JVM G1 源码分析(五)- 新生代回收YGC
1. 简介
G1的YGC仅针对标记为新生代的Region进行回收,因此YGC花费的时间较少。
正如之前章节所介绍的,一个Region属于老年代还是新生代时动态的,每次YGC都会回收全部新生代Region,并在之后的内存分配流程中重新分配Region给新生代。
2. 代码分析
2.1 YGC的流程
YGC的流程如下:
- 首先STW,YGC全过程都在STW时进行,不需要考虑并发场景
- 选择CSet(Collection Set),YGC中CSet即为全部新生代Region
- 根扫描
- 更新RSet
- 深度复制更新对象到Survivor Region
- 重构RSet
- 释放CSet
- 大对象回收
- 动态扩展内存
- 动态调整新生代Region数量
- 启动并发标记,判断是否需要紧接着进行一次混合式GC
2.2 具体步骤介绍
2.2.1 根扫描
void work(uint worker_id) {
{
ResourceMark rm;
HandleMark hm;
ReferenceProcessor* rp = _g1h->ref_processor_stw();
G1ParScanThreadState* pss = _pss->state_for_worker(worker_id);
pss->set_ref_discoverer(rp);
double start_strong_roots_sec = os::elapsedTime();
_root_processor->evacuate_roots(pss, worker_id);
// We pass a weak code blobs closure to the remembered set scanning because we want to avoid
// treating the nmethods visited to act as roots for concurrent marking.
// We only want to make sure that the oops in the nmethods are adjusted with regard to the
// objects copied by the current evacuation.
_g1h->g1_rem_set()->oops_into_collection_set_do(pss, worker_id);
double strong_roots_sec = os::elapsedTime() - start_strong_roots_sec;
double term_sec = 0.0;
size_t evac_term_attempts = 0;
{
double start = os::elapsedTime();
G1ParEvacuateFollowersClosure evac(_g1h, pss, _queues, _terminator.terminator(), G1GCPhaseTimes::ObjCopy);
evac.do_void();
}
}
};
GC并行任务包括跟扫描、更新RSet、对象复制,主要逻辑在g1CollectedHeap.cpp G1ParTask类的work方法中;evacuate_roots为根扫描。
g1RootProcessor.cpp的evacuate_roots主要逻辑如下
void G1RootProcessor::evacuate_roots(G1ParScanThreadState* pss, uint worker_i) {
process_java_roots(closures, phase_times, worker_i);
process_vm_roots(closures, phase_times, worker_i);
process_string_table_roots(closures, phase_times, worker_i);
}
- 处理java根
- 处理jvm根
- 处理string table根
process_java_roots
void G1RootProcessor::process_java_roots(G1RootClosures* closures,
G1GCPhaseTimes* phase_times,
uint worker_i) {
// Iterating over the CLDG and the Threads are done early to allow us to
// first process the strong CLDs and nmethods and then, after a barrier,
// let the thread process the weak CLDs and nmethods.
{
G1GCParPhaseTimesTracker x(phase_times, G1GCPhaseTimes::CLDGRoots, worker_i);
if (_process_strong_tasks.try_claim_task(G1RP_PS_ClassLoaderDataGraph_oops_do)) {
ClassLoaderDataGraph::roots_cld_do(closures->strong_clds(), closures->weak_clds());
}
}
{
G1GCParPhaseTimesTracker x(phase_times, G1GCPhaseTimes::ThreadRoots, worker_i);
bool is_par = n_workers() > 1;
Threads::possibly_parallel_oops_do(is_par,
closures->strong_oops(),
closures->strong_codeblobs());
}
}
- 处理所有已加载类的元数据
- 处理所有Java线程当前栈帧的引用和虚拟机内部线程
process_vm_roots
void G1RootProcessor::process_vm_roots(G1RootClosures* closures,
G1GCPhaseTimes* phase_times,
uint worker_i) {
OopClosure* strong_roots = closures->strong_oops();
{
G1GCParPhaseTimesTracker x(phase_times, G1GCPhaseTimes::UniverseRoots, worker_i);
if (_process_strong_tasks.try_claim_task(G1RP_PS_Universe_oops_do)) {
Universe::oops_do(strong_roots);
}
}
{
G1GCParPhaseTimesTracker x(phase_times, G1GCPhaseTimes::JNIRoots, worker_i);
if (_process_strong_tasks.try_claim_task(G1RP_PS_JNIHandles_oops_do)) {
JNIHandles::oops_do(strong_roots);
}
}
{
