我的Android开发之旅(三):ConstraintLayout的浅入
我的Android开发之旅(三):ConstraintLayout的浅入
- 1. 介绍
- 2. 如何使用ConstraintLayout
- 2.1 添加依赖
- 2.2 相对定位
- 2.3 边距(Margin)
- 2.4 居中和偏移
- 2.4.1 居中
- 2.4.2 偏移
- 2.5 角度定位
- 2.6 尺寸限制
- 2.6.1 ConstraintLayout的最小和最大尺寸
- 2.6.2 尺寸约束
- 2.7 链
- 2.7.1 链头
- 2.7.2 样式
- 2.8 辅助工具
- 2.8.1 GuideLine
- 2.8.2 Barrier
- 2.8.3 Group
- 2.8.4 Placeholder
- 2.8.5 Optimizer
- 3. 总结
1. 介绍
ConstraintLayout(约束布局)是在2016年 Google I/O大会所发布的一个新的布局。它能够兼容 API 9 以上的设备,它的出现是为了解决布局嵌套过多,从而降低运行性能。而使用ConstraintLayout就可以减少布局的层级结构(像我在还没有学会ConstraintLayout时,复杂的界面我一般都是用LinearLayout和RelativeLayout多层嵌套来实现的,带来了很多问题,比如:不容易阅读代码、消耗设备性能使得程序运行不那么流畅) ,相比 RelativeLayout ,更加的灵活、容易使用,配合 Android Studio 的布局编辑器,可以做到像 Visual Studio 开发 C# 的窗体应用程序一样拖拽控件来实现界面效果。
2. 如何使用ConstraintLayout
2.1 添加依赖
如果你的AndroidStudio的版本是2.3以后的版本,那么在新建项目的时候就已经给你默默的添加依赖了,如果你的版本是2.3之前或是旧项目,那么在你的app文件夹下的 build.gradle 文件中添加以下依赖即可使用:
implementation 'androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:1.1.3'
2.2 相对定位
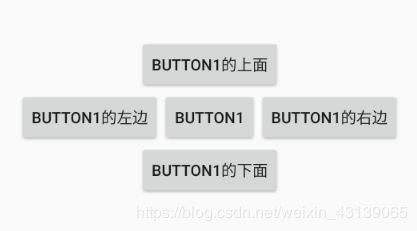
ConstraintLayout 的相对定位其实和 RelativeLayout 差不多,都是当前 View 相对于另外一个 View 的位置。这里用梅花布局来举个例子:
button1的周围4个控件都是相对于button1的上下左右,而它的代码也是和 RelativeLayout 相似,代码如下:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
...>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnCenter"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button1"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button1的上面"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@id/btnCenter"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="@id/btnCenter"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="@id/btnCenter" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button1的左边"
app:layout_constraintBaseline_toBaselineOf="@id/btnCenter"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@id/btnCenter" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button1的右边"
app:layout_constraintBaseline_toBaselineOf="@id/btnCenter"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@id/btnCenter" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button1的下面"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="@id/btnCenter"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="@id/btnCenter"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/btnCenter" />
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
