java并发集合ConcurrentHashMap
ConcurrentHashMap概述
HashMap是我们最常用的数据结构之一,它方便高效,但遗憾的是,HashMap是线程不安全的,在并发环境下,在HashMap的扩容过程中,可能造成散列表的循环锁死。而线程安全的HashTable使用了大量Synchronized锁,导致了效率非常低下。幸运的是,并发编程大师Doug Lea为我们提供了ConcurrentHashMap,它是线程安全版的HashMap。
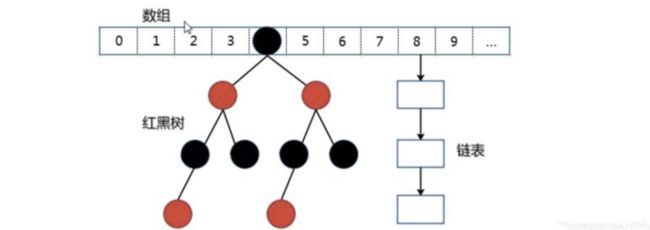
一、数据结构
ConcurrentHashMap底层数据结构和HashMap一样都是:数组+链表+红黑数
//Node数组的最多长度
private static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
//Node数组默认长度
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 16;
static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
private static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16;
//填充因子
private static final float LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
private static final int MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE = 16;
private static int RESIZE_STAMP_BITS = 16;
private static final int MAX_RESIZERS = (1 << (32 - RESIZE_STAMP_BITS)) - 1;
private static final int RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT = 32 - RESIZE_STAMP_BITS;
//获取当前机器的cpu数
static final int NCPU = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
//Node数组
transient volatile Node<K,V>[] table;
private transient volatile Node<K,V>[] nextTable;
private transient volatile long baseCount;
//当前Node数组长度
private transient volatile int sizeCtl;
private transient volatile int transferIndex;
private transient volatile int cellsBusy;
private transient volatile CounterCell[] counterCells;
// views
private transient KeySetView<K,V> keySet;
private transient ValuesView<K,V> values;
private transient EntrySetView<K,V> entrySet;
二、构造器
public ConcurrentHashMap() {
}
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
//如果initialCapacity大于等于最大容量的一半,那么值就是最大容量,否则就把值先扩大1.5倍,在向上取其2的幂
int cap = ((initialCapacity >= (MAXIMUM_CAPACITY >>> 1)) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor(initialCapacity + (initialCapacity >>> 1) + 1));
this.sizeCtl = cap;
}
public ConcurrentHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this.sizeCtl = DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
putAll(m);
}
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
this(initialCapacity, loadFactor, 1);
}
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity,float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) {
if (!(loadFactor > 0.0f) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (initialCapacity < concurrencyLevel) // Use at least as many bins
initialCapacity = concurrencyLevel; // as estimated threads
long size = (long)(1.0 + (long)initialCapacity / loadFactor);
int cap = (size >= (long)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor((int)size);
this.sizeCtl = cap;
}
三、节点的插入
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
//onlyIfAbsent为false表示重复时,进行覆盖
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
//键和值都不能为空,这和hashmap不同
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
//计算当前key的hash值
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
//用局部变量接受table,然后循环
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f;
int n, i, fh;
//如果
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
//// 如果数组"空",进行数组初始化,详情见下
tab = initTable();
// 找该 hash 值对应的数组下标,得到第一个节点 f
//tabAt意思是取出数组tab对应索引的值
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
//如果数组该位置为空,
//用一次 CAS 操作将这个新值放入其中即可,这个 put 操作差不多就结束了,可以拉到最后面了
// 如果 CAS 失败,那就是有并发操作,进到下一个循环就好了
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null, new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break;
}
//走到这里表示对应key算出的索引处的数组值不为null
//也就是说当前节点f的hashcode是-1,说明当前有线程对数组node进行扩容
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
// 帮助其他线程进行数据迁移,这个等到看完数据迁移部分的介绍后,再理解这个就很简单了
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
// 到这里就是说,f是该位置的头结点,而且不为空
V oldVal = null;
// 获取数组该位置的头结点的监视器锁
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {//判断当前头节点是否发生变化
if (fh >= 0) {//头结点的 hash 值大于 0,说明是链表
binCount = 1;// 用于累加,记录链表的长度
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {/ 遍历链表
K ek;
// 如果发现了"相等"的 key,判断是否要进行值覆盖,然后也就可以 break 了
if (e.hash == hash &&((ek = e.key) == key ||(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
// 如果没有找到"相等"的 key,且到了链表的最末端,就将这个新值放到链表的最后面
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null);
break;
}
}
}
// 红黑树
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
// 调用红黑树的插值方法插入新节点
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key, value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}//失去数组该位置的头结点的监视器锁
// binCount != 0 说明上面在做链表操作
if (binCount != 0) {
//判断是否要将链表转换为红黑树,临界值和 HashMap 一样,也是 8
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
// 这个方法和 HashMap 中稍微有一点点不同,那就是它不是一定会进行红黑树转换,
//如果当前数组的长度小于 64,那么会选择进行数组扩容,而不是转换为红黑树
// 具体源码我们就不看了,扩容部分后面说
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
//,将当前ConcurrentHashMap的元素数量baseCount加1,table的扩容是在这里发生的
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
1、节点数baseCount的计数
private transient volatile CounterCell[] counterCells;
@sun.misc.Contended static final class CounterCell {
volatile long value;
CounterCell(long x) { value = x; }
}
private final void addCount(long x, int check) {
CounterCell[] as;
long b, s;
//如果计数数组不为null,或者修改baseCount失败
if ((as = counterCells) != null || !U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, b = baseCount, s = b + x)) {
CounterCell a;
long v;
int m;
boolean uncontended = true;
//如果计数数组为null或者长度小于1
if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||
//每个线程生成一个随机数,如果算出其对应计数数组的下标值,判断其对应索引位置是否为null
(a = as[ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m]) == null ||
//利用cas操作对应线程的计数数组值的value
!(uncontended = U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))
) {
fullAddCount(x, uncontended);
return;
}
if (check <= 1)
return;
s = sumCount();
}
if (check >= 0) {
Node<K,V>[] tab, nt; int n, sc;
while (s >= (long)(sc = sizeCtl) && (tab = table) != null &&
(n = tab.length) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
int rs = resizeStamp(n);
if (sc < 0) {
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null ||
transferIndex <= 0)
break;
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1))
transfer(tab, nt);
}
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,
(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2))
transfer(tab, null);
s = sumCount();
}
}
}
private transient volatile int cellsBusy;
private final void fullAddCount(long x, boolean wasUncontended) {
int h;
//当线程生成一个随机数,注意同一个线程不管调用多少次都不会变,可以理解为线程的hash
if ((h = ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe()) == 0) {
ThreadLocalRandom.localInit(); // force initialization
h = ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe();
wasUncontended = true;
}
boolean collide = false; // True if last slot nonempty
for (;;) {
CounterCell[] as;
CounterCell a;
int n;
long v;
//如果当计数数组不为null,且长度大于0
if ((as = counterCells) != null && (n = as.length) > 0) {
//如果对应线程随机数的计数数组的值为null
if ((a = as[(n - 1) & h]) == null) {
//当前计数数组没有线程在修改
if (cellsBusy == 0) { // Try to attach new Cell
CounterCell r = new CounterCell(x); // Optimistic create
//当前计数数组没有线程在修改 && 成功把CELLSBUSY从0变为1
if (cellsBusy == 0 && U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
boolean created = false;
try { // Recheck under lock
CounterCell[] rs;
int m, j;
//当计数数组不为bull&& 长度大于0 && 对应线程随机数的计数数组的值为null
if ((rs = counterCells) != null &&(m = rs.length) > 0 && rs[j = (m - 1) & h] == null) {
//赋值对应线程随机数产生索引处的计数数组值
rs[j] = r;
created = true;
}
} finally {
//
cellsBusy = 0;
}
if (created)
break;
continue; // Slot is now non-empty
}
}
collide = false;
}
else if (!wasUncontended) // CAS already known to fail
wasUncontended = true; // Continue after rehash
else if (U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))
break;
else if (counterCells != as || n >= NCPU)
collide = false; // At max size or stale
else if (!collide)
collide = true;
//计数数组扩容
else if (cellsBusy == 0 && U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
try {
if (counterCells == as) {// Expand table unless stale
CounterCell[] rs = new CounterCell[n << 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
rs[i] = as[i];
counterCells = rs;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
collide = false;
continue; // Retry with expanded table
}
//当前线程生成一个新的随机数
h = ThreadLocalRandom.advanceProbe(h);
}
//cellsBusy == 0表示当前没有线程竞争,
else if (cellsBusy == 0 && counterCells == as && U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
boolean init = false;
try { // Initialize table
if (counterCells == as) {
CounterCell[] rs = new CounterCell[2];
rs[h & 1] = new CounterCell(x);
counterCells = rs;
init = true;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
if (init)
break;
}
else if (U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, v = baseCount, v + x))
break; // Fall back on using base
