机器学习案例实战:交易数据异常检测
原创文章,如需转载请保留出处
本博客为唐宇迪老师python数据分析与机器学习实战课程学习笔记
一. 案例背景目标
1.1 背景
现给定一些信用卡相关数据,从中剔除异常数据
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
%matplotlib inline
data = pd.read_csv('creditcard.csv')
data.head()
data.shape
(284807, 31)
数据共284807行,31列
Time V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 V6 V7 V8 V9 ... V21 V22 V23 V24 V25 V26 V27 V28 Amount Class
0 0.0 -1.359807 -0.072781 2.536347 1.378155 -0.338321 0.462388 0.239599 0.098698 0.363787 ... -0.018307 0.277838 -0.110474 0.066928 0.128539 -0.189115 0.133558 -0.021053 149.62 0
1 0.0 1.191857 0.266151 0.166480 0.448154 0.060018 -0.082361 -0.078803 0.085102 -0.255425 ... -0.225775 -0.638672 0.101288 -0.339846 0.167170 0.125895 -0.008983 0.014724 2.69 0
2 1.0 -1.358354 -1.340163 1.773209 0.379780 -0.503198 1.800499 0.791461 0.247676 -1.514654 ... 0.247998 0.771679 0.909412 -0.689281 -0.327642 -0.139097 -0.055353 -0.059752 378.66 0
3 1.0 -0.966272 -0.185226 1.792993 -0.863291 -0.010309 1.247203 0.237609 0.377436 -1.387024 ... -0.108300 0.005274 -0.190321 -1.175575 0.647376 -0.221929 0.062723 0.061458 123.50 0
4 2.0 -1.158233 0.877737 1.548718 0.403034 -0.407193 0.095921 0.592941 -0.270533 0.817739 ... -0.009431 0.798278 -0.137458 0.141267 -0.206010 0.502292 0.219422 0.215153 69.99 0
5 rows × 31 columns
二.样本不均衡解决方案
2.1 统计数据
#分别统计0和1个数
count_classes = pd.value_counts(data['Class'],sort = True).sort_index()
print(count_classes)
#画图显示统计个数
count_classes.plot(kind='bar')
plt.title("Fraud class histogram")
plt.xlabel("Class")
plt.ylabel("Frequency")
0 284315(正常数据)
1 492(异常数据)
Name: Class, dtype: int64

2.2 两种采样策略
- 下采样:正常数据284315条,异常数据492条。从正常数据中取和异常数据一样多的数据。
- 过采样:正常数据284315条,异常数据492条。在异常数据生成和正常数据一样多的数据。
2.3 对数据预处理
#导入sklearn下预处理模块preprocessing
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
#fit_transform对数据进行变换操作(不仅计算训练数据的均值和方差,还会基于计算出来的均值和方差来转换训练数据,从而把数据转换成标准的正太分布)
data['normAmount'] = StandardScaler().fit_transform(data['Amount'].values.reshape(-1, 1))
data = data.drop(['Time','Amount'],axis=1)
data.head()
V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 V6 V7 V8 V9 V10 ... V21 V22 V23 V24 V25 V26 V27 V28 Class normAmount
0 -1.359807 -0.072781 2.536347 1.378155 -0.338321 0.462388 0.239599 0.098698 0.363787 0.090794 ... -0.018307 0.277838 -0.110474 0.066928 0.128539 -0.189115 0.133558 -0.021053 0 0.244964
1 1.191857 0.266151 0.166480 0.448154 0.060018 -0.082361 -0.078803 0.085102 -0.255425 -0.166974 ... -0.225775 -0.638672 0.101288 -0.339846 0.167170 0.125895 -0.008983 0.014724 0 -0.342475
2 -1.358354 -1.340163 1.773209 0.379780 -0.503198 1.800499 0.791461 0.247676 -1.514654 0.207643 ... 0.247998 0.771679 0.909412 -0.689281 -0.327642 -0.139097 -0.055353 -0.059752 0 1.160686
3 -0.966272 -0.185226 1.792993 -0.863291 -0.010309 1.247203 0.237609 0.377436 -1.387024 -0.054952 ... -0.108300 0.005274 -0.190321 -1.175575 0.647376 -0.221929 0.062723 0.061458 0 0.140534
4 -1.158233 0.877737 1.548718 0.403034 -0.407193 0.095921 0.592941 -0.270533 0.817739 0.753074 ... -0.009431 0.798278 -0.137458 0.141267 -0.206010 0.502292 0.219422 0.215153 0 -0.073403
5 rows × 30 columns
三.下采样策略
3.1 根据下采样策略生成样本
#找不包括Class列的数据
X = data.loc[:, data.columns != 'Class']
#找只包括Class列的数据
