【C语言】09-构造类型
此笔记由个人整理
塞上苍鹰_fly
课程来自:尚观C语言
一、结构体
产生及意义
- 可以存储不同类型的信息,在一块连续的空间
类型的描述
格式
最后的分号一定要加
结构体只是描述
struct
{
数据类型 成员1;
数据类型 成员2;
... ...
};
案例
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
struct simp_st
{
int i,j;
float f;
char ch;
};
int main()
{
}
嵌套定义
- 在一个结构体中嵌套定义一个或多个结构体
案例
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#define NAMESIZE 32
struct student_st
{
int id;
char name[NAMESIZE];
struct birthday_st
{
int year;
int month;
int day;
}birth;
int math;
int chinese;
};
int main()
{
}
定义变量并初始化及成员引用
格式
- 定义变量并初始化
struct 结构体名 变量名 = {值}
- 成员引用
变量名.成员名
指针->成员名
(*指针).成员名
案例:基础引用
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
struct simp_st
{
int i;
float f;
char ch;
};
int main()
{
struct simp_st a = {123,456.789,'P'};
a.i = 112233;
printf("%d %f %c\n",a.i,a.f,a.ch);
return 0;
}。
- 结果
案例:学生信息管理
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#define NAMESIZE 32
struct student_st
{
int id;
int i;
char name[NAMESIZE];
struct birthday_st
{
int year;
int month;
int day;
}birth;
int math;
int chinese;
};
int main()
{
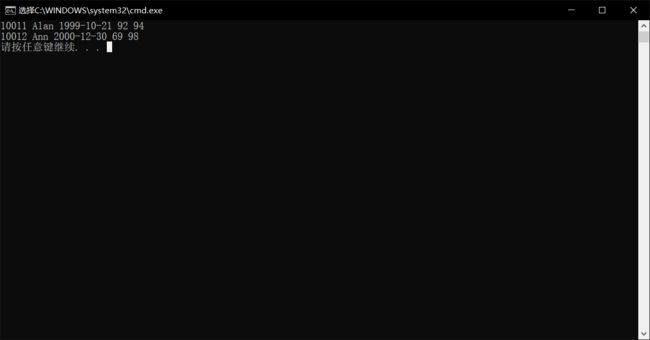
struct student_st stu = {10011,"Alan",{2020,6,30},98,97};//全部初始化
//struct student_st stu = {.math = 91,.chinese = 95};//部分初始化
struct student_st *p = &stu;
struct student_st arr[2] = {{10011,'Alan',{1999,10,21},92,94},{10012,'Ann',{2000,12,30},69,98}};
p = &arr[0];
//普通变量打印
//printf("%d %s %d-%d-%d %d %d\n",stu.id,stu.name,stu.birth.year,stu.birth.month,stu.birth.day,stu.math,stu.chinese);
//结构体指针打印
//printf("%d %s %d-%d-%d %d %d\n",p->id,p->name,p->birth.year,p->birth.month,p->birth.day,p->math,p->chinese);
//数组打印
for(i = 0;i < 2;i++,p++)
{
printf("%d %s %d-%d-%d %d %d\n",p->id,p->name,p->birth.year,p->birth.month,p->birth.day,p->math,p->chinese);
}
return 0;
}
- 结果
占用内存空间大小
- 地址对齐:对于结构体中站内存最大的元素为准,只要超过一个哪怕没有存满,也算一个最大存储空间
公式
addr % sizeof = 0
案例
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
struct simp_st
{
int i;
float f;
char ch;
};
int main()
{
struct simp_st a;
struct simp_st *p = &a;
printf("sizeof(point) = %d\n",sizeof(p));
printf("sizeof(struct) = %d\n",sizeof(a));
}
- 结果
函数传参
- 常用地址传参,值传参浪费形参开销
值传参
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
struct simp_st
{
int i;
float f;
char ch;
};
void func(struct simp_st b)
{
printf("%d\n",sizeof(b));
}
int main()
{
struct simp_st a;
struct simp_st *p = &a;
func(a);
}
- 结果
值传参在结构体传参是不常用,这样会浪费形参开销
地址传参
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
struct simp_st
{
int i;
float f;
char ch;
};
void func(struct simp_st *b)
{
printf("%d\n",sizeof(b));
}
int main()
{
struct simp_st a;
struct simp_st *p = &a;
func(p);//func(&a);
}
- 结果
练习:学生信息管理
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "string.h"
#define NAMESIZE 32
struct student_st
{
int id;
char name[NAMESIZE];
int math;
int chinese;
};
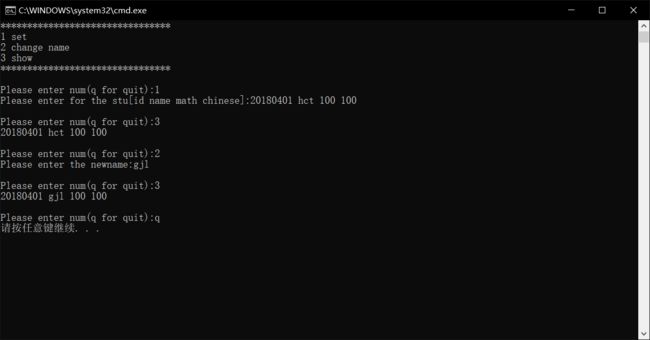
void menu(void)
{
printf("********************************\n");
printf("1 set\n2 change name\n3 show\n");
printf("********************************\n");
}
void stu_set(struct student_st *p,const struct student_st *q)
