#include
using namespace std;
template
struct HuffmanTreeNode
{
HuffmanTreeNode* _left;
HuffmanTreeNode* _right;
HuffmanTreeNode* _parent;
T _weight;
HuffmanTreeNode(const T& x)
:_weight(x)
, _left(NULL)
, _right(NULL)
, _parent(NULL)
{}
};
template
class HuffmanTree
{
typedef HuffmanTreeNode Node;
public:
HuffmanTree()
:_root(NULL)
{}
~HuffmanTree()
{
Destory(_root);
}
template
struct NodeCompare
{
bool operator()(Node *l, Node *r)
{
return l->_weight < r->_weight;
}
};
void CreatTree(const T* a, size_t size, const T& invalid)
{
assert(a);
Heap> minHeap;
for (size_t i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
if (a[i] != invalid)
{
Node* node = new Node(a[i]);
minHeap.Push(node);
}
}
while (minHeap.Size() > 1)
{
Node* left = minHeap.Top();
minHeap.Pop();
Node* right = minHeap.Top();
minHeap.Pop();
Node* parent = new Node(left->_weight + right->_weight);
parent->_left = left;
parent->_right = right;
left->_parent = parent;
right->_parent = parent;
minHeap.Push(parent);
}
_root = minHeap.Top();
}
Node* GetRootNode()
{
return _root;
}
//void Destory(Node* root)
//{
// if (root)
// {
// Destory(root->_left);
// Destory(root->_right);
// delete root;
// root = NULL;
// }
//}
void Destory(Node* root)
{
if (root==NULL)
{
return ;
}
if(root->_left==NULL&&root->_right==NULL)
{
delete root;
root=NULL;
}
else
{
Destory(root->_left);
Destory(root->_right);
}
}
private:
HuffmanTreeNode* _root;
}; 利用哈弗曼树产生哈夫曼编码
代码实现
void _GenerateHuffmanCode(HuffmanTreeNode* root)//创建哈夫曼编码
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
_GenerateHuffmanCode(root->_left);
_GenerateHuffmanCode(root->_right);
if (root->_left == NULL && root->_right == NULL)
{
HuffmanTreeNode* cur = root;
HuffmanTreeNode* parent = cur->_parent;
string& code = _infos[cur->_weight._ch]._code;
while (parent)
{
if (parent->_left == cur)//往左走+0
{
code += '0';
}
else if (parent->_right == cur)//往右走+1
{
code += '1';
}
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
//寻找编码从叶子节点开始。
reverse(code.begin(), code.end());
}
}
//递归实现哈夫曼编码
void _GenerateHuffmanCode_R(HuffmanTreeNode* root,string code)//创建哈夫曼编码
{
if(root==NULL)
return;
_GenerateHuffmanCode_R(root->_left,code+'0');
_GenerateHuffmanCode_R(root->_right,code+'1');
if(root->_left==NULL&&root->_right==NULL)
{
