写在前面
最近在 K8S 1.18.2 版本的集群上搭建DevOps环境,期间遇到了各种坑。目前,搭建环境的过程中出现的各种坑均已被填平,特此记录,并分享给大家!
小伙伴们可以到链接:https://download.csdn.net/download/l1028386804/12579236下载所需要的yaml文件。
服务器规划
| IP | 主机名 | 节点 | 操作系统 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 192.168.175.101 | binghe101 | K8S Master | CentOS 8.0.1905 |
| 192.168.175.102 | binghe102 | K8S Worker | CentOS 8.0.1905 |
| 192.168.175.103 | binghe103 | K8S Worker | CentOS 8.0.1905 |
安装环境版本
| 软件名称 | 软件版本 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Docker | 19.03.8 | 提供容器环境 |
| docker-compose | 1.25.5 | 定义和运行由多个容器组成的应用 |
| K8S | 1.8.12 | 是一个开源的,用于管理云平台中多个主机上的容器化的应用,Kubernetes的目标是让部署容器化的应用简单并且高效(powerful),Kubernetes提供了应用部署,规划,更新,维护的一种机制。 |
| GitLab | 12.1.6 | 代码仓库(与SVN安装一个即可) |
| Harbor | 1.10.2 | 私有镜像仓库 |
| Jenkins | 2.89.3 | 持续集成交付 |
| SVN | 1.10.2 | 代码仓库(与GitLab安装一个即可) |
| JDK | 1.8.0_202 | Java运行基础环境 |
| maven | 3.6.3 | 构建项目的基础插件 |
服务器免密码登录
在各服务器执行如下命令。
ssh-keygen -t rsa
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
将binghe102和binghe103服务器上的id_rsa.pub文件复制到binghe101服务器。
[root@binghe102 ~]# scp .ssh/id_rsa.pub binghe101:/root/.ssh/102
[root@binghe103 ~]# scp .ssh/id_rsa.pub binghe101:/root/.ssh/103
在binghe101服务器上执行如下命令。
cat ~/.ssh/102 >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
cat ~/.ssh/103 >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
然后将authorized_keys文件分别复制到binghe102、binghe103服务器。
[root@binghe101 ~]# scp .ssh/authorized_keys binghe102:/root/.ssh/authorized_keys
[root@binghe101 ~]# scp .ssh/authorized_keys binghe103:/root/.ssh/authorized_keys
删除binghe101节点上~/.ssh下的102和103文件。
rm ~/.ssh/102
rm ~/.ssh/103
安装JDK
需要在每台服务器上安装JDK环境。到Oracle官方下载JDK,我这里下的JDK版本为1.8.0_202,下载后解压并配置系统环境变量。
tar -zxvf jdk1.8.0_212.tar.gz
mv jdk1.8.0_212 /usr/local
接下来,配置系统环境变量。
vim /etc/profile
配置项内容如下所示。
JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/jdk1.8.0_212
CLASS_PATH=.:$JAVA_HOME/lib
PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH
export JAVA_HOME CLASS_PATH PATH
接下来执行如下命令使系统环境变量生效。
source /etc/profile
安装Maven
到Apache官方下载Maven,我这里下载的Maven版本为3.6.3。下载后直接解压并配置系统环境变量。
tar -zxvf apache-maven-3.6.3-bin.tar.gz
mv apache-maven-3.6.3-bin /usr/local
接下来,就是配置系统环境变量。
vim /etc/profile
配置项内容如下所示。
JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/jdk1.8.0_212
MAVEN_HOME=/usr/local/apache-maven-3.6.3-bin
CLASS_PATH=.:$JAVA_HOME/lib
PATH=$MAVEN_HOME/bin:$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH
export JAVA_HOME CLASS_PATH MAVEN_HOME PATH
接下来执行如下命令使系统环境变量生效。
source /etc/profile
接下来,修改Maven的配置文件,如下所示。
/home/repository
将Maven下载的Jar包存储到/home/repository目录下。
安装Docker环境
本文档基于Docker 19.03.8 版本搭建Docker环境。
在所有服务器上创建install_docker.sh脚本,脚本内容如下所示。
export REGISTRY_MIRROR=https://registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com
dnf install yum*
yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2
yum-config-manager --add-repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
dnf install https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/7/x86_64/stable/Packages/containerd.io-1.2.13-3.1.el7.x86_64.rpm
yum install -y docker-ce-19.03.8 docker-ce-cli-19.03.8
systemctl enable docker.service
systemctl start docker.service
docker version
在每台服务器上为install_docker.sh脚本赋予可执行权限,并执行脚本即可。
安装docker-compose
注意:在每台服务器上安装docker-compose
1.下载docker-compose文件
curl -L https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.25.5/docker-compose-`uname -s`-`uname -m` -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
2.为docker-compose文件赋予可执行权限
chmod a+x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
3.查看docker-compose版本
[root@binghe ~]# docker-compose version
docker-compose version 1.25.5, build 8a1c60f6
docker-py version: 4.1.0
CPython version: 3.7.5
OpenSSL version: OpenSSL 1.1.0l 10 Sep 2019
安装K8S集群环境
本文档基于K8S 1.8.12版本来搭建K8S集群
安装K8S基础环境
在所有服务器上创建install_k8s.sh脚本文件,脚本文件的内容如下所示。
#配置阿里云镜像加速器
mkdir -p /etc/docker
tee /etc/docker/daemon.json <<-'EOF'
{
"registry-mirrors": ["https://zz3sblpi.mirror.aliyuncs.com"]
}
EOF
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart docker
#安装nfs-utils
yum install -y nfs-utils
yum install -y wget
#启动nfs-server
systemctl start nfs-server
systemctl enable nfs-server
#关闭防火墙
systemctl stop firewalld
systemctl disable firewalld
#关闭SeLinux
setenforce 0
sed -i "s/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g" /etc/selinux/config
# 关闭 swap
swapoff -a
yes | cp /etc/fstab /etc/fstab_bak
cat /etc/fstab_bak |grep -v swap > /etc/fstab
#修改 /etc/sysctl.conf
# 如果有配置,则修改
sed -i "s#^net.ipv4.ip_forward.*#net.ipv4.ip_forward=1#g" /etc/sysctl.conf
sed -i "s#^net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables.*#net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables=1#g" /etc/sysctl.conf
sed -i "s#^net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables.*#net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables=1#g" /etc/sysctl.conf
sed -i "s#^net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6.*#net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=1#g" /etc/sysctl.conf
sed -i "s#^net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6.*#net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6=1#g" /etc/sysctl.conf
sed -i "s#^net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6.*#net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6=1#g" /etc/sysctl.conf
sed -i "s#^net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding.*#net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding=1#g" /etc/sysctl.conf
# 可能没有,追加
echo "net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
echo "net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
echo "net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
echo "net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
echo "net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
echo "net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6 = 1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
echo "net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding = 1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
# 执行命令以应用
sysctl -p
# 配置K8S的yum源
cat < /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
repo_gpgcheck=0
gpgkey=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg
http://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
EOF
# 卸载旧版本K8S
yum remove -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl
# 安装kubelet、kubeadm、kubectl,这里我安装的是1.18.2版本,你也可以安装1.17.2版本
yum install -y kubelet-1.18.2 kubeadm-1.18.2 kubectl-1.18.2
# 修改docker Cgroup Driver为systemd
# # 将/usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service文件中的这一行 ExecStart=/usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// --containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sock
# # 修改为 ExecStart=/usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// --containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sock --exec-opt native.cgroupdriver=systemd
