MyBatis性能优化
1.延迟加载
1.1 什么是延迟加载(按需加载)
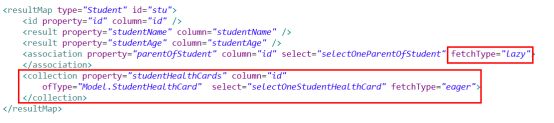
resultMap中的association(has a)和collection(has some)标签具有延迟加载的功能。
延迟加载的意思是说,在关联查询时,利用延迟加载,先加载主信息。需要关联信息时再去按需加载关联信息。这样会大大提高数据库性能,因为查询单表要比关联查询多张表速度要快。
设置延迟加载
Mybatis默认是没开启延迟加载功能的,我们需要手动开启。
需要在SqlMapConfig.xml文件中,在标签中开启延迟加载功能。
lazyLoadingEnabled、aggressiveLazyLoading
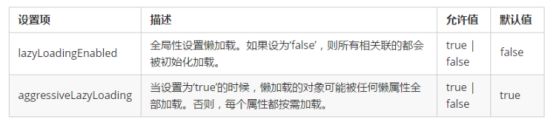
在最新官方MyBatis文档里,有上面这2个属性,一个是延迟加载,一个是分层加载。
lazyLoadingEnabled 默认值为false,那么在有级联关系的resultMap里,查询后会加载出所有的级联关系,当然有时候我们并不需要这些所有的时候,我们就可以应用到延迟加载给我们带来的好处了。
aggressiveLazyLoading默认值是true,这里我称之为分层加载,大概意思是如果它为true,那么当我使用了延迟加载,要么所有级联都不加载,要么如果我加载一个,其他都得加载。
aggressiveLazyLoading值是false 那么就是按需加载,如果是true表示只要使用一个级联对象,就全部加载!
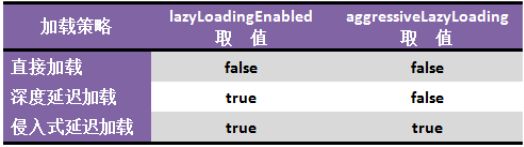
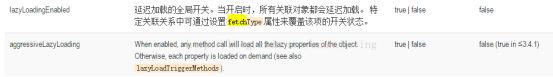
- 全局配置

fetchType是可以注明在association 和 collection里的,选值为eager和lazy,就是为了方便我们结合aggressiveLazyLoading(false)来配合使用的,让延迟加载发挥到极致,即只加载我需要的! - 局部配置
1.2 延迟加载测试
public class Student {
private Integer id;
private String studentName;
private String studentAge;
private List studentHealthCards;
private ParentOfStudent parentOfStudent;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getStudentName() {
return studentName;
}
public void setStudentName(String studentName) {
this.studentName = studentName;
}
public String getStudentAge() {
return studentAge;
}
public void setStudentAge(String studentAge) {
this.studentAge = studentAge;
}
public List getStudentHealthCards() {
return studentHealthCards;
}
public void setStudentHealthCards(List studentHealthCards) {
this.studentHealthCards = studentHealthCards;
}
public ParentOfStudent getParentOfStudent() {
return parentOfStudent;
}
public void setParentOfStudent(ParentOfStudent parentOfStudent) {
this.parentOfStudent = parentOfStudent;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [id=" + id + ", studentName=" + studentName + ", studentAge=" + studentAge + "]";
}
}
- StudentHealthCard:
public class StudentHealthCard {
private Integer id;
private Integer stu_id;
private String name;
private String message;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Integer getStu_id() {
return stu_id;
}
public void setStu_id(Integer stu_id) {
this.stu_id = stu_id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "StudentHealthCard [id=" + id + ", stu_id=" + stu_id + ", name=" + name + ", message=" + message + "]";
}
}
ParentOfStudent:
public class ParentOfStudent {
private Integer id;
private Integer stu_id;
private String name;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Integer getStu_id() {
return stu_id;
}
public void setStu_id(Integer stu_id) {
this.stu_id = stu_id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ParentOfStudent [id=" + id + ", stu_id=" + stu_id + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
}
- Mapper文件
<mapper namespace="com.mybatis.mapper.StudentMapper">
<resultMap type="Student" id="stu">
<id property="id" column="id" />
<result property="studentName" column="studentName" />
<result property="studentAge" column="studentAge" />
<association property="parentOfStudent" column="id"
select="selectOneParentOfStudent" fetchType="eager">
association>
<collection property="studentHealthCards" column="id"
ofType="Model.StudentHealthCard"
select="selectOneStudentHealthCard" fetchType="eager">
collection>
resultMap>
<select id="selectOneStudent" resultMap="stu">
select * from student
where id = #{id}
select>
<select id="selectOneParentOfStudent" resultType="ParentOfStudent">
select * from
parentofstudent where stu_id = #{id}
select>
<select id="selectOneStudentHealthCard" resultType="StudentHealthCard">
select *
from studenthealthcard where stu_id = #{id}
select>
mapper>
- 测试
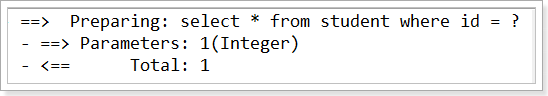
情况1:开启延迟加载,默认分层加载,不开启局部加载
执行语句 Student student = sm.selectOneStudent(1);
以下是运行结果:
执行语句:Student student = sm.selectOneStudent(1);
student.getParentOfStudent();
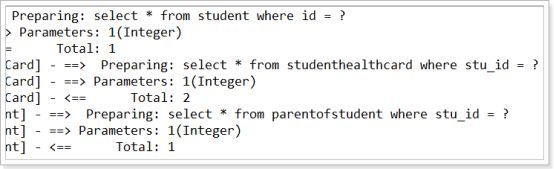
这就是默认分层加载的后果,好的那么现在我把分层加载设置为false
情况2:开启延迟加载,分层加载false,不适用局部加载
执行语句 Student student = sm.selectOneStudent(1);
以下是运行结果:
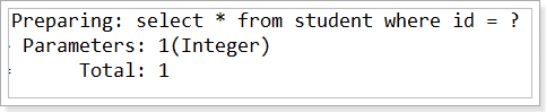
执行语句:Student student = sm.selectOneStudent(1);
student.getParentOfStudent();
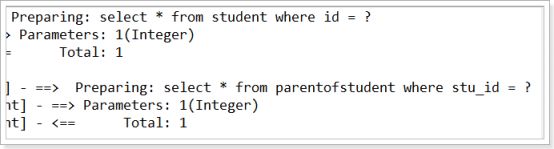
好了 3条sql变成了2条
情况3:就是使用fetchType的情况下,可以指明即使在延迟加载情况下也可以立即加载某个级联关系!
2. MyBatis缓存
2.1 MyBatis缓存分析
mybatis提供查询缓存,如果缓存中有数据就不用从数据库中获取,用于减轻数据压力,提高系统性能
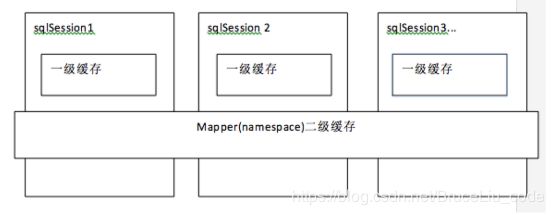
一级缓存是SqlSession级别的缓存。在操作数据库时需要构造 sqlSession对象,在对象中有一个数据结构(HashMap)用于存储缓存数据。不同的sqlSession之间的缓存数据区域(HashMap)是互相不影响的。
二级缓存是mapper级别的缓存,多个SqlSession去操作同一个Mapper的sql语句,多个SqlSession可以共用二级缓存,二级缓存是跨SqlSession的。
Mybatis的缓存,包括一级缓存和二级缓存
一级缓存指的就是sqlsession,在sqlsession中有一个数据区域,是map结构,这个区域就是一级缓存区域。一级缓存中的key是由sql语句、条件、statement等信息组成一个唯一值。一级缓存中的value,就是查询出的结果对象。
二级缓存指的就是同一个namespace下的mapper,二级缓存中,也有一个map结构,这个区域就是二级缓存区域。二级缓存中的key是由sql语句、条件、statement等信息组成一个唯一值。二级缓存中的value,就是查询出的结果对象。
一级缓存是默认使用的。
二级缓存需要手动开启。
2.2 一级缓存

第一次发起查询用户id为1的用户信息,先去找缓存中是否有id为1的用户信息,如果没有,从数据库查询用户信息。得到用户信息,将用户信息存储到一级缓存中。
