tensorflow之综合学习系列实例之SEQ2SEQ+ATTENTION
本文继续和大家一起学习一下在序列网络中引入优化机制-注意力机制,如果在序列很长的情况下,不引入这个机制,识别效果是
不会太好的,首先还是看看seq2seq的基本知识:
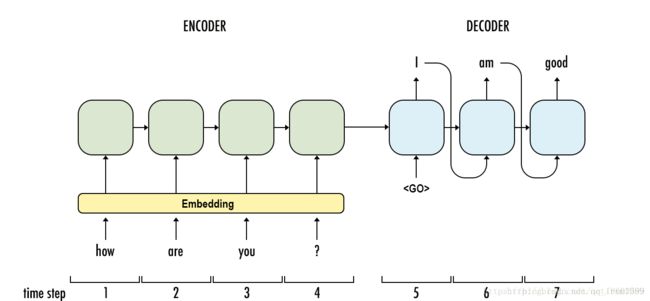
seq2seq就是把一个序列翻译成另一个序列的模型,实质就是两个rnn,一个是encoder,另一个是decoder,encoder负责将source序列编码成固定长度的表达,decoder负责将该固定长度的表达解码成target序列,刚开始是在机器翻译上使用的,其实这个模型应用非常广泛,凡是变长之间的映射关系都可以做,常见是机器翻译,语音识别,摘要提取等等;还可以把encoder和decoder拆开使用。
seq2seq模型的encoder非常简单(上图中ABC对应的部分),就是rnn,可以是多层(simple-rnn,GRU,LSTM),decoder在训练和测试的时候,稍微有点不同
decoder训练的时候输入由两部分组成,一部分是encoder的last state,另一部分是target序列,如上图中的
decoder 测试的时候输入也是由两部分组成,一部分是encoder的last state,另一部分是来自于上一个时刻的输出(上一个时刻的输出作为下一个时刻的输入),直到某个时刻的输出遇到结束符
Attention介绍:
Attention模型的出现是上述的seq2seq模型存在缺陷,即无论之前的encoder的context有多长,包含多少信息量,最终都要被压缩成一个几百维的vector。这意味着context越大,decoder的输入之一的last state 会丢失越多的信息。对于机器翻译问题,意味着输入sentence长度增加后,最终decoder翻译的结果会显著变差。
Attention实质上是一种content-based addressing的机制,即从网络中某些状态集合中选取与给定状态较为相似的状态,进而做后续的信息抽取;说人话就是:首先根据Encoder和Decoder的特征计算权值,然后对Encoder的特征进行加权求和,作为Decoder的输入,其作用是将Encoder的特征以更好的方式呈献给Decoder,即:并不是所有context都对下一个状态的生成产生影响,Attention就是选择恰当的context用它生成下一个状态。
在熟悉完理论知识之后我们一起学习一个实践的应用,就是文本摘要,什么意思?,比如输入一句很长的话'这个手机真漂亮,我很喜欢',概要是什么:'喜欢漂亮手机'类似于这种应用在我们的实际业务场景有很多的应用,比如用户的评价就可以很好的用这个去训练.
但是这个实例使用的是英文资料,因为引入中文的话,处理起来是比较复杂的,但是其核心的本质和流程是没有什么太大的差别,学会举一反三即可,通过训练模型,然后输入一句话,比如'The coffee tasted great and was at such a good price! I highly recommend this to everyone!',我们通过模型能提取出核心摘要'great coffee'
接下来我们就讲解实现的步骤和流程:
1 数据的加载:读取数据到内存中
2 数据非核心列的剔除
3 删除不满足条件的词
4 统计每个词出现的词频
5 填充几个特殊字符号,起始位置 结束位置 无法识别,填充
6 词到ID映射词典的创建
7 ID到词映射词典的创建
8 使用第三方创建好的词向量模型,直接匹配每个词,为每个词匹配一个对应的词向量
9 为不存在在向量文件中的关键字指定一个任意的词向量
10 对词进行排序
11 创建模型的输入参数
12 解码数据处理,一般需要移除最后一个字符
13 创建编码层
14 创建traning decoder:训练用的
15 创建inference decoder:测试用的
16 创建解码层
17 创建序列模型+Attenttion
18 批量训练数据生成
19 训练模型
20 模型测试
步骤讲完了,接下来看看完整实现代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import pandas as pd import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf import re from nltk.corpus import stopwords import time from tensorflow.python.layers.core import Dense from tensorflow.python.ops.rnn_cell_impl import _zero_state_tensors import tensorflow.contrib.seq2seq as seq import nltk # 需要下载这个到本地,否则无法使用nltk部分功能 nltk.download() #读取数据 reviews = pd.read_csv("data/reviews.csv") print('reviews.shape',reviews.shape) print('reviews.isnull.sum',reviews.isnull().sum()) #删除无用的列 reviews = reviews.dropna() reviews = reviews.drop(['Id','ProductId','UserId','ProfileName','HelpfulnessNumerator','HelpfulnessDenominator','Score','Time'], 1) reviews = reviews.reset_index(drop=True) print('reviews',reviews[0:4]) # 定义缩写单词对应的全展开单词 contractions={ "ain't": "am not", "aren't": "are not", "can't": "cannot", "can't've": "cannot have", "'cause": "because", "could've": "could have", "couldn't": "could not", "couldn't've": "could not have", "didn't": "did not", "doesn't": "does not", "don't": "do not", "hadn't": "had not", "hadn't've": "had not have", "hasn't": "has not", "haven't": "have not", "he'd": "he would", "he'd've": "he would have", "he'll": "he will", "he's": "he is", "how'd": "how did", "how'll": "how will", "how's": "how is", "i'd": "i would", "i'll": "i will", "i'm": "i am", "i've": "i have", "isn't": "is not", "it'd": "it would", "it'll": "it will", "it's": "it is", "let's": "let us", "ma'am": "madam", "mayn't": "may not", "might've": "might have", "mightn't": "might not", "must've": "must have", "mustn't": "must not", "needn't": "need not", "oughtn't": "ought not", "shan't": "shall not", "sha'n't": "shall not", "she'd": "she would", "she'll": "she will", "she's": "she is", "should've": "should have", "shouldn't": "should not", "that'd": "that would", "that's": "that is", "there'd": "there had", "there's": "there is", "they'd": "they would", "they'll": "they will", "they're": "they are", "they've": "they have", "wasn't": "was not", "we'd": "we would", "we'll": "we will", "we're": "we are", "we've": "we have", "weren't": "were not", "what'll": "what will", "what're": "what are", "what's": "what is", "what've": "what have", "where'd": "where did", "where's": "where is", "who'll": "who will", "who's": "who is", "won't": "will not", "wouldn't": "would not", "you'd": "you would", "you'll": "you will", "you're": "you are" } #清除不想要的单词(频率比较低的),停用词 def clean_text(text, remove_stopwords=True): '''Remove unwanted characters, stopwords, and format the text to create fewer nulls word embeddings''' # 单词转换为小写 text = text.lower() # 把缩写单词替换成对应的扩展单词 if True: text = text.split() new_text = [] for word in text: if word in contractions: new_text.append(contractions[word]) else: new_text.append(word) text = " ".join(new_text) # 移除单词 text = re.sub(r'https?:\/\/.*[\r\n]*', '', text, flags=re.MULTILINE) text = re.sub(r'\, ' ', text) text = re.sub(r'&', '', text) text = re.sub(r'[_"\-;%()|+&=*%.,!?:#$@\[\]/]', ' ', text) text = re.sub(r'