上面的例子中 app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" 是表示当前View的下面相对于 parent(父布局)的下面。
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="@id/btnCenter" 是表示当前View的起始处(左边)相对于 btnCenter 的起始处(左边)。
app:layout_constraintBaseline_toBaselineOf="@id/btnCenter"是表示当前View的文本基线相对于 btnCenter 的文本基线。
其它的代码也是上述同理。
这里我们除了通过代码的方式实现效果,也可以拖拽控件实现效果,通过选中控件,拖拽View的4个约束点,约束于paren或是view的4个约束点实现:
ConstraintLayout常用的相对定位属性如下:
| 属性 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf | 当前View的左边相对另一个View的左边 |
| layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf | 当前View的左边相对另一个View的右边 |
| layout_constraintRight_toLeftOf | 当前View的右边相对另一个View的左边 |
| layout_constraintRight_toRightOf | 当前View的右边相对另一个View的右边 |
| layout_constraintTop_toTopOf | 当前View的上边相对另一个View的上边 |
| layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf | 当前View的上边相对另一个View的下边 |
| layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf | 当前View的下边相对另一个View的上边 |
| layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf | 当前View的下边相对另一个View的下边 |
| layout_constraintStart_toEndOf | 当前View的开始处相对另一个View的结束处 |
| layout_constraintStart_toStartOf | 当前View的开始处相对另一个View的开始处 |
| layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf | 当前View的结束处相对另一个View的开始处 |
| layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf | 当前View的结束处相对另一个View的结束处 |
| layout_constraintBaseline_toBaselineOf | 当前View的文本基线相对另一个View的文本基线 |
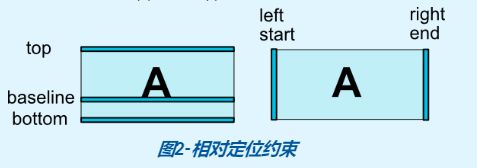
官方文档中的图片就很好的解释了这些位置在哪里:
2.3 边距(Margin)
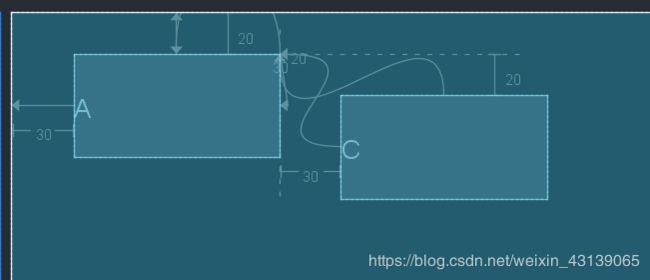
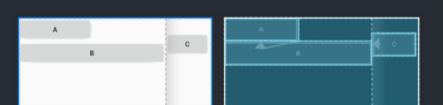
这里的外边距和我们平时用到外边距类似,都是当前的View距离约束的View有多远。不过需要注意的是必须先约束该控件在ConstraintLayout里的相对定位否则将不生效。使用外边距的属性还是和平时一样使用layout_margin进行设置,这里举个例子让:
代码如下:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout ...>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tvA"
...
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tvB"
...
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@id/tvA"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="@id/tvA" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tvC"
...
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@id/tvB"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="@id/tvB" />
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
那如果B的 visibility 属性设置为 Gone 呢?C还是会在原来的位置吗?接下来我们试一下看看:
可以看到C跑到刚刚B的位置去了,为什么会这样呢?我们可以通过AndroidStudio的布局编辑器中的蓝图可以看到B设置为Gone后,它的宽、高和margin都失效了,变为一个点了,但它的约束还生效,位于指定的位置,所以C依旧能相对于B的位置做变化。