_infos[root->_weight._ch]._code=code;
}
} bool Compress(const char* filename)
{
//1.打开文件,统计文件字符出现的次数
Longtype Charcount = 0;
assert(filename);
FILE* fOut = fopen(filename, "rb");//之前用“r”,结果出了一点问题
//"rb"为以二进制方式读取文件,这里的b就是binary。"wb"为以二进制方式写入文件
assert(fOut); //以二进制和文本打开方式区别在于:以文本打开方式会将\r\n
//转换为\n,二进制这不会有这样的转换
//char ch = fgetc(fOut);
int ch = fgetc(fOut);
while (ch != EOF)
{
_infos[(unsigned char)ch]._count++;
ch = fgetc(fOut);
Charcount++;
}
//2.生成对应的huffman编码
GenerateHuffmanCode();
//3.文件压缩
string compressFile = filename;
compressFile += ".compress";
FILE* fwCompress = fopen(compressFile.c_str(), "wb");//以二进制写入
assert(fwCompress);
fseek(fOut, 0, SEEK_SET);
ch = fgetc(fOut);
char inch = 0;
int pos = 0;
while (!feof(fOut))
{
string& code = _infos[(unsigned char)ch]._code;
for (size_t i = 0; i < code.size(); ++i)
{
inch = inch << 1;
if (code[i] == '1')
{
inch |= 1;
}
if (++pos == 8)//对于形成的长串字符编码的切割,每8个bit为一个字节,便于读取
{
fputc(inch, fwCompress);
inch = 0;
pos = 0;
}
}
ch = fgetc(fOut);
}
if (pos)//考虑到可能会有切割完,剩余的字符码不够填充8个bit位的情况
{
inch = inch << (8 - pos);
fputc(inch, fwCompress);
}
//4.配置文件,方便后续的解压缩;
string configFile = filename;
configFile += ".config";
FILE *fconfig = fopen(configFile.c_str(), "wb");
assert(fconfig);
string infoStr;
//char CountStr[128];
char CountStr[128];
_itoa(Charcount >> 32, CountStr, 10);
fputs(CountStr, fconfig);
fputc('\n', fconfig);
_itoa(Charcount & 0xffffffff, CountStr, 10);
//_itoa(Charcount & -1, CountStr, 10);
fputs(CountStr, fconfig);
fputc('\n', fconfig);
CharInfo invalid;
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
if (_infos[i] != invalid)
{
/* fputc(_infos[i]._ch, fconfig);
fputc(',', fconfig);
fputc(_infos[i]._count + '0', fconfig);
fputc('\n', fconfig);*/
infoStr=_infos[i]._ch;
infoStr+=',';
_itoa(_infos[i]._count, CountStr, 10);
infoStr+=CountStr;
infoStr+='\n';
fputs(infoStr.c_str(),fconfig);
}
}
fclose(fOut);
fclose(fwCompress);
fclose(fconfig);
return true;
}利用配置文件获取到文件中每个字符出现的次数
string configfile = filename;
configfile += ".config";
FILE* outConfig = fopen(configfile.c_str(), "rb");
assert(outConfig);
char ch=0;
/*char ch;*/
Longtype Charcount = 0;
string line = ReadLine(outConfig);
Charcount = atoi(line.c_str());
Charcount <<= 32;
line.clear();
line = ReadLine(outConfig);
Charcount += atoi(line.c_str());
line.clear();
while (feof(outConfig))
//feof()遇到文件结束,函数值为非零值,否则为0。当把数据以二进制的形式进行存放时,可能会有-1值的出现,
//所以此时无法利用-1值(EOF)做为eof()函数判断二进制文件结束的标志。
{
line = ReadLine(outConfig);
if (!line.empty())
{
ch = line[0];
_infos[(unsigned char)ch]._count += atoi(line.substr(2).c_str());
//_infos[(unsigned char)ch]._count += atoi(line.c_str());
line.clear();
}
else
{
line = '\n';
}
}利用配置文件用小堆再次建立哈弗曼树
利用配置文件建立的哈弗曼树进行解码生成解压后的文件**.uncompress
HuffmanTree ht;
CharInfo invalid(0);
ht.CreatTree(_infos, 256, invalid);//重新建树
HuffmanTreeNode* root = ht.GetRootNode();
string UnCompressFile = filename;
UnCompressFile += ".uncompress";
FILE* fIn = fopen(UnCompressFile.c_str(), "wb");
string CompressFile = filename;
CompressFile += ".compress";
FILE* fOut = fopen(CompressFile.c_str(), "rb");
int pos = 8;
HuffmanTreeNode* cur = root;
ch=fgetc(fOut);
while ((unsigned char)ch != EOF)
//while(1)
{
--pos;
if ((unsigned char)ch &(1 << pos))
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
if (cur->_left == NULL && cur->_right == NULL)
{
fputc(cur->_weight._ch, fIn);
cur = root;
Charcount--;
}
if (pos == 0)
{
ch = fgetc(fOut);
pos = 8;
}
if (Charcount==0)
{
break;
}}
//文件的解压缩
bool UnCompresss(const char* filename)
{
string configfile = filename;
configfile += ".config";
FILE* outConfig = fopen(configfile.c_str(), "rb");
assert(outConfig);
char ch=0;
/*char ch;*/
Longtype Charcount = 0;
string line = ReadLine(outConfig);
Charcount = atoi(line.c_str());
Charcount <<= 32;
line.clear();
line = ReadLine(outConfig);
Charcount += atoi(line.c_str());
line.clear();
while (feof(outConfig))
//feof()遇到文件结束,函数值为非零值,否则为0。当把数据以二进制的形式进行存放时,可能会有-1值的出现,
//所以此时无法利用-1值(EOF)做为eof()函数判断二进制文件结束的标志。
{
line = ReadLine(outConfig);
if (!line.empty())
{
ch = line[0];
_infos[(unsigned char)ch]._count += atoi(line.substr(2).c_str());
//_infos[(unsigned char)ch]._count += atoi(line.c_str());
line.clear();
}
else
{
line = '\n';
}
}
HuffmanTree ht;
CharInfo invalid(0);
ht.CreatTree(_infos, 256, invalid);//重新建树
HuffmanTreeNode* root = ht.GetRootNode();
string UnCompressFile = filename;
UnCompressFile += ".uncompress";
FILE* fIn = fopen(UnCompressFile.c_str(), "wb");
string CompressFile = filename;
CompressFile += ".compress";
FILE* fOut = fopen(CompressFile.c_str(), "rb");
