python爬虫实战:分析豆瓣中最新电影的影评
本文参考来源:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000010473819【有部分修改,和运行问题优化】
简介
刚接触python不久,做一个小项目来练练手。前几天看了《战狼2》,发现它在最新上映的电影里面是排行第一的,如下图所示。准备把豆瓣上对它的影评做一个分析。
目标总览
主要做了三件事:
- 抓取网页数据
- 清理数据
- 用词云进行展示
使用的python版本是3.6
一、抓取网页数据
第一步要对网页进行访问,python中使用的是urllib库。代码如下:
from urllib import requestresp = request.urlopen('https://movie.douban.com/nowplaying/hangzhou/')html_data = resp.read().decode('utf-8')
其中https://movie.douban.com/nowp...是豆瓣最新上映的电影页面,可以在浏览器中输入该网址进行查看。
html_data是字符串类型的变量,里面存放了网页的html代码。
输入print(html_data)可以查看,如下图所示:
第二步,需要对得到的html代码进行解析,得到里面提取我们需要的数据。
在python中使用BeautifulSoup库进行html代码的解析。
(注:如果没有安装此库,则使用pip install BeautifulSoup进行安装即可!)
BeautifulSoup使用的格式如下:
BeautifulSoup(html,"html.parser")
第一个参数为需要提取数据的html,第二个参数是指定解析器,然后使用find_all()读取html标签中的内容。
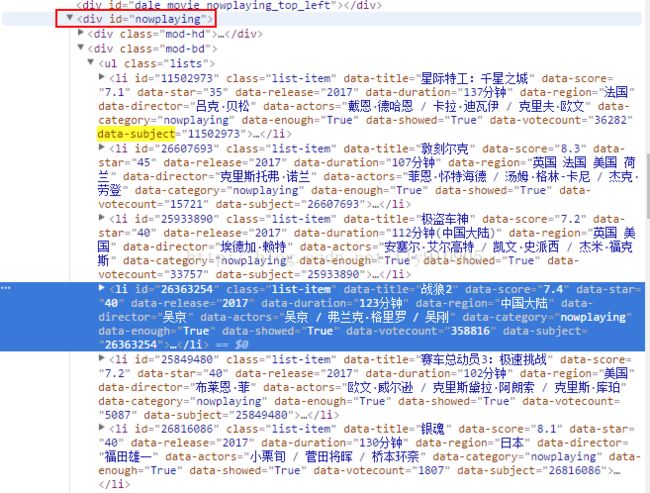
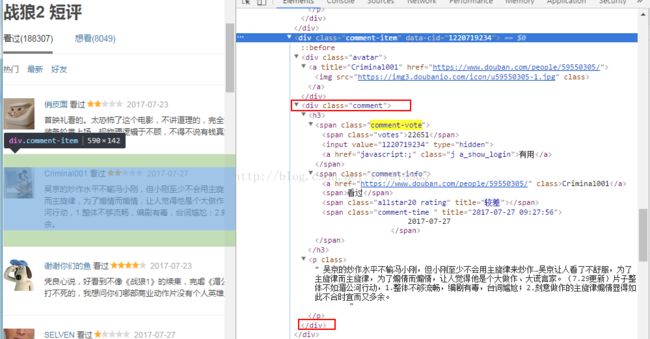
但是html中有这么多的标签,该读取哪些标签呢?其实,最简单的办法是我们可以打开我们爬取网页的html代码,然后查看我们需要的数据在哪个html标签里面,再进行读取就可以了。如下图所示:
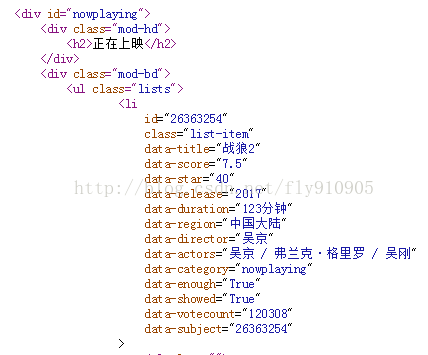
从上图中可以看出在div id="nowplaying"标签开始是我们想要的数据,里面有电影的名称、评分、主演等信息。所以相应的代码编写
nowplaying_movie_list 是一个列表,可以用print(nowplaying_movie_list[0])查看里面的内容,如下图所示:
在上图中可以看到data-subject属性[或id属性]里面放了电影的id号码,而在img标签的alt属性[或data-title属性]里面放了电影的名字,因此我们就通过这两个属性来得到电影的id和名称。(注:打开电影短评的网页时需要用到电影的id,所以需要对它进行解析),编写代码如下:
nowplaying_list = []for item in nowplaying_movie_list:nowplaying_dict = {}nowplaying_dict['id'] = item['data-subject']nowplaying_dict['name'] = item['data-title']# nowplaying_list.append(nowplaying_dict)# for tag_img_item in item.find_all('img'):# nowplaying_dict['name'] = tag_img_item['alt']nowplaying_list.append(nowplaying_dict)
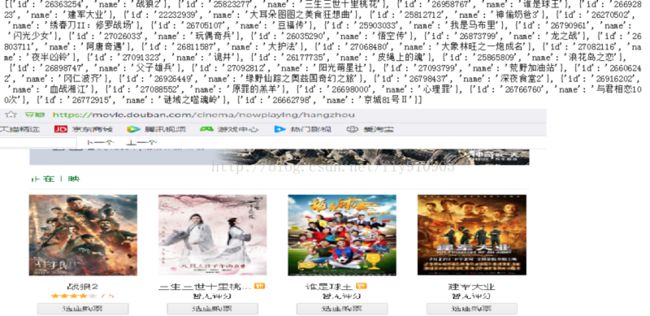
其中列表nowplaying_list中就存放了最新电影的id和名称,可以使用print(nowplaying_list)进行查看,如下图所示:
可以看到和豆瓣网址上面是匹配的。这样就得到了最新电影的信息了。接下来就要进行对最新电影短评进行分析了。例如《战狼2》的短评网址为:https://movie.douban.com/subject/26363254/comments?start=0&limit=20
其中26363254就是电影的id,start=0表示评论的第0条评论。
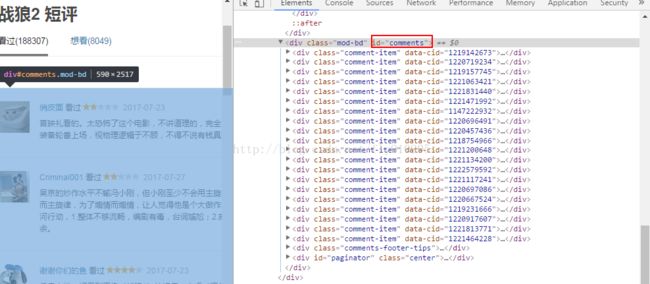
接下来接对该网址进行解析了。打开上图中的短评页面的html代码,我们发现关于评论的数据是在div标签的comment属性下面,如下图所示:
因此对此标签进行解析,代码如下:
requrl = 'https://movie.douban.com/subject/' + nowplaying_list[0]['id'] + '/comments' +'?' +'start=0' + '&limit=20'
resp = request.urlopen(requrl)
html_data = resp.read().decode('utf-8')