那假如项目有要求,让B短暂的消失,但C还保持刚才的位置怎么办呢?有三种解决方案:
-
可以使用Invisible
-
不依赖会Gone的view
-
官方提供了以下属性:
属性 作用 layout_goneMarginStart 当依赖的View为Gone时,才会启用 layout_goneMarginEnd 同上 layout_goneMarginLeft 同上 layout_goneMarginTop 同上 layout_goneMarginRight 同上 layout_goneMarginBottom 同上
2.4 居中和偏移
2.4.1 居中
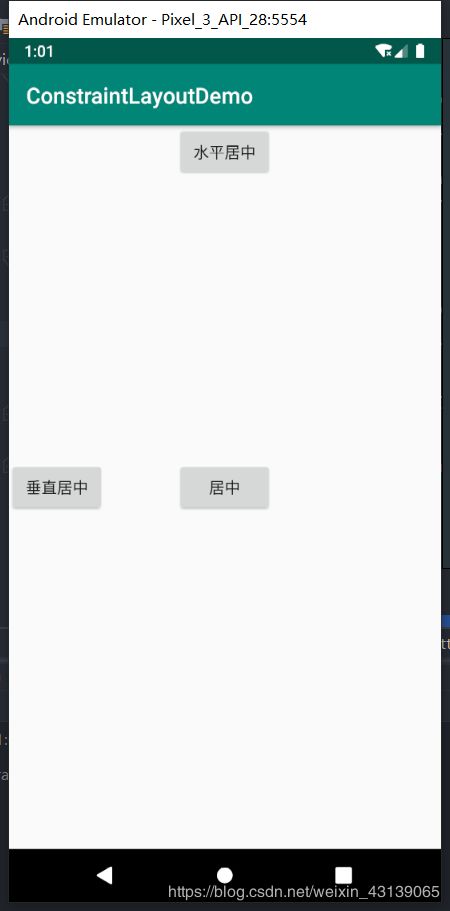
前面我说 ConstraintLayout 和 RelativeLayout 很像,那是不是也有像 layout_centerVertical 一样的属性呢? 如何居中呢?ConstraintLayout 居中的方式有所不同,它是通过相对定位的属性来实现的,具体代码如下:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout ...>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="居中"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="水平居中"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="垂直居中"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
怎么理解这样的写法呢?其实你可以把**约束(Constraint)**理解为一个力,app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"和app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"就是两个力在互相拉扯View,左边和右边的力道相同,那View就居中了。
2.4.2 偏移
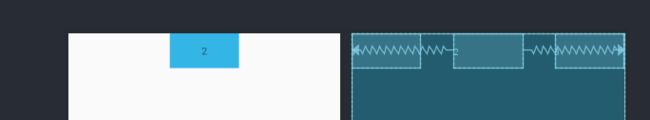
前面我们通过Margin属性来对View进行偏移设置,可如果我们现在想让水平居中的View向左偏移,位于1/3处呢?那么你第一反应可能会想到用layout_marginLeft进行偏移,但是这样就有个问题,数值需要进行计算,这不又给我们开发者增加了工作量?这一点官方也想到了,所以提供了以下属性:
| xml属性 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| layout_constraintHorizontal_bias | 水平偏移(取值范围0~1,0在左边,1在右边) |
| layout_constraintVertical_bias | 垂直偏移水平偏移(取值范围0~1,0在左边,1在右边) |
那如果要让View处于在水平方向的1/3处,可以通过layout_constraintHorizontal_bias属性设置为0.3就能实现效果:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout ...>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="水平偏移"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.3"/>
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
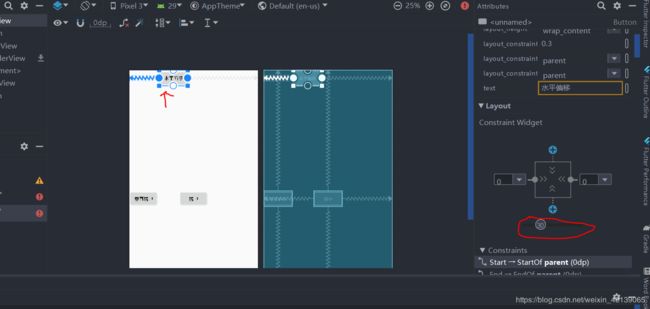
除了用代码方式实现,我们也可以使用AndroidStudio提供的布局编辑器,选中我们要偏移的View,会出现以下样式:
通过拖动小圆球进行偏移,垂直偏移也是同上。
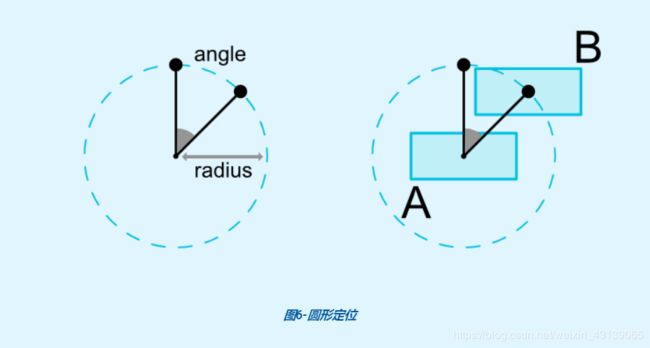
2.5 角度定位
从名字就可以知道是相对于另一个View的中心以一定角度和距离约束一个View的中心。
它有3个属性,如下:
| xml属性 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| layout_constraintCircle | 要约束的View,值是控件的id |
| layout_constraintCircleRadius | 距离约束的View的半径 |
| layout_constraintCircleAngle | 角度(以度为单位,0~360,顺时针方向) |
比如我让B在A的120°方向,距离150dp,效果如下:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout ...>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
... />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
...