int pos = 8;
HuffmanTreeNode* cur = root;
ch=fgetc(fOut);
while ((unsigned char)ch != EOF)
//while(1)
{
--pos;
if ((unsigned char)ch &(1 << pos))
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
if (cur->_left == NULL && cur->_right == NULL)
{
fputc(cur->_weight._ch, fIn);
cur = root;
Charcount--;
}
if (pos == 0)
{
ch = fgetc(fOut);
pos = 8;
}
if (Charcount==0)
{
break;
}
}
fclose(fIn);
fclose(fOut);
fclose(outConfig);
return true;
} 文件压缩代码
FileCompress.h
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#pragma once
#include"HuffmanTree.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef long long Longtype;//为了扩大其范围,int型能处理的范围已经不能满足,所以定义Long Long型予以表示
struct CharInfo
{
unsigned char _ch;//这里必须为unsigned,否则会造成截断,所以从-128~127调至0~255.
Longtype _count;
string _code;
CharInfo(int count = 0)
:_ch(0)
, _count(count)
,_code("")
{}
CharInfo operator+(CharInfo& file)//重载+
{
CharInfo tmp;
tmp._count = _count + file._count;
return tmp;
}
bool operator < (CharInfo& file) const//重载<
{
return _count < file._count;
}
bool operator != (const CharInfo& file) const//重载!=
{
return _count != file._count;
}
};
template
class FileCompress
{
public:
FileCompress()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 256; ++i)//初始化
{
_infos[i]._ch = i;
}
}
bool Compress(const char* filename)
{
//1.打开文件,统计文件字符出现的次数
Longtype Charcount = 0;
assert(filename);
FILE* fOut = fopen(filename, "rb");//之前用“r”,结果出了一点问题
//"rb"为以二进制方式读取文件,这里的b就是binary。"wb"为以二进制方式写入文件
assert(fOut); //以二进制和文本打开方式区别在于:以文本打开方式会将\r\n
//转换为\n,二进制这不会有这样的转换
//char ch = fgetc(fOut);
int ch = fgetc(fOut);
while (ch != EOF)
{
_infos[(unsigned char)ch]._count++;
ch = fgetc(fOut);
Charcount++;
}
//2.生成对应的huffman编码
GenerateHuffmanCode();
//3.文件压缩
string compressFile = filename;
compressFile += ".compress";
FILE* fwCompress = fopen(compressFile.c_str(), "wb");//以二进制写入
assert(fwCompress);
fseek(fOut, 0, SEEK_SET);
ch = fgetc(fOut);
char inch = 0;
int pos = 0;
while (!feof(fOut))
{
string& code = _infos[(unsigned char)ch]._code;
for (size_t i = 0; i < code.size(); ++i)
{
inch = inch << 1;
if (code[i] == '1')
{
inch |= 1;
}
if (++pos == 8)//对于形成的长串字符编码的切割,每8个bit为一个字节,便于读取
{
fputc(inch, fwCompress);
inch = 0;
pos = 0;
}
}
ch = fgetc(fOut);
}
if (pos)//考虑到可能会有切割完,剩余的字符码不够填充8个bit位的情况
{
