Dubbo如何正确捕获业务异常
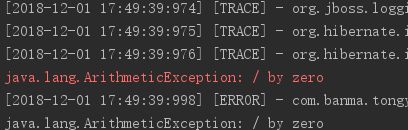
笔者所在的公司,项目正在重构,从一个SpringBoot项目往Dubbo上迁移,但在拆分后发现一个问题,服务消费者(后文用Consumer代替)无法正确捕获服务提供者(后文用provider代替)所抛出的非受检查异常。在未拆分之前,项目都是打成一个jar包运行,service层未处理的unchecked异常,在controller层捕获到后可以正常打印出异常的堆栈信息,方便开发人员快速定位哪行代码抛得异常,但是service和controller分离后,service层部署在provider端,controller部署在Consumer端,发现,如果provider抛了一个unchecked异常,例如NPE、 / by zero,发现不管在provider端还是在custom端都没有很清晰得打印出异常堆栈信息。比如:在provider端抛一个/ by zero异常端,在Consumer端只会打印一行异常信息
对,只有简简单单一行,无论怎样也不会定位出异常发生得位置,经过一翻百度,才知道Dubbo对抛出得异常用一个ExceptionFilter的类进行拦截,下面一起来分析这段源代码:
@Activate(
group = {"provider"}
)
public class ExceptionFilter implements Filter {
private final Logger logger;
public ExceptionFilter() {
this(LoggerFactory.getLogger(ExceptionFilter.class));
}
public ExceptionFilter(Logger logger) {
this.logger = logger;
}
public Result invoke(Invoker invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
try {
//1
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
//2
if (result.hasException() && GenericService.class != invoker.getInterface()) {
try {
//3
Throwable exception = result.getException();
//4
if (!(exception instanceof RuntimeException) && exception instanceof Exception) {
return result;
} else {
try {
//5
Method method = invoker.getInterface().getMethod(invocation.getMethodName(), invocation.getParameterTypes());
Class[] exceptionClassses = method.getExceptionTypes();
Class[] arr$ = exceptionClassses;
int len$ = exceptionClassses.length;
for(int i$ = 0; i$ < len$; ++i$) {
Class exceptionClass = arr$[i$];
//6
if (exception.getClass().equals(exceptionClass)) {
return result;
}
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException var11) {
return result;
}
this.logger.error("Got unchecked and undeclared exception which called by " + RpcContext.getContext().getRemoteHost() + ". service: " + invoker.getInterface().getName() + ", method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", exception: " + exception.getClass().getName() + ": " + exception.getMessage(), exception);
//7
String serviceFile = ReflectUtils.getCodeBase(invoker.getInterface());
String exceptionFile = ReflectUtils.getCodeBase(exception.getClass());
if (serviceFile != null && exceptionFile != null && !serviceFile.equals(exceptionFile)) {
String className = exception.getClass().getName();
if (!className.startsWith("java.") && !className.startsWith("javax.")) {
return (Result)(exception instanceof RpcException ? result : new RpcResult(new RuntimeException(StringUtils.toString(exception))));
} else {
return result;
}
} else {
return result;
}
}
} catch (Throwable var12) {
this.logger.warn("Fail to ExceptionFilter when called by " + RpcContext.getContext().getRemoteHost() + ". service: " + invoker.getInterface().getName() + ", method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", exception: " + var12.getClass().getName() + ": " + var12.getMessage(), var12);
return result;
}
} else {
return result;
}
} catch (RuntimeException var13) {
this.logger.error("Got unchecked and undeclared exception which called by " + RpcContext.getContext().getRemoteHost() + ". service: " + invoker.getInterface().getName() + ", method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", exception: " + var13.getClass().getName() + ": " + var13.getMessage(), var13);
throw var13;
}
}
}如上代码所示,当产生异常时,会执行一个invoke方法对异常对于进行处理。
1、异常对象封装在Result中,invoker是service类中方法的一个代理(Dubbo中Consumer端调用provider端的方法时,其实调用的是一个代理方法,在此处不多介绍)
2、如果service接口没有实现GenericService接口,向下走
3、获取异常对象exception
4、如果异常是checked类型的异常,直接返回Result
5、如果在定义service的时候,throws了异常
6、如果service产生的的异常与service接口throws的异常一致时,返回Result
7、获取invoker接口所在的文件名serviceFile和产生的异常所在的文件名exceptionFile,如果异常包名不是以java.开头或javax.开头(不是JDK中的异常),将异常封装成一个RpcResult返回,否则直接返回。
所以,Dubbo项目中要正确捕获业务异常,而不是简简单单打印一行错误信息,要这样做:
方法1: 将该异常的包名以"java.或者"javax. " 开头
方法2: 使用受检异常(继承Exception)
方法3:不用异常,使用错误码
方法4:把异常放到api的jar包中,供provider和Consumer共享,也就是自定义一个Exception,继承RuntimeException并实现Serializable接口(因为将异常从provider端传递给consumer端是经过RPC传递的),目前,我是这么处理公司的业务异常的。
方法5:provider实现GenericService接口
方法6:service的接口throws 一个自定义异常,在service中throw一个该异常给provider,如下(RpcRuntime Exception是一个自定义异常)
@Override
public String selectByDeleteFlag(String name) throws RpcRuntimeException{
try{
int i = 1 / 0;
}catch (RpcRuntimeException e){
throw e;
}
return "aaa";
}如果满足上面方法中的一个,在custom端便可以打印出正常的异常堆栈信息,方便开发者快速定位异常,在公司中,我是通过上述第四种方式处理的,自定义异常,代码如下:
在api的jar包中自定义异常RpcRuntimeException并打jar包,继承RuntimeException实现Serializable接口
public class RpcRuntimeException extends RuntimeException implements Serializable {
public RpcRuntimeException() {
}
public RpcRuntimeException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
public RpcRuntimeException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
public RpcRuntimeException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
}在provider端用aop实现一个全局异常处理器,将service产生的RuntimeException包装成一个RpcRuntimeException并throws给调用端,也就是Consumer端。
@Aspect
@Component
public class RpcRuntimeExceptionHandler {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RpcRuntimeExceptionHandler.class);
/**
* service层的RuntimeException统一处理器
* 可以将RuntimeException分装成RpcRuntimeException抛给调用端处理
* 或自行处理
* @param exception
*/
@AfterThrowing(throwing="exception",pointcut="execution(* com.banma.tongye.service.*.*(..))")
public void afterThrow(Throwable exception){
if(exception instanceof RuntimeException){
logger.error(exception.getMessage());
throw new RpcRuntimeException(exception);
}
exception.printStackTrace();
}
}这样在Consumer端就可以正常打印异常堆栈信息了。
好了,本文给大家分享的内容就是这些,在接下来的时间里,我会陆续为大家分享java后端技术,敬请期待,加作者微信或关注作者的微信公众号,可以得到更多后端技术。
![]()
![]()