Maven 学习笔记(二) —— 依赖与插件管理
二. 依赖管理
1. 添加依赖
在 pom.xml 中的 dependencies 下添加 dependency, 指定想要的依赖包的坐标, maven 就会为项目添加该依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junitgroupId>
<artifactId>junitartifactId>
<version>3.8.1version>
<type>jartype>
dependency>
dependencies>
添加完依赖后, 需要让 maven 加载新的依赖, eclipse-update, idea-reimport
mvn dependency: resolve
1.1. 传递性依赖
在实际项目中, 我们项目依赖的构件, 可以也依赖于其他的一些构件. maven 支持传递性依赖, 我们只需要在 pom.xml 中添加我们直接依赖的库, maven 获取到这些构件后 (同时也会获取该构件的pom, 根据这个pom获取它的依赖), 会进一步地获取被这些构件依赖的构件并加入我们的项目中.
如果想要了解项目的依赖树, 可以通过命令获取:
mvn dependency: tree
如果有多个不同构件, 依赖了同一个构件的不同版本, maven 会根据 就近原则, 获取依赖层次最低的那个版本. 如果需要使用其他版本, 则可以在我们自己的 pom.xml 中指定需要使用的版本 (改变了该构件在依赖树中的层次).
如果想了解完整的依赖踪迹, 包含那些因为依赖冲突或其他原因被拒绝引入的构件, 可以打开 maven 的调试标记 -X 执行
mvn install -X
1.2. 可选依赖
如果有这么一个接口项目, 声明了一套 API 接口, 并可以选择使用多个不同的实现.
用户在使用时, 可能只是需要其中一个, 而不希望同时引入两套实现, 这种时候可以使用可选依赖.
true
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-txartifactId>
<version>${spring.version}version>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
dependencies>
当在一个项目中将依赖声明为可选依赖后, maven 在组织传递性依赖的时候将不会引入该依赖, 而必须在主项目的 pom 中显式引入要使用的可选依赖.
还有另外一种方式是创建一系列的多个子项目, 每个子项目引用一个特定的实现, 而不是在一个项目中声明可选依赖. 这样最终用户只需要选择合适的子项目, 而不需要在引用项目的同时声明该项目需要的可选依赖.
1.3. 检查直接依赖
可能会存在一种情况, 项目代码中引用了一个传递性依赖, 但并没有在项目 pom 中显式的声明引入. 这会存在一种风险, 如果带来这个传递性依赖升级后去掉了这个传递性依赖, 那么这个传递性依赖将从项目的依赖树中移除, 这个时候, 由于缺少依赖, 项目将构建失败.
为了避免这种情况, 建议总是声明对直接依赖的引用.
使用 maven 的 dependency 插件对项目进行分析, 可以找到未声明的依赖
mvn dependency: analyze
2. 依赖版本管理
2.1. 版本属性变量
实际项目中, 可能会有多个相关的构件, 使用相同的版本号, 若我们为每个构件单独指定版本号, 麻烦而且不便修改. 借助 pom 属性引用, 可以先声明一个属性变量, 然后依赖版本中引用这个属性. 这样可以实现插件版本的统一管理, 而且需要替换版本时也更加方便.
<properties>
<spring.version>4.3.3.RELEASEspring.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-txartifactId>
<version>${spring.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-webartifactId>
<version>${spring.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvcartifactId>
<version>${spring.version}version>
dependency>
dependencies>
2.2. 多模块依赖管理
对于多模块项目, 可以统一在父项目中使用 dependencyManagement 元素声明依赖版本, 而子模块只需要指定依赖的 Gid 和 Aid, 不需关心版本的问题.
dependencyManagement 元素只负责声明依赖, 但并未真正引用依赖, 子模块在需要引用依赖时, 需要在dependencies 元素中指定 Gid 和 Aid
-
在父项目 pom 中使用
dependencyManagement元素声明<dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet.jspgroupId> <artifactId>jsp-apiartifactId> <version>2.2.1-b03version> <scope>providedscope> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servletgroupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet-apiartifactId> <scope>providedscope> <version>${servlet-api.version}version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId> <artifactId>spring-beansartifactId> <version>${spring.version}version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId> <artifactId>spring-jdbcartifactId> <version>${spring.version}version> dependency> dependencies> dependencyManagement> -
在子项目中使用依赖, 版本号从父项目中继承, 如果注明则覆盖父项目中的设置
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jspgroupId>
<artifactId>jsp-apiartifactId>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servletgroupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-apiartifactId>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-beansartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbcartifactId>
dependency>
dependencies>
- 若父模块使用
dependencies元素引入的依赖, 子模块中不需添加任何声明, 都能通过继承而引入. 因此可以在父模块中统一引入所有子模块都会使用的依赖, 比如 junit
2.3. 版本界限
也可以不指定特定的某一个版本, 而是给出一个范围
(a,b) 开区间, 不包含两端
[a,b] 闭区间, 包含两端
[a,b) 半开半闭, 包含一侧
其中版本起止不一定要提供两个参数, 可以省略其中一个
注意:
通常我们使用的版本声明, 如
但如果使用 [] 将版本号括起来, 则是指定必须使用 3.8.1, 如果出现版本冲突, 则会提示构建失败.
