Django框架之DRF序列化与反序列化
概念:
序列化:将Python对象转换为json字符串,反之json字符串反序列化为对象
使用drf序列化组件的步骤如下:
1.在你的app中新建一个py文件,新建一个序列化的类
2.在类中写要序列化的字段
在视图中使用序列化的类
1.实例化出一个序列化的对象,在产生对象的时候,传入序列化的对象(queryset对象)
2.对象.data
3.return Reponse(对象.data)
使用实例:
新建Django项目:settings.py文件注册rest_framework,使用MySQL数据库创建数据:
settings.py
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql',
'NAME': 'drf_ser01', #数据库的名字
'HOST': '127.0.0.1', #数据库的ip
'PORT': 3306, #数据库的端口
'USER': 'root', #数据库的用户名
'PASSWORD': '123'
}
}
# __init__.py
import pymysql
pymysql.install_as_MySQLdb()
from django.db import models
# Create your models here.
class Book(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=32)
price = models.DecimalField(decimal_places=1, max_digits=6)
publish = models.ForeignKey(to='Publish')
author = models.ManyToManyField(to='Author', through='Book2Author', through_fields=('book', 'author'))
class Publish(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
addr = models.CharField(max_length=64, null=True)
class Author(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
age = models.IntegerField()
class Book2Author(models.Model):
book = models.ForeignKey(to='Book')
author = models.ForeignKey(to='Author')
app01新建MySer.py
#先创建一个BookSer序列化类
from rest_framework import serializers
#第一种序列化方法
class BookSer(serializers.Serializer):
id = serializers.CharField()
title = serializers.CharField()
publish = serializers.CharField()
author = serializers.CharField()
#第二种序列化的类
class BookSer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = models.Book
fields = "__all__"
def validate_name(self,values):
if values is None:
raise ValidationError("名字不能为空")
else:
return values
app01视图函数views.py中:
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse,redirect
from app01.MySer import BookSer
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from app01 import models
# Create your views here.
class Book(APIView):
response = {'code': 100, 'msg': '查询成功'}
def get(self, request):
books = models.Book.objects.all()
#注instance用于接受序列化的对象,many表示是queryset对象
books_ser = BookSer(instance=books, many=True)
return Response(books_ser.data)
路由配置:
from django.conf.urls import url
from django.contrib import admin
from app01 import views
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls),
url(r'^books/', views.Books.as_view()),
]
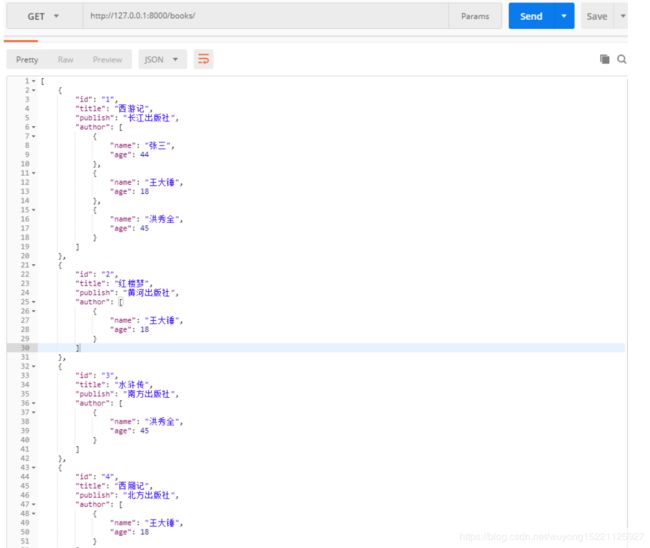
使用Postman发送get请求,获取到数据库中所有图书信息:

可以看出一对多和多对多的外键字段显示的是对象名字,下面进一步使用序列化,让信息显示更完善
-source:可以指定字段(name publish.name),可以指定方法
-SerializerMethodField搭配方法使用(get_字段名字)
publish_detail=serializers.SerializerMethodField(read_only=True)
def get_publish_detail(self,obj):
return {'name':obj.publish.name,'city':obj.publish.city}
更新版本BookSer
from rest_framework import serializers
class BookSer(serializers.Serializer):
id = serializers.CharField()
title = serializers.CharField()
#返回出版社的时候会返回出版社的名字
publish = serializers.CharField(source='publish.name')
author = serializers.SerializerMethodField()
def get_author(self, obj):
authors = []
for author_obj in obj.author.all():
authors.append({'name': author_obj.name, 'age': author_obj.age})
return authors
- read_only:反序列化时,不传
- write_only:序列化时,不显示
序列化的另一种写法,上方有提过:
class BookSer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = models.Book
fields=('id','name')
#要排除的字段
exclude=('name')
#深度控制
depth=1
def validate_name(self,values):
if values is None:
raise ValidationError("名字不能为空")
else:
return values

刚才看到__all__,序列化所有字段,查询到的数据里面publish和author都是对应id值,如果需要获取到对应publish和author的关联信息,可以在BookSer内,Meta外重新写字段,方式同serializers
class BookSer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = models.Book
fields = "__all__"
def validate_name(self,values):
if values is None:
raise ValidationError("名字不能为空")
else:
return values
class AuthorSer(serializers.Serializer):
id = serializers.CharField()
name = serializers.CharField()
age = serializers.CharField()
# 序列化方式二改进:
class BookSer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = models.Book
# fields = ['id', 'title']
fields = ('__all__')
publish = serializers.CharField(source='publish.name')
author = serializers.SerializerMethodField()
def get_author(self, obj):
ret = AuthorSer(obj.author.all(), many=True)
return ret.data
通过post请求新增数据:
对数据进行新增使用反序列化实现,这里反序列化有2种情况进行新增:
使用继承了Serializers序列化类的对象,反序列化(需重写create方法)