', ' ', text) text = re.sub(r'\'', ' ', text) # 去掉停用词 if remove_stopwords: text = text.split() stops = set(stopwords.words("english")) text = [w for w in text if not w in stops] text = " ".join(text) return text #处理文章摘要 clean_summaries = [] for summary in reviews.Summary: clean_summaries.append(clean_text(summary, remove_stopwords=False)) print("Summaries are complete.") #处理评价明细 clean_texts = [] for text in reviews.Text: clean_texts.append(clean_text(text)) print("Texts are complete.") for i in range(5): print("Clean Review #",i+1) print(clean_summaries[i]) print(clean_texts[i]) print() #统计每个句子中每个单词出现的频率 def count_words(count_dict, text): for sentence in text: for word in sentence.split(): if word not in count_dict: count_dict[word] = 1 else: count_dict[word] += 1 # 统计所有词的词频 比如:{'hello':7,'good':3} word_counts = {} count_words(word_counts, clean_summaries) count_words(word_counts, clean_texts) print('count_words',count_words) print("Size of Vocabulary:", len(word_counts)) #把词转换为对应的ID{'hello':11} vocab_to_int = {} value = 0 for word, count in word_counts.items(): if count >= threshold or word in embeddings_index: vocab_to_int[word] = value value += 1 # 填充特殊符号 codes = ["" ,"" ,"" ,"" ] for code in codes: vocab_to_int[code] = len(vocab_to_int) # 单词和ID之间的映射{11:'hello'} int_to_vocab = {} for word, value in vocab_to_int.items(): int_to_vocab[value] = word print("Total number of unique words:", len(word_counts)) print("Number of words we will use:", len(vocab_to_int)) #每个词转换成对应的词向量 {key:embedding} embeddings_index = {} with open('data/numberbatch-en-17.04b.txt', encoding='utf-8') as f: for line in f: values = line.split(' ') word = values[0] embedding = np.asarray(values[1:], dtype='float32') embeddings_index[word] = embedding print('Word embeddings:', len(embeddings_index)) # Need to use 300 for embedding dimensions to match CN's vectors. embedding_dim = 300 nb_words = len(vocab_to_int) # 匹配关键字对应的向量值 word_embedding_matrix = np.zeros((nb_words, embedding_dim), dtype=np.float32) for word, i in vocab_to_int.items(): if word in embeddings_index: word_embedding_matrix[i] = embeddings_index[word] else: # 如果词向量文件不存在该关键字 那么创建一个任意的词向量 new_embedding = np.array(np.random.uniform(-1.0, 1.0, embedding_dim)) embeddings_index[word] = new_embedding word_embedding_matrix[i] = new_embedding print(len(word_embedding_matrix)) # 填充关键字 如果该关键字 不在上面的vocab_to_int 就使用def convert_to_ints(text, word_count, unk_count, eos=False): '''Convert words in text to an integer. If word is not in vocab_to_int, use UNK's integer. Total the number of words and UNKs. Add EOS token to the end of texts''' ints = [] for sentence in text: sentence_ints = [] for word in sentence.split(): word_count += 1 if word in vocab_to_int: sentence_ints.append(vocab_to_int[word]) else: sentence_ints.append(vocab_to_int[" " ]) unk_count += 1 if eos: sentence_ints.append(vocab_to_int["" ]) ints.append(sentence_ints) # ints 包含的[{'a':1,'unk':4}] # word_count 就是实际包含的关键字 # unk_count 就是不包含的关键字 return ints, word_count, unk_count # Apply convert_to_ints to clean_summaries and clean_texts word_count = 0 unk_count = 0 int_summaries, word_count, unk_count = convert_to_ints(clean_summaries, word_count, unk_count) int_texts, word_count, unk_count = convert_to_ints(clean_texts, word_count, unk_count, eos=True) print("Total number of words in headlines:", word_count) print("Total number of UNKs in headlines:", unk_count) #Create a data frame of the sentence lengths from a text' def create_lengths(text): lengths = [] for sentence in text: lengths.append(len(sentence)) return pd.DataFrame(lengths, columns=['counts']) lengths_summaries = create_lengths(int_summaries) lengths_texts = create_lengths(int_texts) print("Summaries:") print(lengths_summaries.describe()) print() print("Texts:") print(lengths_texts.describe()) # Inspect the length of texts print(np.percentile(lengths_texts.counts, 90)) print(np.percentile(lengths_texts.counts, 95)) print(np.percentile(lengths_texts.counts, 99)) # Inspect the length of summaries print(np.percentile(lengths_summaries.counts, 90)) print(np.percentile(lengths_summaries.counts, 95)) print(np.percentile(lengths_summaries.counts, 99)) #统计unk出现的次数 def unk_counter(sentence): '''Counts the number of time UNK appears in a sentence.''' unk_count = 0 for word in sentence: if word == vocab_to_int["" ]: unk_count += 1 return unk_count # Sort the summaries and texts by the length of the texts, shortest to longest # Limit the length of summaries and texts based on the min and max ranges. # Remove reviews that include too many UNKs sorted_summaries = [] sorted_texts = [] max_text_length = 84 max_summary_length = 13 min_length = 2 unk_text_limit = 1 unk_summary_limit = 0 for length in range(min(lengths_texts.counts), max_text_length): for count, words in enumerate(int_summaries): if (len(int_summaries[count]) >= min_length and len(int_summaries[count]) <= max_summary_length and len(int_texts[count]) >= min_length and unk_counter(int_summaries[count]) <= unk_summary_limit and unk_counter(int_texts[count]) <= unk_text_limit and length == len(int_texts[count]) ): sorted_summaries.append(int_summaries[count]) sorted_texts.append(int_texts[count]) # Compare lengths to ensure they match print(len(sorted_summaries)) print(len(sorted_texts)) #创建模型输入的参数 def model_inputs(): input_data = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None, None], name='input') targets = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None, None], name='targets') lr = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name='learning_rate') keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name='keep_prob') summary_length = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, (None,), name='summary_length') max_summary_length = tf.reduce_max(summary_length, name='max_dec_len') text_length = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, (None,), name='text_length') return input_data, targets, lr, keep_prob, summary_length, max_summary_length, text_length #解码数据的处理 移除最后一个单词def process_encoding_input(target_data, vocab_to_int, batch_size): ending = tf.strided_slice(target_data, [0, 0], [batch_size, -1], [1, 1]) dec_input = tf.concat([tf.fill([batch_size, 1], vocab_to_int[' ' ]), ending], 1) return dec_input #创建编码层 ''' rnn_size : rnn size sequence_length : sequence length num_layers: create layer div rnn_inputs: input data keep_prob: save ratio ''' def encoding_layer(rnn_size, sequence_length, num_layers, rnn_inputs, keep_prob): for layer in range(num_layers): with tf.variable_scope('encoder_{}'.format(layer)): # 前向RNN cell_fw = tf.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell(num_units=rnn_size,initializer=tf.random_uniform_initializer(-0.1, 0.1, seed=2)) cell_fw = tf.nn.rnn_cell.DropoutWrapper(cell=cell_fw,input_keep_prob=keep_prob) # 后向RNN cell_bw = tf.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell(num_units=rnn_size,initializer=tf.random_uniform_initializer(-0.1, 0.1, seed=2)) cell_bw = tf.nn.rnn_cell.DropoutWrapper(cell=cell_bw,input_keep_prob=keep_prob) # 双向RNN enc_output, enc_state = tf.nn.bidirectional_dynamic_rnn(cell_fw=cell_fw,cell_bw=cell_bw, inputs=rnn_inputs,sequence_length=sequence_length,dtype=tf.float32) # Join outputs since we are using a bidirectional RNN enc_output = tf.concat(enc_output, 2) return enc_output, enc_state #创建训练的decoder def training_decoding_layer(dec_embed_input, summary_length, dec_cell, initial_state, output_layer, vocab_size, max_summary_length): training_helper = seq.TrainingHelper(inputs=dec_embed_input,sequence_length=summary_length,time_major=False) training_decoder = seq.BasicDecoder(cell=dec_cell,helper=training_helper,initial_state=initial_state,output_layer=output_layer) training_logits, _ = seq.dynamic_decode(training_decoder,output_time_major=False,impute_finished=True,maximum_iterations=max_summary_length) return training_logits #创建测试的decoder def inference_decoding_layer(embeddings, start_token, end_token, dec_cell, initial_state, output_layer, max_summary_length, batch_size): start_tokens = tf.tile(tf.constant([start_token], dtype=tf.int32), [batch_size], name='start_tokens') inference_helper = seq.GreedyEmbeddingHelper(embeddings,start_tokens, end_token) inference_decoder = seq.BasicDecoder(dec_cell,inference_helper,initial_state,output_layer) inference_logits, _ = seq.dynamic_decode(inference_decoder,output_time_major=False,impute_finished=True,maximum_iterations=max_summary_length) return inference_logits #创建真正的解码层 引入注意力机制 def decoding_layer(dec_embed_input, embeddings, enc_output, enc_state, vocab_size, text_length, summary_length, max_summary_length, rnn_size, vocab_to_int, keep_prob, batch_size, num_layers): for layer in range(num_layers): with tf.variable_scope('decoder_{}'.format(layer)): lstm = tf.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell(rnn_size,initializer=tf.random_uniform_initializer(-0.1, 0.1, seed=2)) dec_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.DropoutWrapper(lstm,input_keep_prob=keep_prob) #全连接层 output_layer = Dense(vocab_size,kernel_initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(mean=0.0, stddev=0.1)) attn_mech = seq.BahdanauAttention(rnn_size, enc_output,text_length,normalize=False,name='BahdanauAttention') dec_cell = seq.AttentionWrapper(cell=dec_cell,attention_mechanism=attn_mech,attention_layer_size=rnn_size) # 引入注意力机制 initial_state = seq.AttentionWrapperState(enc_state[0], _zero_state_tensors(rnn_size,batch_size,tf.float32)) with tf.variable_scope("decode"): training_logits = training_decoding_layer(dec_embed_input, summary_length, dec_cell, initial_state, output_layer, vocab_size, max_summary_length) with tf.variable_scope("decode", reuse=True): inference_logits = inference_decoding_layer(embeddings, vocab_to_int['' ], vocab_to_int['' ], dec_cell, initial_state, output_layer, max_summary_length, batch_size) return training_logits, inference_logits #创建序列模型 def seq2seq_model(input_data, target_data, keep_prob, text_length, summary_length, max_summary_length, vocab_size, rnn_size, num_layers, vocab_to_int, batch_size): # Use Numberbatch's embeddings and the newly created ones as our embeddings embeddings = word_embedding_matrix enc_embed_input = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embeddings, input_data) enc_output, enc_state = encoding_layer(rnn_size, text_length, num_layers, enc_embed_input, keep_prob) dec_input = process_encoding_input(target_data, vocab_to_int, batch_size) dec_embed_input = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embeddings, dec_input) training_logits, inference_logits = decoding_layer(dec_embed_input, embeddings, enc_output, enc_state, vocab_size, text_length, summary_length, max_summary_length, rnn_size, vocab_to_int, keep_prob, batch_size, num_layers) return training_logits, inference_logits #填充训练短语的长度 def pad_sentence_batch(sentence_batch): max_sentence = max([len(sentence) for sentence in sentence_batch]) return [sentence + [vocab_to_int['' ]] * (max_sentence - len(sentence)) for sentence in sentence_batch] #生成批量训练 def get_batches(summaries, texts, batch_size): for batch_i in range(0, len(texts) // batch_size): start_i = batch_i * batch_size summaries_batch = summaries[start_i:start_i + batch_size] texts_batch = texts[start_i:start_i + batch_size] pad_summaries_batch = np.array(pad_sentence_batch(summaries_batch)) pad_texts_batch = np.array(pad_sentence_batch(texts_batch)) # Need the lengths for the _lengths parameters pad_summaries_lengths = [] for summary in pad_summaries_batch: pad_summaries_lengths.append(len(summary)) pad_texts_lengths = [] for text in pad_texts_batch: pad_texts_lengths.append(len(text)) yield pad_summaries_batch, pad_texts_batch, pad_summaries_lengths, pad_texts_lengths # 设置超参数 epochs = 100 batch_size = 64 rnn_size = 256 num_layers = 2 learning_rate = 0.005 keep_probability = 0.75 train_graph = tf.Graph() # 设置默认图 with train_graph.as_default(): # 加载输入模型 input_data, targets, lr, keep_prob, summary_length, max_summary_length, text_length = model_inputs() # 创造训练和测试的logists training_logits, inference_logits = seq2seq_model(tf.reverse(input_data, [-1]), targets, keep_prob, text_length, summary_length, max_summary_length, len(vocab_to_int) + 1, rnn_size, num_layers, vocab_to_int, batch_size) # Create tensors for the training logits and inference logits training_logits = tf.identity(training_logits.rnn_output, 'logits') inference_logits = tf.identity(inference_logits.sample_id, name='predictions') # Create the weights for sequence_loss masks = tf.sequence_mask(summary_length, max_summary_length, dtype=tf.float32, name='masks') with tf.name_scope("optimization"): # 计算损失 cost = seq.sequence_loss(training_logits,targets,masks) # 设置优化器 optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate) # 计算梯度 gradients = optimizer.compute_gradients(cost) # 防止梯度爆炸 capped_gradients = [(tf.clip_by_value(grad, -5., 5.), var) for grad, var in gradients if grad is not None] # 应用梯度 train_op = optimizer.apply_gradients(capped_gradients) print("Graph is built.") # 设置训练参数 start = 200000 end = start + 50000 sorted_summaries_short = sorted_summaries[start:end] sorted_texts_short = sorted_texts[start:end] print("The shortest text length:", len(sorted_texts_short[0])) print("The longest text length:",len(sorted_texts_short[-1])) # 训练模型 learning_rate_decay = 0.95 # 衰减因子 min_learning_rate = 0.0005 display_step = 20 # stop_early = 0 stop = 3 # If the update loss does not decrease in 3 consecutive update checks, stop training per_epoch = 3 # Make 3 update checks per epoch update_check = (len(sorted_texts_short)//batch_size//per_epoch)-1 update_loss = 0 batch_loss = 0 summary_update_loss = [] # Record the update losses for saving improvements in the model checkpoint = "best_model.ckpt" with tf.Session(graph=train_graph) as sess: sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) for epoch_i in range(1, epochs + 1): update_loss = 0 batch_loss = 0 for batch_i, (summaries_batch, texts_batch, summaries_lengths, texts_lengths) in enumerate( get_batches(sorted_summaries_short, sorted_texts_short, batch_size)): start_time = time.time() # 训练 _, loss = sess.run([train_op, cost], feed_dict={input_data: texts_batch, targets: summaries_batch, lr: learning_rate, summary_length: summaries_lengths, text_length: texts_lengths, keep_prob: keep_probability}) # 叠加损失函数 batch_loss += loss update_loss += loss end_time = time.time() batch_time = end_time - start_time if batch_i % display_step == 0 and batch_i > 0: print('Epoch {:>3}/{} Batch {:>4}/{} - Loss: {:>6.3f}, Seconds: {:>4.2f}'.format(epoch_i,epochs,batch_i,len(sorted_texts_short) // batch_size,batch_loss / display_step,batch_time * display_step)) batch_loss = 0 if batch_i % update_check == 0 and batch_i > 0: print("Average loss for this update:", round(update_loss / update_check, 3)) #添加损失函数到保存结果中 summary_update_loss.append(update_loss) # 保存模型的条件 if update_loss <= min(summary_update_loss): print('New Record!') stop_early = 0 saver = tf.train.Saver() saver.save(sess, checkpoint) else: print("No Improvement.") stop_early += 1 if stop_early == stop: break update_loss = 0 # Reduce learning rate, but not below its minimum value learning_rate *= learning_rate_decay if learning_rate < min_learning_rate: learning_rate = min_learning_rate if stop_early == stop: print("Stopping Training.") break #文本转序列 def text_to_seq(text): '''Prepare the text for the model''' text = clean_text(text) return [vocab_to_int.get(word, vocab_to_int['' ]) for word in text.split()] # Create your own review or use one from the dataset #input_sentence = "I have never eaten an apple before, but this red one was nice. \ #I think that I will try a green apple next time." #text = text_to_seq(input_sentence) random = np.random.randint(0,len(clean_texts)) #用户输入的句子 input_sentence = clean_texts[random] text = text_to_seq(clean_texts[random]) checkpoint = "./best_model.ckpt" loaded_graph = tf.Graph() # 预测模型 with tf.Session(graph=loaded_graph) as sess: # Load saved model loader = tf.train.import_meta_graph(checkpoint + '.meta') loader.restore(sess, checkpoint) input_data = loaded_graph.get_tensor_by_name('input:0') logits = loaded_graph.get_tensor_by_name('predictions:0') text_length = loaded_graph.get_tensor_by_name('text_length:0') summary_length = loaded_graph.get_tensor_by_name('summary_length:0') keep_prob = loaded_graph.get_tensor_by_name('keep_prob:0') # Multiply by batch_size to match the model's input parameters answer_logits = sess.run(logits, {input_data: [text] * batch_size, summary_length: [np.random.randint(5, 8)], text_length: [len(text)] * batch_size, keep_prob: 1.0})[0] # Remove the padding from the tweet pad = vocab_to_int["" ] print('Original Text:', input_sentence) print('\nText') print(' Word Ids: {}'.format([i for i in text])) print(' Input Words: {}'.format(" ".join([int_to_vocab[i] for i in text]))) print('\nSummary') print(' Word Ids: {}'.format([i for i in answer_logits if i != pad])) print(' Response Words: {}'.format(" ".join([int_to_vocab[i] for i in answer_logits if i != pad])))
上面的代码是基于TF1.2版本的,请注意版本的选择,然后我们看看最后的效果:
- Review(3): love individual oatmeal cups found years ago sam quit selling sound big lots quit selling found target expensive buy individually trilled get entire case time go anywhere need water microwave spoon know quaker flavor packets - Summary(3): love it