# 如果不修改,在添加 worker 节点时可能会碰到如下错误
# [WARNING IsDockerSystemdCheck]: detected "cgroupfs" as the Docker cgroup driver. The recommended driver is "systemd".
# Please follow the guide at https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/cri/
sed -i "s#^ExecStart=/usr/bin/dockerd.*#ExecStart=/usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// --containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sock --exec-opt native.cgroupdriver=systemd#g" /usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service
# 设置 docker 镜像,提高 docker 镜像下载速度和稳定性
# 如果访问 https://hub.docker.io 速度非常稳定,亦可以跳过这个步骤
# curl -sSL https://kuboard.cn/install-script/set_mirror.sh | sh -s ${REGISTRY_MIRROR}
# 重启 docker,并启动 kubelet
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart docker
systemctl enable kubelet && systemctl start kubelet
docker version
在每台服务器上为install_k8s.sh脚本赋予可执行权限,并执行脚本即可。
初始化Master节点
只在binghe101服务器上执行的操作。
1.初始化Master节点的网络环境
注意:下面的命令需要在命令行手动执行。
# 只在 master 节点执行
# export 命令只在当前 shell 会话中有效,开启新的 shell 窗口后,如果要继续安装过程,请重新执行此处的 export 命令
export MASTER_IP=192.168.175.101
# 替换 k8s.master 为 您想要的 dnsName
export APISERVER_NAME=k8s.master
# Kubernetes 容器组所在的网段,该网段安装完成后,由 kubernetes 创建,事先并不存在于物理网络中
export POD_SUBNET=172.18.0.1/16
echo "${MASTER_IP} ${APISERVER_NAME}" >> /etc/hosts
2.初始化Master节点
在binghe101服务器上创建init_master.sh脚本文件,文件内容如下所示。
#!/bin/bash
# 脚本出错时终止执行
set -e
if [ ${#POD_SUBNET} -eq 0 ] || [ ${#APISERVER_NAME} -eq 0 ]; then
echo -e "\033[31;1m请确保您已经设置了环境变量 POD_SUBNET 和 APISERVER_NAME \033[0m"
echo 当前POD_SUBNET=$POD_SUBNET
echo 当前APISERVER_NAME=$APISERVER_NAME
exit 1
fi
# 查看完整配置选项 https://godoc.org/k8s.io/kubernetes/cmd/kubeadm/app/apis/kubeadm/v1beta2
rm -f ./kubeadm-config.yaml
cat < ./kubeadm-config.yaml
apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta2
kind: ClusterConfiguration
kubernetesVersion: v1.18.2
imageRepository: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers
controlPlaneEndpoint: "${APISERVER_NAME}:6443"
networking:
serviceSubnet: "10.96.0.0/16"
podSubnet: "${POD_SUBNET}"
dnsDomain: "cluster.local"
EOF
# kubeadm init
# 根据服务器网速的情况,您需要等候 3 - 10 分钟
kubeadm init --config=kubeadm-config.yaml --upload-certs
# 配置 kubectl
rm -rf /root/.kube/
mkdir /root/.kube/
cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf /root/.kube/config
# 安装 calico 网络插件
# 参考文档 https://docs.projectcalico.org/v3.13/getting-started/kubernetes/self-managed-onprem/onpremises
echo "安装calico-3.13.1"
rm -f calico-3.13.1.yaml
wget https://kuboard.cn/install-script/calico/calico-3.13.1.yaml
kubectl apply -f calico-3.13.1.yaml
赋予init_master.sh脚本文件可执行权限并执行脚本。
3.查看Master节点的初始化结果
(1)确保所有容器组处于Running状态
# 执行如下命令,等待 3-10 分钟,直到所有的容器组处于 Running 状态
watch kubectl get pod -n kube-system -o wide
具体执行如下所示。
[root@binghe101 ~]# watch kubectl get pod -n kube-system -o wide
Every 2.0s: kubectl get pod -n kube-system -o wide binghe101: Sun May 10 11:01:32 2020
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
calico-kube-controllers-5b8b769fcd-5dtlp 1/1 Running 0 118s 172.18.203.66 binghe101
calico-node-fnv8g 1/1 Running 0 118s 192.168.175.101 binghe101
