搭建自己的物体检测模型系列(2)使用自己的数据集来训练模型
1、创建训练和测试数据集并进行标注
注:
①图片的格式要是*jpg,并且命名不可以由中文命名。
②在labelImg中进行标注的时候标签不可以试中文,并且标签中不能有空格。
③检查图片是否都是RGB的,检测代码下面
④标签一定要统一:labelImg内部;xml文件;csv文件;record文件;pbtxt文件这五个的标签一定要统一,任何一处都不能有不同,否则会出现没有方框的情况。
对我而言目标是识别视频中识别特定的物体油桶(oil_drum),首先我们需要下载神经网络需要用到的训练和测试数据集,这可以从网上下载得到.
第一步、在 ./models/research/object_detection目录下新建文件夹images2,并在images2文件夹下新建两个文件夹(一个名为train,另一个为test),把下载的图片分别放到train和test文件夹下,这样数据的准备工作就完成了。接下来进行数据的标注。
第二步、在这里下载用来标注图片的软件labelImg,从github上下载项目(右上角“Clone or download”-“DownloadZIP”),下载到本地目录,解压。
软件使用方法:
在labellmg文件夹下打开powershell(shift+鼠标右键),键入
1、对于pyqt4:
pyrcc4 -o line/resources.py resources.qrc
对于pyqt5:
pyrcc5 -o libs/resources.py resources.qrc
运行这步完成后什么也不会出现
2、python labelImg.py
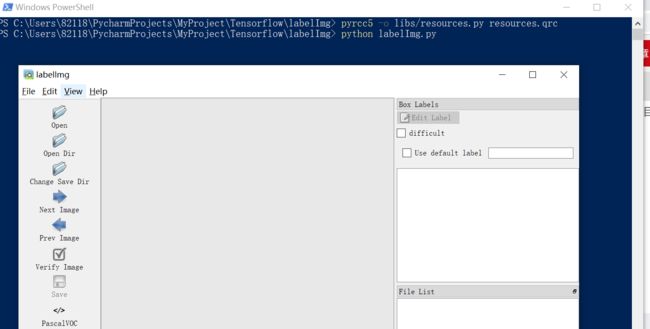
3、在这里分别打开目录models\research\object_detection\images2\train以及models\research\object_detection\images2\test,按住键盘上的w来选择范围,然后来打标签。一张图片一张图片打完标签,然后每一张图片会对应一个xml文件,里面可以看到范围和标签。

检查图片是否都是RGB的.py
from PIL import Image
import os
#path = 'C:/Users/Administrator/PycharmProjects/Tensorflow/models/research/object_detection/images2/test/' #图片目录
path = 'C:/Users/82118/PycharmProjects/MyProject/Tensorflow/models/research/object_detection/images2/test/'
for file in os.listdir(path):
extension = file.split('.')[-1]
if extension == 'jpg':
fileLoc = path+file
img = Image.open(fileLoc)
if img.mode != 'RGB':
print(file+', '+img.mode)
2、*xml文件转*csv文件
注:
①这个文件(文件名为:xml_to_csv.py)里面总共需要更改2处,需要更改的地方为下面代码中两行########之间的部分。
②需要运行两次,分别对train和test进行xml到csv文件的转换。
xml_to_csv.py文件内容
import os
import glob
import pandas as pd
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
###change this##########这里是xml文件的路径,
os.chdir('C:\\Users\\82118\\PycharmProjects\\MyProject\\Tensorflow\\models\\research\\object_detection\\images2\\test')
path = 'C:\\Users\\82118\\PycharmProjects\\MyProject\\Tensorflow\\models\\research\\object_detection\\images2\\test'
########################
def xml_to_csv(path):
xml_list = []
for xml_file in glob.glob(path + '/*.xml'):
tree = ET.parse(xml_file)
root = tree.getroot()
for member in root.findall('object'):
value = (root.find('filename').text,
int(root.find('size')[0].text),
int(root.find('size')[1].text),
member[0].text,
int(member[4][0].text),
int(member[4][1].text),
int(member[4][2].text),
int(member[4][3].text)
)
xml_list.append(value)
column_name = ['filename', 'width', 'height', 'class', 'xmin', 'ymin', 'xmax', 'ymax']
xml_df = pd.DataFrame(xml_list, columns=column_name)
return xml_df
def main():
image_path = path
xml_df = xml_to_csv(image_path)
###change########需要保存为csv文件的命名
xml_df.to_csv('oildrum_test.csv', index=None)
###################
print('Successfully converted xml to csv.')
