Hadoop之MapReduce自定义二次排序流程实例详解
一、概述
MapReduce框架对处理结果的输出会根据key值进行默认的排序,这个默认排序可以满足一部分需求,但是也是十分有限的。在我们实际的需求当中,往往有要对reduce输出结果进行二次排序的需求。对于二次排序的实现,网络上已经有很多人分享过了,但是对二次排序的实现的原理以及整个MapReduce框架的处理流程的分析还是有非常大的出入,而且部分分析是没有经过验证的。本文将通过一个实际的MapReduce二次排序例子,讲述二次排序的实现和其MapReduce的整个处理流程,并且通过结果和map、reduce端的日志来验证所描述的处理流程的正确性。
二、需求描述
1、输入数据:
sort1 1
sort2 3
sort2 77
sort2 54
sort1 2
sort6 22
sort6 221
sort6 20
2、目标输出
sort1 1,2
sort2 3,54,77
sort6 20,22,221
三、解决思路
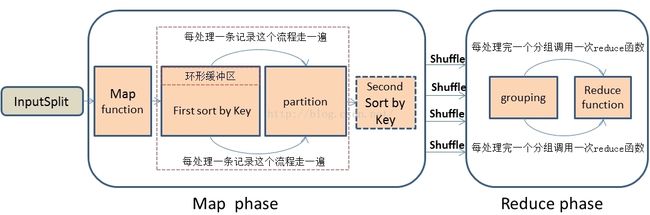
1、首先,在思考解决问题思路时,我们先应该深刻的理解MapReduce处理数据的整个流程,这是最基础的,不然的话是不可能找到解决问题的思路的。我描述一下MapReduce处理数据的大概简单流程:首先,MapReduce框架通过getSplit方法实现对原始文件的切片之后,每一个切片对应着一个map task,inputSplit输入到Map函数进行处理,中间结果经过环形缓冲区的排序,然后分区、自定义二次排序(如果有的话)和合并,再通过shuffle操作将数据传输到reduce task端,reduce端也存在着缓冲区,数据也会在缓冲区和磁盘中进行合并排序等操作,然后对数据按照Key值进行分组,然后没处理完一个分组之后就会去调用一次reduce函数,最终输出结果。大概流程我画了一下,如下图:
2、具体解决思路
(1)Map端处理:
根据上面的需求,我们有一个非常明确的目标就是要对第一列相同的记录合并,并且对合并后的数字进行排序。我们都知道MapReduce框架不管是默认排序或者是自定义排序都只是对Key值进行排序,现在的情况是这些数据不是key值,怎么办?其实我们可以将原始数据的Key值和其对应的数据组合成一个新的Key值,然后新的Key值对应的还是之前的数字。那么我们就可以将原始数据的map输出变成类似下面的数据结构:
{[sort1,1],1}
{[sort2,3],3}
{[sort2,77],77}
{[sort2,54],54}
{[sort1,2],2}
{[sort6,22],22}
{[sort6,221],221}
{[sort6,20],20}
那么我们只需要对[]里面的新key值进行排序就ok了。然后我们需要自定义一个分区处理器,因为我的目标不是想将新key相同的传到同一个reduce中,而是想将新key中的第一个字段相同的才放到同一个reduce中进行分组合并,所以我们需要根据新key值中的第一个字段来自定义一个分区处理器。通过分区操作后,得到的数据流如下:
Partition1:{[sort2,3],3}、{[sort2,54],54}、{[sort2,77],77}
Partition2:{[sort1,1],1}、{[sort1,2],2}
Partition3:{[sort6,20],20}、{[sort6,22],22}、{[sort6,221],221}
第一次排序:
这里的过程就是第一次排序的过程,第一次排序先按FirstKey排序,然后按照secondKey排序。
job.setSortComparatorClass(DefinedComparator.class);
分区:
job.setPartitionerClass(DefinedPartition.class);
(2)Reduce端处理:
分区操作完成之后,我调用自己的自定义排序器对新的Key值进行排序。
{[sort1,1],1}
{[sort1,2],2}
{[sort2,3],3}
{[sort2,54],54}
{[sort2,77],77}
{[sort6,20],20}
{[sort6,22],22}
{[sort6,221],221}
第二次排序:
是对组的排序,这里的这个GroupingComparator就是对key进行了第二次的处理,使得每个key后边可以挂一个val的列表。
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(SecondComparator.class);
经过Shuffle处理之后,数据传输到Reducer端了。在Reducer端对按照组合键的第一个字段来进行分组,并且每处理完一次分组之后就会调用一次reduce函数来对这个分组进行处理输出。最终的各个分组的数据结构变成类似下面的数据结构:
{sort1,[1,2]}
{sort2,[3,54,77]}
{sort6,[20,22,221]}
四、具体实现
1、自定义组合键package com.mr;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.Hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
/**
* 自定义组合键
* @author zenghzhaozheng
*/
public class CombinationKey implements WritableComparable{
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CombinationKey.class);
private Text firstKey;
private IntWritable secondKey;
public CombinationKey() {
this.firstKey = new Text();
this.secondKey = new IntWritable();
}
public Text getFirstKey() {
return this.firstKey;
}
public void setFirstKey(Text firstKey) {
this.firstKey = firstKey;
}
public IntWritable getSecondKey() {
return this.secondKey;
}
public void setSecondKey(IntWritable secondKey) {
