Java实现链表
单链表是一种链式存取的数据结构,用一组地址任意的存储单元存放线性表中的数据元素。链表中的数据是以结点来表示的,每个结点的构成:元素(数据元素的映象) + 指针(指示后继元素存储位置),元素就是存储数据的存储单元,指针就是连接每个结点的地址数据。(逻辑地址相连,物理地址不相连)
我们来用java的内部类来实现单链表的创建
class Link{//一个链表类
public Entry head;//定义链表的头结点
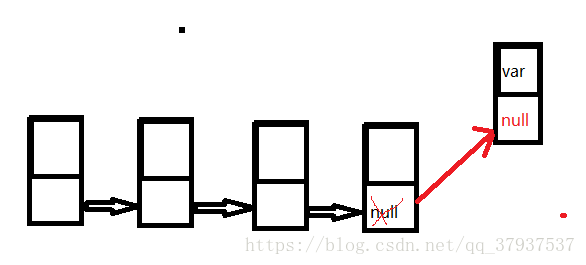
public Link(){//初始化链表时创建一个头结点
head = new Entry();
}
class Entry{//Entry 节点类
int data;//数据域
Entry next;//地址域
public Entry(){//将头结点初始化为 data=-1 next=null
data = -1;
next = null;
}
public Entry(int val){//其他结点所需的构造函数
data = val;
next = null;
}
}
}链表的简单操作
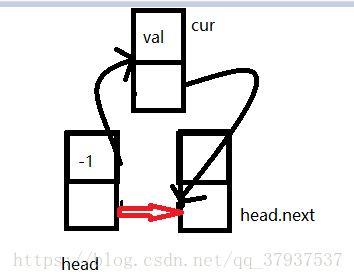
1,头插法
public void insertHead(int val){
//有这么一个节点
Entry cur = new Entry(val);
/*
* 第一种
*/
cur.next = head.next;
head.next = cur;
/*
* 第二种错误的写法
* 注意::一定要保证能能找到后面的那个结点!!!!所以不能先cur给head.next 这样就找不到原来的head.next了
*/
/*head.next = cur;
cur.next = head.next;*/
}2,尾插法
public void insertTail(int val){
Entry tmp;
Entry cur = new Entry(val);
tmp = head;
/*
* 遍历链表到最后一个结点
*/
while(tmp.next != null){
tmp = tmp.next;
}
tmp.next = cur;
cur.next = null;
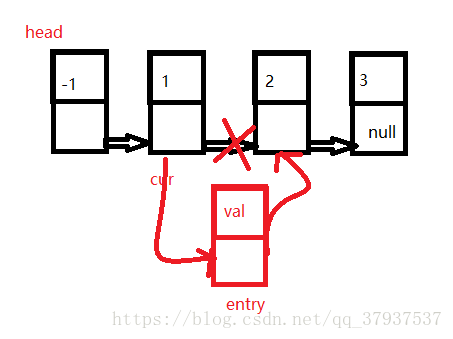
}3,将数据插入指定位置
public boolean insertPos(int pos,int val){
if(pos < 0 || pos > getLength()){
return false;
}else{
Entry cur = head;
//找到插入的地方
for(int i = 0;i <= pos-1;i++){
cur = cur.next;
}
Entry entry = new Entry(val);
//进行插入
entry.next = cur.next;
cur.next = entry;
return true;
}
}
4,得到链表长度
//得到单链表的长度
public int getLength(){
int len = 0;//长度标志量
Entry tmp;
tmp = head.next;
while(tmp != null){//遍历整个链表得到链表长度
len++;
tmp = tmp.next;
}
return len;
}5,打印链表数据
public void show(){
Entry tmp;
tmp = head;
//遍历打印链表
while(tmp.next != null){
System.out.println("data :"+tmp.next.data);
tmp = tmp.next;
}
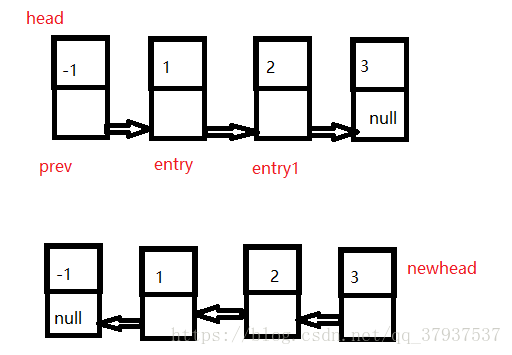
}6,链表的逆置
每次将entry的next指向prev
再prev = entry entry = entry1 entry1 = entry.next;
将它们三个都向后移一个
public Entry reserver(){
Entry newhead = null;//逆置后的新头结点
Entry prev = head;//前驱结点
Entry entry = prev.next;
prev.next = null;
while(entry.next != null){
Entry entry1 = entry.next;
entry.next = prev;
prev = entry;
entry = entry1;
}
entry.next = prev;
//这时entry就是原来链表的最后一个结点,也就是新链表的头结点
newhead = entry;
return newhead;
}7,求倒数第k个结点
两种方法
1> 直接遍历链表到链表长度len -k 这时就是倒数第k个结点
public void lastK(int len,int k){
Entry tmp;
tmp = head;
if(k < 0 ||k > len){
System.out.println("超出链表长度");
}else{
for( int i = 0;i <= len-k;i++ ){ //len就是链表长度,len-k也就是倒数第k个节点
tmp = tmp.next;
}
}
System.out.println(tmp.data);
}2>定义两个引用,将第一个先走k-1步,接下来两个同时向后遍历。直到第一个指向最后一个,另一个就指向倒数第k个
public int newLast(int k){
if(k < 0 || k > getLength()){
return -1;
}
Entry cur1,cur2;
cur1 = head;
cur2 = head;
while(k-1 > 0){
if(cur2.next != null){
cur2 = cur2.next;
k--;
}else{
return -1;
}
}
while(cur2.next != null){
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return cur1.data;
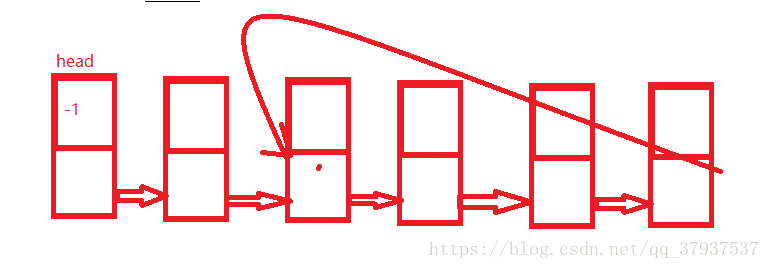
}8,判断一个单链表是否有环,环的入口,环的长度
1>首先创建一个带环的链表
public void createLoop(){
Entry cur = head;
while(cur.next != null){
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = head.next.next;
}2>判断是否有环
//判断单链表是否有环 ( 数学归纳法证明为什么是一个走两步一个走一步) 快引用 慢引用
public boolean isLoop(){
Entry fast = head;//定义一个快引用
Entry slow = head;//定义一个慢引用
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){//两个条件是为了防止fast.next.next空指针异常
fast = fast.next.next;//快的一次走两步
slow = slow.next;//慢的一次走两步
if(fast == slow){//如果相遇代表该链表有环
return true;
}
}
return false;
}3>判断环的入口
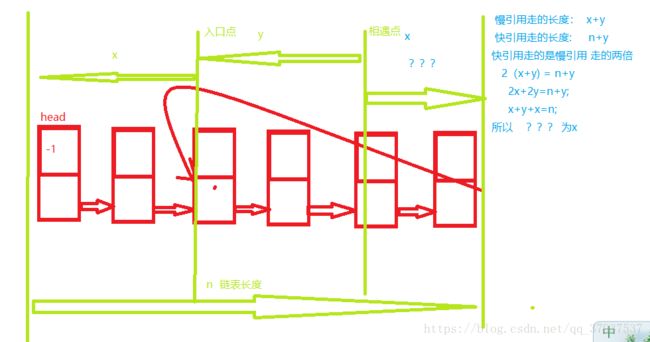
所以当第一次相遇后一个引用留在相遇点,另一个引用回到原点。同时出发保持相同速度下次遇见的地方就是环的入口点
public int getEntryLoop(){
Entry fast = head;
Entry slow = head;
if(!isLoop()){//判断是否有环
return -1;
}
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow){
break;//找到第一个相遇点
}
}
slow = head;//这个引用会到开始
while(fast != slow){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}//同时出发直到相遇
return slow.data;
}4>判断环的长度
第一种:由上图所示,环的长度即是x+y 也就是第一次相遇之后慢引用所走的路程
public int loopLength1(){
int len = 0;
Entry fast = head;
Entry slow = head;
if(!isLoop()){
return -1;
}
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
len++;
if(fast == slow){
break;
}
}
return len;
}
第二种: 第一次相遇和第二次相遇之间的路程为环的长度
public int getLooplength(){
int len = 0;
Entry fast = head;
Entry slow = head;
boolean tag = false;
if(!isLoop()){
return -1;
}
//第一次和第二次相遇之间走的距离就是环的长度
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow && tag == true){//第二次相遇
break;
}
if(fast == slow && tag == false){
tag = true;
}
if(tag == true){
len++;
}
}
return len;
}
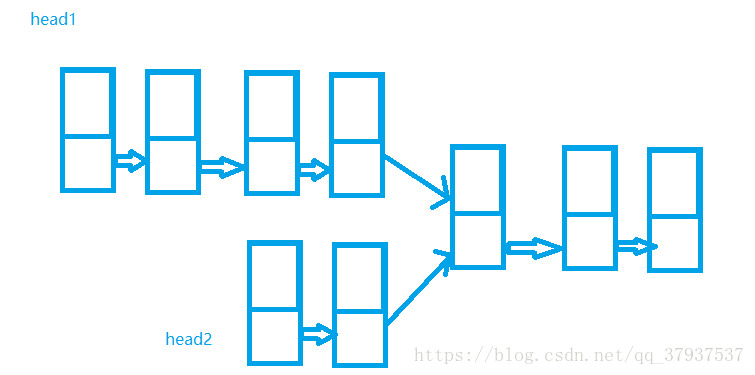
9,判断两个链表是否相交
1>创建两个相交的链表
//创建一个相交的链表
public void createCut(TestLink t1,TestLink t2){
TestLink.Entry head1 = t1.head;
TestLink.Entry head2 = t2.head;
head1.next.next = head2.next.next;
}2> 判断链表是否相交
将长的链表的引用先走两个链表之差个距离
保证开始走的时候两个引用知道结束走的距离一样
public boolean isCut(TestLink t1,TestLink t2){
TestLink.Entry head1 = t1.head;
TestLink.Entry head2 = t2.head;
int len1 = t1.getLength();
int len2 = t2.getLength();
int my_len = len1-len2;
if(my_len < 0){//确定head1指向的单链表是最长的
head1 = t2.head;
head2 = t1.head;
}
for(int i = 0;i < my_len;i++){
head1 = head1.next;
}
while(head1.next != null && head2.next != null && head1 != head2){
head1 = head1.next;
head2 = head2.next;
}
if(head1 == head2 && head1 !=null && head2 != null){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}