y = data.loc[:, data.columns == 'Class']
#让数据等于0的个数和等于1的个数一样少
#class等于1的个数
number_records_fraud = len(data[data.Class == 1])
#class等于1的索引
fraud_indices = np.array(data[data.Class == 1].index)
#class等于0的索引
normal_indices = data[data.Class == 0].index
#np.random.choice 随机选择
#参数:从正常索引里(normal_indices)选取异常的个数(number_records_fraud),replace表示是否可以重用元素,默认为False
random_normal_indices = np.random.choice(normal_indices, number_records_fraud, replace = False)
#转换成数组
random_normal_indices = np.array(random_normal_indices)
#合并两种索引
under_sample_indices = np.concatenate([fraud_indices,random_normal_indices])
#把只有索引值转换成data格式
under_sample_data = data.iloc[under_sample_indices,:]
#把under_sample_data分成两种格式
X_undersample = under_sample_data.loc[:, under_sample_data.columns != 'Class']
y_undersample = under_sample_data.loc[:, under_sample_data.columns == 'Class']
print("Percentage of normal transactions: ", len(under_sample_data[under_sample_data.Class == 0])/len(under_sample_data))
print("Percentage of fraud transactions: ", len(under_sample_data[under_sample_data.Class == 1])/len(under_sample_data))
print("Total number of transactions in resampled data: ", len(under_sample_data))
Percentage of normal transactions: 0.5
Percentage of fraud transactions: 0.5
Total number of transactions in resampled data: 984
四.交叉验证
4.1 交叉验证理解
- 拿到一组数据,选择其中80%当训练数据,建立模型。剩下20%当测试数据验证这个模型。
- 在训练集上平均切除三分,用这三分数据进行交叉验证:
- (1) 用一号和二号训练集建立模型,用三号训练集验证当前模型下的参数
- (2) 用一号和三号训练集建立模型,用二号训练集验证当前模型下的参数
- (3) 用二号和三号训练集建立模型,用一号训练集验证当前模型下的参数
为什么这么做?目的是为了求稳,让模型的评估效果是可信的,三个训练集都有评估的标准,让其平均值作为衡量模型效果
4.2 对数据切分
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
#对元素数据集切分
#test_size:切分比例,30%测试集,70%训练集
#random_state:先洗牌,再切分
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size = 0.3, random_state = 0)
print("Number transactions train dataset:", len(X_train))
print("Number transactions test dataset:", len(X_test))
print("Total number of transactions:", len(X_train)+len(X_test))
#对下采样数据集切分
X_train_undersample, X_test_undersample, y_train_undersample, y_test_undersample = train_test_split(X_undersample,y_undersample,test_size = 0.3,random_state = 0)
print("Number transactions train dataset:", len(X_train_undersample))
print("Number transactions test dataset:", len(X_test_undersample))
print("Total number of transactions:", len(X_train_undersample)+len(X_test_undersample))
Number transactions train dataset: 199364
Number transactions test dataset: 85443
Total number of transactions: 284807
Number transactions train dataset: 688
Number transactions test dataset: 296
Total number of transactions: 984
五.模型评估方法
5.1 召回率(Recall)
召回率是覆盖面的度量,度量有多个正例被分为正例
Recall = TP/(TP+FN)

5.2 举个例子
假设我们手上有60个正样本,40个负样本,我们要找出所有的正样本,系统查找出50个,其中只有40个是真正的正样本,计算上述各指标。
TP: 将正类预测为正类数 40
FN: 将正类预测为负类数 20(60-40个是真正的正样本)
FP: 将负类预测为正类数 10(50-40个是真正的正样本)
TN: 将负类预测为负类数 30(40个负样 -(50-40个是真正的正样本))
准确率(accuracy) = 预测对的/所有 = (TP+TN)/(TP+FN+FP+TN) = 70%
精确率(precision) = TP/(TP+FP) = 80%
召回率(recall) = TP/(TP+FN) = 2/3
六.正交化惩罚
逻辑回归中,其实有些参数需要指定。如正则化惩罚项
6.1 什么是正则化
假设求逻辑回归,A模型(θ1···θ10),B模型(θ1···θ10)。虽然A和B内θ都不一样,A模型θ浮动比较大,B模型θ浮动比较小,但Recall都是90%
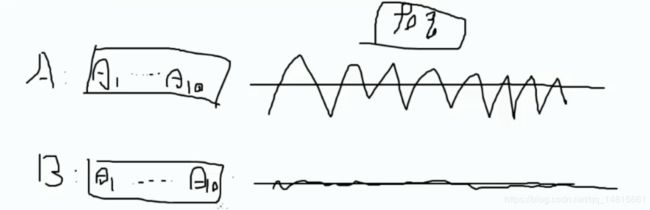
- 我们希望获取浮动较小的模型,因为浮动较小,过拟合的风险较小。(过拟合:模型在训练集上效果表现较好,在测试集上效果表现不好)
- 我们希望得到B模型,如何得到B模型呢?
