蚁群算法求解TSP问题的源代码
旅行商问题大都是用遗传算法求解,不过蚁群算法比它高效得多,在百度的蚁群算法吧里有人发了个注释清晰的代码,有兴趣的可以去研究一下蚁群算法和模拟退火算法,这两者都可以解决旅行商问题。而关于遗传算法和模拟退火算法,博客园里的某位牛人很清楚地介绍了,发个链接吧
遗传算法入门:http://www.cnblogs.com/heaad/archive/2010/12/23/1914725.html
模拟退火算法入门:http://www.cnblogs.com/heaad/archive/2010/12/20/1911614.html
下面给出蚁群算法的源代码:
// AO.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
const double ALPHA=1.0; //启发因子,信息素的重要程度
const double BETA=2.0; //期望因子,城市间距离的重要程度
const double ROU=0.5; //信息素残留参数
const int N_ANT_COUNT=34; //蚂蚁数量
const int N_IT_COUNT=1000; //迭代次数
const int N_CITY_COUNT=51; //城市数量
const double DBQ=100.0; //总的信息素
const double DB_MAX=10e9; //一个标志数,10的9次方
double g_Trial[N_CITY_COUNT][N_CITY_COUNT]; //两两城市间信息素,就是环境信息素
double g_Distance[N_CITY_COUNT][N_CITY_COUNT]; //两两城市间距离
//eil51.tsp城市坐标数据
double x_Ary[N_CITY_COUNT]=
{
37,49,52,20,40,21,17,31,52,51,
42,31,5,12,36,52,27,17,13,57,
62,42,16,8,7,27,30,43,58,58,
37,38,46,61,62,63,32,45,59,5,
10,21,5,30,39,32,25,25,48,56,
30
};
double y_Ary[N_CITY_COUNT]=
{
52,49,64,26,30,47,63,62,33,21,
41,32,25,42,16,41,23,33,13,58,
42,57,57,52,38,68,48,67,48,27,
69,46,10,33,63,69,22,35,15,6,
17,10,64,15,10,39,32,55,28,37,
40
};
//返回指定范围内的随机整数
int rnd(int nLow,int nUpper)
{
return nLow+(nUpper-nLow)*rand()/(RAND_MAX+1);
}
//返回指定范围内的随机浮点数
double rnd(double dbLow,double dbUpper)
{
double dbTemp=rand()/((double)RAND_MAX+1.0);
return dbLow+dbTemp*(dbUpper-dbLow);
}
//返回浮点数四舍五入取整后的浮点数
double ROUND(double dbA)
{
return (double)((int)(dbA+0.5));
}
//定义蚂蚁类
class CAnt
{
public:
CAnt(void);
~CAnt(void);
public:
int m_nPath[N_CITY_COUNT]; //蚂蚁走的路径
double m_dbPathLength; //蚂蚁走过的路径长度
int m_nAllowedCity[N_CITY_COUNT]; //没去过的城市
int m_nCurCityNo; //当前所在城市编号
int m_nMovedCityCount; //已经去过的城市数量
public:
int ChooseNextCity(); //选择下一个城市
void Init(); //初始化
void Move(); //蚂蚁在城市间移动
void Search(); //搜索路径
void CalPathLength(); //计算蚂蚁走过的路径长度
};
//构造函数
CAnt::CAnt(void)
{
}
//析构函数
CAnt::~CAnt(void)
{
}
//初始化函数,蚂蚁搜索前调用
void CAnt::Init()
{
for (int i=0;i 0.0) //总的信息素值大于0
{
dbTemp=rnd(0.0,dbTotal); //取一个随机数
for (int i=0;i int main()
{
//用当前时间点初始化随机种子,防止每次运行的结果都相同
time_t tm;
time(&tm);
unsigned int nSeed=(unsigned int)tm;
srand(nSeed);
//开始搜索
CTsp tsp;
tsp.InitData(); //初始化
tsp.Search(); //开始搜索
//输出结果
printf("\nThe best tour is :\n");
char cBuf[128];
for (int i=0;iSendMessage(m_hWnd,USERMSG_UPDATE,0,0); //注意:此处不能为PostMessage函数,因为需要每一代更新界面,要等消息处理完成才能返回
自定义用户消息如下:
#define USERMSG_UPDATE WM_USER+2
2. 在窗口消息处理函数WndProc中添加代码如下:
1)对WM_PAINT进行相应的代码如下:
hdc = BeginPaint(hWnd,&ps);
// TODO: 在此添加任意绘图代码...
for(int i=0;i<51;i++)
{
RECT rect;
rect.left = x_Ary[i]-2;
rect.right = x_Ary[i]+2;
rect.top = y_Ary[i]-2;
rect.bottom = y_Ary[i]+2;
Rectangle(hdc,rect.left,rect.top,rect.right,rect.bottom);
HGDIOBJ brush = GetStockObject(DC_BRUSH);
COLORREF col(RGB(124,252,0));
SetDCBrushColor(hdc,col);
FillRect(hdc,&rect,(HBRUSH)brush);
char ch[3];
memset(ch,0,3);
sprintf(ch,"%d",i+1);
TextOutA(hdc,x_Ary[i]+2,y_Ary[i]+2,LPCSTR(ch),strlen(ch));
}
EndPaint(hWnd, &ps);2)鼠标左键消息WM_LBUTTONDOWN响应:
RECT rect;
GetClientRect(hWnd,&rect);
InvalidateRect(hWnd,&rect,true);
UpdateWindow(hWnd);
time_t tm;
time(&tm);
unsigned int nSeed=(unsigned int)tm;
srand(nSeed);
//开始搜索
CTsp tsp(hWnd);
tsp.InitData(); //初始化
tsp.Search(); //开始搜索3)对用户自定义消息USERMSG_UPDATE的响应:
RECT rect;
GetClientRect(hWnd,&rect);
InvalidateRect(hWnd,&rect,true);
UpdateWindow(hWnd);
hdc = GetDC(hWnd);
HGDIOBJ pen = GetStockObject(DC_PEN);
COLORREF col(RGB(124,252,0));
SetDCPenColor(hdc,col);
for(int i=0;i<50;i++)
{
int n = bestPath[i];
int m = bestPath[i+1];
MoveToEx(hdc,x_Ary[n],y_Ary[n],NULL);
LineTo(hdc,x_Ary[m],y_Ary[m]);
}
MoveToEx(hdc,x_Ary[bestPath[50]],y_Ary[bestPath[50]],NULL);
LineTo(hdc,x_Ary[bestPath[0]],y_Ary[bestPath[0]]);
ReleaseDC(hWnd, hdc);4)添加全局变量bestPath,用以保存找到的最佳路径,并在TSP类的search函数中每一代进行更新
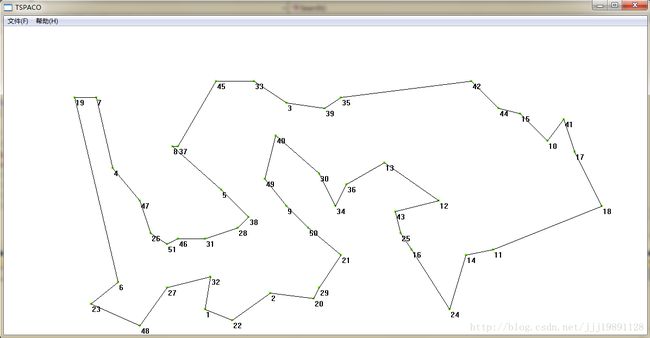
for(int k=0;k最后程序的运行结果如下: