AMS、Activity 启动流程详解
文章目录
- 概述
- 相关类说明
- AMS 服务启动
- Activity 启动流程
概述
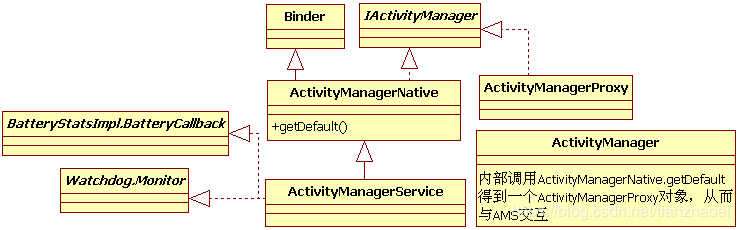
ActivityManagerService(以后简称AMS)都有所耳闻。AMS 是 Android 中最核心的服务,主要负责系统中四大组件的启动、切换、调度及应用进程的管理和调度等工作,其职责与操作系统中的进程管理和调度模块相类似,因此它在 Android 中非常重要。先来看AMS的家族图谱
相关类说明
- ActivityManagerService
AMS由ActivityManagerNative(以后简称AMN)类派生,并实现Watchdog.Monitor和BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback接口。而AMN由Binder派生,实现了IActivityManager接口 - ActivityManager
由于AMS是系统核心服务,很多API不能开放供客户端使用,所以设计者没有让ActivityManager直接加入AMS家族。在ActivityManager类内部通过调用AMN的getDefault函数得到一个ActivityManagerProxy对象,通过它可与AMS通信
AMS 服务启动
与 PMS 启动 类似,AMS 服务也是在 系统引导服务中启动。
第一坨代码是创建并启动了 AMS ,第二坨是将 AMS 服务添加到SystemServer 中。
public final class SystemServer {
private SystemServiceManager mSystemServiceManager;
private void startBootstrapServices() {
......
mActivityManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(
ActivityManagerService.Lifecycle.class).getService();
mActivityManagerService.setSystemServiceManager(mSystemServiceManager);
mActivityManagerService.setInstaller(installer);
......
mActivityManagerService.setSystemProcess();
......
}
}
public class ActivityManagerService extends IActivityManager.Stub
implements Watchdog.Monitor, BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback {
public void setSystemProcess() {
......
ServiceManager.addService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE, this, /* allowIsolated= */ true,
DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_CRITICAL | DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_NORMAL | DUMP_FLAG_PROTO);
......
}
}
public class SystemServiceManager {
public SystemService startService(String className) {
final Class<SystemService> serviceClass;
try {
//通过名字找到相应的 class
serviceClass = (Class<SystemService>)Class.forName(className);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Starting " + className);
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + className
+ ": service class not found, usually indicates that the caller should "
+ "have called PackageManager.hasSystemFeature() to check whether the "
+ "feature is available on this device before trying to start the "
+ "services that implement it", ex);
}
return startService(serviceClass);
}
public <T extends SystemService> T startService(Class<T> serviceClass) {
try {
final String name = serviceClass.getName();
Slog.i(TAG, "Starting " + name);
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER, "StartService " + name);
// Create the service.
if (!SystemService.class.isAssignableFrom(serviceClass)) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create " + name
+ ": service must extend " + SystemService.class.getName());
}
final T service;
try {
//创建相应的 class
Constructor<T> constructor = serviceClass.getConstructor(Context.class);
service = constructor.newInstance(mContext);
} catch (InstantiationException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service could not be instantiated", ex);
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service must have a public constructor with a Context argument", ex);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service must have a public constructor with a Context argument", ex);
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service constructor threw an exception", ex);
}
startService(service);
return service;
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER);
}
}
public void startService(@NonNull final SystemService service) {
// Register it.
mServices.add(service);
// Start it.
long time = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
try {
//启动服务
service.onStart();
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to start service " + service.getClass().getName()
+ ": onStart threw an exception", ex);
}
warnIfTooLong(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - time, service, "onStart");
}
}
Activity 启动流程
Activity 启动我们在熟悉不过了,我们就以 startActivity 为入口来梳理下。
前面没有什么过多代码,顺着走下去发现调用了 AMS 的 startActivity 方法。但是呢,AMS 是运行在系统进程中的,这里就用到了 Binder 进行 IPC 通信。
startActivity(new Intent(this,NewActivity.class));
public class Activity extends ContextThemeWrapper{
private Instrumentation mInstrumentation;
public void startActivityForResult(@RequiresPermission Intent intent, int requestCode,
@Nullable Bundle options) {
......
Instrumentation.ActivityResult ar =
mInstrumentation.execStartActivity(
this, mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), mToken, this,
intent, requestCode, options);
......
}
}
public class Instrumentation {
public ActivityResult execStartActivity(
Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, Activity target,
Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) {
......
int result = ActivityManager.getService()
.startActivity(whoThread, who.getBasePackageName(), intent,
intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(who.getContentResolver()),
token, target != null ? target.mEmbeddedID : null,
requestCode, 0, null, options);
......
}
}
public class ActivityManager {
public static IActivityManager getService() {
return IActivityManagerSingleton.get();
}
private static final Singleton<IActivityManager> IActivityManagerSingleton =
new Singleton<IActivityManager>() {
@Override
protected IActivityManager create() {
final IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
final IActivityManager am = IActivityManager.Stub.asInterface(b);
return am;
}
};
}
上面只贴了怎么从用户进程通过 Binder 调用系统进程的相关服务。系统进程服务处理完相应工作后,也通过 Binder 调用用户进程的启动服务,下面在贴出总体的调用链,大伙可以自己在跟一下后续的调用链。