引入正则化惩罚,希望能大力度的惩罚A模型,小力度的惩罚B模型
如:L2正则化
L2正则化:在目标函数(损失函数)加上1/2W²
即,loss+1/2W²
A模型的浮动大,则W²更大,B模型W²小,虽然两个模型Recall值是一样的,但通过计算loss+1/2W²,比较哪个模型效果更好。
附:L1正则化:在目标函数(损失函数)加上|W| - 引入惩罚力度(λ)
λL2
通过控制λ,调整惩罚力度
七.逻辑回归模型
7.1 模型的评估标准
def printing_Kfold_scores(x_train_data,y_train_data):
#先传入原始数据len(y_train_data),再做5倍的交叉验证
fold = KFold(5,shuffle=False)
c_param_range = [0.01,0.1,1,10,100]
results_table = pd.DataFrame(index = range(len(c_param_range),2), columns = ['C_paramter','Mean recall score'])
results_table['C_parameter'] = c_param_range
j = 0
#循环c_param_range,比较哪个值好
for c_param in c_param_range:
print('----------------------------------------')
print('C_parameter:' , c_param)
print('----------------------------------------')
print('')
recall_accs = []
#循环交叉验证
for iteration, indices in enumerate(fold.split(x_train_data)):
#C:惩罚力度
#penalty:选择哪种惩罚l1或l2
lr = LogisticRegression(C = c_param, penalty = 'l1')
#fit:交叉验证,建立模型
lr.fit(x_train_data.iloc[indices[0],:],y_train_data.iloc[indices[0],:].values.ravel())
y_pred_undersample = lr.predict(x_train_data.iloc[indices[1],:].values)
recall_acc = recall_score(y_train_data.iloc[indices[1],:].values,y_pred_undersample)
recall_accs.append(recall_acc)
print('Iteration',iteration,': recall score = ', recall_acc)
results_table.loc[j,'Mean recall score'] = np.mean(recall_accs)
j += 1
print('')
print('Mean recall score', np.mean(recall_accs))
print('')
best_c=results_table.loc[results_table['Mean recall score'].astype('float64').idxmax()]['C_parameter']
print('*****************************************************************')
print('Best model to choose from cross validation is with C parameter = ', best_c)
print('*****************************************************************')
return best_c
best_c=printing_Kfold_scores(X_train_undersample,y_train_undersample)
C_parameter: 0.01
Iteration 0 : recall score = 0.9315068493150684
Iteration 1 : recall score = 0.9178082191780822
Iteration 2 : recall score = 1.0
Iteration 3 : recall score = 0.9459459459459459
Iteration 4 : recall score = 0.9696969696969697
Mean recall score 0.9529915968272131
C_parameter: 0.1
Iteration 0 : recall score = 0.8493150684931506
Iteration 1 : recall score = 0.863013698630137
Iteration 2 : recall score = 0.9491525423728814
Iteration 3 : recall score = 0.9459459459459459
Iteration 4 : recall score = 0.9090909090909091
Mean recall score 0.9033036329066049
C_parameter: 1
Iteration 0 : recall score = 0.863013698630137
Iteration 1 : recall score = 0.8904109589041096
Iteration 2 : recall score = 0.9830508474576272
Iteration 3 : recall score = 0.9459459459459459
Iteration 4 : recall score = 0.9090909090909091
Mean recall score 0.9183024720057457
C_parameter: 10
Iteration 0 : recall score = 0.863013698630137
Iteration 1 : recall score = 0.8904109589041096
