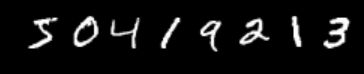caffe详解之minist手写体识别
从零开始,一步一步学习caffe的使用,期间贯穿深度学习和调参的相关知识!
加载库文件设置路径
#加载必要的库
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
import sys,os,caffe
#设置当前目录
caffe_root = '/home/xuke/caffe/'
sys.path.insert(0, caffe_root + 'python')
os.chdir(caffe_root)
下载并准备数据集
# 采用脚本下载mnist数据集
!data/mnist/get_mnist.sh
# 准备数据
!examples/mnist/create_mnist.sh
# back to examples
os.chdir('examples')
Downloading...
Creating lmdb...
I0210 09:03:31.028940 3770 db_lmdb.cpp:35] Opened lmdb examples/mnist/mnist_train_lmdb
I0210 09:03:31.030318 3770 convert_mnist_data.cpp:88] A total of 60000 items.
I0210 09:03:31.030331 3770 convert_mnist_data.cpp:89] Rows: 28 Cols: 28
I0210 09:03:31.486696 3770 convert_mnist_data.cpp:108] Processed 60000 files.
I0210 09:03:31.614672 3785 db_lmdb.cpp:35] Opened lmdb examples/mnist/mnist_test_lmdb
I0210 09:03:31.616041 3785 convert_mnist_data.cpp:88] A total of 10000 items.
I0210 09:03:31.616056 3785 convert_mnist_data.cpp:89] Rows: 28 Cols: 28
I0210 09:03:31.679352 3785 convert_mnist_data.cpp:108] Processed 10000 files.
Done.
创建网络结构
from caffe import layers as L, params as P
def lenet(lmdb, batch_size):
# our version of LeNet: a series of linear and simple nonlinear transformations
n = caffe.NetSpec()
n.data, n.label = L.Data(batch_size=batch_size, backend=P.Data.LMDB, source=lmdb,
transform_param=dict(scale=1./255), ntop=2)
n.conv1 = L.Convolution(n.data, kernel_size=5, num_output=20, weight_filler=dict(type='xavier'))
n.pool1 = L.Pooling(n.conv1, kernel_size=2, stride=2, pool=P.Pooling.MAX)
n.conv2 = L.Convolution(n.pool1, kernel_size=5, num_output=50, weight_filler=dict(type='xavier'))
n.pool2 = L.Pooling(n.conv2, kernel_size=2, stride=2, pool=P.Pooling.MAX)
n.fc1 = L.InnerProduct(n.pool2, num_output=500, weight_filler=dict(type='xavier'))
n.relu1 = L.ReLU(n.fc1, in_place=True)
n.score = L.InnerProduct(n.relu1, num_output=10, weight_filler=dict(type='xavier'))
n.loss = L.SoftmaxWithLoss(n.score, n.label)
return n.to_proto()
with open('mnist/lenet_auto_train.prototxt', 'w') as f:
f.write(str(lenet('mnist/mnist_train_lmdb', 64)))
with open('mnist/lenet_auto_test.prototxt', 'w') as f:
f.write(str(lenet('mnist/mnist_test_lmdb', 100)))
查看lenet_auto_train.prototxt
!cat mnist/lenet_auto_train.prototxt
layer {
name: "data"
type: "Data"
top: "data"
top: "label"
transform_param {
scale: 0.00392156862745
}
data_param {
source: "mnist/mnist_train_lmdb"
batch_size: 64
backend: LMDB
}
}
layer {
name: "conv1"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "data"
top: "conv1"
convolution_param {
num_output: 20
kernel_size: 5
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "pool1"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv1"
top: "pool1"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "conv2"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "pool1"
top: "conv2"
convolution_param {
num_output: 50
kernel_size: 5
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "pool2"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv2"
top: "pool2"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "fc1"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "pool2"
top: "fc1"
inner_product_param {
num_output: 500
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu1"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "fc1"
top: "fc1"
}
layer {
name: "score"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "fc1"
top: "score"
inner_product_param {
num_output: 10
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "loss"
type: "SoftmaxWithLoss"
bottom: "score"
bottom: "label"
top: "loss"
}
设置求解器
caffe.set_mode_cpu()
solver = caffe.SGDSolver('/home/xuke/caffe/examples/mnist/lenet_auto_solver.prototxt')
查看lenet_solver.prototxt
!cat mnist/lenet_solver.prototxt
# The train/test net protocol buffer definition
net: "examples/mnist/lenet_train_test.prototxt"