app:layout_constraintCircle="@id/button1"
app:layout_constraintCircleRadius="150dp"
app:layout_constraintCircleAngle="120"/>
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
2.6 尺寸限制
2.6.1 ConstraintLayout的最小和最大尺寸
我们可以对ConstraintLayout自身定义最小和最大尺寸,属性如下:
| 属性 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| android:minWidth | 设置布局的最小宽度 |
| android:minHeight | 设置布局的最小高度 |
| android:maxWidth | 设置布局的最大宽度 |
| android:maxHeight | 设置布局的最大高度 |
注意:必须在宽或高为wrap_content时,才可以使用这些属性来控制最大和最小。当ConstraintLayout为1.1版本以下时,需要用这两个属性强制生效:
app:layout_constrainedWidth=”true|false”和app:layout_constrainedHeight=”true|false”。
2.6.2 尺寸约束
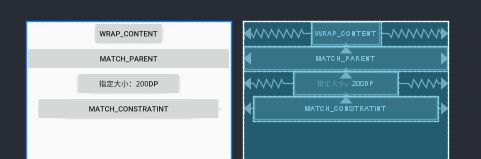
设置View的大小除了以往我们常用的wrap_content、match_parent(官方不推荐使用)和指定尺寸(即130dp等)之外,还新增了一个match_constraint属性用来代替match_parent,match_constraint将按照与设置的约束匹配的方式来调整自身的大小,如果设置了边距,那么在绘制的过程中也会生效。如何使用match_constraint呢?设置为0dp即可。效果如下:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout ...>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="match_parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/button1" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="指定大小:200dp"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/button2" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button4"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="match_constratint"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/button3"
android:layout_marginHorizontal="20dp"/>
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
当尺寸设置为MATCH_CONSTRAINT(即odp)时,0dp在ConstraintLayout可不是指大小是0dp,而是有特殊含义的。他的作用会随着属性app:layout_constraintWidth_default或app:layout_constraintHeight_default不同的设置有不同的含义:
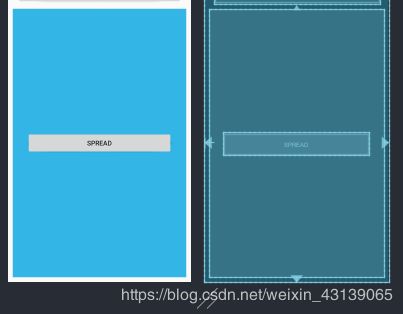
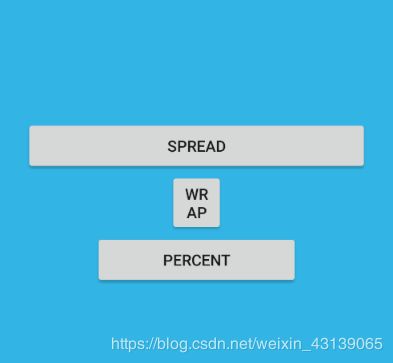
- spread:尽可能扩展视图以满足每侧的约束条件。这是默认行为。
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout ...>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button5"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="spread"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintWidth_default="spread"
android:layout_marginHorizontal="30dp"/>
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
- wrap:仅在需要时扩展视图以适应其内容,但如有约束条件限制,视图仍然可以小于其内容。因此,它与使用 wrap_content之间的区别在于,将宽度设为wrap_content会强行使宽度始终与内容宽度完全匹配;而使用
app:layout_constraintWidth_default设置为wrap时,视图可以小于内容宽度。
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout ...>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button5"
.../>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button6"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="wrap"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/button5"
app:layout_constraintWidth_default="wrap"
app:layout_constraintWidth_max="50dp"/>
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
| 属性 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| layout_constraintWidth_min | 设置最小宽度 |
| layout_constraintHeight_min | 设置最小高度 |
| layout_constraintWidth_max | 设置最大宽度 |
| layout_constraintHeight_max | 设置最大高度 |
- percent:根据父布局的大小,按照百分比设置,例如percent宽度占父布局的50%,效果如下:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout ...>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button5"
... />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button6"
... />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button7"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="percent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/button6"
app:layout_constraintWidth_default="percent"
app:layout_constraintWidth_percent="0.5"/>androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
| 属性 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| layout_constraintWidth_percent | 宽度百分比(数值范围0~1,例如30%即0.3) |
| layout_constraintHeight_percent | 高度百分比 |
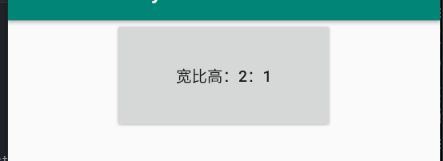
除了上述所讲到的属性,还有一种宽高比属性,可将宽度按照高度一定的比例显示或是高度按照宽度一定的比例显示。但前提条件是至少有一个高度或宽度设置为0dp(match_constraint),然后通过app:layout_constraintDimensionRatio属性设置比例,它的值可以是一个小数(例如:4:3,即1.3),也可以是宽度:高度的形式。效果如下:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout ...>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:text="宽比高:2:1"
app:layout_constraintDimensionRatio="2:1"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" />
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
那假如宽度和高度都设为0dp了怎么办?那么在app:layout_constraintDimensionRatio的值前面添加W,或H,来表示,注意用 , 分割。效果如下:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout ...>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:text="宽比高:16:9"
app:layout_constraintDimensionRatio="h,16:9"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" />
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
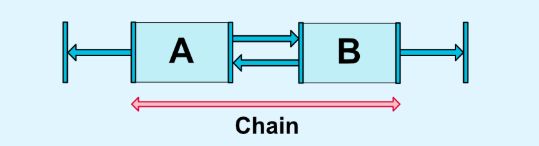
2.7 链
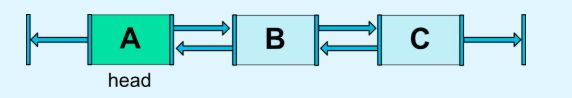
链,我们最先想到的就是链条,环环相扣。而这里也是类似的,如果两个或两个以上的控件水平方向或垂直方向相互约束,我们可以认为它们在一条链上。
2.7.1 链头
链的第一个元素称为链头(水平方向的最左侧,垂直方向的最顶部)。
2.7.2 样式
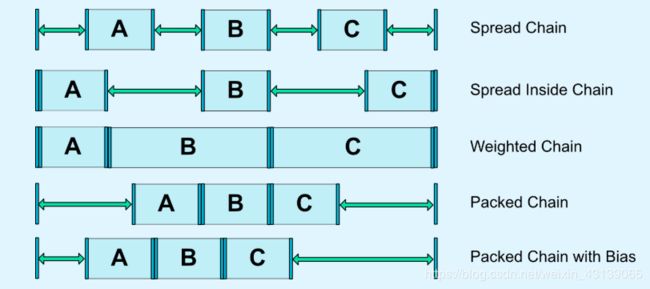
官方给我们提供了5种样式,通过layout_constraintHorizontal_chainStyle或layout_constraintVertical_chainStyle属性在链头设置即可:
- Spread Chain:展开视图,即
spread默认属性,将可用的空间以均匀分布的方式展开View,它在宽度或高度非0dp的情况下生效,效果如下:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout...>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="A"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@id/button2"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_chainStyle="spread"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="B"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@id/button3"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@id/button1" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="C"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@id/button4"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@id/button2" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="D"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@id/button3" />
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
- Spread Inside Chain:内部展开,即
spread_inside,将链中最左边和最右边的视图对齐边缘。它在ChainStyle为spread_inside和视图的宽度或高度非0dp时生效,效果如下:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout ...>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button5"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="A"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/button6"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_chainStyle="spread_inside"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button6"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="B"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/button7"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/button5"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button7"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="C"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/button6" />androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
- Weighted Chain:权重链,和我们平常用的weight是一个意思,它在ChainStyle为spread和视图的高度或宽度为0dp时生效,效果如下:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout ...>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button8"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="A"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_weight="1"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@id/button9"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button9"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="B"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_weight="2"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@id/button8"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@id/button10"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button10"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="B"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_weight="3"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@id/button9"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"/>