this.secondKey = secondKey;
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput dateInput) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
this.firstKey.readFields(dateInput);
this.secondKey.readFields(dateInput);
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput outPut) throws IOException {
this.firstKey.write(outPut);
this.secondKey.write(outPut);
}
/**
* 自定义比较策略
* 注意:该比较策略用于mapreduce的第一次默认排序,也就是发生在map阶段的sort小阶段,
* 发生地点为环形缓冲区(可以通过io.sort.mb进行大小调整)
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(CombinationKey combinationKey) {
logger.info("-------CombinationKey flag-------");
return this.firstKey.compareTo(combinationKey.getFirstKey());
}
} 由于后面的进行了CombinationKey 对象的相等比较操作,最好重写hashCode()和equal()方法。
参考代码如下:主要是让类中个每个成员变量都参与计算和比较
public static class IntPair
implements WritableComparable {
private int first = 0;
private int second = 0;
/**
* Set the left and right values.
*/
public void set(int left, int right) {
first = left;
second = right;
}
public int getFirst() {
return first;
}
public int getSecond() {
return second;
}
/**
* Read the two integers.
* Encoded as: MIN_VALUE -> 0, 0 -> -MIN_VALUE, MAX_VALUE-> -1
*/
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
first = in.readInt() + Integer.MIN_VALUE;
second = in.readInt() + Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeInt(first - Integer.MIN_VALUE);
out.writeInt(second - Integer.MIN_VALUE);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {//重写hashCode()方法
return first * 157 + second;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object right) {//重写equals()方法
if (right instanceof IntPair) {
IntPair r = (IntPair) right;
return r.first == first && r.second == second;
} else {
return false;
}
}
@Override
public int compareTo(IntPair o) {
if (first != o.first) {
return first < o.first ? -1 : 1;
} else if (second != o.second) {
return second < o.second ? -1 : 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
} 2、自定义分区器
package com.mr;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
/**
* 自定义分区
* @author zengzhaozheng
*/
public class DefinedPartition extends Partitioner{
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DefinedPartition.class);
/**
* 数据输入来源:map输出
* @author zengzhaozheng
* @param key map输出键值
* @param value map输出value值
* @param numPartitions 分区总数,即reduce task个数
*/
@Override
public int getPartition(CombinationKey key, IntWritable value,int numPartitions) {
logger.info("--------enter DefinedPartition flag--------");
/**
* 注意:这里采用默认的hash分区实现方法
* 根据组合键的第一个值作为分区
* 这里需要说明一下,如果不自定义分区的话,mapreduce框架会根据默认的hash分区方法,
* 将整个组合将相等的分到一个分区中,这样的话显然不是我们要的效果
*/
logger.info("--------out DefinedPartition flag--------");
return (key.getFirstKey().hashCode()&Integer.MAX_VALUE)%numPartitions; //字符串的分区写法
}
} 数字的分区写法,可参考如下代码:
/**
* Partition based on the first part of the pair.
