网络模型--Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks
Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks
https://arxiv.org/abs/1709.01507
ILSVRC 2017 image classification winner
https://github.com/hujie-frank/SENet
本文主要提出了一个新的网络模块 Squeeze-and-Excitation block,作用就是对不同 channel 给予不同的权重, selectively emphasise informative features and suppress less useful ones
网络简单,效果显著啊!
3 Squeeze-and-Excitation Blocks
首先来看看我们要解决的问题是如何描述的?
对于任意一个给定 transformation F
![]()
为了简化问题的描述,我们假定 F 为一个标准的卷积运算,我们用 V = [v 1 ,v 2 ,…,v C ] 表示学习到的一组滤波器,U = [u 1 ,u 2 ,…,u C ] 表示卷积的输出
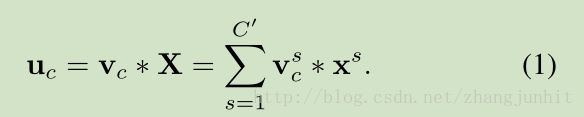
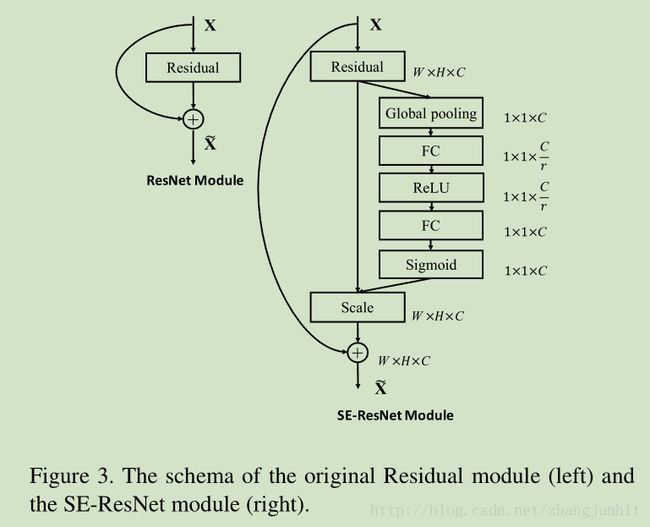
输出 U 是将所有的 channels 综合到一起得到的(summation),所以通道的相关性被隐性的包含在 vc中,但是这些相关性又被滤波器捕获的空间相关性 交错在一起。
Since the output is produced by a summation through all channels, the channel dependencies are implicitly embedded in v c , but these dependencies
are entangled with the spatial correlation captured by the filters.
我们的目标就是确保网络能够 增加有用信息的重要性,这些信息将在后续网络层被利用,抑制那些不重要的信息
Our goal is to ensure that the network is able to increase its sensitivity to informative features so that they can be exploited by subsequent transformations, and to suppress less useful ones.
我们通过下面这个模块实现上述功能 Squeeze-and-Excitation Blocks
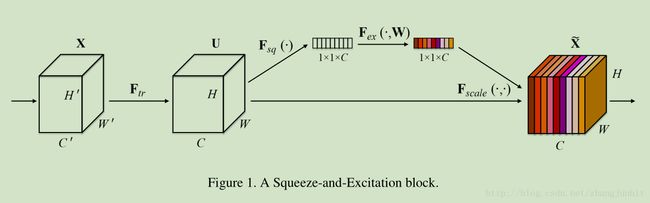
3.1. Squeeze: Global Information Embedding
为了分析 channel dependencies ,我们首先分析每个 channel的信息,从整体上来看看该 channel 的特征吧
因为每个滤波器只对应局部的感受野,所有U 的每个单元不能分析该感受野以外的 contextual information, 当网络前面层的感受野较小时这个问题变得更加的严重。为此我们首先压缩全局空间信息,将其变为一个 channel 描述子
we propose to squeeze global spatial information into a channel descriptor, 具体是由 global average pooling 来实现

3.2. Excitation: Adaptive Recalibration