soup = bs(html_data, 'html.parser')
comment_div_lits = soup.find_all('div', class_='comment') 此时在comment_div_lits 列表中存放的就是div标签和comment属性下面的html代码了。在上图中还可以发现在p标签下面存放了网友对电影的评论
因此对comment_div_lits 代码中的html代码继续进行解析,代码如下:
eachCommentList = [];
for item in comment_div_lits:
if item.find_all('p')[0].string is not None:
eachCommentList.append(item.find_all('p')[0].string)使用print(eachCommentList)查看eachCommentList列表中的内容,可以看到里面存里我们想要的影评。如下图所示:
好的,至此我们已经爬取了豆瓣最近播放电影的评论数据,接下来就要对数据进行清洗和词云显示了。
二、数据清洗
为了方便进行数据进行清洗,我们将列表中的数据放在一个字符串数组中,代码如下:
comments = ''
for k in range(len(eachCommentList)):
comments = comments + (str(eachCommentList[k])).strip()使用print(comments)进行查看,如下图所示:
可以看到所有的评论已经变成一个字符串了,但是我们发现评论中还有不少的标点符号等。这些符号对我们进行词频统计时根本没有用,因此要将它们清除。所用的方法是正则表达式。python中正则表达式是通过re模块来实现的。代码如下:
import re
pattern = re.compile(r'[\u4e00-\u9fa5]+')
filterdata = re.findall(pattern, comments)
cleaned_comments = ''.join(filterdata)继续使用print(cleaned_comments)语句进行查看,如下图所示:
我们可以看到此时评论数据中已经没有那些标点符号了,数据变得“干净”了很多。
因此要进行词频统计,所以先要进行中文分词操作。在这里我使用的是结巴分词。如果没有安装结巴分词,可以在控制台使用pip install jieba进行安装。(注:可以使用pip list查看是否安装了这些库)。代码如下所示:
import jieba #分词包
import pandas as pd
segment = jieba.lcut(cleaned_comments)
words_df=pd.DataFrame({'segment':segment})因为结巴分词要用到pandas,所以我们这里加载了pandas包。可以使用words_df.head()查看分词之后的结果,如下图所示:
从上图可以看到我们的数据中有“看”、“太”、“的”等虚词(停用词),而这些词在任何场景中都是高频时,并且没有实际的含义,所以我们要他们进行清除。
我把停用词放在一个stopwords.txt文件中,将我们的数据与停用词进行比对即可(注:只要在百度中输入stopwords.txt,就可以下载到该文件)。去停用词代码如下代码如下:
stopwords=pd.read_csv("stopwords.txt",index_col=False,quoting=3,sep="\t",names=['stopword'], encoding='utf-8')#quoting=3全不引用words_df=words_df[~words_df.segment.isin(stopwords.stopword)]
继续使用words_df.head()语句来查看结果,如下图所示,停用词已经被出去了。
接下来就要进行词频统计了,代码如下:
用words_stat.head()进行查看,结果如下:
由于我们前面只是爬取了第一页的评论,所以数据有点少,在最后给出的完整代码中,我爬取了10页的评论,所数据还是有参考价值。
三、用词云进行显示
代码如下:
# 用词云进行显示backgroud_Image = plt.imread('man.jpg')wordcloud = WordCloud(background_color='white',mask=backgroud_Image,font_path='C:\Windows\Fonts\STZHONGS.TTF', # 若是有中文的话,这句代码必须添加,不然会出现方框,不出现汉字max_words=2000,stopwords=STOPWORDS,max_font_size=150,random_state=30)word_frequence = {x[0]:x[1] for x in words_stat.head(1000).values}print("[用词云进行显示--字典类型]:\r\n", word_frequence)word_frequence_list = []for key in word_frequence:temp = (key,word_frequence[key])word_frequence_list.append(temp)print("[用词云进行显示--LIST]:\r\n", word_frequence_list)# fit_words(frequencies) //根据词频生成词云# generate(text) //根据文本生成词云# generate_from_frequencies(frequencies[, ...]) //根据词频生成词云# generate_from_text(text) //根据文本生成词云# word_frequence 为字典类型,可以直接传入wordcloud.fit_words()# word_frequence = {x[0]:x[1] for x in words_stat.head(1000).values}# wordcloud = wordcloud.fit_words(word_frequence)# def fit_words(self, frequencies):# """Create a word_cloud from words and frequencies.## Alias to generate_from_frequencies.## Parameters# ----------# frequencies : dict from string to float# A contains words and associated frequency.## Returns# -------# self# """# return self.generate_from_frequencies(frequencies)wordcloud=wordcloud.fit_words(word_frequence)plt.imshow(wordcloud)plt.show()
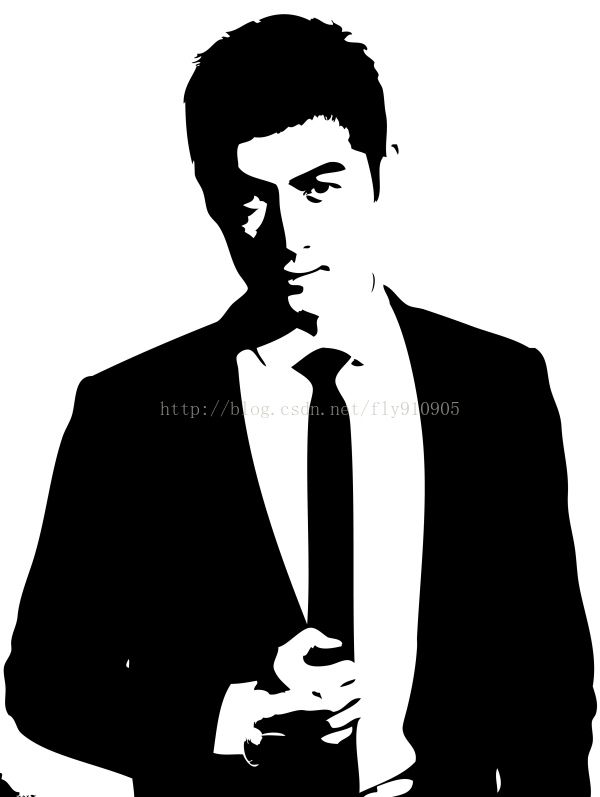
使用的图片:
完整代码如下:
from urllib import requestfrom bs4 import BeautifulSoup as bsimport reimport jieba #分词包import pandas as pdimport numpy #numpy计算包from wordcloud import WordCloud, STOPWORDS, ImageColorGeneratorimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt# %matplotlib inline是jupyer notebook 的命令# %matplotlib inlineimport matplotlibmatplotlib.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (10.0, 5.0)resp = request.urlopen('https://movie.douban.com/nowplaying/hangzhou/')html_data_comment = resp.read().decode('utf-8')# 获取HTML页面内容# print("豆瓣最新上映的电影页面内容:",html_data)soup = bs(html_data_comment, 'html.parser')# find_all 返回值是数组nowplaying_movie = soup.find_all('div', id='nowplaying')# 获取电影列表nowplaying_movie_list = nowplaying_movie[0].find_all('li', class_='list-item')# print("电影列表:\r\n",nowplaying_movie_list)# 获取电影的id和名称。nowplaying_list = []for item in nowplaying_movie_list:nowplaying_dict = {}nowplaying_dict['id'] = item['data-subject']nowplaying_dict['name'] = item['data-title']# nowplaying_list.append(nowplaying_dict)# for tag_img_item in item.find_all('img'):# nowplaying_dict['name'] = tag_img_item['alt']nowplaying_list.append(nowplaying_dict)# print("电影的id和名称:\r\n",nowplaying_list)# 网友对电影的评论requrl = 'https://movie.douban.com/subject/' + nowplaying_list[5]['id'] + '/comments' +'?' +'start=0' + '&limit=20'resp = request.urlopen(requrl)html_data_comment = resp.read().decode('utf-8')soup = bs(html_data_comment, 'html.parser')comment_div_lits = soup.find_all('div', class_='comment')# print("网友对电影-战狼的评论HTML内容:\r\n",comment_div_lits)eachCommentList = [];for item in comment_div_lits:if item.find_all('p')[0].string is not None:eachCommentList.append(item.find_all('p')[0].string)# print("网友对电影-战狼的评论:",comment_div_lits)# 为了方便进行数据进行清洗,我们将列表中的数据放在一个字符串数组中comments = ''for k in range(len(eachCommentList)):comments = comments + (str(eachCommentList[k])).strip()# print("网友对电影-战狼的评论[数据清洗后]:\r\n",comments)# /^(\w|-|[\u4E00-\u9FA5])*$/# ^ 以后面的为开头# $ 以前面的为结尾# \w 数字,字母,下划线,.# \u4E00-\u9FA5 中文# * 代表前面出现0次或多次# | 或者# 所以整个的意思是匹配一个 数字,字母,下划线,-,.,中文组成的一个字串# 使用Pattern匹配文本,获得匹配结果,无法匹配时将返回Nonepattern = re.compile(r'[\u4e00-\u9fa5]+')filterdata = re.findall(pattern, comments)cleaned_comments = ''.join(filterdata)# print("网友对电影-战狼的评论[数据清洗后]:\r\n",cleaned_comments)# 进行词频统计,先要进行中文分词操作。这里使用的是结巴分词segment = jieba.lcut(cleaned_comments)words_df=pd.DataFrame({'segment':segment})# print("[分词之后的结果]:\r\n",words_df)# 清除停用词# 停用词放在一个stopwords.txt文件中,将我们的数据与停用词进行比对即可#quoting=3全不引用stopwords=pd.read_csv("stopwords.txt",index_col=False,quoting=3,sep="\t",names=['stopword'], encoding='utf-8')words_df=words_df[~words_df.segment.isin(stopwords.stopword)]# print("[清除停用词后]:\r\n",words_df.head())# 词频统计words_stat=words_df.groupby(by=['segment'])['segment'].agg({"计数":numpy.size})words_stat=words_stat.reset_index().sort_values(by=["计数"],ascending=False)# print("[词频统计后]:\r\n",words_stat.head())# 用词云进行显示backgroud_Image = plt.imread('man.jpg')wordcloud = WordCloud(background_color='white',mask=backgroud_Image,font_path='C:\Windows\Fonts\STZHONGS.TTF', # 若是有中文的话,这句代码必须添加,不然会出现方框,不出现汉字max_words=2000,stopwords=STOPWORDS,max_font_size=150,random_state=30)word_frequence = {x[0]:x[1] for x in words_stat.head(1000).values}print("[用词云进行显示--字典类型]:\r\n", word_frequence)word_frequence_list = []for key in word_frequence:temp = (key,word_frequence[key])word_frequence_list.append(temp)print("[用词云进行显示--LIST]:\r\n", word_frequence_list)# fit_words(frequencies) //根据词频生成词云# generate(text) //根据文本生成词云# generate_from_frequencies(frequencies[, ...]) //根据词频生成词云# generate_from_text(text) //根据文本生成词云# word_frequence 为字典类型,可以直接传入wordcloud.fit_words()# word_frequence = {x[0]:x[1] for x in words_stat.head(1000).values}# wordcloud = wordcloud.fit_words(word_frequence)# def fit_words(self, frequencies):# """Create a word_cloud from words and frequencies.