*
* 根据第一部分,分区
*
*/
public static class FirstPartitioner extends Partitioner{
@Override
public int getPartition(IntPair key, IntWritable value,
int numPartitions) {
return Math.abs(key.getFirst() * 127) % numPartitions;//数值型key分区写法
}
} 说明:具体说明看代码注释。
3、自定义比较器
package com.mr;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
/**
* 自定义二次排序策略
* @author zengzhaoheng
*/
public class DefinedComparator extends WritableComparator {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DefinedComparator.class);
public DefinedComparator() {
super(CombinationKey.class,true);
}
@Override
public int compare(WritableComparable combinationKeyOne,
WritableComparable CombinationKeyOther) {
logger.info("---------enter DefinedComparator flag---------");
CombinationKey c1 = (CombinationKey) combinationKeyOne;
CombinationKey c2 = (CombinationKey) CombinationKeyOther;
/**
* 确保进行排序的数据在同一个区内,如果不在同一个区则按照组合键中第一个键排序
* 另外,这个判断是可以调整最终输出的组合键第一个值的排序
* 下面这种比较对第一个字段的排序是升序的,如果想降序这将c1和c2颠倒过来(假设1)
*/
if(!c1.getFirstKey().equals(c2.getFirstKey())){
logger.info("---------out DefinedComparator flag---------");
return c1.getFirstKey().compareTo(c2.getFirstKey());
}
else{//按照组合键的第二个键的升序排序,将c1和c2倒过来则是按照数字的降序排序(假设2)
logger.info("---------out DefinedComparator flag---------");
return c1.getSecondKey().get()-c2.getSecondKey().get();//0,负数,正数
}
/**
* (1)按照上面的这种实现最终的二次排序结果为:
* sort1 1,2
* sort2 3,54,77
* sort6 20,22,221
* (2)如果实现假设1,则最终的二次排序结果为:
* sort6 20,22,221
* sort2 3,54,77
* sort1 1,2
* (3)如果实现假设2,则最终的二次排序结果为:
* sort1 2,1
* sort2 77,54,3
* sort6 221,22,20
*/
}
}4.具体的mapreduce代码
/**
* 二次排序demo
* @author hadoop
*
*/
public class SecondSort extends Configured implements Tool{
public static class Map extends Mapper{
private Text firstKey = new Text();
private IntWritable secondKey = new IntWritable(0);
public void map(LongWritable key,Text value,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException{
String line = value.toString();
StringTokenizer tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(line);
while(tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()){
firstKey.set(tokenizer.nextToken());
if(tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()){//如果还存在下一个记录
String num=tokenizer.nextToken();//获得
int scoreInt=Integer.parseInt(num);//将字符串转为数字
secondKey.set(scoreInt);
CombinationKey ckey = new CombinationKey();
ckey.setFirstKey(firstKey);
ckey.setSecondKey(secondKey);
context.write(ckey, new IntWritable(scoreInt));
}
}
}
}
public static class Reduce extends Reducer{
private final Text first = new Text();
public void reduce(CombinationKey key,Iterable values,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException{
for (IntWritable val : values) {
context.write( key.getFirstKey(), val);
}
}
}
@Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
String[] otherArgs = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args).getRemainingArgs();
if (otherArgs.length != 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: secondarysort ");
System.exit(2);
}
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "SecondSort");
job.setJarByClass(SecondSort.class);
job.setJobName("SecondSort");
job.setMapperClass(Map.class);
job.setReducerClass(Reduce.class);
//指定map输出时key值的排序,如果不指定,默认使用key对象CombinationKey的比较方法compareTo()
job.setSortComparatorClass(DefinedComparator.class);
job.setPartitionerClass(DefinedPartition.class);//分区
//指定分组排序使用的比较器,默认使用key对象自身的compareTo()方法
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(SecondComparator.class);
//map输出
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(CombinationKey.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
//reduce输出
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
job.setNumReduceTasks(1);//设置reduce Task的数量,默认是1
boolean success = job.waitForCompletion(true);
return success ?0 : 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
String[] ars=new String[]{"hdfs://192.168.137.100:9000/user/root/data/secondSort","hdfs://192.168.137.100:9000/user/root/output/secondSort"};
int ret = ToolRunner.run(new SecondSort(), ars);
System.exit(ret);
}
}