coredns-546565776c-27t7h 1/1 Running 0 2m1s 172.18.203.67 binghe101
coredns-546565776c-hjb8z 1/1 Running 0 2m1s 172.18.203.65 binghe101
etcd-binghe101 1/1 Running 0 2m7s 192.168.175.101 binghe101
kube-apiserver-binghe101 1/1 Running 0 2m7s 192.168.175.101 binghe101
kube-controller-manager-binghe101 1/1 Running 0 2m7s 192.168.175.101 binghe101
kube-proxy-dvgsr 1/1 Running 0 2m1s 192.168.175.101 binghe101
kube-scheduler-binghe101 1/1 Running 0 2m7s 192.168.175.101 binghe101
(2) 查看 Master 节点初始化结果
kubectl get nodes -o wide
具体执行如下所示。
[root@binghe101 ~]# kubectl get nodes -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
binghe101 Ready master 3m28s v1.18.2 192.168.175.101 CentOS Linux 8 (Core) 4.18.0-80.el8.x86_64 docker://19.3.8
初始化Worker节点
1.获取join命令参数
在Master节点(binghe101服务器)上执行如下命令获取join命令参数。
kubeadm token create --print-join-command
具体执行如下所示。
[root@binghe101 ~]# kubeadm token create --print-join-command
W0510 11:04:34.828126 56132 configset.go:202] WARNING: kubeadm cannot validate component configs for API groups [kubelet.config.k8s.io kubeproxy.config.k8s.io]
kubeadm join k8s.master:6443 --token 8nblts.62xytoqufwsqzko2 --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:1717cc3e34f6a56b642b5751796530e367aa73f4113d09994ac3455e33047c0d
其中,有如下一行输出。
kubeadm join k8s.master:6443 --token 8nblts.62xytoqufwsqzko2 --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:1717cc3e34f6a56b642b5751796530e367aa73f4113d09994ac3455e33047c0d
这行代码就是获取到的join命令。
注意:join命令中的token的有效时间为 2 个小时,2小时内,可以使用此 token 初始化任意数量的 worker 节点。
2.初始化Worker节点
针对所有的 worker 节点执行,在这里,就是在binghe102服务器和binghe103服务器上执行。
在命令分别手动执行如下命令。
# 只在 worker 节点执行
# 192.168.175.101 为 master 节点的内网 IP
export MASTER_IP=192.168.175.101
# 替换 k8s.master 为初始化 master 节点时所使用的 APISERVER_NAME
export APISERVER_NAME=k8s.master
echo "${MASTER_IP} ${APISERVER_NAME}" >> /etc/hosts
# 替换为 master 节点上 kubeadm token create 命令输出的join
kubeadm join k8s.master:6443 --token 8nblts.62xytoqufwsqzko2 --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:1717cc3e34f6a56b642b5751796530e367aa73f4113d09994ac3455e33047c0d
具体执行如下所示。
[root@binghe102 ~]# export MASTER_IP=192.168.175.101
[root@binghe102 ~]# export APISERVER_NAME=k8s.master
[root@binghe102 ~]# echo "${MASTER_IP} ${APISERVER_NAME}" >> /etc/hosts
[root@binghe102 ~]# kubeadm join k8s.master:6443 --token 8nblts.62xytoqufwsqzko2 --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:1717cc3e34f6a56b642b5751796530e367aa73f4113d09994ac3455e33047c0d
W0510 11:08:27.709263 42795 join.go:346] [preflight] WARNING: JoinControlPane.controlPlane settings will be ignored when control-plane flag is not set.
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[WARNING FileExisting-tc]: tc not found in system path
[preflight] Reading configuration from the cluster...
[preflight] FYI: You can look at this config file with 'kubectl -n kube-system get cm kubeadm-config -oyaml'
[kubelet-start] Downloading configuration for the kubelet from the "kubelet-config-1.18" ConfigMap in the kube-system namespace
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet
[kubelet-start] Waiting for the kubelet to perform the TLS Bootstrap...
This node has joined the cluster:
* Certificate signing request was sent to apiserver and a response was received.
* The Kubelet was informed of the new secure connection details.
Run 'kubectl get nodes' on the control-plane to see this node join the cluster.
根据输出结果可以看出,Worker节点加入了K8S集群。
注意:kubeadm join…就是master 节点上 kubeadm token create 命令输出的join。
3.查看初始化结果
在Master节点(binghe101服务器)执行如下命令查看初始化结果。
kubectl get nodes -o wide
具体执行如下所示。
[root@binghe101 ~]# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
binghe101 Ready master 20m v1.18.2
binghe102 Ready 2m46s v1.18.2
binghe103 Ready 2m46s v1.18.2
注意:kubectl get nodes命令后面加上-o wide参数可以输出更多的信息。
重启K8S集群引起的问题
1.Worker节点故障不能启动
Master 节点的 IP 地址发生变化,导致 worker 节点不能启动。需要重新安装K8S集群,并确保所有节点都有固定的内网 IP 地址。
2.Pod崩溃或不能正常访问
重启服务器后使用如下命令查看Pod的运行状态。
kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
发现很多 Pod 不在 Running 状态,此时,需要使用如下命令删除运行不正常的Pod。
kubectl delete pod -n
注意:如果Pod 是使用 Deployment、StatefulSet 等控制器创建的,K8S 将创建新的 Pod 作为替代,重新启动的 Pod 通常能够正常工作。
K8S安装ingress-nginx
注意:在Master节点(binghe101服务器上执行)
1.创建ingress-nginx命名空间
创建ingress-nginx-namespace.yaml文件,文件内容如下所示。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: ingress-nginx
labels:
name: ingress-nginx
执行如下命令创建ingress-nginx命名空间。
kubectl apply -f ingress-nginx-namespace.yaml
2.安装ingress controller
创建ingress-nginx-mandatory.yaml文件,文件内容如下所示。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: ingress-nginx
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: default-http-backend
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: default-http-backend
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
namespace: ingress-nginx
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: default-http-backend
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: default-http-backend
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
spec:
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 60
containers:
- name: default-http-backend
# Any image is permissible as long as:
# 1. It serves a 404 page at /
# 2. It serves 200 on a /healthz endpoint
image: registry.cn-qingdao.aliyuncs.com/kubernetes_xingej/defaultbackend-amd64:1.5
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /healthz
port: 8080
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 30
timeoutSeconds: 5
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
resources:
limits:
cpu: 10m
memory: 20Mi
requests:
cpu: 10m
memory: 20Mi
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: default-http-backend
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: default-http-backend
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 8080
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/name: default-http-backend
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
---
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: nginx-configuration
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
---
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: tcp-services
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
---
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: udp-services
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress-serviceaccount
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress-clusterrole
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- configmaps
- endpoints
- nodes
- pods
- secrets
verbs:
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- nodes
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- services
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- "extensions"
resources:
- ingresses
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- events
verbs:
- create
- patch
- apiGroups:
- "extensions"
resources:
- ingresses/status
verbs:
- update
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress-role
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- configmaps
- pods
- secrets
- namespaces
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- configmaps
resourceNames:
# Defaults to "-"
# Here: "-"
# This has to be adapted if you change either parameter
# when launching the nginx-ingress-controller.
- "ingress-controller-leader-nginx"
verbs:
- get
- update
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- configmaps
verbs:
- create
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- endpoints
verbs:
- get
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress-role-nisa-binding
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: nginx-ingress-role
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: nginx-ingress-serviceaccount
namespace: ingress-nginx
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress-clusterrole-nisa-binding
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: nginx-ingress-clusterrole
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: nginx-ingress-serviceaccount
namespace: ingress-nginx
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress-controller
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
annotations:
prometheus.io/port: "10254"
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
spec:
serviceAccountName: nginx-ingress-serviceaccount
containers:
- name: nginx-ingress-controller
image: registry.cn-qingdao.aliyuncs.com/kubernetes_xingej/nginx-ingress-controller:0.20.0
args:
- /nginx-ingress-controller
- --default-backend-service=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/default-http-backend
- --configmap=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/nginx-configuration
- --tcp-services-configmap=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/tcp-services
- --udp-services-configmap=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/udp-services
- --publish-service=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/ingress-nginx
- --annotations-prefix=nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io
securityContext:
capabilities:
drop:
- ALL
add:
- NET_BIND_SERVICE
# www-data -> 33
runAsUser: 33
env:
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
- name: https
containerPort: 443
livenessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /healthz
port: 10254
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 1
readinessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /healthz
port: 10254
scheme: HTTP
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 1
---
执行如下命令安装ingress controller。
kubectl apply -f ingress-nginx-mandatory.yaml
3.安装K8S SVC:ingress-nginx
主要是用来用于暴露pod:nginx-ingress-controller。
创建service-nodeport.yaml文件,文件内容如下所示。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: ingress-nginx
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 80
protocol: TCP
nodePort: 30080
- name: https
port: 443
targetPort: 443
protocol: TCP
nodePort: 30443
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
执行如下命令安装。
kubectl apply -f service-nodeport.yaml
4.访问K8S SVC:ingress-nginx
查看ingress-nginx命名空间的部署情况,如下所示。
[root@binghe101 k8s]# kubectl get pod -n ingress-nginx
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
default-http-backend-796ddcd9b-vfmgn 1/1 Running 1 10h
nginx-ingress-controller-58985cc996-87754 1/1 Running 2 10h
在命令行服务器命令行输入如下命令查看ingress-nginx的端口映射情况。
kubectl get svc -n ingress-nginx
具体如下所示。
[root@binghe101 k8s]# kubectl get svc -n ingress-nginx
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
default-http-backend ClusterIP 10.96.247.2 80/TCP 7m3s
ingress-nginx NodePort 10.96.40.6 80:30080/TCP,443:30443/TCP 4m35s
所以,可以通过Master节点(binghe101服务器)的IP地址和30080端口号来访问ingress-nginx,如下所示。
[root@binghe101 k8s]# curl 192.168.175.101:30080
default backend - 404
也可以在浏览器打开http://192.168.175.101:30080 来访问ingress-nginx,如下所示。

K8S安装gitlab代码仓库
注意:在Master节点(binghe101服务器上执行)
1.创建k8s-ops命名空间
创建k8s-ops-namespace.yaml文件,文件内容如下所示。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: k8s-ops
labels:
name: k8s-ops
执行如下命令创建命名空间。
kubectl apply -f k8s-ops-namespace.yaml
2.安装gitlab-redis
创建gitlab-redis.yaml文件,文件的内容如下所示。
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: redis
namespace: k8s-ops
labels:
name: redis
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: redis