}
}
2、Node数组的初始化
private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() {
Node<K,V>[] tab;
int sc;
//循环条件是数组为null且长度为0
while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
// 初始化的"功劳"被其他线程"抢去"了
if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0)
Thread.yield(); // lost initialization race; just spin
// CAS 一下,将 sizeCtl 设置为 -1,代表抢到了锁
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
try {
//数组为null且长度为0
if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
//如果设置的数组长度小于0,就取默认值 16
int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
//动态初始化数组
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n];
//将数组赋值给成员变量table
table = tab = nt;
// 如果 n 为 16 的话,那么这里 sc = 12
// 其实就是 0.75 * n,设置数组的阈值
sc = n - (n >>> 2);
}
} finally {
//将计算好的阈值赋值给成员变量sizeCtl
sizeCtl = sc;
}
break;
}
}
return tab;
}
3、链表转红黑树
treeifyBin 不一定就会进行红黑树转换,也可能是仅仅做数组扩容
private final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int index) {
Node<K,V> b;
int n, sc;
if (tab != null) {
//如果数组的长度小于64,那么就对其进行扩容
if ((n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)
tryPresize(n << 1);
//如果数组的长度大于64
//如果对应索引位置的节点不为空,且hash大于0,开始进行链表转红黑树
else if ((b = tabAt(tab, index)) != null && b.hash >= 0) {
synchronized (b) {//获取当前节点锁
if (tabAt(tab, index) == b) {//判断当前位置的节点是否被改变
TreeNode<K,V> hd = null;
TreeNode<K,V> tl = null;
//循环遍历当前链表,当单向链表改为双向链表
for (Node<K,V> e = b; e != null; e = e.next) {
TreeNode<K,V> p = new TreeNode<K,V>(e.hash, e.key, e.val,null, null);
if ((p.prev = tl) == null)
hd = p;
else
tl.next = p;
tl = p;
}
//将双向链表改为红黑树
setTabAt(tab, index, new TreeBin<K,V>(hd));
}
}//失去当前节点锁
}
}
}
4、扩容
final Node<K,V>[] helpTransfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V> f) {
Node<K,V>[] nextTab;
int sc;
//如果数组不为null,
if (tab != null && (f instanceof ForwardingNode) &&(nextTab = ((ForwardingNode<K,V>)f).nextTable) != null) {
int rs = resizeStamp(tab.length);
while (nextTab == nextTable && table == tab &&(sc = sizeCtl) < 0) {
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 || sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || transferIndex <= 0)
break;
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1)) {
//数据迁移
transfer(tab, nextTab);
break;
}
}
return nextTab;
}
return table;
}
四、节点的删除
public V remove(Object key) {
return replaceNode(key, null, null);
}
final V replaceNode(Object key, V value, Object cv) {
//ConcurrentHashMap对key对hashCode进行二次处理
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f;
int n, i, fh;
//如果数组为null或者数组长度为null或者对应key数组索引位置上的值为null
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0 || (f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null)
break;
//如果对应key查询到的头节点Node的hash是-1
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)//MOVED = -1
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
boolean validated = false;
//锁住头节点Node
synchronized (f) {
//进行二次判断对应key数组索引位置上的节点Node是否改变,如果没有改变,进入代码块
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
validated = true;
for (Node<K,V> e = f, pred = null;;) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
V ev = e.val;
if (cv == null || cv == ev ||
(ev != null && cv.equals(ev))) {
oldVal = ev;
if (value != null)
e.val = value;
else if (pred != null)
pred.next = e.next;
else
setTabAt(tab, i, e.next);
}
break;
}
pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null)
break;
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
validated = true;
TreeBin<K,V> t = (TreeBin<K,V>)f;
TreeNode<K,V> r, p;
if ((r = t.root) != null &&
(p = r.findTreeNode(hash, key, null)) != null) {
V pv = p.val;
if (cv == null || cv == pv ||
(pv != null && cv.equals(pv))) {
oldVal = pv;
if (value != null)
p.val = value;
else if (t.removeTreeNode(p))
setTabAt(tab, i, untreeify(t.first));
}
}
}
}
}
if (validated) {
if (oldVal != null) {
if (value == null)
addCount(-1L, -1);
return oldVal;
}
break;
}
}
}
return null;
}
五、节点的查询
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab;
Node<K,V> e, p;
int n, eh;
K ek;
//ConcurrentHashMap对key对hashCode进行二次处理
int h = spread(key.hashCode());
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
}
else if (eh < 0)
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
while ((e = e.next) != null) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}
1、ConcurrentHashMap对key对hashCode进行二次处理
static final int spread(int h) {
return (h ^ (h >>> 16)) & HASH_BITS;
}