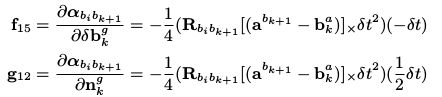手写VIO学习总结(三)
文章目录
- 1. 作业1
- 作业1.1
- 作业1.2
- 作业1.3
- 2.作业2
- 3.作业3
- 作业2&3的解答:
系列笔记:
手写VIO学习总结(一)
手写VIO学习总结(二)
1. 作业1
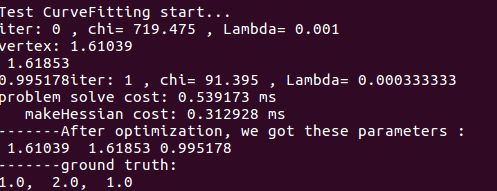
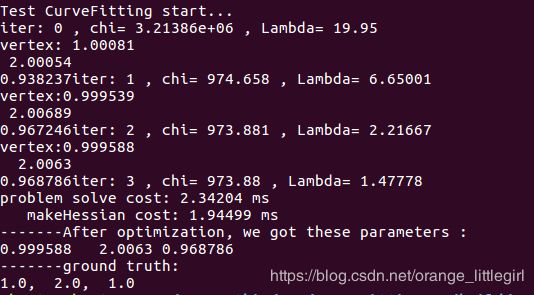
1 样例代码给出了使用LM 算法来估计曲线y = exp(ax2 + bx + c)
参数a, b, c 的完整过程。
作业1.1
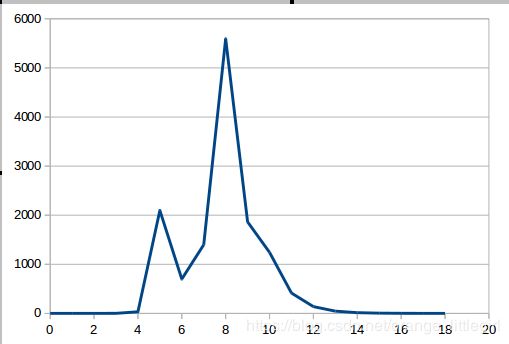
- (1)请绘制样例代码中LM 阻尼因子μ 随着迭代变化的曲线图。
参考我以前的博文视觉slam14讲学习(四)之Ceres和G2O使用
那篇博文是用高斯牛顿法求解的,具体原理:

- 我们现在要利用LM算法求解,具体原理:

- 阻尼因子作用:

- 阻尼因子迭代更新:

