PCL——点云分割(基于法线微分的分割——DON)
基于点云频率的滤波方法
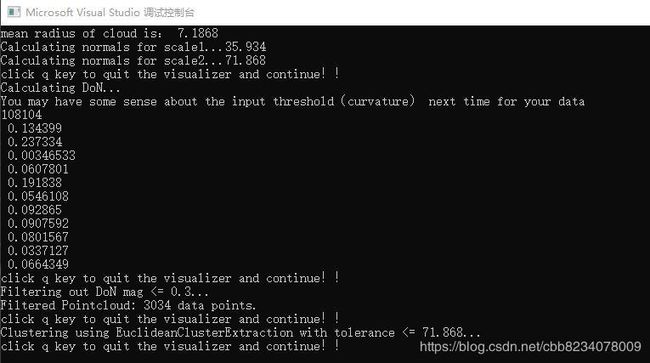
DON点云滤波
DoN算法应该算是一种比较先进的点云滤波算法。分割本质上还是由欧式分割算法完成的。算法的目的是在去除点云低频滤波,低频信息(例如建筑物墙面,地面)往往会对分割产生干扰,高频信息(例如建筑物窗框,路面障碍锥)往往尺度上很小,直接采用 基于临近信息 的滤波器会将此类信息合并至墙面或路面中。所以DoN算法利用了多尺度空间的思想,算法如下:
(1) 在小尺度上计算点云法线1
(2)在大尺度上计算点云法线2
(3)法线1-法线2
(4) 滤去3中值较小的点
(5) 欧式分割
显然,在小尺度上是可以对高频信息进行检测的,此算法可以很好的小尺度高频信息。其在大规模点云(如LiDar点云)中优势尤其明显。
实现算法:
// Create a search tree, use KDTreee for non-organized data.
pcl::search::Search<PointXYZRGB>::Ptr tree;
if (cloud->isOrganized ())
{
tree.reset (new pcl::search::OrganizedNeighbor<PointXYZRGB> ());
}
else
{
tree.reset (new pcl::search::KdTree<PointXYZRGB> (false));
}
// Set the input pointcloud for the search tree
tree->setInputCloud (cloud);
//生成法线估计器(OMP是并行计算,忽略)
pcl::NormalEstimationOMP<PointXYZRGB, PointNormal> ne;
ne.setInputCloud (cloud);
ne.setSearchMethod (tree);
//设定法线方向(要做差,同向很重要)
ne.setViewPoint (std::numeric_limits<float>::max (), std::numeric_limits<float>::max (), std::numeric_limits<float>::max ());
//计算小尺度法线
pcl::PointCloud<PointNormal>::Ptr normals_large_scale (new pcl::PointCloud<PointNormal>);
ne.setRadiusSearch (scale2);
ne.compute (*normals_large_scale);
//计算大尺度法线
pcl::PointCloud<PointNormal>::Ptr normals_large_scale (new pcl::PointCloud<PointNormal>);
ne.setRadiusSearch (scale2);
ne.compute (*normals_large_scale);
//生成DoN分割器
pcl::DifferenceOfNormalsEstimation<PointXYZRGB, PointNormal, PointNormal> don;
don.setInputCloud (cloud);
don.setNormalScaleLarge (normals_large_scale);
don.setNormalScaleSmall (normals_small_scale);
//计算法线差
PointCloud<PointNormal>::Ptr doncloud (new pcl::PointCloud<PointNormal>);
copyPointCloud<PointXYZRGB, PointNormal>(*cloud, *doncloud);
don.computeFeature (*doncloud);
//生成滤波条件:把法线差和阈值比
pcl::ConditionOr<PointNormal>::Ptr range_cond (
new pcl::ConditionOr<PointNormal> ()
);
range_cond->addComparison (pcl::FieldComparison<PointNormal>::ConstPtr (
new pcl::FieldComparison<PointNormal> ("curvature", pcl::ComparisonOps::GT, threshold))
);
//生成条件滤波器,输入滤波条件和点云
pcl::ConditionalRemoval<PointNormal> condrem (range_cond);
condrem.setInputCloud (doncloud);
//导出滤波结果
pcl::PointCloud<PointNormal>::Ptr doncloud_filtered (new pcl::PointCloud<PointNormal>);
condrem.filter (*doncloud_filtered);
//欧式聚类~~~(略)
基于法线微分的分割——DON
点云分割——DON
根据不同尺度下法向量特征的差异性,利用pcl::DifferenceOfNormalsEstimation实现点云分割,在处理有较大尺度变化的场景点云分割效果较好,利用不同支撑半径去估算同一点的两个单位法向量,单位法向量的差定义DoN特征。

DoN算法:
DoN特征源于观察到基于所给半径估计的表面法向量可以反映曲面的内在几何特征,因此这种分割算法是基于法线估计的,需要计算点云中某一点的法线估计。而通常在计算法线估计的时候都会用到邻域信息,很明显邻域大小的选取会影响法线估计的结果。而在DoN算法中,邻域选择的大小就被称为support radius(支持半径)。对点云中某一点选取不同的支持半径,即可以得到不同的法线估计,而法线之间的差异,就是是所说的法线差异。
在这里插入图片描述
代码例程:
(1)对于输入点云数据中的每一点,利用较大的支撑半径rl计算法向量;
(2)对于输入点云数据中的每一点,利用较大的支撑半径rs计算法向量;
(3)对于输入点云数据中的每一点,单位化每一点的法向量差异
(4)过滤所得的向量域(DoN特征向量),分割出目标尺寸对应的点云;
#include