Iteration 2 : recall score = 0.9830508474576272
Iteration 3 : recall score = 0.9324324324324325
Iteration 4 : recall score = 0.9090909090909091
Mean recall score 0.9155997693030431
C_parameter: 100
Iteration 0 : recall score = 0.8904109589041096
Iteration 1 : recall score = 0.9041095890410958
Iteration 2 : recall score = 0.9830508474576272
Iteration 3 : recall score = 0.9459459459459459
Iteration 4 : recall score = 0.9090909090909091
Mean recall score 0.9265216500879376
Best model to choose from cross validation is with C parameter = 0.01
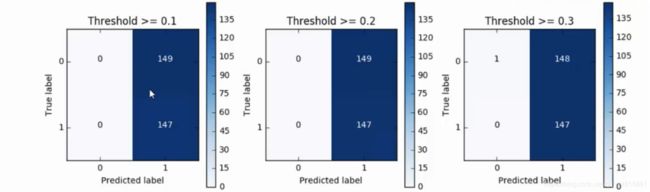
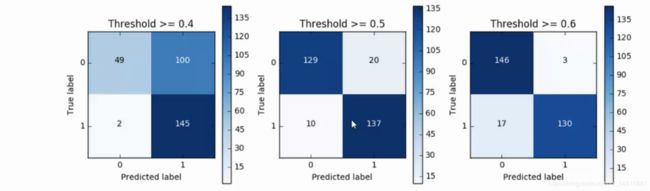
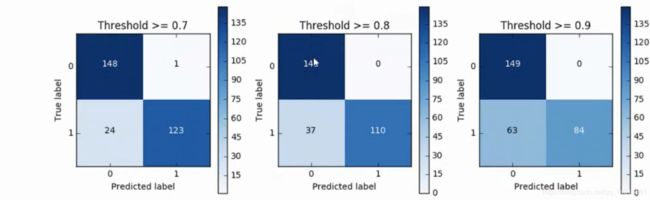
八.混淆矩阵
8.1 下采样数据集的混淆矩阵
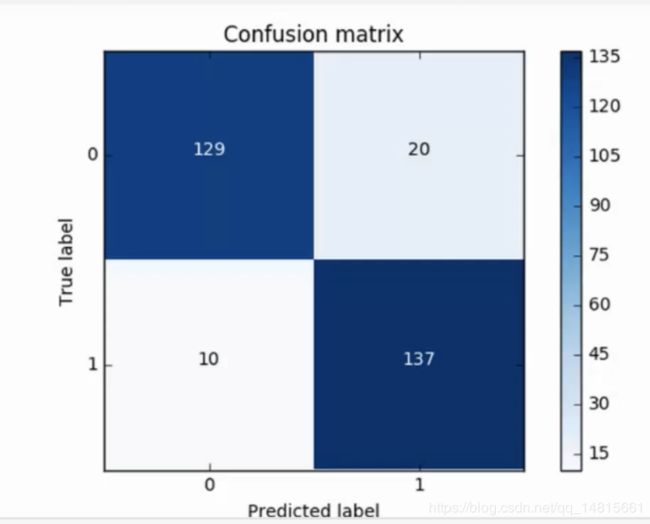
8.2 原始数据集的混淆矩阵

#原始数据,不带下采样
best_c=printing_Kfold_scores(X_train,y_train)
----------------------------------------
C_parameter: 0.01
----------------------------------------
Iteration 0 : recall score = 0.4925373134328358
Iteration 1 : recall score = 0.6027397260273972
Iteration 2 : recall score = 0.6833333333333333
Iteration 3 : recall score = 0.5692307692307692
Iteration 4 : recall score = 0.45
Mean recall score 0.5595682284048672
----------------------------------------
C_parameter: 0.1
----------------------------------------
Iteration 0 : recall score = 0.5671641791044776
Iteration 1 : recall score = 0.6164383561643836
Iteration 2 : recall score = 0.6833333333333333
Iteration 3 : recall score = 0.5846153846153846
Iteration 4 : recall score = 0.525
Mean recall score 0.5953102506435158
----------------------------------------
C_parameter: 1
----------------------------------------
Iteration 0 : recall score = 0.5522388059701493
Iteration 1 : recall score = 0.6164383561643836
Iteration 2 : recall score = 0.7166666666666667
Iteration 3 : recall score = 0.6153846153846154
Iteration 4 : recall score = 0.5625
Mean recall score 0.612645688837163
----------------------------------------
C_parameter: 10
----------------------------------------
Iteration 0 : recall score = 0.5522388059701493
Iteration 1 : recall score = 0.6164383561643836
Iteration 2 : recall score = 0.7333333333333333
Iteration 3 : recall score = 0.6153846153846154
Iteration 4 : recall score = 0.575
Mean recall score 0.6184790221704963
----------------------------------------
C_parameter: 100
----------------------------------------
Iteration 0 : recall score = 0.5522388059701493
Iteration 1 : recall score = 0.6164383561643836
Iteration 2 : recall score = 0.7333333333333333
Iteration 3 : recall score = 0.6153846153846154
Iteration 4 : recall score = 0.575
Mean recall score 0.6184790221704963
*****************************************************************
Best model to choose from cross validation is with C parameter = 10.0
*****************************************************************