MS COCO:指标问题 MAP,MAR: 以项目:mmdetection(v1.0rc0)为例
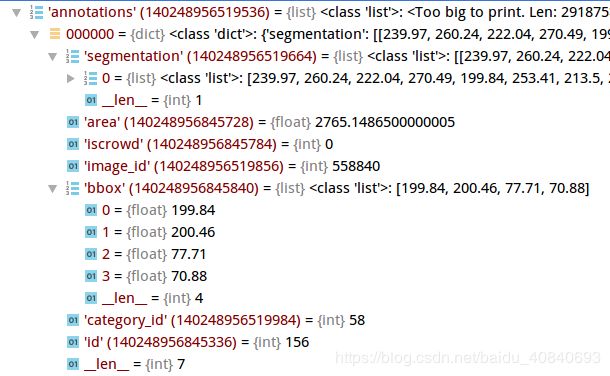
COCO数据集:
{
"info": info,
"licenses": [license],
"images": [image],
"annotations": [annotation],
"categories": [category]
}数据集信息
许可
类别:大类-小类(80)
images:40504
annotations:291875
coco.py 中定义了以下 API:
COCO 类 - 用于加载 COCO 标注文件并准备所需的数据结构.
decodeMask - Decode binary mask M encoded via run-length encoding.
encodeMask - Encode binary mask M using run-length encoding.
getAnnIds - 获取满足条件的标注信息的 ids.
getCatIds - 获取满足条件的类别的 ids.
getImgIds - 获取满足条件的图片的 ids.
loadAnns - 加载指定 ids 对应的标注信息.
loadCats - 加载指定 ids 对应的类别.
loadImgs - 加载指定 ids 对应的图片.
annToMask - 将 segmentation 标注信息转换为二值 mask.
showAnns - 显示指定 ids 的标注信息到对应的图片上.
loadRes - 加载算法的结果并创建可用于访问数据的 API .
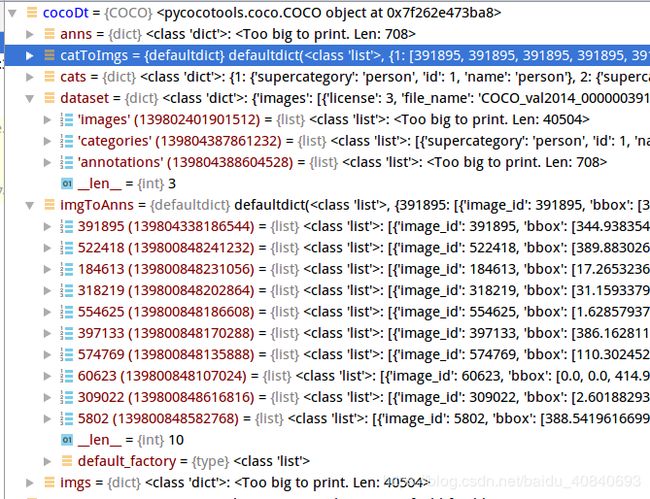
download - 从 mscoco.org 服务器下载 COCO 图片数据集.- imgToAnns: 将图片 id 和标注信息 关联;
- catToImgs: 将类别 id 和图片 id 关联.
这样做的好处就是: 对于给定的图片 id, 就可以快速找到其所有的标注信息; 对于给定的类别 id, 就可以快速找到属于该类的所有图片.
def createIndex(self):
"""
创建索引, 属于构造函数的一部分.
"""
# create index
print('creating index...')
anns, cats, imgs = {}, {}, {}
# imgToAnns: 将图片 id 和标注信息 关联; 给定图片 id, 就可以找到其所有的标注信息
# catToImgs: 将类别 id 和图片 id 关联; 给定类别 id, 就可以找到属于这类的所有图片
imgToAnns,catToImgs = defaultdict(list),defaultdict(list)
if 'annotations' in self.dataset:
for ann in self.dataset['annotations']:
imgToAnns[ann['image_id']].append(ann)
anns[ann['id']] = ann
if 'images' in self.dataset:
for img in self.dataset['images']:
imgs[img['id']] = img
if 'categories' in self.dataset:
for cat in self.dataset['categories']:
cats[cat['id']] = cat
if 'annotations' in self.dataset and 'categories' in self.dataset:
for ann in self.dataset['annotations']:
catToImgs[ann['category_id']].append(ann['image_id'])
print('index created!!!')
# 给几个类成员赋值
self.anns = anns
self.imgs = imgs
self.cats = cats
self.imgToAnns = imgToAnns
self.catToImgs = catToImgs关于指标问题:
概要:
https://m.oldpan.me/archives/understand-coco-metric
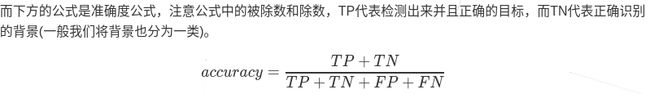
Pixel Accuracy像素准确度
表示检测物体的准确度,重点判断标准为是否检测到了物体
Pixel Precision像素精度
代表检测到所有的物体中覆盖的精确度,重点判断mask是否精确地覆盖到了该物体。
像素精度是在已经检测到的基础上(不论检测是否失误)进行评测的标准
IOU概念:
https://oldpan.me/archives/iu-iou-intersection-over-union-python
语义分割
https://blog.csdn.net/u014593748/article/details/71698246?fps=1&locationNum=5
检测-分类
https://oldpan.me/archives/understand-coco-metric
https://blog.csdn.net/Gentleman_Qin/article/details/84519388
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/33273532
https://blog.csdn.net/syoung9029/article/details/56276567#t0
这里有个需求,这边想建立一个统一的标准,去判断mask-rcnn和deeplabv3的算法性能好坏,我是这样设想的,首先是resize应该是同一大小,数据集类别数目统一,数据增强统一,然后mask-rcnn的掩膜作为分割,与GroundTruth对比,计算mIOU,这里阈值取定为0.5,这样就可以统一,和deeplab计算的mIOU去对比,把mask-rcnn当成一个语义分割问题对待,个人想法,不知道是否对
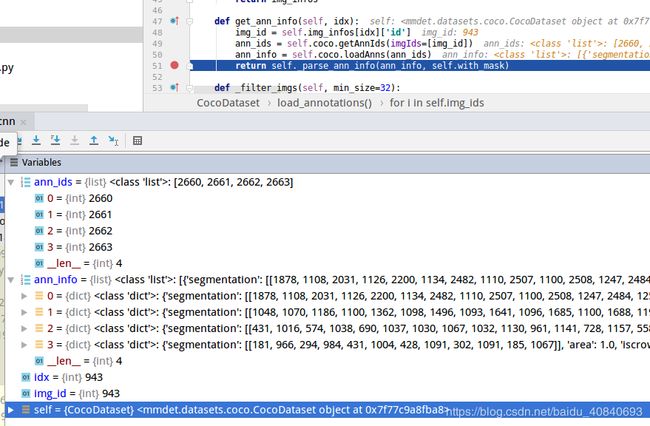
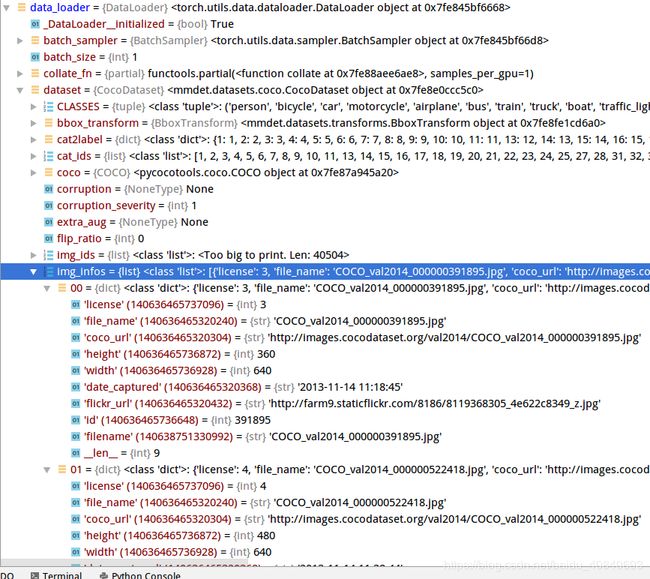
COCO数据集太长了,val2014高达40504张,我们只做一些小测试,修改代码,只载入一部分:
mmdetection/mmdet/datasets/coco.py
def load_annotations(self, ann_file):
self.coco = COCO(ann_file)
self.cat_ids = self.coco.getCatIds()
self.cat2label = {
cat_id: i + 1
for i, cat_id in enumerate(self.cat_ids)
}
self.img_ids = self.coco.getImgIds()
img_infos = []
# for i in self.img_ids:
# info = self.coco.loadImgs([i])[0]
# info['filename'] = info['file_name']
# img_infos.append(info)
for key, i in enumerate(self.img_ids):
if key == 10:
break
info = self.coco.loadImgs([i])[0]
info['filename'] = info['file_name']
img_infos.append(info)
return img_infos通过枚举函数控制多少个,我们这里只需要10个
接着我们看下图片经过网络后的输出:
mmdetection/tools/test.py
