【Tomcat】容器 之 Wrapper(Servlet)
tomcat4.0版本。
wrapper是四大容器最底层的容器,是请求处理的真正容器。与servlet的区别是:wrapper本质并未处理请求,而是加载对应的servlet来处理,在这之前也会调用filter。
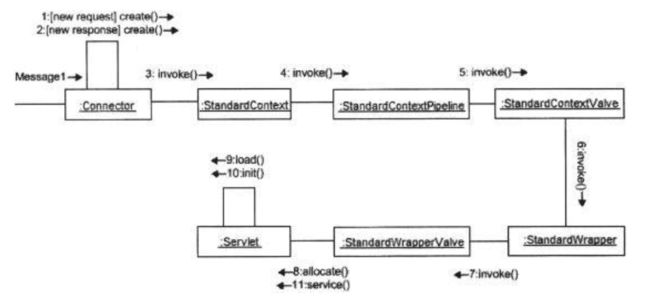
首先来看一个context和wrapper容器的调用时序图:
与之前容器一样,也是在构造方法里设置自己pipeline的basic 的valve:
/**
* Create a new StandardWrapper component with the default basic Valve.
*/
public StandardWrapper() {
super();
swValve=new StandardWrapperValve();
pipeline.setBasic(swValve);
}那么调用wrapper的invoke方法最终会进入到valve的invoke方法:
/**
* Invoke the servlet we are managing, respecting the rules regarding
* servlet lifecycle and SingleThreadModel support.
*
* @param request Request to be processed
* @param response Response to be produced
* @param valveContext Valve context used to forward to the next Valve
*
* @exception IOException if an input/output error occurred
* @exception ServletException if a servlet error occurred
*/
public void invoke(Request request, Response response,
ValveContext valveContext)
throws IOException, ServletException {
long t1=System.currentTimeMillis();
requestCount++;
// Initialize local variables we may need
boolean unavailable = false;
Throwable throwable = null;
StandardWrapper wrapper = (StandardWrapper) getContainer();
ServletRequest sreq = request.getRequest();
ServletResponse sres = response.getResponse();
Servlet servlet = null;
HttpServletRequest hreq = null;
if (sreq instanceof HttpServletRequest)
hreq = (HttpServletRequest) sreq;
HttpServletResponse hres = null;
if (sres instanceof HttpServletResponse)
hres = (HttpServletResponse) sres;
// Check for the application being marked unavailable
if (!((Context) wrapper.getParent()).getAvailable()) {
hres.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE,
sm.getString("standardContext.isUnavailable"));
unavailable = true;
}
// Check for the servlet being marked unavailable
if (!unavailable && wrapper.isUnavailable()) {
log(sm.getString("standardWrapper.isUnavailable",
wrapper.getName()));
if (hres == null) {
; // NOTE - Not much we can do generically
} else {
long available = wrapper.getAvailable();
if ((available > 0L) && (available < Long.MAX_VALUE))
hres.setDateHeader("Retry-After", available);
hres.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE,
sm.getString("standardWrapper.isUnavailable",
wrapper.getName()));
}
unavailable = true;
}
// Allocate a servlet instance to process this request
try {
if (!unavailable) {
servlet = wrapper.allocate();
}
} catch (ServletException e) {
log(sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocateException",
wrapper.getName()), e);
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
servlet = null;
} catch (Throwable e) {
log(sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocateException",
wrapper.getName()), e);
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
servlet = null;
}
// Acknowlege the request
try {
response.sendAcknowledgement();
} catch (IOException e) {
sreq.removeAttribute(Globals.JSP_FILE_ATTR);
log(sm.getString("standardWrapper.acknowledgeException",
wrapper.getName()), e);
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
} catch (Throwable e) {
log(sm.getString("standardWrapper.acknowledgeException",
wrapper.getName()), e);
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
servlet = null;
}
// Create the filter chain for this request
ApplicationFilterChain filterChain =
createFilterChain(request, servlet);
// Call the filter chain for this request
// NOTE: This also calls the servlet's service() method
try {
String jspFile = wrapper.getJspFile();
if (jspFile != null)
sreq.setAttribute(Globals.JSP_FILE_ATTR, jspFile);
else
sreq.removeAttribute(Globals.JSP_FILE_ATTR);
if ((servlet != null) && (filterChain != null)) {
filterChain.doFilter(sreq, sres);
}
sreq.removeAttribute(Globals.JSP_FILE_ATTR);
} catch (IOException e) {
sreq.removeAttribute(Globals.JSP_FILE_ATTR);
log(sm.getString("standardWrapper.serviceException",
wrapper.getName()), e);
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
} catch (UnavailableException e) {
sreq.removeAttribute(Globals.JSP_FILE_ATTR);
log(sm.getString("standardWrapper.serviceException",
wrapper.getName()), e);
// throwable = e;
// exception(request, response, e);
wrapper.unavailable(e);
long available = wrapper.getAvailable();
if ((available > 0L) && (available < Long.MAX_VALUE))
hres.setDateHeader("Retry-After", available);
hres.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE,
sm.getString("standardWrapper.isUnavailable",
wrapper.getName()));
// Do not save exception in 'throwable', because we
// do not want to do exception(request, response, e) processing
} catch (ServletException e) {
sreq.removeAttribute(Globals.JSP_FILE_ATTR);
log(sm.getString("standardWrapper.serviceException",
wrapper.getName()), e);
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
} catch (Throwable e) {
sreq.removeAttribute(Globals.JSP_FILE_ATTR);
log(sm.getString("standardWrapper.serviceException",
wrapper.getName()), e);
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
}
// Release the filter chain (if any) for this request
try {
if (filterChain != null)
filterChain.release();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log(sm.getString("standardWrapper.releaseFilters",
wrapper.getName()), e);
if (throwable == null) {
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
}
}
// Deallocate the allocated servlet instance
try {
if (servlet != null) {
wrapper.deallocate(servlet);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
log(sm.getString("standardWrapper.deallocateException",
wrapper.getName()), e);
if (throwable == null) {
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
}
}
// If this servlet has been marked permanently unavailable,
// unload it and release this instance
try {
if ((servlet != null) &&
(wrapper.getAvailable() == Long.MAX_VALUE)) {
wrapper.unload();
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
log(sm.getString("standardWrapper.unloadException",
wrapper.getName()), e);
if (throwable == null) {
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
}
}
long t2=System.currentTimeMillis();
long time=t2-t1;
processingTime+=time;
if( time > maxTime ) maxTime=time;
}这个方法很长,但是最核心的就是做了这些事情:
调用allocate加载一个servlet;生成过滤链并执行过滤链(最后的部分是执行加载的servlet处理请求)。
首先看下allocate方法:
/**
* Allocate an initialized instance of this Servlet that is ready to have
* its service() method called. If the servlet class does
* not implement SingleThreadModel, the (only) initialized
* instance may be returned immediately. If the servlet class implements
* SingleThreadModel, the Wrapper implementation must ensure
* that this instance is not allocated again until it is deallocated by a
* call to deallocate().
*
* @exception ServletException if the servlet init() method threw
* an exception
* @exception ServletException if a loading error occurs
*/
public Servlet allocate() throws ServletException {
if (debug >= 1)
log("Allocating an instance");
// If we are currently unloading this servlet, throw an exception
if (unloading)
throw new ServletException
(sm.getString("standardWrapper.unloading", getName()));
// If not SingleThreadedModel, return the same instance every time
if (!singleThreadModel) {
// Load and initialize our instance if necessary
if (instance == null) {
synchronized (this) {
if (instance == null) {
try {
instance = loadServlet();
} catch (ServletException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new ServletException
(sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocate"), e);
}
}
}
}
if (!singleThreadModel) {
if (debug >= 2)
log(" Returning non-STM instance");
countAllocated++;
return (instance);
}
}
synchronized (instancePool) {
while (countAllocated >= nInstances) {
// Allocate a new instance if possible, or else wait
if (nInstances < maxInstances) {
try {
instancePool.push(loadServlet());
nInstances++;
} catch (ServletException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new ServletException
(sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocate"), e);
}
} else {
try {
instancePool.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
;
}
}
}
if (debug >= 2)
log(" Returning allocated STM instance");
countAllocated++;
return (Servlet) instancePool.pop();
}
}这个加载分两部分,对非stm的servlet加载和stm的servlet加载。
STM指的是single thread model,是一个标记接口,是早期tomcat为了实现servlet多线程同步的方式,但是现在已经废除。
非stm加载方式:比较简单,就是一个单例。
stm加载方式:比较复杂。tomcat stm保证同步的思路是让service方法同步处理,那么servlet默认是单例的,这样一同步会极大降低吞吐量,所以对应的策略是加载多个servlet,将stm的servlet池化。
与stm对应的变量:
/**
* The count of allocations that are currently active (even if they
* are for the same instance, as will be true on a non-STM servlet).
*/
private int countAllocated = 0;
/**
* Maximum number of STM instances.
*/
private int maxInstances = 20;
/**
* Number of instances currently loaded for a STM servlet.
*/
private int nInstances = 0;
/**
* Stack containing the STM instances.
*/
private Stack instancePool = null;逻辑是:如果countAllocate大于等于nInstance,那么就进入到创建servlet实例的分支。如果创建数目没有超过上限,那么就创建,否则就阻塞。一旦可以创建,那么nInstance会自增,下一次就会跳出循环,返回一个池里的对象。被阻塞的线程会在执行deallocate方法时被唤醒:
/**
* Return this previously allocated servlet to the pool of available
* instances. If this servlet class does not implement SingleThreadModel,
* no action is actually required.
*
* @param servlet The servlet to be returned
*
* @exception ServletException if a deallocation error occurs
*/
public void deallocate(Servlet servlet) throws ServletException {
// If not SingleThreadModel, no action is required
if (!singleThreadModel) {
countAllocated--;
return;
}
// Unlock and free this instance
synchronized (instancePool) {
countAllocated--;
instancePool.push(servlet);
instancePool.notify();
}
}deallocate卸载servlet时只是把相关的计数器减一,并未真正的卸载,这样下次再用就不需要loadclass了,效率更高。
接着是loadServlet方法:
/**
* Load and initialize an instance of this servlet, if there is not already
* at least one initialized instance. This can be used, for example, to
* load servlets that are marked in the deployment descriptor to be loaded
* at server startup time.
*/
public synchronized Servlet loadServlet() throws ServletException {
// Nothing to do if we already have an instance or an instance pool
if (!singleThreadModel && (instance != null))
return instance;
PrintStream out = System.out;
if (swallowOutput) {
SystemLogHandler.startCapture();
}
Servlet servlet = null;
try {
// If this "servlet" is really a JSP file, get the right class.
// HOLD YOUR NOSE - this is a kludge that avoids having to do special
// case Catalina-specific code in Jasper - it also requires that the
// servlet path be replaced by the element content in
// order to be completely effective
String actualClass = servletClass;
if ((actualClass == null) && (jspFile != null)) {
Wrapper jspWrapper = (Wrapper)
((Context) getParent()).findChild(Constants.JSP_SERVLET_NAME);
if (jspWrapper != null)
actualClass = jspWrapper.getServletClass();
}
// Complain if no servlet class has been specified
if (actualClass == null) {
unavailable(null);
throw new ServletException
(sm.getString("standardWrapper.notClass", getName()));
}
// Acquire an instance of the class loader to be used
Loader loader = getLoader();
if (loader == null) {
unavailable(null);
throw new ServletException
(sm.getString("standardWrapper.missingLoader", getName()));
}
ClassLoader classLoader = loader.getClassLoader();
// Special case class loader for a container provided servlet
if (isContainerProvidedServlet(actualClass)) {
classLoader = this.getClass().getClassLoader();
log(sm.getString
("standardWrapper.containerServlet", getName()));
}
// Load the specified servlet class from the appropriate class loader
Class classClass = null;
try {
if (classLoader != null) {
classClass = classLoader.loadClass(actualClass);
} else {
classClass = Class.forName(actualClass);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
unavailable(null);
throw new ServletException
(sm.getString("standardWrapper.missingClass", actualClass),
e);
}
if (classClass == null) {
unavailable(null);
throw new ServletException
(sm.getString("standardWrapper.missingClass", actualClass));
}
// Instantiate and initialize an instance of the servlet class itself
try {
servlet = (Servlet) classClass.newInstance();
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
unavailable(null);
// Restore the context ClassLoader
throw new ServletException
(sm.getString("standardWrapper.notServlet", actualClass), e);
} catch (Throwable e) {
unavailable(null);
// Restore the context ClassLoader
throw new ServletException
(sm.getString("standardWrapper.instantiate", actualClass), e);
}
// Check if loading the servlet in this web application should be
// allowed
if (!isServletAllowed(servlet)) {
throw new SecurityException
(sm.getString("standardWrapper.privilegedServlet",
actualClass));
}
// Special handling for ContainerServlet instances
if ((servlet instanceof ContainerServlet) &&
isContainerProvidedServlet(actualClass)) {
((ContainerServlet) servlet).setWrapper(this);
}
// Call the initialization method of this servlet
try {
instanceSupport.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.BEFORE_INIT_EVENT,
servlet);
servlet.init(facade);
// Invoke jspInit on JSP pages
if ((loadOnStartup >= 0) && (jspFile != null)) {
// Invoking jspInit
HttpRequestBase req = new HttpRequestBase();
HttpResponseBase res = new HttpResponseBase();
req.setServletPath(jspFile);
req.setQueryString("jsp_precompile=true");
servlet.service(req, res);
}
instanceSupport.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_INIT_EVENT,
servlet);
} catch (UnavailableException f) {
instanceSupport.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_INIT_EVENT,
servlet, f);
unavailable(f);
throw f;
} catch (ServletException f) {
instanceSupport.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_INIT_EVENT,
servlet, f);
// If the servlet wanted to be unavailable it would have
// said so, so do not call unavailable(null).
throw f;
} catch (Throwable f) {
instanceSupport.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_INIT_EVENT,
servlet, f);
// If the servlet wanted to be unavailable it would have
// said so, so do not call unavailable(null).
throw new ServletException
(sm.getString("standardWrapper.initException", getName()), f);
}
// Register our newly initialized instance
singleThreadModel = servlet instanceof SingleThreadModel;
if (singleThreadModel) {
if (instancePool == null)
instancePool = new Stack();
}
fireContainerEvent("load", this);
} finally {
if (swallowOutput) {
String log = SystemLogHandler.stopCapture();
if (log != null && log.length() > 0) {
if (getServletContext() != null) {
getServletContext().log(log);
} else {
out.println(log);
}
}
}
}
return servlet;
} 主要做了:通过反射得到得应的class对象,然后newInstance创建实例,触发相应的相应的生命周期事件,调用serlvet的init方法初始化。
接下来看一下与过滤链相关的代码:
首先是生成过滤链的方法,在valve里面:
/**
* Construct and return a FilterChain implementation that will wrap the
* execution of the specified servlet instance. If we should not execute
* a filter chain at all, return null.
*
* FIXME - Pool the chain instances!
*
* @param request The servlet request we are processing
* @param servlet The servlet instance to be wrapped
*/
private ApplicationFilterChain createFilterChain(Request request,
Servlet servlet) {
// If there is no servlet to execute, return null
if (servlet == null)
return (null);
// Create and initialize a filter chain object
ApplicationFilterChain filterChain =
new ApplicationFilterChain();
filterChain.setServlet(servlet);
StandardWrapper wrapper = (StandardWrapper) getContainer();
filterChain.setSupport(wrapper.getInstanceSupport());
// Acquire the filter mappings for this Context
StandardContext context = (StandardContext) wrapper.getParent();
FilterMap filterMaps[] = context.findFilterMaps();
// If there are no filter mappings, we are done
if ((filterMaps == null) || (filterMaps.length == 0))
return (filterChain);
// if (debug >= 1)
// log("createFilterChain: Processing " + filterMaps.length +
// " filter map entries");
// Acquire the information we will need to match filter mappings
String requestPath = null;
if (request instanceof HttpRequest) {
HttpServletRequest hreq =
(HttpServletRequest) request.getRequest();
String contextPath = hreq.getContextPath();
if (contextPath == null)
contextPath = "";
String requestURI = ((HttpRequest) request).getDecodedRequestURI();
if (requestURI.length() >= contextPath.length())
requestPath = requestURI.substring(contextPath.length());
}
String servletName = wrapper.getName();
// if (debug >= 1) {
// log(" requestPath=" + requestPath);
// log(" servletName=" + servletName);
// }
int n = 0;
// Add the relevant path-mapped filters to this filter chain
for (int i = 0; i < filterMaps.length; i++) {
// if (debug >= 2)
// log(" Checking path-mapped filter '" +
// filterMaps[i] + "'");
if (!matchFiltersURL(filterMaps[i], requestPath))
continue;
ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig = (ApplicationFilterConfig)
context.findFilterConfig(filterMaps[i].getFilterName());
if (filterConfig == null) {
// if (debug >= 2)
// log(" Missing path-mapped filter '" +
// filterMaps[i] + "'");
; // FIXME - log configuration problem
continue;
}
// if (debug >= 2)
// log(" Adding path-mapped filter '" +
// filterConfig.getFilterName() + "'");
filterChain.addFilter(filterConfig);
n++;
}
// Add filters that match on servlet name second
for (int i = 0; i < filterMaps.length; i++) {
// if (debug >= 2)
// log(" Checking servlet-mapped filter '" +
// filterMaps[i] + "'");
if (!matchFiltersServlet(filterMaps[i], servletName))
continue;
ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig = (ApplicationFilterConfig)
context.findFilterConfig(filterMaps[i].getFilterName());
if (filterConfig == null) {
// if (debug >= 2)
// log(" Missing servlet-mapped filter '" +
// filterMaps[i] + "'");
; // FIXME - log configuration problem
continue;
}
// if (debug >= 2)
// log(" Adding servlet-mapped filter '" +
// filterMaps[i] + "'");
filterChain.addFilter(filterConfig);
n++;
}
// Return the completed filter chain
// if (debug >= 2)
// log(" Returning chain with " + n + " filters");
return (filterChain);
}
这里会把servlet设置到过滤链中,然后拿到过滤链的配置(web.xml),逐一加入到链子中,并且如果有配置项,就为其添加。
这里只是拿到了每一个filter的配置,具体加载配置会调用fitlerConfig的方法:
/**
* Return the application Filter we are configured for.
*
* @exception ClassCastException if the specified class does not implement
* the javax.servlet.Filter interface
* @exception ClassNotFoundException if the filter class cannot be found
* @exception IllegalAccessException if the filter class cannot be
* publicly instantiated
* @exception InstantiationException if an exception occurs while
* instantiating the filter object
* @exception ServletException if thrown by the filter's init() method
*/
Filter getFilter() throws ClassCastException, ClassNotFoundException,
IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, ServletException {
// Return the existing filter instance, if any
if (this.filter != null)
return (this.filter);
// Identify the class loader we will be using
String filterClass = filterDef.getFilterClass();
ClassLoader classLoader = null;
if (filterClass.startsWith("org.apache.catalina."))
