在一个ViewGroup中添加子view
所有的Android中的控件都是继承于View,ViewGroup也不例外。在ViewGroup中有个addView的方法能动态的添加一个子view。
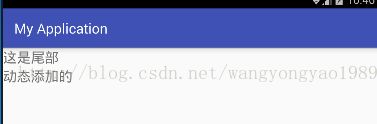
这个是一个简单的例子,能在代码中动态的添加一个子view:
示例图片:
package com.example.foreveross.myapplication;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView;
import android.view.Gravity;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private LinearLayout mLay;
private Button mBtn1;
private Button mBtn2;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initView();
initData();
initEvent();
}
private void initEvent() {
mBtn1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
mBtn2.setBackgroundColor(Color.RED);
}
});
}
private void initData() {
TextView tv = new TextView(this);
tv.setText("动态添加的");
tv.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER);
tv.setTextSize(20);
LinearLayout.LayoutParams layoutParams = new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(LinearLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LinearLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
mLay.addView(tv, layoutParams);
}
private void initView() {
mLay = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.llay);
mBtn1 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn1);
mBtn2 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn2);
}
}
1.关于ViewGroup的源码也翻看了一些:
关于addView有下面几种方法重载:
1.直接传入一个view进行添加:
public void addView(View child) {
addView(child, -1);
} public void addView(View child, int index) {
if (child == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot add a null child view to a ViewGroup");
}
LayoutParams params = child.getLayoutParams(); //获取子view的layout参数
if (params == null) {
params = generateDefaultLayoutParams();
if (params == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("generateDefaultLayoutParams() cannot return null");
}
}
addView(child, index, params);
}public void addView(View child, int width, int height) {
final LayoutParams params = generateDefaultLayoutParams();
params.width = width;
params.height = height;
addView(child, -1, params);
}
public void addView(View child, LayoutParams params) {
addView(child, -1, params);
}
public void addView(View child, int index, LayoutParams params) {
if (DBG) {
System.out.println(this + " addView");
}
if (child == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot add a null child view to a ViewGroup");
}
// addViewInner() will call child.requestLayout() when setting the new LayoutParams
// therefore, we call requestLayout() on ourselves before, so that the child's request
// will be blocked at our level
requestLayout(); //当view的布局失效改变时会调用这个,它会按规则重新布局view的树(view tree)
invalidate(true);
addViewInner(child, index, params, false); //call子view
}所以当加入子view时必须设置LayoutParams的值,对于LayoutParams只是传入子view的宽高和位置的信息:
public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs); //传入xml文件中设置的属性值,存于R文件中
public LayoutParams(int width, int height); //直接传入宽高的值
public LayoutParams(LayoutParams source) //传宽高的source值
protected void setBaseAttributes(TypedArray a, int widthAttr, int heightAttr); //布局setLayoutDimension之后的宽高值 在这里有一个MarginLayoutParams是继承于LayoutParams的,能在这里设置Margin的值总结与感悟:
之前开发过程中不习惯于去查看源码,对一些API都只是存在只会用不知道其中的原理
及当中的流程执行过程。当自己真正的静下心来去看源码的过程中无形之中汲取了源码
中优秀精简的程序设计精华,不积跬步无以至千里。相信当量的积累到一定程度那必然
是质的飞越!!!