G1GCParPhaseTimesTracker x(phase_times, G1GCPhaseTimes::ObjectSynchronizerRoots, worker_i);
if (_process_strong_tasks.try_claim_task(G1RP_PS_ObjectSynchronizer_oops_do)) {
ObjectSynchronizer::oops_do(strong_roots);
}
}
{
G1GCParPhaseTimesTracker x(phase_times, G1GCPhaseTimes::ManagementRoots, worker_i);
if (_process_strong_tasks.try_claim_task(G1RP_PS_Management_oops_do)) {
Management::oops_do(strong_roots);
}
}
{
G1GCParPhaseTimesTracker x(phase_times, G1GCPhaseTimes::JVMTIRoots, worker_i);
if (_process_strong_tasks.try_claim_task(G1RP_PS_jvmti_oops_do)) {
JvmtiExport::oops_do(strong_roots);
}
}
#if INCLUDE_AOT
if (UseAOT) {
G1GCParPhaseTimesTracker x(phase_times, G1GCPhaseTimes::AOTCodeRoots, worker_i);
if (_process_strong_tasks.try_claim_task(G1RP_PS_aot_oops_do)) {
AOTLoader::oops_do(strong_roots);
}
}
#endif
{
G1GCParPhaseTimesTracker x(phase_times, G1GCPhaseTimes::SystemDictionaryRoots, worker_i);
if (_process_strong_tasks.try_claim_task(G1RP_PS_SystemDictionary_oops_do)) {
SystemDictionary::oops_do(strong_roots);
}
}
}
- 处理JVM内部使用的引用(Universe和SystemDictionary)
- 处理JNI句柄
- 处理对象锁的引用
- 处理java.lang.management管理和监控相关类的引用
- 处理JVMTI(JVM Tool Interface)的引用
- 处理AOT静态编译的引用
process_string_table_roots
void G1RootProcessor::process_string_table_roots(G1RootClosures* closures,
G1GCPhaseTimes* phase_times,
uint worker_i) {
assert(closures->weak_oops() != NULL, "Should only be called when all roots are processed");
G1GCParPhaseTimesTracker x(phase_times, G1GCPhaseTimes::StringTableRoots, worker_i);
// All threads execute the following. A specific chunk of buckets
// from the StringTable are the individual tasks.
StringTable::possibly_parallel_oops_do(&_par_state_string, closures->weak_oops());
}
- 处理StringTable JVM字符串哈希表的引用
2.2.2 对象复制
g1OopClosures.inline.hpp
void G1ParCopyClosure::do_oop_work(T* p) {
T heap_oop = RawAccess<>::oop_load(p);
if (CompressedOops::is_null(heap_oop)) {
return;
}
oop obj = CompressedOops::decode_not_null(heap_oop);
assert(_worker_id == _par_scan_state->worker_id(), "sanity");
const InCSetState state = _g1h->in_cset_state(obj);
if (state.is_in_cset()) {
oop forwardee;
markOop m = obj->mark_raw();
if (m->is_marked()) {
forwardee = (oop) m->decode_pointer();
} else {
forwardee = _par_scan_state->copy_to_survivor_space(state, obj, m);
}
assert(forwardee != NULL, "forwardee should not be NULL");
RawAccess::oop_store(p, forwardee);
if (barrier == G1BarrierCLD) {
do_cld_barrier(forwardee);
}
} else {
if (state.is_humongous()) {
_g1h->set_humongous_is_live(obj);
} else if (state.is_optional()) {
_par_scan_state->remember_root_into_optional_region(p);
}
// The object is not in collection set. If we're a root scanning
// closure during an initial mark pause then attempt to mark the object.
if (do_mark_object == G1MarkFromRoot) {
mark_object(obj);
}
}
trim_queue_partially();
}
- 判断对象是否在CSet中,如是则判断对象是否已经copy过了
- 如果已经copy过,则直接找到新对象
- 如果没有copy过,则调用copy_to_survivor_space函数copy对象到survivor区
- 修改老对象的对象头,指向新对象地址,并将锁标志位置为11
copy_to_survivor_space在g1ParScanThreadState.cpp中
oop G1ParScanThreadState::copy_to_survivor_space(InCSetState const state,
oop const old,
markOop const old_mark) {
const size_t word_sz = old->size();
HeapRegion* const from_region = _g1h->heap_region_containing(old);
// +1 to make the -1 indexes valid...
const int young_index = from_region->young_index_in_cset()+1;
assert( (from_region->is_young() && young_index > 0) ||
(!from_region->is_young() && young_index == 0), "invariant" );
uint age = 0;
InCSetState dest_state = next_state(state, old_mark, age);
// The second clause is to prevent premature evacuation failure in case there
// is still space in survivor, but old gen is full.
if (_old_gen_is_full && dest_state.is_old()) {
return handle_evacuation_failure_par(old, old_mark);
}
HeapWord* obj_ptr = _plab_allocator->plab_allocate(dest_state, word_sz);
// PLAB allocations should succeed most of the time, so we'll
// normally check against NULL once and that's it.
if (obj_ptr == NULL) {
bool plab_refill_failed = false;
obj_ptr = _plab_allocator->allocate_direct_or_new_plab(dest_state, word_sz, &plab_refill_failed);
if (obj_ptr == NULL) {
obj_ptr = allocate_in_next_plab(state, &dest_state, word_sz, plab_refill_failed);
if (obj_ptr == NULL) {
// This will either forward-to-self, or detect that someone else has
// installed a forwarding pointer.
return handle_evacuation_failure_par(old, old_mark);
}
}
if (_g1h->_gc_tracer_stw->should_report_promotion_events()) {
// The events are checked individually as part of the actual commit
report_promotion_event(dest_state, old, word_sz, age, obj_ptr);
}
}
assert(obj_ptr != NULL, "when we get here, allocation should have succeeded");
assert(_g1h->is_in_reserved(obj_ptr), "Allocated memory should be in the heap");
#ifndef PRODUCT
// Should this evacuation fail?
if (_g1h->evacuation_should_fail()) {
// Doing this after all the allocation attempts also tests the
// undo_allocation() method too.
_plab_allocator->undo_allocation(dest_state, obj_ptr, word_sz);
return handle_evacuation_failure_par(old, old_mark);
}
#endif // !PRODUCT
// We're going to allocate linearly, so might as well prefetch ahead.
Prefetch::write(obj_ptr, PrefetchCopyIntervalInBytes);
const oop obj = oop(obj_ptr);
const oop forward_ptr = old->forward_to_atomic(obj, old_mark, memory_order_relaxed);
if (forward_ptr == NULL) {
Copy::aligned_disjoint_words((HeapWord*) old, obj_ptr, word_sz);
if (dest_state.is_young()) {
if (age < markOopDesc::max_age) {
age++;
}
if (old_mark->has_displaced_mark_helper()) {
// In this case, we have to install the mark word first,
// otherwise obj looks to be forwarded (the old mark word,
// which contains the forward pointer, was copied)
obj->set_mark_raw(old_mark);
markOop new_mark = old_mark->displaced_mark_helper()->set_age(age);
old_mark->set_displaced_mark_helper(new_mark);
} else {
obj->set_mark_raw(old_mark->set_age(age));
}
_age_table.add(age, word_sz);
} else {
obj->set_mark_raw(old_mark);
}
if (G1StringDedup::is_enabled()) {
const bool is_from_young = state.is_young();
const bool is_to_young = dest_state.is_young();
assert(is_from_young == _g1h->heap_region_containing(old)->is_young(),
"sanity");
assert(is_to_young == _g1h->heap_region_containing(obj)->is_young(),
"sanity");
G1StringDedup::enqueue_from_evacuation(is_from_young,
is_to_young,
_worker_id,
obj);
}
_surviving_young_words[young_index] += word_sz;
if (obj->is_objArray() && arrayOop(obj)->length() >= ParGCArrayScanChunk) {
// We keep track of the next start index in the length field of
// the to-space object. The actual length can be found in the
// length field of the from-space object.
arrayOop(obj)->set_length(0);
oop* old_p = set_partial_array_mask(old);
do_oop_partial_array(old_p);
} else {
G1ScanInYoungSetter x(&_scanner, dest_state.is_young());
obj->oop_iterate_backwards(&_scanner);
}
return obj;
} else {
_plab_allocator->undo_allocation(dest_state, obj_ptr, word_sz);
return forward_ptr;
}
}
- 根据age判断copy到新生代还是老年代
- 先尝试在PLAB中分配对象
- PLAB分配失败后的逻辑与TLAB类似,先申请一个新的PLAB,在旧PLAB中填充dummy对象,在新PLAB中分配,如果还是失败,则在新生代Region中直接分配
- 如果还是失败,则尝试在老年代Region中重新分配
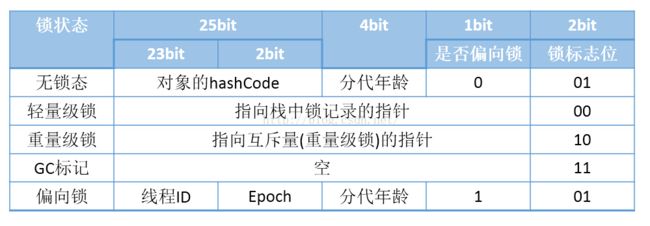
- age加1,由于锁升级机制,当对象锁状态是轻量级锁或重量级锁时,对象头被修改为指向栈锁记录的指针或者互斥量的指针,修改age需要特殊处理
- 对于字符串去重的处理
- 如果是数组,且数组长度超过ParGCArrayScanChunk(默认50)时,将对象放入队列而不是深度搜索栈中,防止搜索时溢出
2.2.3 深度搜索复制
G1ParTask的work函数调用evac.do_void()进行对象复制
void G1ParEvacuateFollowersClosure::do_void() {
EventGCPhaseParallel event;
G1ParScanThreadState* const pss = par_scan_state();
pss->trim_queue();
event.commit(GCId::current(), pss->worker_id(), G1GCPhaseTimes::phase_name(_phase));
do {
EventGCPhaseParallel event;
pss->steal_and_trim_queue(queues());
event.commit(GCId::current(), pss->worker_id(), G1GCPhaseTimes::phase_name(_phase));
} while (!offer_termination());
}
- 并行线程处理完当前任务后,可以窃取其他线程没有处理完的对象
具体复制逻辑在trim_queue函数中
inline void G1ParScanThreadState::trim_queue_to_threshold(uint threshold) {
StarTask ref;
// Drain the overflow stack first, so other threads can potentially steal.
while (_refs->pop_overflow(ref)) {
if (!_refs->try_push_to_taskqueue(ref)) {
dispatch_reference(ref);
}
}
while (_refs->pop_local(ref, threshold)) {
dispatch_reference(ref);
}
}
inline void G1ParScanThreadState::deal_with_reference(oop* ref_to_scan) {
if (!has_partial_array_mask(ref_to_scan)) {
do_oop_evac(ref_to_scan);
} else {
do_oop_partial_array(ref_to_scan);
}
}
template void G1ParScanThreadState::do_oop_evac(T* p) {
// Reference should not be NULL here as such are never pushed to the task queue.
oop obj = RawAccess::oop_load(p);
// Although we never intentionally push references outside of the collection
// set, due to (benign) races in the claim mechanism during RSet scanning more
// than one thread might claim the same card. So the same card may be
// processed multiple times, and so we might get references into old gen here.
// So we need to redo this check.
const InCSetState in_cset_state = _g1h->in_cset_state(obj);
// References pushed onto the work stack should never point to a humongous region
// as they are not added to the collection set due to above precondition.
assert(!in_cset_state.is_humongous(),
"Obj " PTR_FORMAT " should not refer to humongous region %u from " PTR_FORMAT,
p2i(obj), _g1h->addr_to_region((HeapWord*)obj), p2i(p));
if (!in_cset_state.is_in_cset()) {
// In this case somebody else already did all the work.
return;
}
markOop m = obj->mark_raw();
if (m->is_marked()) {
obj = (oop) m->decode_pointer();
} else {
obj = copy_to_survivor_space(in_cset_state, obj, m);
}
RawAccess::oop_store(p, obj);
assert(obj != NULL, "Must be");
if (HeapRegion::is_in_same_region(p, obj)) {
return;
}
HeapRegion* from = _g1h->heap_region_containing(p);
if (!from->is_young()) {
enqueue_card_if_tracked(p, obj);
}
}
- 调用do_oop_evac复制一般对象,调用do_oop_partial_array处理大数组对象
- 如果对象已经复制,则无需再次复制
- 否则,调用copy_to_survivor_space复制对象
- 更新引用者field地址
- 如果引用者与当前对象不在同一个分区,且引用者不在新生代分区中,则更新RSet信息入队
3. 引用
jdk12源代码[https://hg.openjdk.java.net/jdk/jdk12]