MySQL之复合查询(多表查询,单行、多行、多列子查询)
复合查询
1.基本查询回顾
- 查询工资高于500或岗位为MANAGER的雇员,同时还要满足他们的姓名首字母为大写的J
select sal,job,ename from EMP where (sal>500 or job='MANAGER') and ename like 'J%';
- 按照部门号升序而雇员的工资降序排序
select ename deptno,sal from EMP order by deptno asc,sal desc;
- 使用年薪进行降序排序
--年薪total=sal*12+comm
select ename,sal*12+ifnull(comm,0) as total
from EMP
order by total desc;
- 显示工资最高的员工的姓名和工作岗位
select ename,job
from EMP
where sal=(select max(sal) from EMP);
- 显示工资高于平均工资的员工信息
select * from EMP
where sal>(select avg(sal)from EMP);
- 显示每个部门的平均工资和最高工资
select deptno,avg(sal),max(sal)
from EMP
group by deptno;
- 显示平均工资低于2000的部门号和它的平均工资
select deptno,avg(sal)
from EMP
group by deptno
having avg(sal)<2000;
- 显示每种岗位的雇员总数,平均工资
select job,count(*),avg(sal)
from EMP
group by job;
2.多表查询
笛卡尔积:从第一张表中选出第一条记录,和第二张表中的所有记录进行组合;然后从第一张表中取出第二条记录,和第二张表中所有记录进行组合,以此类推得到的结果成为笛卡尔积
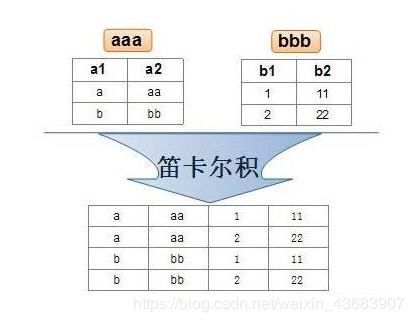
- 显示雇员名,雇员工资以及所在部门的名称,因为这些数据来自EMP和DEPT表,因此要联合查询
select emp.ename,emp.sal,dept.dname
from emp,dept
where emp.deptno=dept.deptno;
--通过deptno 将两张表关联起来
- 显示部门号为10的部门名,员工名和工资
select emp.ename,emp.sal,dept.deptno,dept.dname
from emp,dept
where emp.deptno=dept.deptno and dept.deptno=10;
- 显示各个员工的姓名,工资,及工资级别
select e.ename,e.sal,s.grade
from emp e,salgrade s--给两张表分别起了别名
where e.sal between s.losal and s.hisal;
3.自连接
自连接是指在同一张表连接查询
案例:显示员工FORD的上级领导的编号和姓名(mgr是员工领导的编号-empno)
- 使用子查询:
mysql> select empno,ename from emp
-> where emp.empno=(
-> select mgr from emp where ename='FORD');
+--------+-------+
| empno | ename |
+--------+-------+
| 007566 | JONES |
+--------+-------+
- 使用多表查询(自连接)
mysql> select leader.empno,leader.ename
->from emp leader, emp worker
->where leader.empno = worker.mgr
->and worker.ename='FORD';
+--------+-------+
| empno | ename |
+--------+-------+
| 007566 | JONES |
+--------+-------+
4.子查询
子查询是指嵌入在其他sql语句中的select语句,也叫嵌套查询
4.1单行子查询(返回一行记录)
- 显示SMITH同一部门的员工
select * from EMP where deptno =(select deptno from EMP where ename='SMITH');
4.2多行子查询(返回多行记录)
- in关键字:查询和10号部门的工作相同的雇员的名字,岗位,工资,部门号,但是不包含10自己的
select ename,job,sal,empno from emp
where job in(select distinct job from emp where deptno=10)
and deptno<>10;
- all关键字:显示工资比部门30的所有员工的工资高的员工的姓名、工资和部门号
select ename, sal, deptno from EMP
where sal > all(select sal from EMP where deptno=30);
- any关键字:显示工资比部门30的任意员工的工资高的员工的姓名、工资和部门号
select ename, sal, deptno from EMP
where sal > any(select sal from EMP where deptno=30);
4.3多列子查询
多列子查询是指查询返回多个列数据的子查询语句
- 查询SMITH的部门和岗位完全相同的所有雇员,不含SMITH本人
select ename from emp
where (deptno,job)=(select deptno,job from emp where
ename='SMITH') and ename<>"SMITH';
4.4在from子句中使用子查询
子查询语句出现在from子句中,把一个子查询当做一个临时表使用
- 显示高于自己部门平均工资的员工的姓名、部门、工资、平均工资
select ename, deptno, sal, format(asal,2) from EMP,
(select avg(sal) asal, deptno dt from EMP group by deptno) tmp
where EMP.sal > tmp.asal and EMP.deptno=tmp.dt;
- 查找每个部门工资最高的人的姓名、工资、部门、最高工资
select EMP.ename, EMP.sal, EMP.deptno, ms from EMP,
(select max(sal) ms, deptno from EMP group by deptno) tmp
where EMP.deptno=tmp.deptno and EMP.sal=tmp.ms;
- 显示每个部门的信息(部门名,编号,地址)和人员数量
--方法1:多表查询
select DEPT.dname, DEPT.deptno, DEPT.loc,count(*) '部门人数' from EMP, DEPT
where EMP.deptno=DEPT.deptno
group by DEPT.deptno,DEPT.dname,DEPT.loc;
--方法2:使用子查询
-- 1. 对EMP表进行人员统计
select count(*), deptno from EMP group by deptno;
-- 2. 将上面的表看作临时表
select DEPT.deptno, dname, mycnt, loc from DEPT,
(select count(*) mycnt, deptno from EMP group by deptno) tmp
where DEPT.deptno=tmp.deptno;