- 马夸尔特阻尼法
bool Problem::Solve(int iterations) {
if (edges_.size() == 0 || verticies_.size() == 0) {
std::cerr << "\nCannot solve problem without edges or verticies" << std::endl;
return false;
}
TicToc t_solve;
// 统计优化变量的维数,为构建 H 矩阵做准备
SetOrdering();
// 遍历edge, 构建 H = J^T * J 矩阵
MakeHessian();
// LM 初始化
ComputeLambdaInitLM();
// LM 算法迭代求解
bool stop = false;
int iter = 0;
while (!stop && (iter < iterations)) {
std::cout << "iter: " << iter << " , chi= " << currentChi_ << " , Lambda= " << currentLambda_
<< std::endl;
bool oneStepSuccess = false;
int false_cnt = 0;
while (!oneStepSuccess) // 不断尝试 Lambda, 直到成功迭代一步
{
// setLambda
AddLambdatoHessianLM();
// 第四步,解线性方程 H X = B
SolveLinearSystem();
//
RemoveLambdaHessianLM();
// 优化退出条件1: delta_x_ 很小则退出
if (delta_x_.squaredNorm() <= 1e-6 || false_cnt > 10) {
stop = true;
break;
}
// 更新状态量 X = X+ delta_x
UpdateStates();
// 判断当前步是否可行以及 LM 的 lambda 怎么更新
oneStepSuccess = IsGoodStepInLM();
// 后续处理,
if (oneStepSuccess) {
// 在新线性化点 构建 hessian
MakeHessian();
// TODO:: 这个判断条件可以丢掉,条件 b_max <= 1e-12 很难达到,这里的阈值条件不应该用绝对值,而是相对值
// double b_max = 0.0;
// for (int i = 0; i < b_.size(); ++i) {
// b_max = max(fabs(b_(i)), b_max);
// }
// // 优化退出条件2: 如果残差 b_max 已经很小了,那就退出
// stop = (b_max <= 1e-12);
false_cnt = 0;
} else {
false_cnt++;
RollbackStates(); // 误差没下降,回滚
}
}
iter++;
// 优化退出条件3: currentChi_ 跟第一次的chi2相比,下降了 1e6 倍则退出
if (sqrt(currentChi_) <= stopThresholdLM_)
stop = true;
}
std::cout << "problem solve cost: " << t_solve.toc() << " ms" << std::endl;
std::cout << " makeHessian cost: " << t_hessian_cost_ << " ms" << std::endl;
return true;
}
注意:
oneStepSuccess = IsGoodStepInLM();
//可能会出现rho无异常,跳出一次while,改变lambda
// 判断当前步是否可行以及 LM 的 lambda 怎么更新
//误差上升的时候,false,继续优化迭代;误差下降的时候,true,跳出循环记录下来
要记录完整的迭代lambda值必须把记录的方法写在第二个while()里面
record_lambdas.add(lambda_iter,currentLambda_);
lambda_iter++;
作业1.2
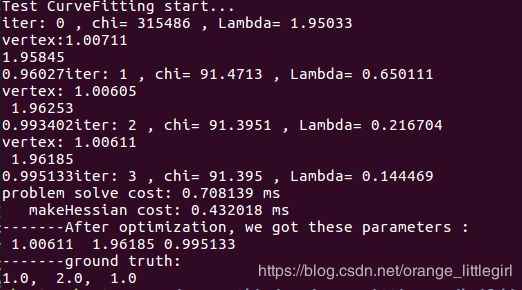
将曲线函数改成 y = ax 2 + bx + c,请修改样例代码中残差计算,雅克比计算等函数,完成曲线参数估计。
- 代码更改部分:
// 曲线模型的顶点,模板参数:优化变量维度和数据类型
class CurveFittingVertex: public Vertex
{
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
CurveFittingVertex(): Vertex(3) {} // abc: 三个参数, Vertex 是 3 维的
virtual std::string TypeInfo() const { return "abc"; }
};
// 误差模型 模板参数:观测值维度,类型,连接顶点类型
class CurveFittingEdge: public Edge
{
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
CurveFittingEdge( double x, double y ): Edge(1,1, std::vector{"abc"}) {
x_ = x;
y_ = y;
}
// 计算曲线模型误差
virtual void ComputeResidual() override
{
Vec3 abc = verticies_[0]->Parameters(); // 估计的参数
residual_(0) = ( abc(0)*x_*x_ + abc(1)*x_ + abc(2) ) - y_; // 构建残差
}
// 计算残差对变量的雅克比
virtual void ComputeJacobians() override
{
// Vec3 abc = verticies_[0]->Parameters();
// double exp_y = std::exp( abc(0)*x_*x_ + abc(1)*x_ + abc(2) );
Eigen::Matrix jaco_abc; // 误差为1维,状态量 3 个(a,b,c),所以是 1x3 的雅克比矩阵
jaco_abc << x_ * x_ , x_ , 1 ;
jacobians_[0] = jaco_abc;
}
/// 返回边的类型信息
virtual std::string TypeInfo() const override { return "CurveFittingEdge"; }
public:
double x_,y_; // x 值, y 值为 _measurement
};
作业1.3
如果有实现其他阻尼因子更新策略可加分(选做)
bool Problem::IsGoodStepInLM() {
double scale = 0;
scale = delta_x_.transpose() * (currentLambda_ * delta_x_ + b_);
scale += 1e-3; // make sure it's non-zero :)
// recompute residuals after update state
// 统计所有的残差
double tempChi = 0.0;
for (auto edge: edges_) {
edge.second->ComputeResidual();
tempChi += edge.second->Chi2();//当前残差
}
double rho = (currentChi_ - tempChi) / scale;
if (rho > 0 && isfinite(tempChi)) // last step was good, 误差在下降
{
double alpha = 1. - pow((2 * rho - 1), 3);
alpha = std::min(alpha, 2. / 3.);
double scaleFactor = (std::max)(1. / 3., alpha);
currentLambda_ *= scaleFactor;
ni_ = 2;// 控制 Lambda 缩放大小
currentChi_ = tempChi;
return true;
} else {// 误差在上升
currentLambda_ *= ni_;
ni_ *= 2;
return false;
}
}
bool Problem::IsGoodStepInLM2() {
// recompute residuals after update state
// 统计所有的残差
double tempChi = 0.0;
for (auto edge: edges_) {
edge.second->ComputeResidual();
tempChi += edge.second->Chi2();//当前残差
}
double frac1 = delta_x_.transpose()* b_;
double alpha = frac1 / (((tempChi - currentLambda_)/2) + 2*frac1);
RollbackStates();
delta_x_ *= alpha;
UpdateStates();
double scale = 0;
scale = delta_x_.transpose() * (currentLambda_ * delta_x_ + b_);
scale += 1e-3;
double rho = (currentChi_ - tempChi) / scale;
//迭代策略2
if (rho > 0 && isfinite(tempChi)) // last step was good, 误差在下降
{
currentLambda_ = std::max(currentLambda_/(1. + alpha), 1e-7);
currentChi_ = tempChi;
return true;
} else {// 误差在上升
currentLambda_ += abs(tempChi - currentChi_)/(2.*alpha);
return false;
}
}
2.作业2
公式推导,根据课程知识,完成 F, G 中如下两项的推导过程: