动手学习深度学习 | 部分python函数详解
(1):维度dim,保持原有维度keepdim
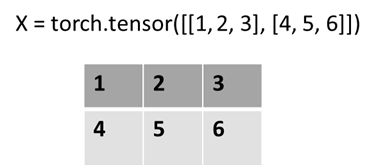
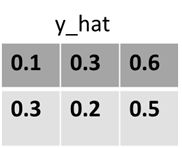
下面通过图像的形式直观的展示了这两个参数的作用。
X = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
print(X.sum(dim=0, keepdim=True))
print(X.sum(dim=1, keepdim=True))
print(X.sum(dim=0, keepdim=False))
print(X.sum(dim=1, keepdim=False))
(2):view函数的用法
view函数的用法如下所示,就是用于改变tensor的维度。其中-1表示当前维度会根据其余指定维度自适应得到。
y = torch.LongTensor([0, 2])
print(y,y.shape)
print(y.view(-1, 1),y.view(-1, 1).shape)
#-------------------------
tensor([0, 2]) torch.Size([2])
tensor([[0],
[2]]) torch.Size([2, 1])
(3):gather函数的用法
ganther函数的用法如下所示,用于批量取出目标tensor中对应维度的数据。
y_hat = torch.tensor([[0.1, 0.3, 0.6], [0.3, 0.2, 0.5]])
y1 = torch.LongTensor([[0, 1, 1]])
y2 = torch.LongTensor([[1,2]])
print(y_hat.gather(0, y1.view(1, -1)))
print(y_hat.gather(1, y2.view(-1, 1)))
#---------------------
tensor([[0.1000, 0.2000, 0.5000]])
tensor([[0.3000],
[0.5000]])
(4):argmax函数的用法
y_hat = torch.tensor([[0.1, 0.3, 0.6], [0.3, 0.2, 0.5]])
print(y_hat.argmax(dim=0))
print(y_hat.argmax(dim=1))
#-----------------------
tensor([1, 0, 0])
tensor([2, 2])