{
*p = *q;
}
void stu_show(struct student_st *p)
{
printf("%d %s %d %d\n",p->id,p->name,p->math,p->chinese);
}
void stu_changename(struct student_st *p,const char *newname)
{
strcpy(p->name,newname);
}
int main()
{
int choice;
int ret;
char newname[NAMESIZE];
struct student_st stu;
struct student_st tmp;
menu();
do
{
printf("\nPlease enter num(q for quit):");
ret = scanf("%d",&choice);
if(ret != 1)
break;
switch(choice)
{
case 1:
printf("Please enter for the stu[id name math chinese]:");
scanf("%d %s %d %d",&tmp.id,&tmp.name,&tmp.math,&tmp.chinese);
stu_set(&stu,&tmp);
break;
case 2:
printf("Please enter the newname:");
scanf("%s",newname);
stu_changename(&stu,newname);
break;
case 3:
stu_show(&stu);
break;
default:
exit(1);
}
}while(1);
exit(0);
}
- 结果
二、共用体
产生及意义
- 多个成员共享同一个空间,同一时刻只有一个成员存在,不能同时存在
类型描述
格式
union 共用体名
{
数据类型 成员名1;
数据类型 成员名2;
... ...
};
嵌套定义
格式
//结构体嵌套共用体
struct
{
int i;
char ch;
union
{
int a;
int c;
};
float f;
};
//共用体嵌套结构体
union
{
int a;
double d;
struct
{
int arr[10];
float f;
}c;
};
案例:高四位与低四位相加
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "stdint.h"
union
{
struct
{
uint16_t i;
uint16_t j;
}x;
uint32_t y;
}a;
int main()
{
//uint32_t i = 0x11223344;
//printf("%#x",(i >> 16) + i & 0xFFFF);
a.y = 0x11223344;
printf("%#x\n",a.x.i+a.x.j);
exit(0);
}
- 结果
定义变量,初始化及成员引用
多个成员变量不能同时共存
格式
- 定义变量并初始化
union 共用体名 变量名;
- 成员引用
变量名.成员名
指针->成员名
(*指针).成员名
案例:基本引用
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
union test_un
{
int i;
float f;
double d;
char ch;
};
int main()
{
union test_un a;
union test_un *p = &a;
p->f = 345.678;
printf("%f\n",p->f);
}
- 结果
占用内存空间大小
- 根据共同体中最大的成员变量所占大小决定
函数传参
- 常用地址传参,值传参浪费形参开销
值传递
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
union test_un
{
int i;
float f;
double d;
char ch;
};
void func(union test_un b)
{
printf("%d\n",sizeof(b));
}
int main()
{
union test_un a;
union test_un *p = &a;
func(a);
}
- 结果
地址传递
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
union test_un
{
int i;
float f;
double d;
char ch;
};
void func(union test_un *b)
{
printf("%d\n",sizeof(b));
}
int main()
{
union test_un a;
union test_un *p = &a;
func(p);//func(*a)
}
- 结果
位域
负数的补码形式
案例
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "stdint.h"
union
{
struct
{
char a:1;
char b:2;
char c:1;
}x;
char y;
}w;
int main()
{
w.y = 1;
printf("%d\n"w.x.a);
//a:1-->0-->1-->-1
//先减1,再取反,之后取负数
exit(0);
}
- 结果
三、枚举
相当于有值的宏,更方便理解代码,增强代码的可阅读性
类型描述
格式
enum 标志符
{
成员1;
成员2;
... ...
};
定义变量,初始化
格式
- 定义变量并初始化
enum 共用体名 变量名;
案例:基本调用
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
enum day
{
MON = 1,
TUS,
THR,
WES,
FRI,
SAT,
SUN
};
int main()
{
enum day a = MON;
printf("%d\n",a);
exit(0);
}
案例:
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
enum STA_en
{
STATE_RUNNING = 1,
STATE_CANCELED,
STATE_OVER
};
struct job_st
{
int id;
int state;
time_t start,end;
};
int main()
{
struct job_st job1;
//伪码
switch(job1.state)
{
case STATE_RUNNING:
break;
case STATE_CANCELED:
break;
case STATE_OVER:
break;
default:
exit();
}
exit(0);
}