def single_gpu_test(model, data_loader, show=False, ids=None, groundtruth=None, scale_test=None):
model.eval()
results = []
dataset = data_loader.dataset
prog_bar = mmcv.ProgressBar(len(dataset))
for i, data in enumerate(data_loader):
with torch.no_grad():
result = model(return_loss=False, rescale=not show, **data)mmdetection/mmdet/models/detectors/base.py
def show_result(self,
data,
result,
img_norm_cfg,
dataset=None,
score_thr=0.3,
ids=None,
groundtruth=None,
scale_test=None,
ori_hW=None):
if isinstance(result, tuple):
bbox_result, segm_result = result
else:
bbox_result, segm_result = result, None两个都是0-79,共80类
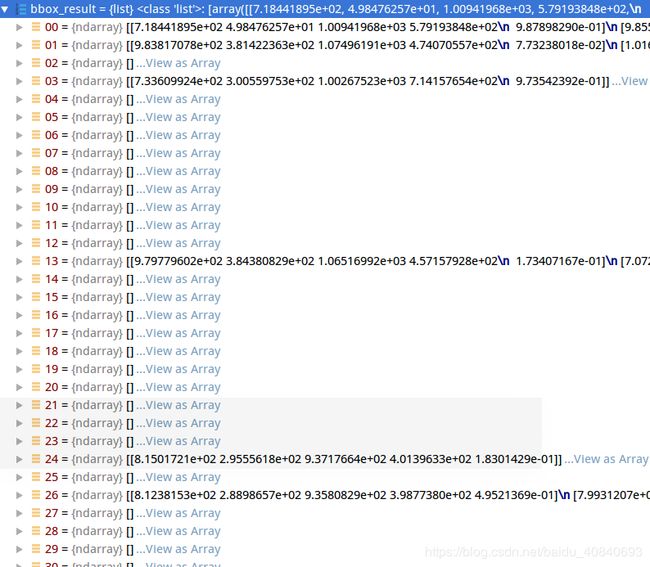
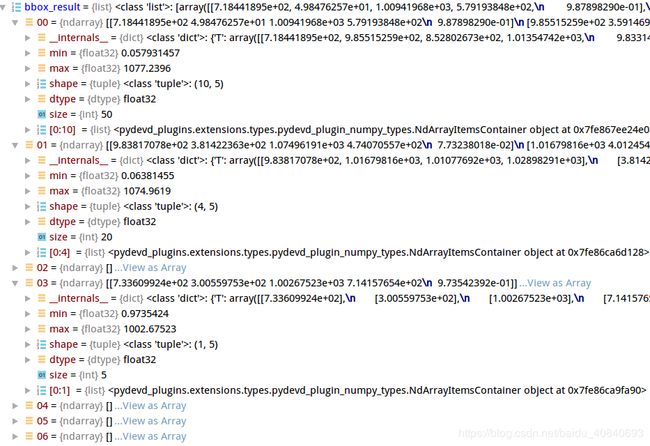
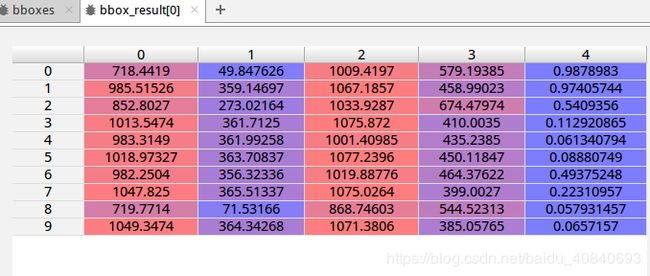
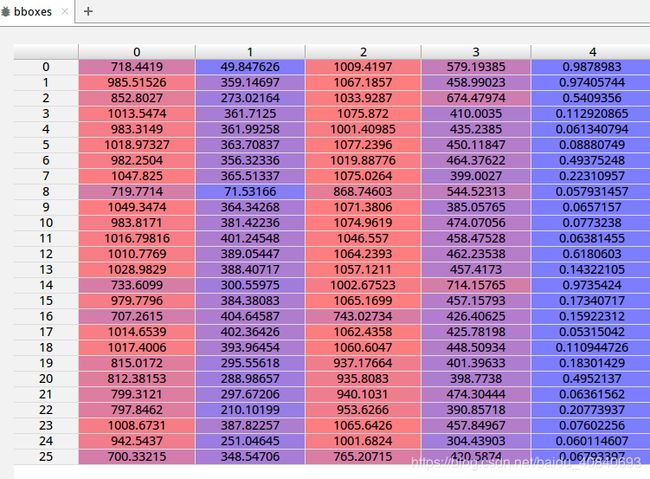
以bbox为例,每一类有很多框或分割:
可视化展示一下第一类的(10,5)
一共五个属性
在mmcv/visualization/image.py中可以知道,是左上x,y 右下x,y 置信度
for bbox, label in zip(bboxes, labels):
bbox_int = bbox.astype(np.int32)
left_top = (bbox_int[0], bbox_int[1])
right_bottom = (bbox_int[2], bbox_int[3])
cv2.rectangle(
img, left_top, right_bottom, bbox_color, thickness=thickness)
label_text = class_names[
label] if class_names is not None else 'cls {}'.format(label)
if len(bbox) > 4:
label_text += '|{:.02f}'.format(bbox[-1])
cv2.putText(img, label_text, (bbox_int[0], bbox_int[1] - 2),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, font_scale, text_color)直接合并成一个array:
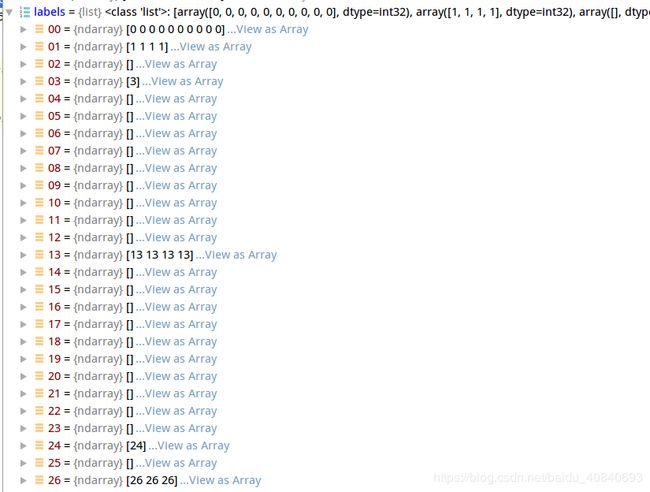
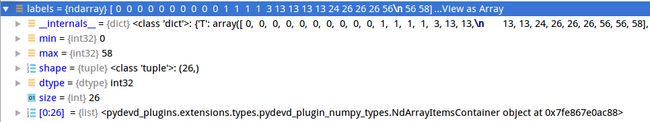
bboxes = np.vstack(bbox_result) 合并后的array有其对应的lable:
labels = [
np.full(bbox.shape[0], i, dtype=np.int32)
for i, bbox in enumerate(bbox_result)
]
labels = np.concatenate(labels)置信度阈值为
score_thr=0.3大于阈值的显示:
if score_thr > 0:
assert bboxes.shape[1] == 5
scores = bboxes[:, -1]
inds = scores > score_thr
bboxes = bboxes[inds, :]
labels = labels[inds]
bbox_color = color_val(bbox_color)
text_color = color_val(text_color)
for bbox, label in zip(bboxes, labels):
bbox_int = bbox.astype(np.int32)
left_top = (bbox_int[0], bbox_int[1])
right_bottom = (bbox_int[2], bbox_int[3])
cv2.rectangle(
img, left_top, right_bottom, bbox_color, thickness=thickness)
label_text = class_names[
label] if class_names is not None else 'cls {}'.format(label)
if len(bbox) > 4:
label_text += '|{:.02f}'.format(bbox[-1])
cv2.putText(img, label_text, (bbox_int[0], bbox_int[1] - 2),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, font_scale, text_color)以segm_result为例:
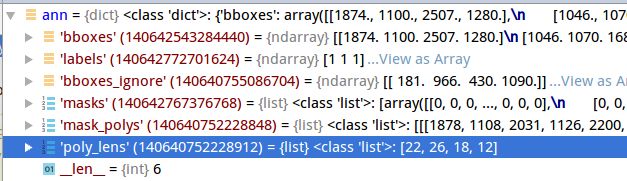
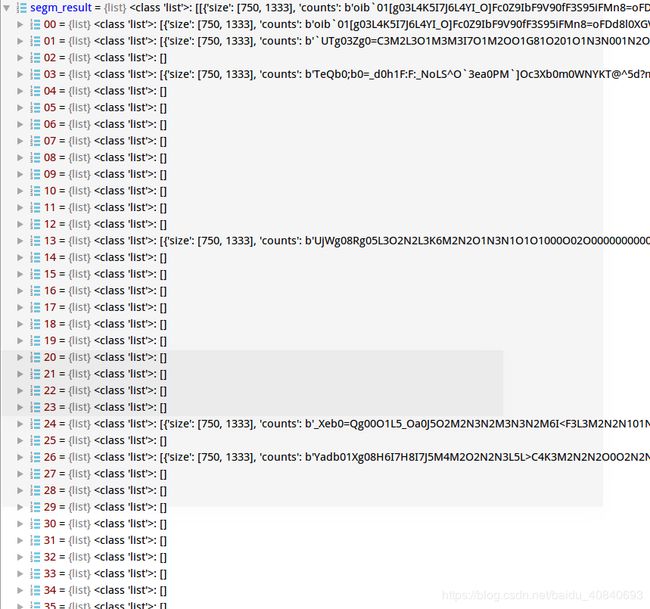
if segm_result is not None:
segms = mmcv.concat_list(segm_result)
inds = np.where(bboxes[:, -1] > score_thr)[0]
for i in inds:
color_mask = np.random.randint(
0, 256, (1, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
mask = maskUtils.decode(segms[i]).astype(np.bool)
img_show[mask] = img_show[mask] * 0.5 + color_mask * 0.5segms:通过阈值0.3判断哪些mask和bbox会被显示:
遍历符合阈值的mask,随机生成颜色(因为是实例分割):
color_mask = np.random.randint(0, 256, (1, 3), dtype=np.uint8)这里返回的seg是被编码后的,需要
pycocotools解码:
mask = maskUtils.decode(segms[i]).astype(np.bool)让我们回到mmdetection/tools/test.py
def single_gpu_test(model, data_loader, show=False, ids=None, groundtruth=None, scale_test=None):返回我们需要的数据结果集合
results一共10张图像的结果:
第一张:COCO_val2014_000000391895.jpg
configs/mask_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x.py checkpoints/mask_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_20181010-069fa190.pth --eval bbox segm --out temp_pred/maskrcnn_out.pkl
进行评估:检测和分割
evaluate bbox and segm
先保存到json
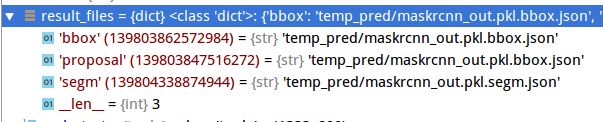
def results2json(dataset, results, out_file):
result_files = dict()
if isinstance(results[0], list):
json_results = det2json(dataset, results)
result_files['bbox'] = '{}.{}.json'.format(out_file, 'bbox')
result_files['proposal'] = '{}.{}.json'.format(out_file, 'bbox')
mmcv.dump(json_results, result_files['bbox'])
elif isinstance(results[0], tuple):
json_results = segm2json(dataset, results)
result_files['bbox'] = '{}.{}.json'.format(out_file, 'bbox')
result_files['proposal'] = '{}.{}.json'.format(out_file, 'bbox')
result_files['segm'] = '{}.{}.json'.format(out_file, 'segm')
mmcv.dump(json_results[0], result_files['bbox'])
mmcv.dump(json_results[1], result_files['segm'])
elif isinstance(results[0], np.ndarray):
json_results = proposal2json(dataset, results)
result_files['proposal'] = '{}.{}.json'.format(out_file, 'proposal')
mmcv.dump(json_results, result_files['proposal'])
else:
raise TypeError('invalid type of results')
return result_files
进入
coco_eval(result_files, eval_types, dataset.coco)def coco_eval(result_files, result_types, coco, max_dets=(100, 300, 1000)):
for res_type in result_types:
assert res_type in [
'proposal', 'proposal_fast', 'bbox', 'segm', 'keypoints'
]
if mmcv.is_str(coco):
coco = COCO(coco)
assert isinstance(coco, COCO)
if result_types == ['proposal_fast']:
ar = fast_eval_recall(result_files, coco, np.array(max_dets))
for i, num in enumerate(max_dets):
print('AR@{}\t= {:.4f}'.format(num, ar[i]))
return
for res_type in result_types:
result_file = result_files[res_type]
assert result_file.endswith('.json')
coco_dets = coco.loadRes(result_file)
img_ids = coco.getImgIds()
iou_type = 'bbox' if res_type == 'proposal' else res_type
cocoEval = COCOeval(coco, coco_dets, iou_type)
cocoEval.params.imgIds = img_ids
if res_type == 'proposal':
cocoEval.params.useCats = 0
cocoEval.params.maxDets = list(max_dets)
cocoEval.evaluate()
cocoEval.accumulate()
cocoEval.summarize()coco_det:
一共10个图像:
708条记录-bbox+seg:
遍历
for res_type in result_types:读取
coco_dets = coco.loadRes(result_file)进入
from pycocotools.cocoeval import COCOevalcocoEval = COCOeval(coco, coco_dets, iou_type)
接着进入:
cocoEval.evaluate()
cocoEval.accumulate()
cocoEval.summarize()这里没看懂,先运行一次结果,好低。。。,发现,原来他必须是按照COCO(json)载入在判断,果断用自己的数据集,放弃这种选取10张图片的方式
DONE (t=46.13s).
Accumulating evaluation results...
DONE (t=6.32s).
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.002
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.003
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.75 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.002
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=100 ] = 0.001
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=100 ] = 0.001
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=100 ] = 0.001
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets= 1 ] = 0.000
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets= 10 ] = 0.000
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.000
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=100 ] = 0.000
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=100 ] = 0.000
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=100 ] = 0.000
Loading and preparing results...
DONE (t=0.01s)
creating index...
index created!
Running per image evaluation...
Evaluate annotation type *segm*
DONE (t=49.32s).
Accumulating evaluation results...
DONE (t=6.34s).
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.002
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.003
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.75 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.002
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=100 ] = 0.001
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=100 ] = 0.001
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=100 ] = 0.001
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets= 1 ] = 0.000
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets= 10 ] = 0.000
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.000
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=100 ] = 0.000
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=100 ] = 0.000
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=100 ] = 0.000
先接着走流程吧,哎心累
首先是cocoEval.evaluate()
def evaluate(self):
'''
Run per image evaluation on given images and store results (a list of dict) in self.evalImgs
:return: None
'''
tic = time.time()
print('Running per image evaluation...')
p = self.params
# add backward compatibility if useSegm is specified in params
if not p.useSegm is None:
p.iouType = 'segm' if p.useSegm == 1 else 'bbox'
print('useSegm (deprecated) is not None. Running {} evaluation'.format(p.iouType))
print('Evaluate annotation type *{}*'.format(p.iouType))
p.imgIds = list(np.unique(p.imgIds))
if p.useCats:
p.catIds = list(np.unique(p.catIds))
p.maxDets = sorted(p.maxDets)
self.params=p
self._prepare()
# loop through images, area range, max detection number
catIds = p.catIds if p.useCats else [-1]
if p.iouType == 'segm' or p.iouType == 'bbox':
computeIoU = self.computeIoU
elif p.iouType == 'keypoints':
computeIoU = self.computeOks
self.ious = {(imgId, catId): computeIoU(imgId, catId) \
for imgId in p.imgIds
for catId in catIds}
evaluateImg = self.evaluateImg
maxDet = p.maxDets[-1]
self.evalImgs = [evaluateImg(imgId, catId, areaRng, maxDet)
for catId in catIds
for areaRng in p.areaRng
for imgId in p.imgIds
]
self._paramsEval = copy.deepcopy(self.params)
toc = time.time()
print('DONE (t={:0.2f}s).'.format(toc-tic))拿到gt和pred
self._prepare() if p.useCats:
gts=self.cocoGt.loadAnns(self.cocoGt.getAnnIds(imgIds=p.imgIds, catIds=p.catIds))
dts=self.cocoDt.loadAnns(self.cocoDt.getAnnIds(imgIds=p.imgIds, catIds=p.catIds))
else:
gts=self.cocoGt.loadAnns(self.cocoGt.getAnnIds(imgIds=p.imgIds))
dts=self.cocoDt.loadAnns(self.cocoDt.getAnnIds(imgIds=p.imgIds))参考:
(一) COCO Python API - 使用篇
https://blog.csdn.net/gzj2013/article/details/82385164
(二) COCO Python API - 源码分析篇https://blog.csdn.net/gzj2013/article/details/82421166
(三) COCO Python API - 数据集类数量分布
https://blog.csdn.net/gzj2013/article/details/82425954
COCO目标检测测评指标
https://www.jianshu.com/p/d7a06a720a2b
计算IOU:
self.ious = {(imgId, catId): computeIoU(imgId, catId) \
for imgId in p.imgIds
for catId in catIds}这里看不到IOU计算的代码,是c语言写的:
https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/96/84/9a07b1095fd8555ba3f3d519517c8743c2554a245f9476e5e39869f948d2/pycocotools-2.0.0.tar.gz
_mask.pyx
# iou computation. support function overload (RLEs-RLEs and bbox-bbox).
def iou( dt, gt, pyiscrowd ):
def _preproc(objs):
if len(objs) == 0:
return objs
if type(objs) == np.ndarray:
if len(objs.shape) == 1:
objs = objs.reshape((objs[0], 1))
# check if it's Nx4 bbox
if not len(objs.shape) == 2 or not objs.shape[1] == 4:
raise Exception('numpy ndarray input is only for *bounding boxes* and should have Nx4 dimension')
objs = objs.astype(np.double)
elif type(objs) == list:
# check if list is in box format and convert it to np.ndarray
isbox = np.all(np.array([(len(obj)==4) and ((type(obj)==list) or (type(obj)==np.ndarray)) for obj in objs]))
isrle = np.all(np.array([type(obj) == dict for obj in objs]))
if isbox:
objs = np.array(objs, dtype=np.double)
if len(objs.shape) == 1:
objs = objs.reshape((1,objs.shape[0]))
elif isrle:
objs = _frString(objs)
else:
raise Exception('list input can be bounding box (Nx4) or RLEs ([RLE])')
else:
raise Exception('unrecognized type. The following type: RLEs (rle), np.ndarray (box), and list (box) are supported.')