如果sqlSession去执行commit操作(执行插入、更新、删除),清空SqlSession中的一级缓存,这样做的目的为了让缓存中存储的是最新的信息,避免脏读。
第二次发起查询用户id为1的用户信息,先去找缓存中是否有id为1的用户信息,缓存中有,直接从缓存中获取用户信息。
Mybatis默认支持一级缓存。
- 测试1
@Test
public void test1(){
Student s1 = mapper.selectOneStudent(1);
Student s2 = mapper.selectOneStudent(1);
System.out.println(s1==s2);
}
- 测试2
@Test
public void test1(){
Student s1 = mapper.selectOneStudent(1);
//session.commit();
//session.clearCache();
Student s2 = mapper.selectOneStudent(1);
System.out.println(s1==s2);
}
-
应用
正式开发,是将mybatis和spring进行整合开发,事务控制在service中。
一个service方法中包括很多mapper方法调用。
service{//开始执行时,开启事务,创建SqlSession对象 //第一次调用mapper的方法findUserById(1) //第二次调用mapper的方法findUserById(1),从一级缓存中取数据 //方法结束,sqlSession关闭}
如果是执行两次service调用查询相同的用户信息,不走一级缓存,因为session方法结束,sqlSession就关闭,一级缓存就清空。
2.3二级缓存
下图是多个sqlSession请求UserMapper的二级缓存图解。
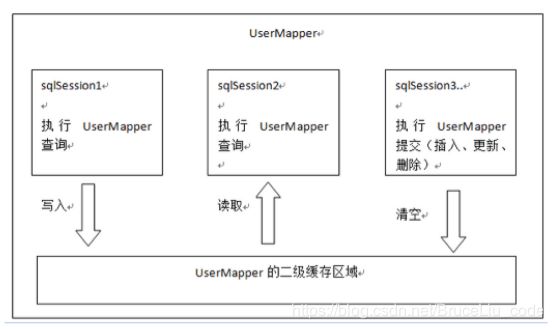
二级缓存是mapper级别的。
第一次调用mapper下的SQL去查询用户信息。查询到的信息会存到该mapper对应的二级缓存区域内。
第二次调用相同namespace下的mapper映射文件(xml)中相同的SQL去查询用户信息。会去对应的二级缓存内取结果。
如果调用相同namespace下的mapper映射文件中的增删改SQL,并执行了commit操作。此时会清空该namespace下的二级缓存。
- 开启二级缓存
Mybatis默认是没有开启二级缓存
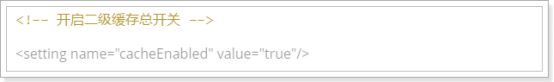
1.在核心配置文件SqlMapConfig.xml中加入以下内容(开启二级缓存总开关):
在settings标签中添加以下内容:
2.在StudentMapper映射文件中,加入以下内容,开启二级缓存
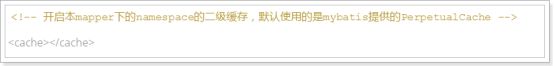
3.实现序列化
由于二级缓存的数据不一定都是存储到内存中,它的存储介质多种多样,所以需要给缓存的对象执行序列化。
缓存默认是存入内存中,但是如果需要把缓存对象存入硬盘那么久需要序列化(实体类要实现)
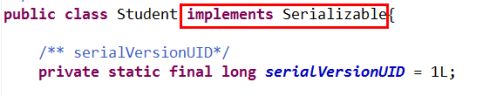
如果该类存在父类,那么父类也要实现序列化。 - 测试1
@Test
public void test2(){
SqlSessionFactory factory = MyBatisUtil.getSqlSessionFactory();
SqlSession session1 = factory.openSession();
StudentMapper mapper1 = session1.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student s1 = mapper1.selectOneStudent(1);
System.out.println(s1);
session1.close();
SqlSession session2 = factory.openSession();
StudentMapper mapper2 = session2.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student s2 = mapper2.selectOneStudent(1);
System.out.println(s2);
}
- 测试2
@Test
public void test2(){
SqlSessionFactory factory = MyBatisUtil.getSqlSessionFactory();
SqlSession session1 = factory.openSession();
StudentMapper mapper1 = session1.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student s1 = mapper1.selectOneStudent(1);
System.out.println(s1);
session1.close();
SqlSession session2 = factory.openSession();
StudentMapper mapper2 = session2.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
s1.setStudentName("王二小");
mapper2.updateStudent(s1);
session2.commit();