inch = inch << (8 - pos);
fputc(inch, fwCompress);
}
//4.配置文件,方便后续的解压缩;
string configFile = filename;
configFile += ".config";
FILE *fconfig = fopen(configFile.c_str(), "wb");
assert(fconfig);
string infoStr;
//char CountStr[128];
char CountStr[128];
_itoa(Charcount >> 32, CountStr, 10);
fputs(CountStr, fconfig);
fputc('\n', fconfig);
_itoa(Charcount & 0xffffffff, CountStr, 10);
//_itoa(Charcount & -1, CountStr, 10);
fputs(CountStr, fconfig);
fputc('\n', fconfig);
CharInfo invalid;
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
if (_infos[i] != invalid)
{
/* fputc(_infos[i]._ch, fconfig);
fputc(',', fconfig);
fputc(_infos[i]._count + '0', fconfig);
fputc('\n', fconfig);*/
infoStr=_infos[i]._ch;
infoStr+=',';
_itoa(_infos[i]._count, CountStr, 10);
infoStr+=CountStr;
infoStr+='\n';
fputs(infoStr.c_str(),fconfig);
}
}
fclose(fOut);
fclose(fwCompress);
fclose(fconfig);
return true;
}
//文件的解压缩
bool UnCompresss(const char* filename)
{
string configfile = filename;
configfile += ".config";
FILE* outConfig = fopen(configfile.c_str(), "rb");
assert(outConfig);
char ch=0;
/*char ch;*/
Longtype Charcount = 0;
string line = ReadLine(outConfig);
Charcount = atoi(line.c_str());
Charcount <<= 32;
line.clear();
line = ReadLine(outConfig);
Charcount += atoi(line.c_str());
line.clear();
while (feof(outConfig))
//feof()遇到文件结束,函数值为非零值,否则为0。当把数据以二进制的形式进行存放时,可能会有-1值的出现,
//所以此时无法利用-1值(EOF)做为eof()函数判断二进制文件结束的标志。
{
line = ReadLine(outConfig);
if (!line.empty())
{
ch = line[0];
_infos[(unsigned char)ch]._count += atoi(line.substr(2).c_str());
//_infos[(unsigned char)ch]._count += atoi(line.c_str());
line.clear();
}
else
{
line = '\n';
}
}
HuffmanTree ht;
CharInfo invalid(0);
ht.CreatTree(_infos, 256, invalid);//重新建树
HuffmanTreeNode* root = ht.GetRootNode();
string UnCompressFile = filename;
UnCompressFile += ".uncompress";
FILE* fIn = fopen(UnCompressFile.c_str(), "wb");
string CompressFile = filename;
CompressFile += ".compress";
FILE* fOut = fopen(CompressFile.c_str(), "rb");
int pos = 8;
HuffmanTreeNode* cur = root;
ch=fgetc(fOut);
while ((unsigned char)ch != EOF)
//while(1)
{
--pos;
if ((unsigned char)ch &(1 << pos))
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
if (cur->_left == NULL && cur->_right == NULL)
{
fputc(cur->_weight._ch, fIn);
cur = root;
Charcount--;
}
if (pos == 0)
{
ch = fgetc(fOut);
pos = 8;
}
if (Charcount==0)
{
break;
}
}
fclose(fIn);
fclose(fOut);
fclose(outConfig);
return true;
}
protected:
string ReadLine(FILE* fOut)
{
assert(fOut);
char ch = fgetc(fOut);
if (feof(fOut))
{
return 0;
}
string line;
while (ch != '\n')
{
line += ch;
ch = fgetc(fOut);
if (feof(fOut))
break;
}
return line;
}
void GenerateHuffmanCode()
{
HuffmanTree hft;
CharInfo invalid;
hft.CreatTree(_infos, 256, invalid);
_GenerateHuffmanCode(hft.GetRootNode());
}
protected:
void _GenerateHuffmanCode(HuffmanTreeNode* root)//创建哈夫曼编码
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
_GenerateHuffmanCode(root->_left);
_GenerateHuffmanCode(root->_right);
if (root->_left == NULL && root->_right == NULL)
{
HuffmanTreeNode* cur = root;
HuffmanTreeNode* parent = cur->_parent;
string& code = _infos[cur->_weight._ch]._code;
while (parent)
{
if (parent->_left == cur)//往左走+0
{
code += '0';
}
else if (parent->_right == cur)//往右走+1
{
code += '1';
}
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
//寻找编码从叶子节点开始。
reverse(code.begin(), code.end());
}
}
//递归实现哈夫曼编码
void _GenerateHuffmanCode_R(HuffmanTreeNode* root,string code)//创建哈夫曼编码
{
if(root==NULL)
return;
_GenerateHuffmanCode_R(root->_left,code+'0');
_GenerateHuffmanCode_R(root->_right,code+'1');
if(root->_left==NULL&&root->_right==NULL)
{
_infos[root->_weight._ch]._code=code;
}
}
private:
CharInfo _infos[256];
};
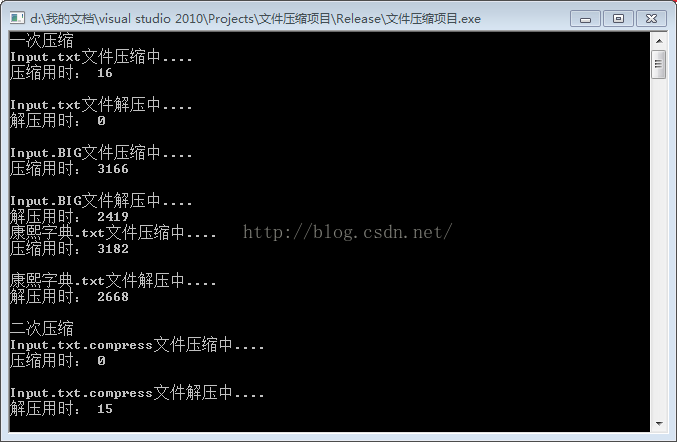
void TestFileCompress()
{
cout<<"一次压缩"< fc;
cout << "Input.txt文件压缩中...." << endl;
cout << "压缩用时: ";
int begin1 = GetTickCount();//记录开始时间
fc.Compress("Input.txt");//
int end1 = GetTickCount();// 记录结束时间
cout << end1 - begin1 << endl << endl;//压缩时间
cout << "Input.txt文件解压中...." << endl;;
cout << "解压用时: ";
int begin2 = GetTickCount();
fc.UnCompresss("Input.txt");
int end2 = GetTickCount();
cout << end2 - begin2 << endl << endl;//解压用时
FileCompress fc1;
cout << "Input.BIG文件压缩中...." << endl;
cout << "压缩用时: ";
int begin3 = GetTickCount();
fc1.Compress("Input.BIG");//
int end3 = GetTickCount();//
cout << end3 - begin3 << endl << endl;
cout << "Input.BIG文件解压中...." << endl;
cout << "解压用时: ";
int begin4 = GetTickCount();
fc1.UnCompresss("Input.BIG");
int end4 = GetTickCount();
cout << (end4 - begin4 )<< endl;
FileCompress fc2;
cout << "康熙字典.txt文件压缩中...." << endl;
cout << "压缩用时: ";
int begin5 = GetTickCount();//记录开始时间
fc2.Compress("康熙字典.txt");//
int end5 = GetTickCount();// 记录结束时间
cout << end5 - begin5 << endl << endl;//压缩时间
cout << "康熙字典.txt文件解压中...." << endl;;
cout << "解压用时: ";
int begin6 = GetTickCount();
fc2.UnCompresss("康熙字典.txt");
int end6 = GetTickCount();
cout << end6 - begin6 << endl << endl;//解压用时
}
void TestFileCompressAgain()//二次压缩
{
cout<<"二次压缩"< fc;
cout << "Input.txt.compress文件压缩中...." << endl;
cout << "压缩用时: ";
int begin1 = GetTickCount();//记录开始时间
fc.Compress("Input.txt.compress");//
int end1 = GetTickCount();// 记录结束时间
cout << end1 - begin1 << endl << endl;//压缩时间
cout << "Input.txt.compress文件解压中...." << endl;;
cout << "解压用时: ";
int begin2 = GetTickCount();
fc.UnCompresss("Input.txt.compress");
int end2 = GetTickCount();
cout << end2 - begin2 << endl << endl;//解压用时
FileCompress fc1;
cout << "Input.BIG.compress文件压缩中...." << endl;
cout << "压缩用时: ";
int begin3 = GetTickCount();//记录开始时间
fc1.Compress("Input.BIG.compress");//
int end3 = GetTickCount();// 记录结束时间
cout << end3 - begin3 << endl << endl;//压缩时间
cout << "Input.BIG.compress文件解压中...." << endl;;
cout << "解压用时: ";
int begin4 = GetTickCount();
fc1.UnCompresss("Input.BIG.compress");
int end4 = GetTickCount();
cout << end4 - begin4 << endl << endl;//解压用时
}
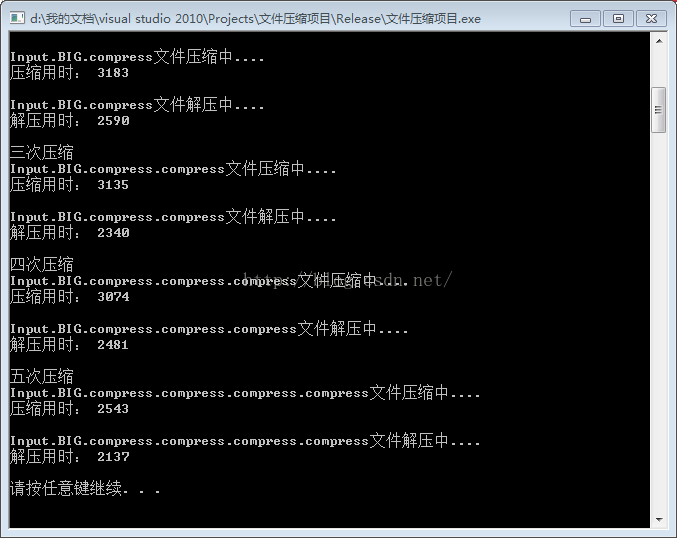
void TestFileCompressThree()
{
cout<<"三次压缩"< fc;
cout << "Input.BIG.compress.compress文件压缩中...." << endl;
cout << "压缩用时: ";
int begin5 = GetTickCount();//记录开始时间
fc.Compress("Input.BIG.compress.compress");//
int end5 = GetTickCount();// 记录结束时间
cout << end5 - begin5 << endl << endl;//压缩时间
cout << "Input.BIG.compress.compress文件解压中...." << endl;;
cout << "解压用时: ";
int begin6 = GetTickCount();
fc.UnCompresss("Input.BIG.compress.compress");
int end6 = GetTickCount();
cout << end6 - begin6 << endl << endl;//解压用时
}
void TestFileCompressFour()
{
cout<<"四次压缩"< fc;
cout << "Input.BIG.compress.compress.compress文件压缩中...." << endl;
cout << "压缩用时: ";
int begin5 = GetTickCount();//记录开始时间
fc.Compress("Input.BIG.compress.compress.compress");//
int end5 = GetTickCount();// 记录结束时间
cout << end5 - begin5 << endl << endl;//压缩时间
cout << "Input.BIG.compress.compress.compress文件解压中...." << endl;;
cout << "解压用时: ";
int begin6 = GetTickCount();
fc.UnCompresss("Input.BIG.compress.compress.compress");
int end6 = GetTickCount();
cout << end6 - begin6 << endl << endl;//解压用时
}
void TestFileCompressFive()
{
cout<<"五次压缩"< fc;
cout << "Input.BIG.compress.compress.compress.compress文件压缩中...." << endl;
cout << "压缩用时: ";
int begin5 = GetTickCount();//记录开始时间
fc.Compress("Input.BIG.compress.compress.compress.compress");//
int end5 = GetTickCount();// 记录结束时间
cout << end5 - begin5 << endl << endl;//压缩时间
cout << "Input.BIG.compress.compress.compress.compress文件解压中...." << endl;;
cout << "解压用时: ";
int begin6 = GetTickCount();
fc.UnCompresss("Input.BIG.compress.compress.compress.compress");
int end6 = GetTickCount();
cout << end6 - begin6 << endl << endl;//解压用时
}
void TestFileCompressPhoto()
{
cout<<"图片压缩"< fc;
cout << "166.jpg文件压缩中...." << endl;
cout << "压缩用时: ";
int begin5 = GetTickCount();//记录开始时间
fc.Compress("166.jpg");//
int end5 = GetTickCount();// 记录结束时间
cout << end5 - begin5 << endl << endl;//压缩时间
cout << "166.jpg文件解压中...." << endl;;
cout << "解压用时: ";
int begin6 = GetTickCount();
fc.UnCompresss("166.jpg");
int end6 = GetTickCount();
cout << end6 - begin6 << endl << endl;//解压用时
}
void TestFileCompressVadio()
{
cout<<"视频压缩"< fc;
cout << "釜山行_hd.mp4文件压缩中...." << endl;
cout << "压缩用时: ";
int begin5 = GetTickCount();//记录开始时间
fc.Compress("釜山行_hd.mp4");//
int end5 = GetTickCount();// 记录结束时间
cout << end5 - begin5 << endl << endl;//压缩时间
cout << "釜山行_hd.mp4文件解压中...." << endl;;
cout << "解压用时: ";
int begin6 = GetTickCount();
fc.UnCompresss("釜山行_hd.mp4");
int end6 = GetTickCount();
cout << end6 - begin6 << endl << endl;//解压用时
} #include "FileCompress.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
TestFileCompress();
TestFileCompressAgain();
TestFileCompressThree();
TestFileCompressFour();
TestFileCompressFive();
TestFileCompressPhoto();
TestFileCompressVadio();
system("pause");
return 0;
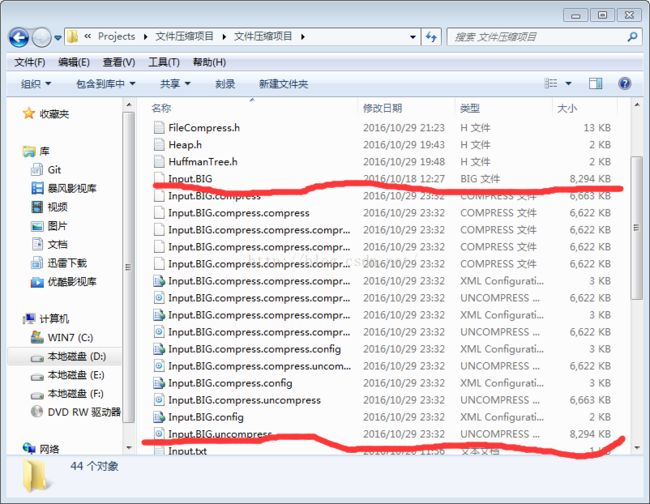
}1、多次压缩普通文件
时间分析
正确性分析
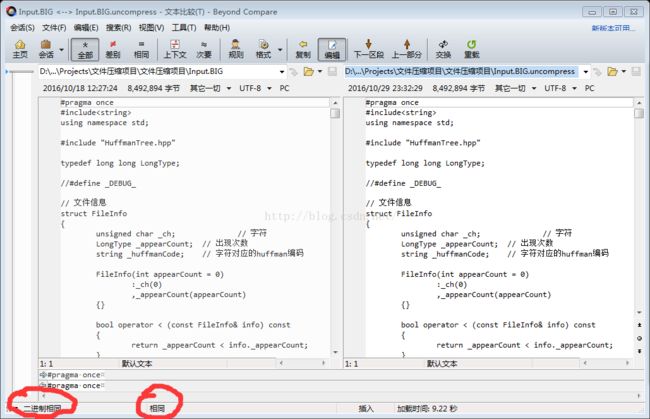
源文件和解压完结果完全相同
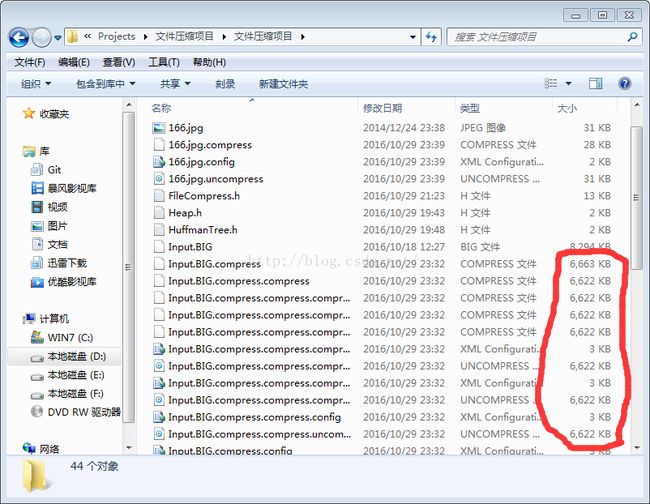
大小分析
源文件和解压完结果完全相同
由于文件太小倒置后面几次压缩大小未发生改变
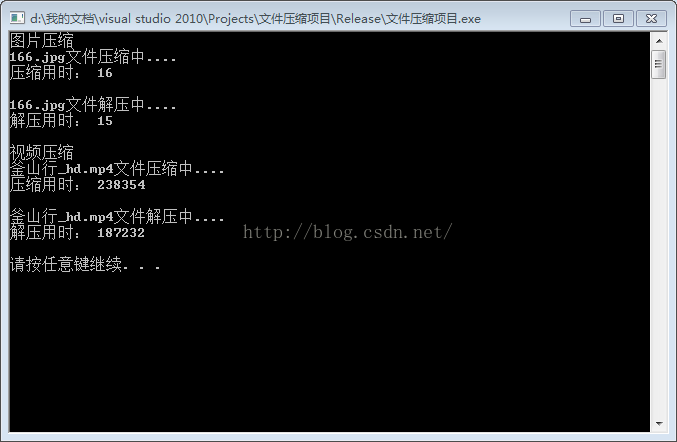
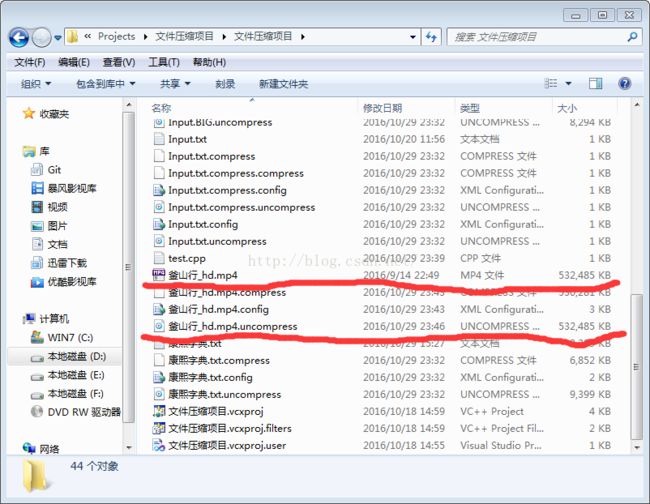
2、解压图片文件及视频文件
时间分析
视频文件较大用时238354ms
图片正确性分析
源文件和解压完结果完全相同
分析大小
源文件和解压完结果完全相同