# test_iter specifies how many forward passes the test should carry out.
# In the case of MNIST, we have test batch size 100 and 100 test iterations,
# covering the full 10,000 testing images.
test_iter: 100
# Carry out testing every 500 training iterations.
test_interval: 500
# The base learning rate, momentum and the weight decay of the network.
base_lr: 0.01
momentum: 0.9
weight_decay: 0.0005
# The learning rate policy
lr_policy: "inv"
gamma: 0.0001
power: 0.75
# Display every 100 iterations
display: 100
# The maximum number of iterations
max_iter: 10000
# snapshot intermediate results
snapshot: 5000
snapshot_prefix: "examples/mnist/model/lenet"
# solver mode: CPU or GPU
solver_mode: CPU
查看每一层的输出结构
# each output is (batch size, feature dim, spatial dim)
[(k, v.data.shape) for k, v in solver.net.blobs.items()]
[('data', (64, 1, 28, 28)),
('label', (64,)),
('conv1', (64, 20, 24, 24)),
('pool1', (64, 20, 12, 12)),
('conv2', (64, 50, 8, 8)),
('pool2', (64, 50, 4, 4)),
('fc1', (64, 500)),
('score', (64, 10)),
('loss', ())]
测试网络
solver.net.forward() # 训练数据作为输入,进行一次前向传播:
solver.test_nets[0].forward() # 测试数据作为输入,进行一次前向传播:
{'loss': array(2.4025168418884277, dtype=float32)}
from pylab import *
%matplotlib inline
# we use a little trick to tile the first eight images
imshow(solver.net.blobs['data'].data[:8, 0].transpose(1, 0, 2).reshape(28, 8*28), cmap='gray'); axis('off')
print 'train labels:', solver.net.blobs['label'].data[:8]
train labels: [ 5. 0. 4. 1. 9. 2. 1. 3.]
imshow(solver.test_nets[0].blobs['data'].data[:8, 0].transpose(1, 0, 2).reshape(28, 8*28), cmap='gray'); axis('off')
print 'test labels:', solver.test_nets[0].blobs['label'].data[:8]
test labels: [ 7. 2. 1. 0. 4. 1. 4. 9.]
训练网络
solver.step(1) # 进行完整的一次计算(minibatch):solver.step(1):(包括数据的前向传播,误差反向传播,以及网络权值的update)
imshow(solver.net.params['conv1'][0].diff[:, 0].reshape(4, 5, 5, 5)
.transpose(0, 2, 1, 3).reshape(4*5, 5*5), cmap='gray'); axis('off')
(-0.5, 24.5, 19.5, -0.5)
训练并保存Loss与Accuracy值
%%time
niter = 200
test_interval = 25
# losses will also be stored in the log
train_loss = zeros(niter)
test_acc = zeros(int(np.ceil(niter / test_interval)))
output = zeros((niter, 8, 10))
# the main solver loop
for it in range(niter):
solver.step(1) # SGD by Caffe
# store the train loss
train_loss[it] = solver.net.blobs['loss'].data
# store the output on the first test batch
# (start the forward pass at conv1 to avoid loading new data)
solver.test_nets[0].forward(start='conv1')
output[it] = solver.test_nets[0].blobs['score'].data[:8]
# run a full test every so often
# (Caffe can also do this for us and write to a log, but we show here
# how to do it directly in Python, where more complicated things are easier.)
if it % test_interval == 0:
print 'Iteration', it, 'testing...'
correct = 0
for test_it in range(100):
solver.test_nets[0].forward()
correct += sum(solver.test_nets[0].blobs['score'].data.argmax(1)
== solver.test_nets[0].blobs['label'].data)
test_acc[it // test_interval] = correct / 1e4
Iteration 0 testing...
Iteration 25 testing...
Iteration 50 testing...
Iteration 75 testing...
Iteration 100 testing...
Iteration 125 testing...
Iteration 150 testing...
Iteration 175 testing...
CPU times: user 1min 2s, sys: 98.5 ms, total: 1min 2s
Wall time: 1min 1s
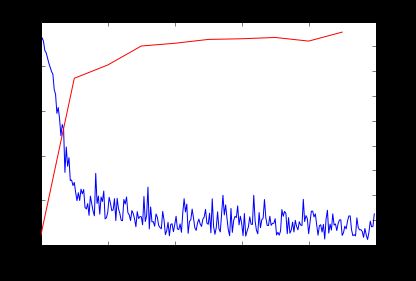
绘制Loss曲线
_, ax1 = subplots()
ax2 = ax1.twinx()
ax1.plot(arange(niter), train_loss)
ax2.plot(test_interval * arange(len(test_acc)), test_acc, 'r')
ax1.set_xlabel('iteration')
ax1.set_ylabel('train loss')
ax2.set_ylabel('test accuracy')
ax2.set_title('Test Accuracy: {:.2f}'.format(test_acc[-1]))
综合
train_net_path = 'mnist/custom_auto_train.prototxt'
test_net_path = 'mnist/custom_auto_test.prototxt'
solver_config_path = 'mnist/custom_auto_solver.prototxt'
### define net
def custom_net(lmdb, batch_size):