session2.close();
SqlSession session3= factory.openSession();
StudentMapper mapper3 = session3.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student s2 = mapper3.selectOneStudent(1);
System.out.println(s2);
}
根据SQL分析,确实是清空了二级缓存了。
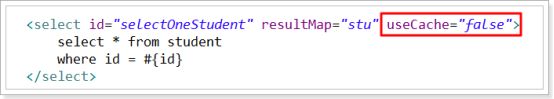
- 禁用二级缓存
该statement中设置useCache=false,可以禁用当前select语句的二级缓存,即每次查询都是去数据库中查询,默认情况下是true,即该statement使用二级缓存。
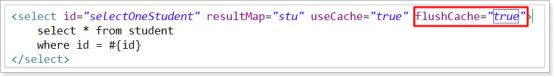
- 刷新二级缓存
该statement中设置flushCache=true可以刷新当前的二级缓存,默认情况下如果是select语句,那么flushCache是false。如果是insert、update、delete语句,那么flushCache是true。
如果查询语句设置成true,那么每次查询都是去数据库查询,即意味着该查询的二级缓存失效。
如果查询语句设置成false,即使用二级缓存,那么如果在数据库中修改了数据,而缓存数据还是原来的,这个时候就会出现脏读。

2.4整合ehcache
- ehcache使用
Ehcache是一个分布式缓存。
分布式缓存
系统为了提高性能,通常会对系统采用分布式部署(集群部署方式)
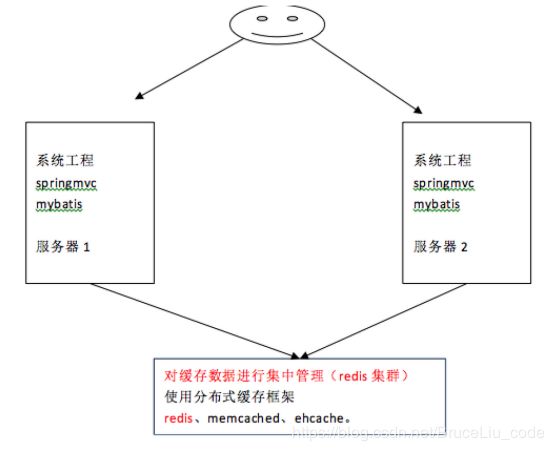
不使用分布式缓存,缓存的数据在各个服务单独存储,不方便开发。所以要使用分布式缓存对缓存数据进行集中式管理。
Mybatis自身无法实现分布式缓存,需要和其它分布式缓存框架进行整合。
整合思路(重点)
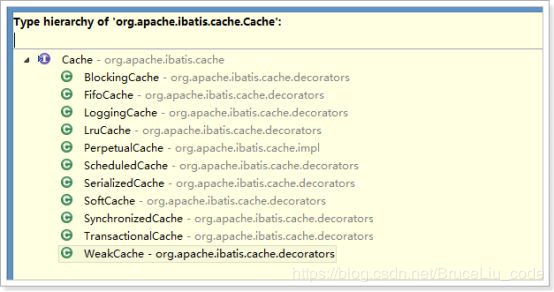
Mybatis提供了一个cache接口,同时它自己有一个默认的实现类 PerpetualCache。
通过实现cache接口可以实现mybatis缓存数据通过其他缓存数据库整合,mybatis的特长是sql,缓存数据管理不是mybatis的特长,为了提高mybatis的性能,所以需要mybatis和第三方缓存数据库整合,比如ehcache、memcache、redis等
Mybatis提供接口如下:
Mybatis的默认实现类:
- 整合ehcache的步骤
引入ehcache的jar包;
在mapper映射文件中,配置cache标签的type为ehcache对cache接口的实现类类型。
加入ehcache的配置文件
第一步:引入ehcache的jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.ehcachegroupId>
<artifactId>ehcacheartifactId>
<version>3.5.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.cachesgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-ehcacheartifactId>
<version>1.1.0version>
dependency>
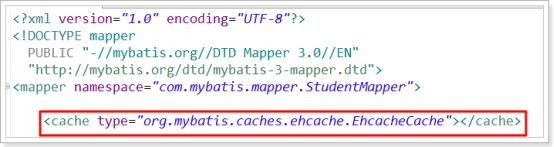
第二步:配置cache的type属性
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache" />
第三步:添加ehcache的配置文件
在classpath下添加ehcache.xml
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="../config/ehcache.xsd">
<diskStore path="F:\develop\ehcache" />
<defaultCache maxElementsInMemory="1000"
maxElementsOnDisk="10000000"
eternal="false"
overflowToDisk="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="120"
timeToLiveSeconds="120"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU">
defaultCache>
ehcache>
-
应用场景
使用场景:对于访问响应速度要求高,但是实时性不高的查询,可以采用二级缓存技术。
注意:在使用二级缓存的时候,要设置一下刷新间隔(cache标签中有一个flashInterval属性)来定时刷新二级缓存,这个刷新间隔根据具体需求来设置,比如设置30分钟、60分钟等,单位为毫秒。 -
局限性
Mybatis二级缓存对细粒度的数据级别的缓存实现不好。
场景:对商品信息进行缓存,由于商品信息查询访问量大,但是要求用户每次查询都是最新的商品信息,此时如果使用二级缓存,就无法实现当一个商品发生变化只刷新该商品的缓存信息而不刷新其他商品缓存信息,因为二级缓存是mapper级别的,当一个商品的信息发送更新,所有的商品信息缓存数据都会清空。
解决此类问题,需要在业务层根据需要对数据有针对性的缓存。比如可以对经常变化的 数据操作单独放到另一个namespace的mapper中。