【目标追踪】三帧差法原理及实现
三帧差法原理及实现
- (一)帧差法原理及实现:
- (二)帧差法存在的问题:
- (三)三帧差法的原理:
- (四)三帧差法的实现代码:
- (五)视频中的目标追踪效果:
(一)帧差法原理及实现:
这里可以看一下我的这篇博客,这里就不赘述了:【目标追踪】python帧差法原理及其实现
(二)帧差法存在的问题:
运动物体本身颜色相近时,会出现较大的空洞。
位置变化缓慢时,难以检测到目标。
对光线非常敏感。
(三)三帧差法的原理:
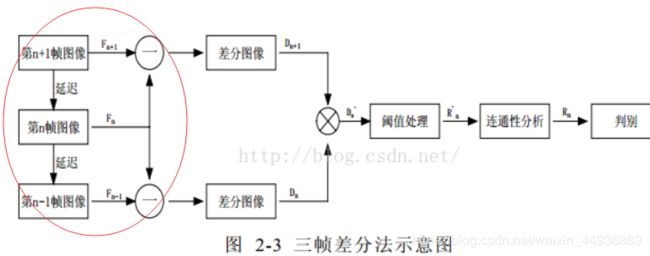
三帧差法的关键是,不再仅仅采用相邻的两帧图片作差查找运动目标,而是在相邻三帧图片的两张帧差图中取“与”操作,即:
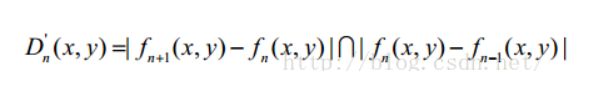
(四)三帧差法的实现代码:
(具体处理和代码解析还是推荐看一下我的上一篇博客:【目标追踪】python帧差法原理及其实现)
代码:
import cv2
import numpy as np
from nms import py_cpu_nms
from time import sleep
class Detector(object):
def __init__(self, name='my_video', frame_num=10, k_size=7, color=(0, 255, 0)):
self.name = name
self.color = color
self.nms_threshold = 0.3
self.time = 1/frame_num # 频率
self.es = cv2.getStructuringElement(
cv2.MORPH_ELLIPSE, (k_size, k_size))
def catch_video(self, video_index=0, k_size=7,
iterations=3, threshold=20, bias_num=1,
min_area=360, show_test=True, nms=True,
logical='or'):
# video_index:摄像头索引(数字)或者视频路径(字符路径)
# k_size:中值滤波的滤波器大小
# iteration:腐蚀+膨胀的次数,0表示不进行腐蚀和膨胀操作
# threshold:二值化阙值
# bias_num:计算帧差图时的帧数差
# min_area:目标的最小面积
# show_test:是否显示二值化图片
# nms:是否进行非极大值抑制
# logical:三帧差取or或and
logical = logical.lower()
if not bias_num > 0:
raise Exception('bias_num must > 0')
if isinstance(video_index, str):
is_camera = False
# 如果是视频,则需要调整帧率
else:
is_camera = True
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(video_index) # 创建摄像头识别类
if not cap.isOpened():
# 如果没有检测到摄像头,报错
raise Exception('Check if the camera is on.')
frame_num = 0
previous = []
while cap.isOpened():
catch, frame = cap.read() # 读取每一帧图片
if not catch:
raise Exception('Unexpected Error.')
if frame_num < bias_num:
value = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
previous = [value]*bias_num
frame_num += 1
raw = frame.copy()
gray1 = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
gray1 = cv2.absdiff(gray1, previous[0])
gray1 = cv2.medianBlur(gray1, k_size)
_, mask1 = cv2.threshold(
gray1, threshold, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
gray2 = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
gray2 = cv2.absdiff(gray2, previous[1])
gray2 = cv2.medianBlur(gray2, k_size)
_, mask2 = cv2.threshold(
gray2, threshold, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
if logical == 'or':
mask = (np.logical_or(mask1, mask2) + 0)
elif logical == 'and':
mask = (np.logical_and(mask1, mask2) + 0)
else:
raise Exception('Logical must be \'OR\' or \'AND\'')
mask = (mask * 255).astype(np.uint8)
mask = cv2.dilate(mask, self.es, iterations)
mask = cv2.erode(mask, self.es, iterations)
_, cnts, _ = cv2.findContours(
mask.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
bounds = self.nms_cnts(cnts, mask, min_area, nms=nms)
for b in bounds:
x, y, w, h = b
thickness = (w*h)//min_area
thickness = thickness if thickness <= 3 else 3
thickness = thickness if thickness >= 1 else 1
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (x+w, y+h), self.color, thickness)
if not is_camera:
sleep(self.time)
cv2.imshow(self.name, frame) # 在window上显示图片
if show_test:
cv2.imshow(self.name+'_frame', mask) # 边界
value = cv2.cvtColor(raw, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
previous = self.pop(previous, value)
cv2.waitKey(10)
if cv2.getWindowProperty(self.name, cv2.WND_PROP_AUTOSIZE) < 1:
# 点x退出
break
if show_test and cv2.getWindowProperty(self.name+'_frame', cv2.WND_PROP_AUTOSIZE) < 1:
# 点x退出
break
# 释放摄像头
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
def nms_cnts(self, cnts, mask, min_area, nms=True):
# 对检测到的边界框使用非极大值抑制
bounds = [cv2.boundingRect(
c) for c in cnts if cv2.contourArea(c) > min_area]
if len(bounds) == 0:
return []
if not nms:
return bounds
scores = [self.calculate(b, mask) for b in bounds]
bounds = np.array(bounds)
scores = np.expand_dims(np.array(scores), axis=-1)
keep = py_cpu_nms(np.hstack([bounds, scores]), self.nms_threshold)
return bounds[keep]
def calculate(self, bound, mask):
x, y, w, h = bound
area = mask[y:y+h, x:x+w]
pos = area > 0
pos = pos.astype(np.float)
# 得分应与检测框大小也有关系
score = np.sum(pos)/(w*h)
return score
def pop(self, l, value):
l.pop(0)
l.append(value)
return l
if __name__ == "__main__":
detector = Detector(name='test')
detector.catch_video('./test.avi', bias_num=2, iterations=1,
k_size=5, show_test=True, min_area=360, nms=False)