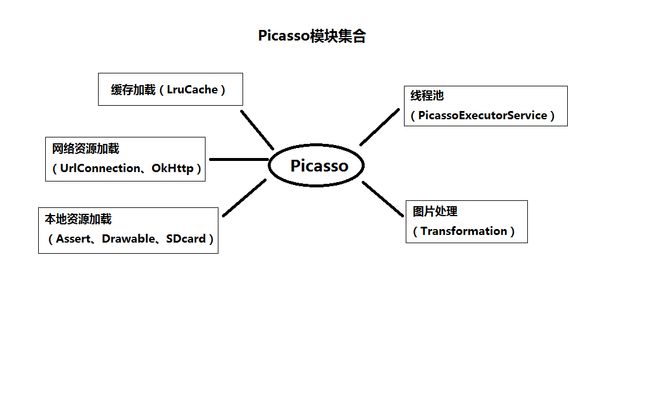
项目中之前一直是使用ImageLoader加载图片,使用起来比较繁琐,加载图片的速度也比较慢,而且这个框架没有人维护了,所以改用Picasso加载图片。(缓存)(解决主要的问题:加载大量图片导致的卡顿)(在宏观层面上,用图去表达会更好)
我们看一下它的调用方式:
Picasso.with(context)
.load(imageUrl)
.into(imageView);
很简单,设置imageView、地址 就可以从网络中加载一张图片展示到ImageView中了(大多数图片框架都可以通过一句代码实现图片获取和显示)。
接着看Picasso类的代码
/**
* Image downloading, transformation, and caching manager.
*
* Use {@link #with(android.content.Context)} for the global singleton instance or construct your
* own instance with {@link Builder}.
*/
public class Picasso {
}
开头讲明了Picasso的作用,Image downloading, transformation, and caching manager.
并提示我们使用单例调用或自己构建实例。
如: Picasso.with(context),这就是获取Picasso的单例对象。
public static Picasso with(Context context) {
if (singleton == null) {
synchronized (Picasso.class) {
if (singleton == null) {
singleton = new Builder(context).build();
}
}
}
return singleton;
}
接下来,我们分析主要的两个方法,load() 和into()。
Load():
public RequestCreator load(Uri uri) {
return new RequestCreator(this, uri, 0);
}
public RequestCreator load(String path) {}
public RequestCreator load(File file) {}
public RequestCreator load(int resourceId) {}
很明显支持加载不同路径图片。
主要看这个:new RequestCreator(this, uri, 0);
一个请求构建类。
RequestCreator(Picasso picasso, Uri uri, int resourceId) {
if (picasso.shutdown) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Picasso instance already shut down. Cannot submit new requests.");
}
this.picasso = picasso;
this.data = new Request.Builder(uri, resourceId, picasso.defaultBitmapConfig);
}
在Builder的构造函数中:将值传递进去了。
Builder(Uri uri, int resourceId, Bitmap.Config bitmapConfig) {
this.uri = uri;
this.resourceId = resourceId;
this.config = bitmapConfig;
}
Into():
/**
* Asynchronously fulfills the request into the specified {@link ImageView} and invokes the
* target {@link Callback} if it's not {@code null}.
*
* Note: The {@link Callback} param is a strong reference and will prevent your
* {@link android.app.Activity} or {@link android.app.Fragment} from being garbage collected. If
* you use this method, it is strongly recommended you invoke an adjacent
* {@link Picasso#cancelRequest(android.widget.ImageView)} call to prevent temporary leaking.
*/
public void into(ImageView target, Callback callback) {
long started = System.nanoTime();
checkMain();
if (target == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Target must not be null.");
}
if (!data.hasImage()) {//uri为null进入
picasso.cancelRequest(target);
if (setPlaceholder) {//为ImageView设置图片占位符
setPlaceholder(target, getPlaceholderDrawable());
}
return;
}
if (deferred) {//支持延迟到图片尺寸计算完成加载
if (data.hasSize()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Fit cannot be used with resize.");
}
int width = target.getWidth();
int height = target.getHeight();
if (width == 0 || height == 0) {
if (setPlaceholder) {
setPlaceholder(target, getPlaceholderDrawable());
}
picasso.defer(target, new DeferredRequestCreator(this, target, callback));
return;
}
data.resize(width, height);
}
Request request = createRequest(started);//构建请求
String requestKey = createKey(request);//使用requestKey可以从缓存中获取图片
if (shouldReadFromMemoryCache(memoryPolicy)) {//是否设置了缓存,这样可以先从缓存中读取。
Bitmap bitmap = picasso.quickMemoryCacheCheck(requestKey);
if (bitmap != null) {
picasso.cancelRequest(target);
setBitmap(target, picasso.context, bitmap, MEMORY, noFade, picasso.indicatorsEnabled);
if (picasso.loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_MAIN, VERB_COMPLETED, request.plainId(), "from " + MEMORY);
}
if (callback != null) {
callback.onSuccess();
}
return;
}
}
if (setPlaceholder) {
setPlaceholder(target, getPlaceholderDrawable());
}
//创建ImageViewAction
Action action =
new ImageViewAction(picasso, target, request, memoryPolicy, networkPolicy, errorResId,
errorDrawable, requestKey, tag, callback, noFade);
picasso.enqueueAndSubmit(action);
}
接着调用: picasso.enqueueAndSubmit(action);
void enqueueAndSubmit(Action action) {
Object target = action.getTarget();//在Map中每一个action的target不一样。
if (target != null && targetToAction.get(target) != action) {
// This will also check we are on the main thread.
cancelExistingRequest(target);
targetToAction.put(target, action);//键值对保存Action的信息。
}
submit(action);
}
//然后将保含图片信息的Action提交给dispatcher。
void submit(Action action) {
dispatcher.dispatchSubmit(action);
}
//构造函数
Dispatcher(Context context, ExecutorService service, Handler mainThreadHandler,
Downloader downloader, Cache cache, Stats stats) {}
void dispatchSubmit(Action action) {
handler.sendMessage(handler.obtainMessage(REQUEST_SUBMIT, action));
}
void dispatchCancel(Action action) {}
void dispatchPauseTag(Object tag) {}
void dispatchResumeTag(Object tag) {}
void dispatchComplete(BitmapHunter hunter) {}
void dispatchRetry(BitmapHunter hunter) {}
void dispatchFailed(BitmapHunter hunter) {}
void dispatchNetworkStateChange(NetworkInfo info) {}
void dispatchAirplaneModeChange(boolean airplaneMode) {}
void performSubmit(Action action, boolean dismissFailed) {}
void performCancel(Action action) {}
void performPauseTag(Object tag) {}
void performResumeTag(Object tag) {}
void performRetry(BitmapHunter hunter) {}
void performComplete(BitmapHunter hunter) {}
void performBatchComplete() {}
void performError(BitmapHunter hunter, boolean willReplay){}
Dispatcher 负责分发和处理 Action,包括提交、暂停、继续、取消、网络状态变化、重试等等。
需要注意的一点是: Dispatcher 中的static class NetworkBroadcastReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {}中注册了ACTION_AIRPLANE_MODE_CHANGED和CONNECTIVITY_ACTION两个广播,支持飞行模式、并发线程数根据网络类型而变
手机切换到飞行模式或网络类型变换时会自动调整线程池最大并发数。
接着DispatcherHandler 调用performSubmit。
void performSubmit(Action action, boolean dismissFailed) {
...
BitmapHunter hunter = (BitmapHunter)this.hunterMap.get(action.getKey());//一个Runnable
...
hunter = BitmapHunter.forRequest(action.getPicasso(), this, this.cache, this.stats, action);
hunter.future = this.service.submit(hunter);//将Runnable提交到service线程池中
...
}
将任务提交后,在Picasso类的Handler中获取到回调信息。
static final Handler HANDLER = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()) {
@Override public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case HUNTER_BATCH_COMPLETE: {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") List batch = (List) msg.obj;
//noinspection ForLoopReplaceableByForEach
for (int i = 0, n = batch.size(); i < n; i++) {
BitmapHunter hunter = batch.get(i);
hunter.picasso.complete(hunter);
}
break;
}
//然后
void complete(BitmapHunter hunter) {
if (single != null) {
deliverAction(result, from, single);
}
//然后
private void deliverAction(Bitmap result, LoadedFrom from, Action action) {
action.complete(result, from);
}
//在ImageAction中:
@Override public void complete(Bitmap result, Picasso.LoadedFrom from) {
ImageView target = this.target.get();
if (target == null) {
return;
}
Context context = picasso.context;
boolean indicatorsEnabled = picasso.indicatorsEnabled;
PicassoDrawable.setBitmap(target, context, result, from, noFade, indicatorsEnabled);//通过PicassoDrawable展示图片
Picasso加载图片流程:Picasso 收到加载及显示图片的任务,然后从MemoryCache中获取图片,如果没有缓存则创建 ImageViewAction并将它交给 Dispatcher,Dispatcher 分发任务到具体 Handler中,然后通过线程池执行BitmapHunter(Runnable)任务, 最后通过Handler(数据获取接口) 获取图片,最终回调到Picasso类中的handler中处理,图片获取成功后通过 PicassoDrawable 显示到 Target 中。