3. 范围控制
可以在添加依赖时通过 scope 元素指定依赖的作用范围, 如:
<dependency>
<groupId>junitgroupId>
<artifactId>junitartifactId>
<type>pomtype>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
-
compile
编译并打包, 默认使用, 会被添加到 classpath 中参与编译与打包
-
test
只在测试编译和测试运行时会包含在 classpath 中, 不参与打包
只对测试有效,
src/test/java中可以使用, 而在src/main/java中不可用 -
provided
开发时需要, 但不加入build path, 通常是外部容器提供的, 打包时不需要包含进 war 中, 如 servlet-api
-
runtime
runtime 依赖在运行和测试系统的时候不要, 但在编译的时候不需要
比如在编译时之需要 jdbc api, 而在运行时才需要 jdbc 驱动实现
-
system
与 provided 类似, 但是必须显示提供一个对于本地系统中 jar 文件的路径, 这么做是为了允许给予本地对象编译, 而这些对象是系统类库的一部分, 这样的构件应该是一直可用的, maven 也不会再仓库中去寻找它.
如果一个依赖的范围设置成 system, 你必须同时提供一个 systemPath 元素, 该范围不建议使用.
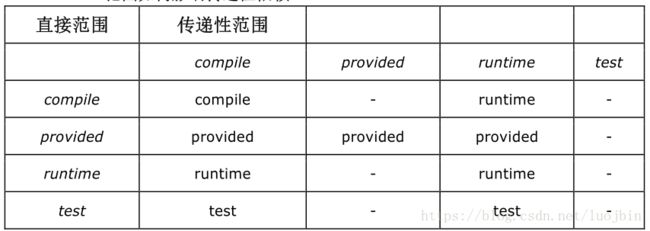
对于传递性依赖, 其有效范围如下;
4. 排除与替换
有时候需要排除一个传递性依赖, 比如想要使用另外一个依赖, 来替代这个传递性依赖.
可以使用 exclusions 元素排除传递性依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.testgroupId>
<artifactId>project-aartifactId>
<version>1.0.1version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>com.testgroupId>
<artifactId>project-bartifactId>
exclusion>
exclusions>
dependency>
如果需要替换被排除的依赖, 只需要显式引用一个提供相同 api 的依赖即可, 但不需要提供额外的标记表明这是被排除依赖的一个替代
<dependency>
<groupId>com.testgroupId>
<artifactId>project-cartifactId>
<version>1.0.1version>
dependency>
三. 插件管理
1. 添加插件
类似于添加依赖, 通过 GAV 来指定插件, 其中对于maven官方插件, 可以省略 GroupId
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.pluginsgroupId>
<artifactId>maven-clean-pluginartifactId>
<version>3.0.0version>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
2. 插件版本控制
与控制依赖版本类似, 可以通过引用属性和 pluginManagement 对项目中的插件版本进行统一管理.
注意 pluginManagement 元素需要放在 build 元素之下
<build>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-clean-pluginartifactId>
<version>3.0.0version>
plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-resources-pluginartifactId>
<version>3.0.2version>
plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-pluginartifactId>
<version>3.7.0version>
plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-pluginartifactId>
<version>2.20.1version>
plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-war-pluginartifactId>
<version>3.2.0version>
plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-install-pluginartifactId>
<version>2.5.2version>
plugin>
plugins>
pluginManagement>
build>
3. 插件行为修改
3.1. configuration
大多数插件都可通过
某些插件还支持使用声明的属性进行配置
如可声明
3.2. 设置编译级别
maven 默认编译版本为 1.5, 如果需要使用更高版本, 应该显式配置 compile 插件, 并声明使用 1.8 的编译版本
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.pluginsgroupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-pluginartifactId>
<version>3.3version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8source>
<target>1.8target>
<encoding>UTF-8encoding>
configuration>
plugin>
也可以在 maven 的 setting.xml 中设置, 这样使用该 maven 的所有项目都会使用 1.8 , 不需在项目 pom 中声明
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>JDK-1.8id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>trueactiveByDefault>
<jdk>1.8jdk>
activation>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8maven.compiler.target>
<maven.compiler.compilerVersion>1.8maven.compiler.compilerVersion>
properties>
profile>
profiles>
3.3. 资源目录与过滤
大部分生命周期, 将 resources: resources 目标绑定到 process-resources 阶段,
这个目标会将资源目录 src/main/resources 的文件, 复制到输出目录 traget/classes , 如果设置了过滤规则, 这个目标还会将资源文件中的某些内容做出处理, 替换掉其中的一些变量值
比如resources 下有一个 jdbc.xml, 记录了数据库URL 和登录信息, 内容如下:
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.mysql.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.mysql.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.mysql.password}" />
bean>
其中的数据库具体信息, 都用一个 ${...} 表达式表示.
而则在另外一个properties 文件中, 定义了这些变量具体的值
jdbc.mysql.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.3.224:3306/demo
jdbc.mysql.username=root
jdbc.mysql.password=123456
maven 的资源过滤, 可以在构建过程中, 自动读取properties 文件中的值, 并填入到 jdbc.xml 文件中的对应位置.
maven 默认不会进行资源过滤, 需要在项目pom.xml 中进行如下配置才能实现资源过滤 :
- 定义过滤器
- 定义资源目录, 并显示声明需要过滤, 可以定义多个资源目录, 并单独声明是否需要过滤
<build>
<filters>
<filter>../conf.propertiesfilter>
filters>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resourcesdirectory>
<includes>
<include>**/*include>
includes>
<filtering>truefiltering>
<targetPath>target/conftargetPath>
resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/imgdirectory>
<targetPath>target/imgtargetPath>
resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/xmldirectory>
<targetPath>target/xmltargetPath>
resource>
resources>
build>
3.4. 跳过单元测试
默认情况下, 构建时会执行单元测试, 如果希望不经测试直接构建, 可以设置跳过单元测试
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-pluginartifactId>
<configuration>
<skip>trueskip>
configuration>
plugin>
3.5. 忽略失败的测试
默认情况下, 测试失败后会中止构建过程, 如果希望测试失败后不影响构建, 可以将失败的测试忽略
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-pluginartifactId>
<configuration>
<testFailureIgnore>truetestFailureIgnore>
configuration>
plugin>