深度学习:Attention机制(Bahdanau attention & Luong Attention)
文章目录
- Bahdanau Attention Mechanism
- Luong attention mechanism
- Differences between Bahdanau and Luong attention mechanism
- Reference
传统seq2seq模型中encoder将输入序列编码成一个context向量,decoder将context向量作为初始隐状态,生成目标序列。随着输入序列长度的增加,编码器难以将所有输入信息编码为单一context向量,编码信息缺失,难以完成高质量的解码。
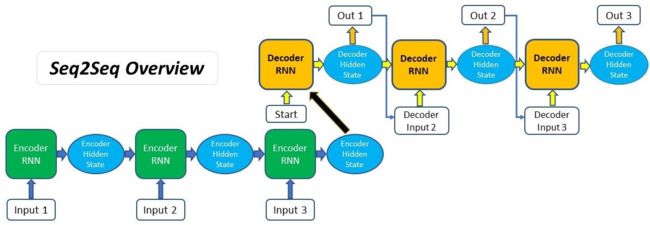
注意力机制是在每个时刻解码时,基于当前时刻解码器的隐状态、输入或输出等信息,计算其对输入序列各位置隐状态的注意力(分数)并加权生成context向量用于当前时刻解码。引入注意力机制,使得不同时刻的解码能够关注不同位置的输入信息,提高预测准确性。
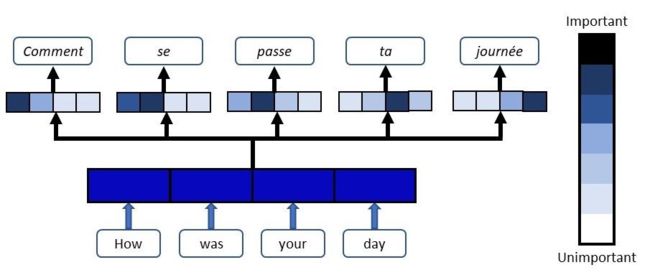
Bahdanau Attention Mechanism
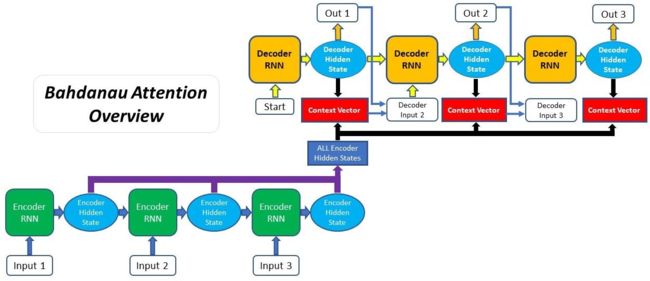
Overall process for Bahdanau Attention seq2seq model
Bahdanau本质是一种 加性attention机制,将decoder的隐状态和encoder所有位置输出通过线性组合对齐,得到context向量,用于改善序列到序列的翻译模型
Bahdanau的特点为:
- 编码器隐状态 :编码器对于每一个输入向量产生一个隐状态向量;
- 计算对齐分数:使用上一时刻的隐状态 s t − 1 \boldsymbol s_{t-1} st−1和编码器每个位置输出 x i \boldsymbol x_i xi计算对齐分数(使用前馈神经网络计算),编码器最终时刻隐状态可作为解码器初始时刻隐状态;
- 概率化对齐分数:解码器上一时刻隐状态 s t − 1 \boldsymbol s_{t-1} st−1在编码器每个位置输出的对齐分数,通过softmax转化为概率分布向量;
- 计算上下文向量:根据概率分布化的对齐分数,加权编码器各位置输出,得上下文向量 c t \boldsymbol c_t ct;
- 解码器输出:将上下文向量 c t \boldsymbol c_t ct和上一时刻编码器输出 y ^ t − 1 \hat y_{t-1} y^t−1对应的embedding拼接,作为当前时刻编码器输入,经RNN网络产生新的输出和隐状态,训练过程中有真实目标序列 y = ( y 1 ⋯ y m ) \boldsymbol y=(y_1\cdots y_m) y=(y1⋯ym),多使用 y t − 1 y_{t-1} yt−1取代 y ^ t − 1 \hat y_{t-1} y^t−1作为解码器 t t t时刻输入;
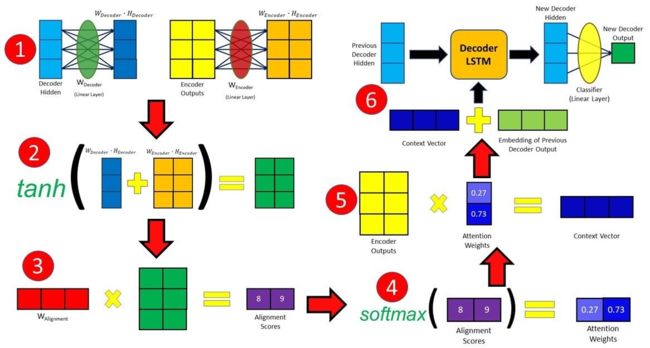
时刻 t t t,解码器的隐状态表示为
s t = f ( s t − 1 , c t , y t − 1 ) \boldsymbol s_t = f(\boldsymbol s_{t-1},\boldsymbol c_t,y_{t-1}) st=f(st−1,ct,yt−1)
时刻 t t t的隐状态 s t − 1 \boldsymbol s_{t-1} st−1对编码器各时刻输出 X X X的注意力分数为:
α t ( s t − 1 , X ) = softmax ( tanh ( s t − 1 W d e c o d e r + X W e n c o d e r ) W a l i g n m e n t ) , c t = ∑ i α t i x i \boldsymbol\alpha_t(\boldsymbol s_{t-1}, X) = \text{softmax}(\tanh( \boldsymbol s_{t-1}W_{decoder}+X W_{encoder})W_{alignment}),\quad \boldsymbol c_t=\sum_i\alpha_{ti}\boldsymbol x_i αt(st−1,X)=softmax(tanh(st−1Wdecoder+XWencoder)Walignment),ct=i∑αtixi
使用Bahdanau注意力机制的解码过程:
Overall process for Bahdanau Attention seq2seq model
Tensorflow源码实现
def _bahdanau_score(processed_query, keys, attention_v):
"""Implements Bahdanau-style (additive) scoring function.
Args:
processed_query: Tensor, shape `[batch_size, num_units]` to compare to
keys.
keys: Processed memory, shape `[batch_size, max_time, num_units]`.
attention_v: Tensor, shape `[num_units]`.
Returns:
A `[batch_size, max_time]` tensor of unnormalized score values.
"""
# Reshape from [batch_size, ...] to [batch_size, 1, ...] for broadcasting.
processed_query = tf.expand_dims(processed_query, 1)
return tf.reduce_sum(attention_v * tf.tanh(keys + processed_query), [2])
def _calculate_attention(self, query, state):
"""Score the query based on the keys and values.
Args:
query: Tensor of dtype matching `self.values` and shape
`[batch_size, query_depth]`.
state: Tensor of dtype matching `self.values` and shape
`[batch_size, alignments_size]`
(`alignments_size` is memory's `max_time`).
Returns:
alignments: Tensor of dtype matching `self.values` and shape
`[batch_size, alignments_size]` (`alignments_size` is memory's
`max_time`).
next_state: same as alignments.
"""
processed_query = self.query_layer(query) if self.query_layer else query
score = _bahdanau_score(
processed_query,
self.keys,
self.attention_v,
)
alignments = self.probability_fn(score, state)
next_state = alignments
return alignments, next_state
Tensorflow自定义实现
# Bahdanau Attention
self.att_w1 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(self.dec_units)
self.att_w2 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(self.dec_units)
self.att_v = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)
def bahdanau_attention(self, query, values):
"""Bahdanau Attention注意力机制
query: shape=(batch_size, hidden_size), 解码器隐状态
values: shape=(batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size),编码器输出
"""
query = tf.expand_dims(query, axis=1)
# shape=(batch_size, seq_len, 1)
score = self.att_v(tf.nn.tanh(self.att_w1(query) + self.att_w2(values)))
weight = tf.nn.softmax(score, axis=1)
# shape=(batch_size, hidden_size)
context = tf.reduce_sum(weight * values, axis=1)
return context, weight
Luong attention mechanism
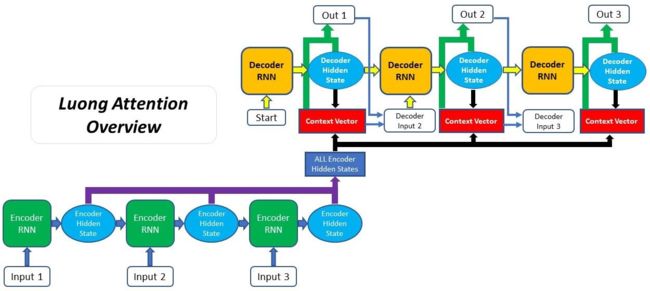
Overall process for Luong Attention seq2seq model
Luong本质是一种 乘性attention机制,将解码器隐状态和编码器输出进行矩阵乘法,得到上下文向量。
Luong注意力机制是对Bahdanau注意力机制的改进,根据是否全部使用所有编码器输出分为两种:全局注意力和局部注意力,全局注意力适合用于短输入序列,局部注意力适合用于长输入序列(计算全局注意力代价高),以下内容仅介绍全局注意力。
Luong注意力机制与Bahdanau注意力机制的主要不同点:
- 对齐分数计算:使用当前时刻的隐状态 s t \boldsymbol s_{t} st计算在编码器位置i输出的对齐分数;
- 解码器输出:解码器在 t t t时刻,拼接上下文向量 c t \boldsymbol c_t ct和当前时刻隐状态 s t \boldsymbol s_t st,经全连接层,产生当前时刻输出 y ^ t + 1 \hat y_{t+1} y^t+1,并作为下一时刻输入;
- 流程图当前时刻计算的context向量,会被应用到下一时刻的输入???
Luong注意力的三种计算方法:
 |
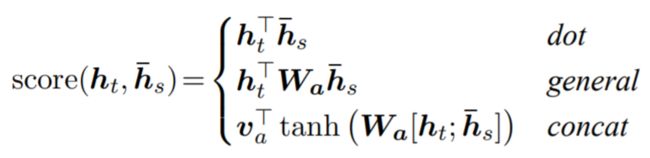 |
Tensorflow源码实现
def _calculate_attention(self, query, state):
"""Score the query based on the keys and values.
Args:
query: Tensor of dtype matching `self.values` and shape
`[batch_size, query_depth]`.
state: Tensor of dtype matching `self.values` and shape
`[batch_size, alignments_size]`
(`alignments_size` is memory's `max_time`).
Returns:
alignments: Tensor of dtype matching `self.values` and shape
`[batch_size, alignments_size]` (`alignments_size` is memory's
`max_time`).
next_state: Same as the alignments.
"""
score = _luong_score(query, self.keys, self.scale_weight)
alignments = self.probability_fn(score, state)
next_state = alignments
return alignments, next_state
def _luong_score(query, keys, scale):
"""Implements Luong-style (multiplicative) scoring function.
To enable the second form, call this function with `scale=True`.
Args:
query: Tensor, shape `[batch_size, num_units]` to compare to keys.
keys: Processed memory, shape `[batch_size, max_time, num_units]`.
scale: the optional tensor to scale the attention score.
Returns:
A `[batch_size, max_time]` tensor of unnormalized score values.
Raises:
ValueError: If `key` and `query` depths do not match.
"""
# Reshape from [batch_size, depth] to [batch_size, 1, depth]
query = tf.expand_dims(query, 1)
score = tf.matmul(query, keys, transpose_b=True)
score = tf.squeeze(score, [1])
if scale is not None:
score = scale * score
return score
Differences between Bahdanau and Luong attention mechanism
I. context的计算方式不同
解码器在第t步,Bahdanau注意力机制使用decoder第t-1步的隐状态 s t − 1 \boldsymbol s_{t-1} st−1与encoder的各位置的输出 s ‾ i \boldsymbol{\overline s}_i si加权得到 c t \boldsymbol c_t ct,而Luong注意力机制使用decoder当前时刻的隐状态 s t \boldsymbol s_t st与encoder的每一个隐状态 s ‾ i \boldsymbol{\overline s}_i si加权得到 c t \boldsymbol c_t ct。
II. decoder的输入输出不同
解码器在第t步,Bahdanau注意力机制将前一时刻隐状态 s t − 1 \boldsymbol s_{t-1} st−1与 c t \boldsymbol c_t ct拼接作为decoder输入,经RNN运算得到 s t \boldsymbol s_{t} st,并直接输出 y ^ t + 1 \hat y_{t+1} y^t+1;Luong注意力机制将当前时刻隐状态 s t \boldsymbol s_t st与 c t \boldsymbol c_t ct拼接,并通过全连接网络输出 y ^ t + 1 \hat y_{t+1} y^t+1,Luong注意力机制只处理最顶层!!!
解码器t时刻输出是 o t o_t ot,由于其是下一时刻输出,所以多记作 y ^ t + 1 \hat y_{t+1} y^t+1。
III. 总结
Bahdanau的计算流程为 s t − 1 → a t → c t → s t \boldsymbol s_{t-1}\to \boldsymbol a_t \to \boldsymbol c_t \to\boldsymbol s_t st−1→at→ct→st,而Luong的计算流程为 s t → a t → c t → s ~ t \boldsymbol s_t\to\boldsymbol a_t \to\boldsymbol c_t \to\tilde\boldsymbol s_t st→at→ct→s~t。
Reference
1. Attention: Sequence 2 Sequence model with Attention Mechanism
2. NEURAL MACHINE TRANSLATION BY JOINTLY LEARNING TO ALIGN AND TRANSLATE
3. Effective Approaches to Attention-based Neural Machine Translation
4. Attention Mechanism