from django.db import models
# Create your models here.
class User(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
password = models.CharField(max_length=64)
choices = (('1', 'Super_Admin'), ('2', 'General_Admin'), ('3', 'General_User') )
user_type = models.CharField(max_length=6, choices=choices, default='3')
class Book(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=32)
price = models.DecimalField(decimal_places=1, max_digits=6)
publish = models.ForeignKey(to='Publish', null=True)
author = models.ManyToManyField(to='Author')
class Publish(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
addr = models.CharField(max_length=64, null=True)
class Author(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
age = models.IntegerField()
class Book(APIView):
def post(self, request):
response = {'code': 100, 'msg': '新增成功'}
# 使用继承了Serializers序列化类的对象,反序列化
book = BookSer(data=request.data)
if book.is_valid():
# 清洗通过的数据,需要在MySer.py中重写create
book.create(book.validated_data)
return Response(response)
class BookSer(serializers.Serializer):
# read_only 反序列化的时候,该字段不传
# 这里id可以不传自增,publish、author不传,当然需要在models里面把不传字段设置为null=True
# author多对多字段不能设置null=True
id = serializers.CharField(read_only=True)
title = serializers.CharField()
price = serializers.CharField()
publish = serializers.CharField(source='publish.id', read_only=True)
author = serializers.SerializerMethodField(read_only=True)
def get_author(self, obj):
ret = AuthorSer(obj.author.all(), many=True)
return ret.data
# 重写create方法,才能在使用Serializer发序列化方法进行新增数据
def create(self, validated_data):
res = models.Book.objects.create(**validated_data)
return res
使用继承了ModelSerializers序列化类的对象,反序列化
from django.db import models
# Create your models here.
class User(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
password = models.CharField(max_length=64)
choices = (('1', 'Super_Admin'), ('2', 'General_Admin'), ('3', 'General_User') )
user_type = models.CharField(max_length=6, choices=choices, default='3')
class Book(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=32)
price = models.DecimalField(decimal_places=1, max_digits=6)
publish = models.ForeignKey(to='Publish', null=True)
author = models.ManyToManyField(to='Author')
class Publish(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
addr = models.CharField(max_length=64, null=True)
class Author(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
age = models.IntegerField()
class BookSer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = models.Book
fields = "__all__"
class Book(APIView):
def post(self, request):
response = {'code': 100, 'msg': '新增成功'}
# 使用继承了ModelSerializers序列化类的对象,反序列化
book_ser = BookSer(data=request.data)
if book_ser.is_valid():
book_ser.save()
else:
response['error'] = book_ser.errors['name'][0]
return Response(response)
使用ModelSerializer反序列化save数据后,多对多关联的那张表也会自动关联产生新的数据。
局部校验和全局校验
# MySer.py
from rest_framework.exceptions import ValidationError
class BookSer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = models.Book
fields = "__all__"
def validate_title(self, value):
if value.startswith('sb'):
raise ValidationError('不能以sb开头')
return value
def validate(self, attrs):
title = attrs.get('title')
price = attrs.get('price')
if title.startswith('禁书') or int(price) <= 15:
raise ValidationError('书名或价格不正常')
return attrs
总结:
-反序列化的校验
-validate_字段名(self,value):
-如果校验失败,抛出ValidationError(抛出的异常信息需要去bookser.errors中取)
-如果校验通过直接return value
-validate(self,attrs)
-attrs所有校验通过的数据,是个字典
-如果校验失败,抛出ValidationError
-如果校验通过直接return attrs