main()
3、*csv文件转*record文件
注:
①将2个csv文件都存放在models\research\object_detection\data文件夹下
②这个文件(文件名为:csv_to_tfrecords.py)里面总共需要更改3处,需要更改的地方为下面代码中两行########之间的部分。
③需要运行两次,分别对train和test进行csv到record文件的转换。
④运行方法:代码前面说明
csv_to_tfrecords.py文件内容
#运行方法:
# 定位到 tensorflow/models/reserach/object_detection/目录下,打开Powershell窗口
# Create train data:
#python csv_to_tfrecords.py --csv_input=data/oildrum_train.csv --output_path=oildrum_train.record
# Create test data:
#python csv_to_tfrecords.py --csv_input=data/oildrum_test.csv --output_path=oildrum_test.record
import os
import io
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
from PIL import Image
from object_detection.utils import dataset_util
from collections import namedtuple, OrderedDict
###change######################################定位到自己的object_detection目录下
os.chdir('C:\\Users\\82118\\PycharmProjects\\MyProject\\Tensorflow\\models\\research\\object_detection\\')
###############################################
flags = tf.app.flags
flags.DEFINE_string('csv_input', '', 'Path to the CSV input')
flags.DEFINE_string('output_path', '', 'Path to output TFRecord')
FLAGS = flags.FLAGS
#########自己的标签以及标签的个数#######################################
# TO-DO replace this with label map
def class_text_to_int(row_label):
if row_label == 'oildrum':
return 1
else:
None
####################################################
def split(df, group):
data = namedtuple('data', ['filename', 'object'])
gb = df.groupby(group)
return [data(filename, gb.get_group(x)) for filename, x in zip(gb.groups.keys(), gb.groups)]
def create_tf_example(group, path):
with tf.gfile.GFile(os.path.join(path, '{}'.format(group.filename)), 'rb') as fid:
encoded_jpg = fid.read()
encoded_jpg_io = io.BytesIO(encoded_jpg)
image = Image.open(encoded_jpg_io)
width, height = image.size
filename = group.filename.encode('utf8')
image_format = b'jpg'
xmins = []
xmaxs = []
ymins = []
ymaxs = []
classes_text = []
classes = []
for index, row in group.object.iterrows():
xmins.append(row['xmin'] / width)
xmaxs.append(row['xmax'] / width)
ymins.append(row['ymin'] / height)
ymaxs.append(row['ymax'] / height)
classes_text.append(row['class'].encode('utf8'))
classes.append(class_text_to_int(row['class']))
tf_example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'image/height': dataset_util.int64_feature(height),
'image/width': dataset_util.int64_feature(width),
'image/filename': dataset_util.bytes_feature(filename),
'image/source_id': dataset_util.bytes_feature(filename),
'image/encoded': dataset_util.bytes_feature(encoded_jpg),
'image/format': dataset_util.bytes_feature(image_format),
'image/object/bbox/xmin': dataset_util.float_list_feature(xmins),
'image/object/bbox/xmax': dataset_util.float_list_feature(xmaxs),
'image/object/bbox/ymin': dataset_util.float_list_feature(ymins),
'image/object/bbox/ymax': dataset_util.float_list_feature(ymaxs),
'image/object/class/text': dataset_util.bytes_list_feature(classes_text),
'image/object/class/label': dataset_util.int64_list_feature(classes),
}))
return tf_example
def main(_):
writer = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(FLAGS.output_path)
#################是对test(train)文件夹下的就改为test(train)###############
path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'images2\\test')
################################################################
examples = pd.read_csv(FLAGS.csv_input)
grouped = split(examples, 'filename')
for group in grouped:
tf_example = create_tf_example(group, path)
writer.write(tf_example.SerializeToString())
writer.close()
output_path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), FLAGS.output_path)
print('Successfully created the TFRecords: {}'.format(output_path))
if __name__ == '__main__':
tf.app.run()
4、配置文件和模型
注:
①在\models\research\object_detection目录下新建training文件夹。
②在文件夹下添加配置文件ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco.config(这个可以从模型文件中获得)代码见下面。
③需要更改的地方5处,需要更改的的地方在#######两行中间。
④新建*pbtxt文件
ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco.config文件内容:
# SSD with Mobilenet v1 configuration for MSCOCO Dataset.
# Users should configure the fine_tune_checkpoint field in the train config as
# well as the label_map_path and input_path fields in the train_input_reader and
# eval_input_reader. Search for "PATH_TO_BE_CONFIGURED" to find the fields that
# should be configured.
model {
ssd {
############自己的类别数目,就是打标签时候的不同标签的数目##########
num_classes: 1
################################################
box_coder {
faster_rcnn_box_coder {
y_scale: 10.0
x_scale: 10.0
height_scale: 5.0
width_scale: 5.0
}
}
matcher {
argmax_matcher {
matched_threshold: 0.5
unmatched_threshold: 0.5
ignore_thresholds: false
negatives_lower_than_unmatched: true
force_match_for_each_row: true
}
}
similarity_calculator {
iou_similarity {
}
}
anchor_generator {
ssd_anchor_generator {
num_layers: 6
min_scale: 0.2
max_scale: 0.95
aspect_ratios: 1.0
aspect_ratios: 2.0
aspect_ratios: 0.5
aspect_ratios: 3.0
aspect_ratios: 0.3333
}
}
image_resizer {
fixed_shape_resizer {
height: 300
width: 300
}
}
box_predictor {
convolutional_box_predictor {
min_depth: 0
max_depth: 0
num_layers_before_predictor: 0
use_dropout: false
dropout_keep_probability: 0.8
kernel_size: 1
box_code_size: 4
apply_sigmoid_to_scores: false
conv_hyperparams {
activation: RELU_6,
regularizer {
l2_regularizer {
weight: 0.00004
}
}
initializer {
truncated_normal_initializer {
stddev: 0.03
mean: 0.0
}
}
batch_norm {
train: true,
scale: true,
center: true,
decay: 0.9997,
epsilon: 0.001,
}
}
}
}
feature_extractor {
type: 'ssd_mobilenet_v1'
min_depth: 16
depth_multiplier: 1.0
conv_hyperparams {
activation: RELU_6,
regularizer {
l2_regularizer {
weight: 0.00004
}
}
initializer {
truncated_normal_initializer {
stddev: 0.03
mean: 0.0
}
}
batch_norm {
train: true,
scale: true,
center: true,
decay: 0.9997,
epsilon: 0.001,
}
}
}
loss {
classification_loss {
weighted_sigmoid {
}
}
localization_loss {
weighted_smooth_l1 {
}
}
hard_example_miner {
num_hard_examples: 3000
iou_threshold: 0.99
loss_type: CLASSIFICATION
max_negatives_per_positive: 3
min_negatives_per_image: 0
}
classification_weight: 1.0
localization_weight: 1.0
}
normalize_loss_by_num_matches: true
post_processing {
batch_non_max_suppression {
score_threshold: 1e-8
iou_threshold: 0.6
max_detections_per_class: 100
max_total_detections: 100
}
score_converter: SIGMOID
}
}
}
train_config: {
########根据电脑的配置来设置,显存不够或者笔记本来的就改为1,不能再低了####
batch_size: 24
############################################
optimizer {
rms_prop_optimizer: {
learning_rate: {
exponential_decay_learning_rate {
initial_learning_rate: 0.004
decay_steps: 800720
decay_factor: 0.95
}
}
momentum_optimizer_value: 0.9
decay: 0.9
epsilon: 1.0
}
}
###################注释掉下面两行#######
fine_tune_checkpoint: "training/ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco_11_06_2017/model.ckpt"
from_detection_checkpoint: true
########################################
# Note: The below line limits the training process to 200K steps, which we
# empirically found to be sufficient enough to train the pets dataset. This
# effectively bypasses the learning rate schedule (the learning rate will
# never decay). Remove the below line to train indefinitely.
num_steps: 200000
data_augmentation_options {
random_horizontal_flip {
}
}
data_augmentation_options {
ssd_random_crop {
}
}
}
train_input_reader: {
tf_record_input_reader {
######################改为自己的record文件名和pbtxt文件名##############
input_path: "data/oildrum_train.record"
}
label_map_path: "data/oildrum.pbtxt"
}
#############################################
eval_config: {
num_examples: 8000
# Note: The below line limits the evaluation process to 10 evaluations.
# Remove the below line to evaluate indefinitely.
max_evals: 10
}
eval_input_reader: {
tf_record_input_reader {
##############record文件名和pbtxt文件名############
input_path: "data/oildrum_test.record"
}
label_map_path: "data/oildrum.pbtxt"
######################################################
shuffle: false
num_readers: 1
}
oildrum.pbtxt文件内容(你有几个标签就添加几个)
item {
id: 1
name: "oildrum"
}
5、以上完成后所有的需要的文件以及文件所在的目录结构,这是新添加的,没有列出本来还包括的。
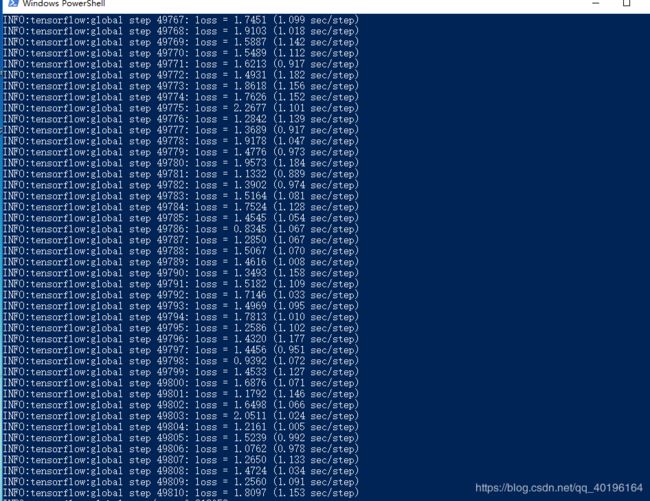
6、训练模型
进入到 models\research\object_detection文件夹下,运行如下命令:
python ./legacy/train.py --logtostderr --train_dir=training/ --pipeline_config_path=training/ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco.config
正常的话会出现下面的情况:
可视化命令:
tensorboard --logdir='training'
7、导出训练好的模型
进入到 models\research\object_detection 文件夹下,运行命令:
python export_inference_graph.py \ --input_type image_tensor \ --pipeline_config_path training/ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco.config \ --trained_checkpoint_prefix training/model.ckpt-xxx \ --output_directory oildrum_detection
这个checkpoint(.ckpt-后面的数字)可以在training文件夹下找到你自己训练的模型的情况,填上对应的数字(如果有多个,选最大的)
–output_directory 后面填写需要保存模型的位置
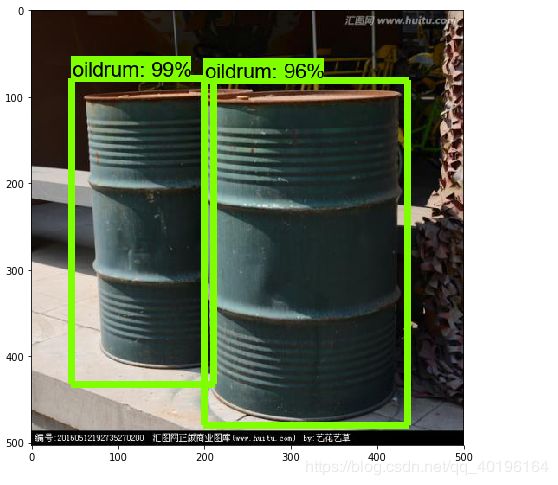
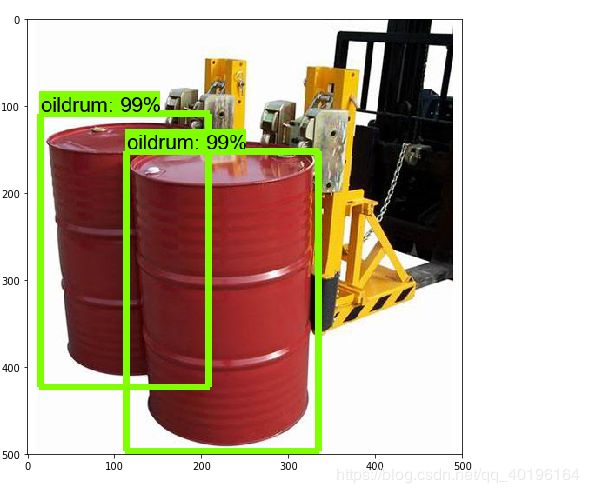
8、用自己训练好的模型进行测试
oildrum_detection.py(在spyder中运行这个文件),2处需要更改。两行#########中间是需要进行更改的部分,
import numpy as np
import os
import six.moves.urllib as urllib
import sys
import tarfile
import tensorflow as tf
import zipfile
from distutils.version import StrictVersion
from collections import defaultdict
from io import StringIO
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image
# This is needed since the notebook is stored in the object_detection folder.
sys.path.append("..")
from object_detection.utils import ops as utils_ops
# if StrictVersion(tf.__version__) < StrictVersion('1.12.0'):
# raise ImportError('Please upgrade your TensorFlow installation to v1.12.*.')
# ## Env setup
# In[2]:
# This is needed to display the images.
get_ipython().run_line_magic('matplotlib', 'inline')
# ## Object detection imports
# Here are the imports from the object detection module.
# In[3]:
# from utils import label_map_util
# from utils import visualization_utils as vis_util
import label_map_util
import visualization_utils as vis_util
# # Model preparation
# ## Variables
#
# Any model exported using the `export_inference_graph.py` tool can be loaded here simply by changing `PATH_TO_FROZEN_GRAPH` to point to a new .pb file.
#
# By default we use an "SSD with Mobilenet" model here. See the [detection model zoo](https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/research/object_detection/g3doc/detection_model_zoo.md) for a list of other models that can be run out-of-the-box with varying speeds and accuracies.
# In[4]:
# What model to download.###########change###############
MODEL_NAME = 'oildrum_detection'
#MODEL_FILE = MODEL_NAME + '.tar.gz'
#DOWNLOAD_BASE = 'http://download.tensorflow.org/models/object_detection/'
# Path to frozen detection graph. This is the actual model that is used for the object detection.
PATH_TO_FROZEN_GRAPH = MODEL_NAME + '/frozen_inference_graph.pb'
# List of the strings that is used to add correct label for each box.
PATH_TO_LABELS = os.path.join('data', 'oildrum.pbtxt')
NUM_CLASSES = 1
#######################################################
# ## Download Model
# In[5]:
#opener = urllib.request.URLopener()
#opener.retrieve(DOWNLOAD_BASE + MODEL_FILE, MODEL_FILE)
#tar_file = tarfile.open(MODEL_FILE)
#for file in tar_file.getmembers():
#file_name = os.path.basename(file.name)
#if 'frozen_inference_graph.pb' in file_name:
#tar_file.extract(file, os.getcwd())
# ## Load a (frozen) Tensorflow model into memory.
# In[6]:
detection_graph = tf.Graph()
with detection_graph.as_default():
od_graph_def = tf.GraphDef()
with tf.gfile.GFile(PATH_TO_FROZEN_GRAPH, 'rb') as fid:
serialized_graph = fid.read()
od_graph_def.ParseFromString(serialized_graph)
tf.import_graph_def(od_graph_def, name='')
# ## Loading label map
# Label maps map indices to category names, so that when our convolution network predicts `5`, we know that this corresponds to `airplane`. Here we use internal utility functions, but anything that returns a dictionary mapping integers to appropriate string labels would be fine
# In[7]:
category_index = label_map_util.create_category_index_from_labelmap(PATH_TO_LABELS, use_display_name=True)
# ## Helper code
# In[8]:
def load_image_into_numpy_array(image):
(im_width, im_height) = image.size
return np.array(image.getdata()).reshape(
(im_height, im_width, 3)).astype(np.uint8)