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
- Packed Chain:即
packed,将链中的视图紧紧的挨在一起。它在ChainStyle为packed和视图的宽度或高度为0dp时生效,效果如下:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout ...>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button11"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="A"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/button12"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_chainStyle="packed"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button12"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="B"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/button13"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/button11"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button13"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="C"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/button12" />
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
- Packed Chain with Bias:在Packed的基础上增加了一个偏移属性,用法也是和packed一致的,效果如下:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout ...>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button14"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="A"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/button15"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_chainStyle="packed"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.3"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button15"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="B"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/button16"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/button14" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button16"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="C"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/button15" />
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
2.8 辅助工具
除了官方提供的ConstraintLayout自身的属性之外,还提供了一些特殊工具辅助我们进行布局。
2.8.1 GuideLine
即引导线的意思,有水平参考线和竖直参考线两种。这些线不会显示到界面上,但是能够利用这些线条来添加约束去完成界面的布局。GuideLine常用的属性如下:
| 属性 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| android:orientation | 表示是水平或垂直方向的引导线 |
| layout_constraintGuide_begin | 距离左边或顶部一个固定距离 |
| layout_constraintGuide_end | 距离右边或底部一个固定距离 |
| layout_constraintGuide_percent | 水平或垂直方向的一个百分比距离 |
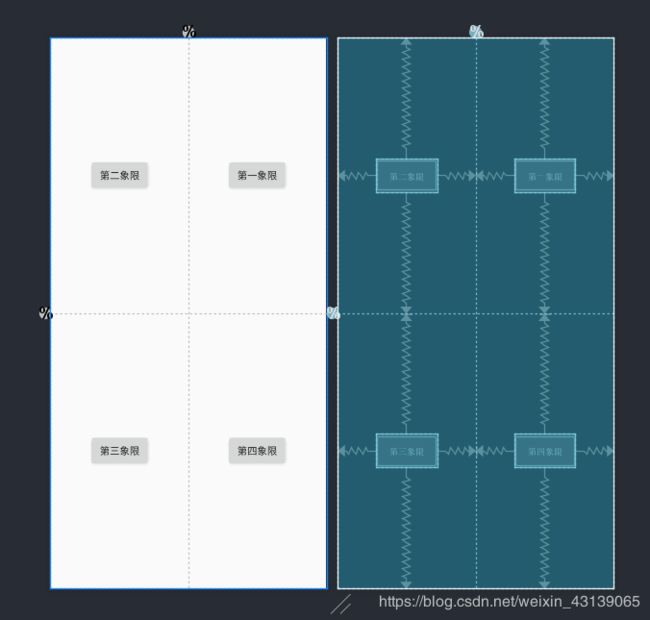
接下来我们举个例子,我想把布局分为4个象限,每个象限中的Button都处于中间位置。效果如下:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout ...>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.Guideline
android:id="@+id/guideline_horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
app:layout_constraintGuide_percent="0.5" />
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.Guideline
android:id="@+id/guideline_vertical"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
app:layout_constraintGuide_percent="0.5" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="第一象限"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@+id/guideline_horizontal"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="@id/guideline_vertical"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="第二象限"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@+id/guideline_horizontal"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/guideline_vertical"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="第三象限"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/guideline_vertical"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="@+id/guideline_horizontal" />