return objs
def _rleIou(RLEs dt, RLEs gt, np.ndarray[np.uint8_t, ndim=1] iscrowd, siz m, siz n, np.ndarray[np.double_t, ndim=1] _iou):
rleIou( dt._R, gt._R, m, n, iscrowd.data, _iou.data )
def _bbIou(np.ndarray[np.double_t, ndim=2] dt, np.ndarray[np.double_t, ndim=2] gt, np.ndarray[np.uint8_t, ndim=1] iscrowd, siz m, siz n, np.ndarray[np.double_t, ndim=1] _iou):
bbIou( dt.data, gt.data, m, n, iscrowd.data, _iou.data )
def _len(obj):
cdef siz N = 0
if type(obj) == RLEs:
N = obj.n
elif len(obj)==0:
pass
elif type(obj) == np.ndarray:
N = obj.shape[0]
return N
# convert iscrowd to numpy array
cdef np.ndarray[np.uint8_t, ndim=1] iscrowd = np.array(pyiscrowd, dtype=np.uint8)
# simple type checking
cdef siz m, n
dt = _preproc(dt)
gt = _preproc(gt)
m = _len(dt)
n = _len(gt)
if m == 0 or n == 0:
return []
if not type(dt) == type(gt):
raise Exception('The dt and gt should have the same data type, either RLEs, list or np.ndarray')
# define local variables
cdef double* _iou = 0
cdef np.npy_intp shape[1]
# check type and assign iou function
if type(dt) == RLEs:
_iouFun = _rleIou
elif type(dt) == np.ndarray:
_iouFun = _bbIou
else:
raise Exception('input data type not allowed.')
_iou = malloc(m*n* sizeof(double))
iou = np.zeros((m*n, ), dtype=np.double)
shape[0] = m*n
iou = np.PyArray_SimpleNewFromData(1, shape, np.NPY_DOUBLE, _iou)
PyArray_ENABLEFLAGS(iou, np.NPY_OWNDATA)
_iouFun(dt, gt, iscrowd, m, n, iou)
return iou.reshape((m,n), order='F') maskApi.c
void rleIou( RLE *dt, RLE *gt, siz m, siz n, byte *iscrowd, double *o ) {
siz g, d; BB db, gb; int crowd;
db=malloc(sizeof(double)*m*4); rleToBbox(dt,db,m);
gb=malloc(sizeof(double)*n*4); rleToBbox(gt,gb,n);
bbIou(db,gb,m,n,iscrowd,o); free(db); free(gb);
for( g=0; g0) {
crowd=iscrowd!=NULL && iscrowd[g];
if(dt[d].h!=gt[g].h || dt[d].w!=gt[g].w) { o[g*m+d]=-1; continue; }
siz ka, kb, a, b; uint c, ca, cb, ct, i, u; int va, vb;
ca=dt[d].cnts[0]; ka=dt[d].m; va=vb=0;
cb=gt[g].cnts[0]; kb=gt[g].m; a=b=1; i=u=0; ct=1;
while( ct>0 ) {
c=umin(ca,cb); if(va||vb) { u+=c; if(va&&vb) i+=c; } ct=0;
ca-=c; if(!ca && a 通过代码我们简单的看出,seg的IOU计算,是对整个图像,也就是n*m的矩阵进行对比,当然这里细节还不理解,比如,一个图里有很多类,每一个类有很多框,对应GT也是如此
那么怎么匹配的计算IOU