# # Detection
# In[9]:
# For the sake of simplicity we will use only 2 images:
# image1.jpg
# image2.jpg
# If you want to test the code with your images, just add path to the images to the TEST_IMAGE_PATHS.
#######################change###################
PATH_TO_TEST_IMAGES_DIR = 'test_images'
#TEST_IMAGE_PATHS = [ os.path.join(PATH_TO_TEST_IMAGES_DIR, 'image{}.jpg'.format(i)) for i in range(1, 3) ]
TEST_IMAGE_PATHS = os.listdir('C:\\Users\\82118\\PycharmProjects\\MyProject\\Tensorflow\\models\\research\\object_detection\\test_images')
os.chdir('C:\\Users\\82118\\PycharmProjects\\MyProject\\Tensorflow\\models\\research\\object_detection\\test_images')
###################################################
# Size, in inches, of the output images.
IMAGE_SIZE = (12, 8)
# In[10]:
def run_inference_for_single_image(image, graph):
with graph.as_default():
with tf.Session() as sess:
# Get handles to input and output tensors
ops = tf.get_default_graph().get_operations()
all_tensor_names = {output.name for op in ops for output in op.outputs}
tensor_dict = {}
for key in [
'num_detections', 'detection_boxes', 'detection_scores',
'detection_classes', 'detection_masks'
]:
tensor_name = key + ':0'
if tensor_name in all_tensor_names:
tensor_dict[key] = tf.get_default_graph().get_tensor_by_name(
tensor_name)
if 'detection_masks' in tensor_dict:
# The following processing is only for single image
detection_boxes = tf.squeeze(tensor_dict['detection_boxes'], [0])
detection_masks = tf.squeeze(tensor_dict['detection_masks'], [0])
# Reframe is required to translate mask from box coordinates to image coordinates and fit the image size.
real_num_detection = tf.cast(tensor_dict['num_detections'][0], tf.int32)
detection_boxes = tf.slice(detection_boxes, [0, 0], [real_num_detection, -1])
detection_masks = tf.slice(detection_masks, [0, 0, 0], [real_num_detection, -1, -1])
detection_masks_reframed = utils_ops.reframe_box_masks_to_image_masks(
detection_masks, detection_boxes, image.shape[1], image.shape[2])
detection_masks_reframed = tf.cast(
tf.greater(detection_masks_reframed, 0.5), tf.uint8)
# Follow the convention by adding back the batch dimension
tensor_dict['detection_masks'] = tf.expand_dims(
detection_masks_reframed, 0)
image_tensor = tf.get_default_graph().get_tensor_by_name('image_tensor:0')
# Run inference
output_dict = sess.run(tensor_dict,
feed_dict={image_tensor: image})
# all outputs are float32 numpy arrays, so convert types as appropriate
output_dict['num_detections'] = int(output_dict['num_detections'][0])
output_dict['detection_classes'] = output_dict[
'detection_classes'][0].astype(np.int64)
output_dict['detection_boxes'] = output_dict['detection_boxes'][0]
output_dict['detection_scores'] = output_dict['detection_scores'][0]
if 'detection_masks' in output_dict:
output_dict['detection_masks'] = output_dict['detection_masks'][0]
return output_dict
# In[11]:
for image_path in TEST_IMAGE_PATHS:
image = Image.open(image_path)
# the array based representation of the image will be used later in order to prepare the
# result image with boxes and labels on it.
image_np = load_image_into_numpy_array(image)
# Expand dimensions since the model expects images to have shape: [1, None, None, 3]
image_np_expanded = np.expand_dims(image_np, axis=0)
# Actual detection.
output_dict = run_inference_for_single_image(image_np_expanded, detection_graph)
print(output_dict)
# Visualization of the results of a detection.
vis_util.visualize_boxes_and_labels_on_image_array(
image_np,
output_dict['detection_boxes'],
output_dict['detection_classes'],
output_dict['detection_scores'],
category_index,
instance_masks=output_dict.get('detection_masks'),
use_normalized_coordinates=True,
line_thickness=8)
plt.figure(figsize=IMAGE_SIZE)
plt.imshow(image_np)