classLoader = this.getClass().getClassLoader();
else
classLoader = context.getLoader().getClassLoader();
ClassLoader oldCtxClassLoader =
Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
// Instantiate a new instance of this filter and return it
Class clazz = classLoader.loadClass(filterClass);
this.filter = (Filter) clazz.newInstance();
if (context instanceof StandardContext &&
((StandardContext)context).getSwallowOutput()) {
try {
SystemLogHandler.startCapture();
filter.init(this);
} finally {
String log = SystemLogHandler.stopCapture();
if (log != null && log.length() > 0) {
getServletContext().log(log);
}
}
} else {
filter.init(this);
}
return (this.filter);
} /**
* The set of filters that will be executed on this chain.
*/
private ArrayList filters = new ArrayList();
/**
* The iterator that is used to maintain the current position in the filter chain.
* This iterator is called the first time that doFilter()
* is called.
*/
private Iterator iterator = null;过滤链被实现为一个arraylist。
下面就是最终要的doFilter方法了:
/**
* Invoke the next filter in this chain, passing the specified request
* and response. If there are no more filters in this chain, invoke
* the service() method of the servlet itself.
*
* @param request The servlet request we are processing
* @param response The servlet response we are creating
*
* @exception IOException if an input/output error occurs
* @exception ServletException if a servlet exception occurs
*/
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if( System.getSecurityManager() != null ) {
final ServletRequest req = request;
final ServletResponse res = response;
try {
java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
new java.security.PrivilegedExceptionAction()
{
public Object run() throws ServletException, IOException {
internalDoFilter(req,res);
return null;
}
}
);
} catch( PrivilegedActionException pe) {
Exception e = pe.getException();
if (e instanceof ServletException)
throw (ServletException) e;
else if (e instanceof IOException)
throw (IOException) e;
else if (e instanceof RuntimeException)
throw (RuntimeException) e;
else
throw new ServletException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
} else {
internalDoFilter(request,response);
}
}
private void internalDoFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// Construct an iterator the first time this method is called
if (this.iterator == null)
this.iterator = filters.iterator();
// Call the next filter if there is one
if (this.iterator.hasNext()) {
ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig =
(ApplicationFilterConfig) iterator.next();
Filter filter = null;
try {
filter = filterConfig.getFilter();
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.BEFORE_FILTER_EVENT,
filter, request, response);
filter.doFilter(request, response, this);
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_FILTER_EVENT,
filter, request, response);
} catch (IOException e) {
if (filter != null)
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_FILTER_EVENT,
filter, request, response, e);
throw e;
} catch (ServletException e) {
if (filter != null)
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_FILTER_EVENT,
filter, request, response, e);
throw e;
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
if (filter != null)
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_FILTER_EVENT,
filter, request, response, e);
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
if (filter != null)
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_FILTER_EVENT,
filter, request, response, e);
throw new ServletException
(sm.getString("filterChain.filter"), e);
}
return;
}
// We fell off the end of the chain -- call the servlet instance
try {
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.BEFORE_SERVICE_EVENT,
servlet, request, response);
if ((request instanceof HttpServletRequest) &&
(response instanceof HttpServletResponse)) {
servlet.service((HttpServletRequest) request,
(HttpServletResponse) response);
} else {
servlet.service(request, response);
}
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_SERVICE_EVENT,
servlet, request, response);
} catch (IOException e) {
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_SERVICE_EVENT,
servlet, request, response, e);
throw e;
} catch (ServletException e) {
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_SERVICE_EVENT,
servlet, request, response, e);
throw e;
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_SERVICE_EVENT,
servlet, request, response, e);
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
support.fireInstanceEvent(InstanceEvent.AFTER_SERVICE_EVENT,
servlet, request, response, e);
throw new ServletException
(sm.getString("filterChain.servlet"), e);
}
}通过迭代器逐一调用filter,最后再调用servlet。
还有一点,上面添加filter的时候,是从context拿了配置