<Button
android:text="第四象限"
.../>
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
注意:GuideLine的绝大多数属性都是不会生效的,而它的位置确定是由
layout_constraintGuide_begin、layout_constraintGuide_end和layout_constraintGuide_percent三个其中一个决定的。
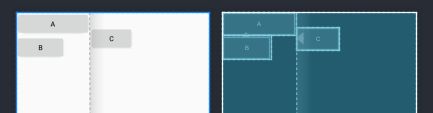
2.8.2 Barrier
界线,类似于GuideLine,当依赖的视图大小有所变化时,Barrier也有可能跟着变化。效果如下:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout ...>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="A" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="B"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/button1" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="C"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/barrier"
tools:layout_editor_absoluteY="30dp" />
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.Barrier
android:id="@+id/barrier"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:barrierDirection="right"
app:constraint_referenced_ids="button1,button2" />
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
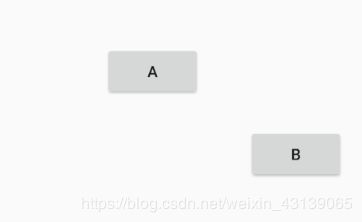
当B的宽度变得比A还要宽时,C就会随B的变化而移动位置
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout ...>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="150dp"
.../>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="200dp"
... />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
.../>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.Barrier
android:id="@+id/barrier"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:barrierDirection="right"
app:constraint_referenced_ids="button1,button2" />
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
Barrier的属性:
| 属性 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| barrierDirection | 控制哪个方向的View |
| constraint_referenced_ids | 依赖的控件,会将最大宽度或高度最大的那个一个作为自己的位置 |
2.8.3 Group
即组的意思,类似于RadioGroup。可以把多个视图归为一组,方便隐藏或显示一组视图,它的效果如下:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout ...>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.Group
android:id="@+id/group"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:visibility="invisible"
app:constraint_referenced_ids="textView1,textView3"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
.../>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView2"
.../>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView3"
.../>
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
注意:
- 优先级:group的优先级高于view,如果group的visibility属性设置了invisible,那么view的visibility属性将不生效。xml文件中排在最下面的group的优先级高于前面的group。
- group只可以引用当前ConstraintLayout下的view,子布局下的view不可以。
2.8.4 Placeholder
占位符,通过占位符,让view移动到占位符处。而它的使用方法也非常简单,将app:content属性设置一个id,此时view就会移动过去。
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout ...>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.Placeholder
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:content="@id/button"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
2.8.5 Optimizer
优化器,这是在1.1版本新增的一个功能,用于优化布局的约束,从而提高布局速度。只需要在ConstraintLayout标签中添加app:layout_optimizationLevel属性即可。app:layout_optimizationLevel有6个属性,如下:
- none:不优化
- standard:默认形式,会优化direct和barrier这两种类型的约束。
- direct :优化direct约束
- barrier:优化barrier约束
- chain:优化链约束(实验性)
- dimensions:尺寸优化,减少测量次数(实验性)
3. 总结
曾经我是非常的喜欢用LinearLayout和RelativeLayout组合在一起疯狂的无下限的嵌套,感觉能没有什么布局是做不到的,可是再快的AE86也追不上坐在奔驰上的夏树,LinearLayout和RelativeLayout就好比AE86,而ConstraintLayout就好比奔驰,用了你就会发现夏树坐在奔驰上也不是没有道理的!如果你觉得我的这篇文章不错的话就给我点个赞吧!
参考:
官方文档
ConstraintLayout在项目中实践与总结
ConstraintLayout 用法全解析
带你了解 Android 约束布局 ConstraintLayout
约束布局ConstraintLayout看这一篇就够了
ConstraintLayout学起来!
ConstraintLayout 全解析
Android ConstraintLayout 构建自适应界面
ConstraintLayout,看完一篇真的就够了么?