# define your own net!
n = caffe.NetSpec()
# keep this data layer for all networks
n.data, n.label = L.Data(batch_size=batch_size, backend=P.Data.LMDB, source=lmdb,
transform_param=dict(scale=1./255), ntop=2)
# EDIT HERE to try different networks
# this single layer defines a simple linear classifier
# (in particular this defines a multiway logistic regression)
# n.score = L.InnerProduct(n.data, num_output=10, weight_filler=dict(type='xavier'))
# EDIT HERE this is the LeNet variant we have already tried
n.conv1 = L.Convolution(n.data, kernel_size=5, num_output=20, weight_filler=dict(type='xavier'))
n.pool1 = L.Pooling(n.conv1, kernel_size=2, stride=2, pool=P.Pooling.MAX)
n.conv2 = L.Convolution(n.pool1, kernel_size=5, num_output=50, weight_filler=dict(type='xavier'))
n.pool2 = L.Pooling(n.conv2, kernel_size=2, stride=2, pool=P.Pooling.MAX)
n.fc1 = L.InnerProduct(n.pool2, num_output=500, weight_filler=dict(type='xavier'))
# EDIT HERE consider L.ELU or L.Sigmoid for the nonlinearity
n.relu1 = L.ReLU(n.fc1, in_place=True)
n.score = L.InnerProduct(n.fc1, num_output=10, weight_filler=dict(type='xavier'))
# keep this loss layer for all networks
n.loss = L.SoftmaxWithLoss(n.score, n.label)
return n.to_proto()
with open(train_net_path, 'w') as f:
f.write(str(custom_net('mnist/mnist_train_lmdb', 64)))
with open(test_net_path, 'w') as f:
f.write(str(custom_net('mnist/mnist_test_lmdb', 100)))
### define solver
from caffe.proto import caffe_pb2
s = caffe_pb2.SolverParameter()
# Set a seed for reproducible experiments:
# this controls for randomization in training.
s.random_seed = 0xCAFFE
# Specify locations of the train and (maybe) test networks.
s.train_net = train_net_path
s.test_net.append(test_net_path)
s.test_interval = 500 # Test after every 500 training iterations.
s.test_iter.append(100) # Test on 100 batches each time we test.
s.max_iter = 10000 # no. of times to update the net (training iterations)
# EDIT HERE to try different solvers
# solver types include "SGD", "Adam", and "Nesterov" among others.
s.type = "SGD"
# Set the initial learning rate for SGD.
s.base_lr = 0.01 # EDIT HERE to try different learning rates
# Set momentum to accelerate learning by
# taking weighted average of current and previous updates.
s.momentum = 0.9
# Set weight decay to regularize and prevent overfitting
s.weight_decay = 5e-4
# Set `lr_policy` to define how the learning rate changes during training.
# This is the same policy as our default LeNet.
s.lr_policy = 'inv'
s.gamma = 0.0001
s.power = 0.75
# EDIT HERE to try the fixed rate (and compare with adaptive solvers)
# `fixed` is the simplest policy that keeps the learning rate constant.
# s.lr_policy = 'fixed'
# Display the current training loss and accuracy every 1000 iterations.
s.display = 1000
# Snapshots are files used to store networks we've trained.
# We'll snapshot every 5K iterations -- twice during training.
s.snapshot = 5000
s.snapshot_prefix = 'mnist/custom_net'
# Train on the GPU
s.solver_mode = caffe_pb2.SolverParameter.CPU
# Write the solver to a temporary file and return its filename.
with open(solver_config_path, 'w') as f:
f.write(str(s))
### load the solver and create train and test nets
solver = None # ignore this workaround for lmdb data (can't instantiate two solvers on the same data)
solver = caffe.get_solver(solver_config_path)
### solve
niter = 250 # EDIT HERE increase to train for longer
test_interval = niter / 10
# losses will also be stored in the log
train_loss = zeros(niter)
test_acc = zeros(int(np.ceil(niter / test_interval)))
# the main solver loop
for it in range(niter):
solver.step(1) # SGD by Caffe
# store the train loss
train_loss[it] = solver.net.blobs['loss'].data
# run a full test every so often
# (Caffe can also do this for us and write to a log, but we show here
# how to do it directly in Python, where more complicated things are easier.)
if it % test_interval == 0:
print 'Iteration', it, 'testing...'
correct = 0
for test_it in range(100):
solver.test_nets[0].forward()
correct += sum(solver.test_nets[0].blobs['score'].data.argmax(1)
== solver.test_nets[0].blobs['label'].data)
test_acc[it // test_interval] = correct / 1e4
_, ax1 = subplots()
ax2 = ax1.twinx()
ax1.plot(arange(niter), train_loss)
ax2.plot(test_interval * arange(len(test_acc)), test_acc, 'r')
ax1.set_xlabel('iteration')
ax1.set_ylabel('train loss')
ax2.set_ylabel('test accuracy')
ax2.set_title('Custom Test Accuracy: {:.2f}'.format(test_acc[-1]))
Iteration 0 testing...
Iteration 25 testing...
Iteration 50 testing...
Iteration 75 testing...
Iteration 100 testing...
Iteration 125 testing...
Iteration 150 testing...
Iteration 175 testing...
Iteration 200 testing...
Iteration 225 testing...
参考
caffe(https://github.com/BVLC/caffe/tree/master/examples/mnist)
![]()