## Alias to generate_from_frequencies.## Parameters# ----------# frequencies : dict from string to float# A contains words and associated frequency.## Returns# -------# self# """# return self.generate_from_frequencies(frequencies)wordcloud=wordcloud.fit_words(word_frequence)plt.imshow(wordcloud)plt.show()
完整代码[分页]
#coding:utf-8__author__ = 'hang'import warningswarnings.filterwarnings("ignore")import jieba #分词包import numpy #numpy计算包import codecs #codecs提供的open方法来指定打开的文件的语言编码,它会在读取的时候自动转换为内部unicodeimport reimport pandas as pdimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom urllib import requestfrom bs4 import BeautifulSoup as bs# %matplotlib inlineimport matplotlibmatplotlib.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (10.0, 5.0)from wordcloud import WordCloud, STOPWORDS, ImageColorGenerator#词云包#分析网页函数def getNowPlayingMovie_list():resp = request.urlopen('https://movie.douban.com/nowplaying/hangzhou/')html_data = resp.read().decode('utf-8')soup = bs(html_data, 'html.parser')nowplaying_movie = soup.find_all('div', id='nowplaying')nowplaying_movie_list = nowplaying_movie[0].find_all('li', class_='list-item')nowplaying_list = []for item in nowplaying_movie_list:nowplaying_dict = {}nowplaying_dict['id'] = item['data-subject']for tag_img_item in item.find_all('img'):nowplaying_dict['name'] = tag_img_item['alt']nowplaying_list.append(nowplaying_dict)return nowplaying_list#爬取评论函数def getCommentsById(movieId, pageNum):eachCommentList = [];if pageNum>0:start = (pageNum-1) * 20else:return Falserequrl = 'https://movie.douban.com/subject/' + movieId + '/comments' +'?' +'start=' + str(start) + '&limit=20'print(requrl)resp = request.urlopen(requrl)html_data = resp.read().decode('utf-8')soup = bs(html_data, 'html.parser')comment_div_lits = soup.find_all('div', class_='comment')for item in comment_div_lits:if item.find_all('p')[0].string is not None:eachCommentList.append(item.find_all('p')[0].string)return eachCommentListdef main():#循环获取第一个电影的前10页评论commentList = []NowPlayingMovie_list = getNowPlayingMovie_list()for i in range(10):num = i + 1commentList_temp = getCommentsById(NowPlayingMovie_list[0]['id'], num)commentList.append(commentList_temp)#将列表中的数据转换为字符串comments = ''for k in range(len(commentList)):comments = comments + (str(commentList[k])).strip()#使用正则表达式去除标点符号pattern = re.compile(r'[\u4e00-\u9fa5]+')filterdata = re.findall(pattern, comments)cleaned_comments = ''.join(filterdata)#使用结巴分词进行中文分词segment = jieba.lcut(cleaned_comments)words_df=pd.DataFrame({'segment':segment})#去掉停用词stopwords=pd.read_csv("stopwords.txt",index_col=False,quoting=3,sep="\t",names=['stopword'], encoding='utf-8')#quoting=3全不引用words_df=words_df[~words_df.segment.isin(stopwords.stopword)]#统计词频words_stat=words_df.groupby(by=['segment'])['segment'].agg({"计数":numpy.size})words_stat=words_stat.reset_index().sort_values(by=["计数"],ascending=False)# 用词云进行显示backgroud_Image = plt.imread('man.jpg')wordcloud = WordCloud(background_color='white',mask=backgroud_Image,font_path='C:\Windows\Fonts\STZHONGS.TTF', # 若是有中文的话,这句代码必须添加,不然会出现方框,不出现汉字max_words=2000,stopwords=STOPWORDS,max_font_size=150,random_state=30)word_frequence = {x[0]: x[1] for x in words_stat.head(1000).values}print("[用词云进行显示--字典类型]:\r\n", word_frequence)word_frequence_list = []for key in word_frequence:temp = (key, word_frequence[key])word_frequence_list.append(temp)print("[用词云进行显示--LIST]:\r\n", word_frequence_list)# fit_words(frequencies) //根据词频生成词云# generate(text) //根据文本生成词云# generate_from_frequencies(frequencies[, ...]) //根据词频生成词云# generate_from_text(text) //根据文本生成词云# word_frequence 为字典类型,可以直接传入wordcloud.fit_words()# def fit_words(self, frequencies):# """Create a word_cloud from words and frequencies.## Alias to generate_from_frequencies.## Parameters# ----------# frequencies : dict from string to float# A contains words and associated frequency.## Returns# -------# self# """# return self.generate_from_frequencies(frequencies)wordcloud = wordcloud.fit_words(word_frequence)img_colors = ImageColorGenerator(backgroud_Image)wordcloud.recolor(color_func=img_colors)plt.imshow(wordcloud)plt.axis('off')plt.show()print('display success!')#主函数main()
上图基本反映了《敦刻尔克》这部电影的情况。
参考来源: https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000010473819