为了充分利用 上面一步压缩后的信息,这里我们为了 fully capture channel-wise dependencies 设计了第二步运算。 该运算需要满足两个条件:1)足够的灵活(特别是能够学习channel之间的非线性相关性),2)它必须能够学习一个非相互排斥的关系,a non-mutually-exclusive relationship,因为 multiple channels are allowed to be emphasised opposed to one-hot activation 多通道可以共同抑制一个 激活相应,为此我们采用了一个 simple gating mechanism with a sigmoid activation
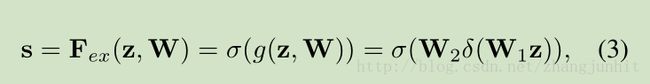
δ refers to the ReLU
最后是对每个通道乘以对应的权重系数
The final output of the block is obtained by rescaling the transformation output U with the activations
3.3. Exemplars: SE-Inception and SE-ResNet
SE-Inception
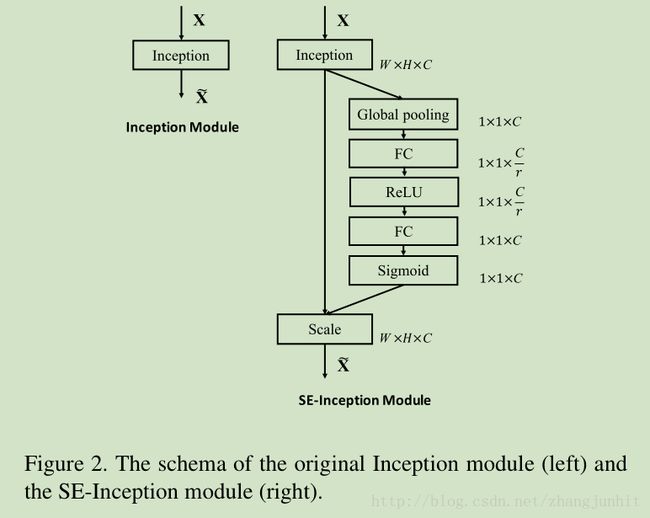
4 Model and Computational Complexity
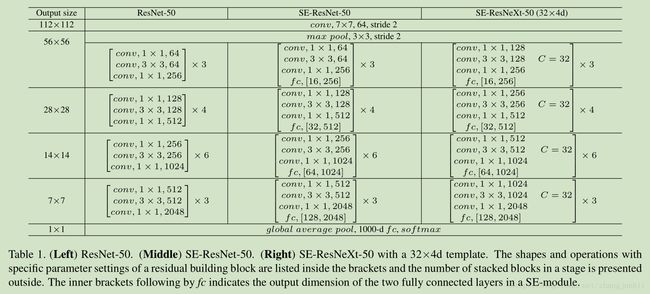
总体上计算资源增加的不多。
SE-ResNet-50 requires ∼3.87 GFLOPs, corresponding to only a 0.26% relative increase over the original ResNet-50
对于 ResNet-50 , corresponding to a ∼10% increase in the total number of parameters
6 Experiments
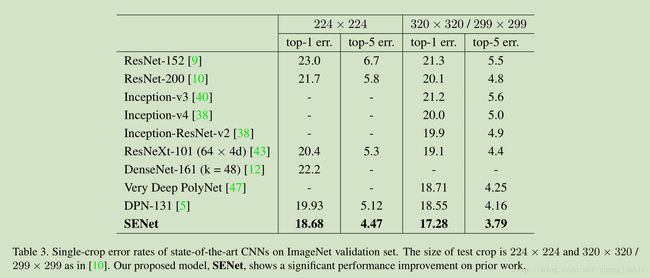
ImageNet validation set
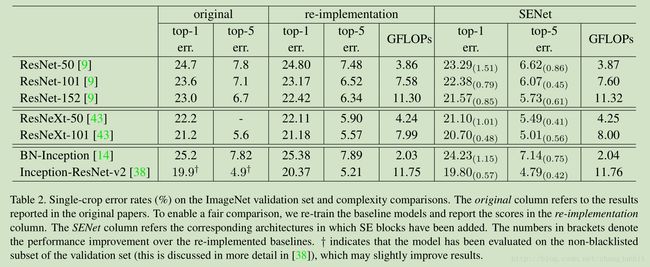
Single-crop error rates of state-of-the-art CNNs on ImageNet validation set
Activations induced by Excitation in the different modules of SE-ResNet-50 on ImageNet


对于 SENets 中的 Excitation 我们观察到以下三点信息:
1) the distribution across different classes is nearly identical in lower layers, e.g. SE_2_3
2)at greater depth, the value of each channel becomes much more class-specific as different classes exhibit different preferences to the discriminative value of features e.g. SE_4_6 and SE_5_1
3) SE_5_2 exhibits an interesting tendency towards a saturated state in which most of the activations are close to 1 and the remainder are close to 0
This suggests that SE_5_2 and SE_5_3 are less important than previous blocks in providing recalibration to the network.