template:
metadata:
name: redis
labels:
name: redis
spec:
containers:
- name: redis
image: sameersbn/redis
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- name: redis
containerPort: 6379
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/lib/redis
name: data
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- redis-cli
- ping
initialDelaySeconds: 30
timeoutSeconds: 5
readinessProbe:
exec:
command:
- redis-cli
- ping
initialDelaySeconds: 10
timeoutSeconds: 5
volumes:
- name: data
hostPath:
path: /data1/docker/xinsrv/redis
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: redis
namespace: k8s-ops
labels:
name: redis
spec:
ports:
- name: redis
port: 6379
targetPort: redis
selector:
name: redis
首先,在命令行执行如下命令创建/data1/docker/xinsrv/redis目录。
mkdir -p /data1/docker/xinsrv/redis
执行如下命令安装gitlab-redis。
kubectl apply -f gitlab-redis.yaml
3.安装gitlab-postgresql
创建gitlab-postgresql.yaml,文件内容如下所示。
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: postgresql
namespace: k8s-ops
labels:
name: postgresql
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: postgresql
template:
metadata:
name: postgresql
labels:
name: postgresql
spec:
containers:
- name: postgresql
image: sameersbn/postgresql
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
env:
- name: DB_USER
value: gitlab
- name: DB_PASS
value: passw0rd
- name: DB_NAME
value: gitlab_production
- name: DB_EXTENSION
value: pg_trgm
ports:
- name: postgres
containerPort: 5432
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/lib/postgresql
name: data
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- pg_isready
- -h
- localhost
- -U
- postgres
initialDelaySeconds: 30
timeoutSeconds: 5
readinessProbe:
exec:
command:
- pg_isready
- -h
- localhost
- -U
- postgres
initialDelaySeconds: 5
timeoutSeconds: 1
volumes:
- name: data
hostPath:
path: /data1/docker/xinsrv/postgresql
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: postgresql
namespace: k8s-ops
labels:
name: postgresql
spec:
ports:
- name: postgres
port: 5432
targetPort: postgres
selector:
name: postgresql
首先,执行如下命令创建/data1/docker/xinsrv/postgresql目录。
mkdir -p /data1/docker/xinsrv/postgresql
接下来,安装gitlab-postgresql,如下所示。
kubectl apply -f gitlab-postgresql.yaml
4.安装gitlab
(1)配置用户名和密码
首先,在命令行使用base64编码为用户名和密码进行转码,本示例中,使用的用户名为admin,密码为admin.1231
转码情况如下所示。
[root@binghe101 k8s]# echo -n 'admin' | base64
YWRtaW4=
[root@binghe101 k8s]# echo -n 'admin.1231' | base64
YWRtaW4uMTIzMQ==
转码后的用户名为:YWRtaW4= 密码为:YWRtaW4uMTIzMQ==
也可以对base64编码后的字符串解码,例如,对密码字符串解码,如下所示。
[root@binghe101 k8s]# echo 'YWRtaW4uMTIzMQ==' | base64 --decode
admin.1231
接下来,创建secret-gitlab.yaml文件,主要是用户来配置GitLab的用户名和密码,文件内容如下所示。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
namespace: k8s-ops
name: git-user-pass
type: Opaque
data:
username: YWRtaW4=
password: YWRtaW4uMTIzMQ==
执行配置文件的内容,如下所示。
kubectl create -f ./secret-gitlab.yaml
(2)安装GitLab
创建gitlab.yaml文件,文件的内容如下所示。
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: gitlab
namespace: k8s-ops
labels:
name: gitlab
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: gitlab
template:
metadata:
name: gitlab
labels:
name: gitlab
spec:
containers:
- name: gitlab
image: sameersbn/gitlab:12.1.6
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
env:
- name: TZ
value: Asia/Shanghai
- name: GITLAB_TIMEZONE
value: Beijing
- name: GITLAB_SECRETS_DB_KEY_BASE
value: long-and-random-alpha-numeric-string
- name: GITLAB_SECRETS_SECRET_KEY_BASE
value: long-and-random-alpha-numeric-string
- name: GITLAB_SECRETS_OTP_KEY_BASE
value: long-and-random-alpha-numeric-string
- name: GITLAB_ROOT_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: git-user-pass
key: password
- name: GITLAB_ROOT_EMAIL
value: [email protected]
- name: GITLAB_HOST
value: gitlab.binghe.com
- name: GITLAB_PORT
value: "80"
- name: GITLAB_SSH_PORT
value: "30022"
- name: GITLAB_NOTIFY_ON_BROKEN_BUILDS
value: "true"
- name: GITLAB_NOTIFY_PUSHER
value: "false"
- name: GITLAB_BACKUP_SCHEDULE
value: daily
- name: GITLAB_BACKUP_TIME
value: 01:00
- name: DB_TYPE
value: postgres
- name: DB_HOST
value: postgresql
- name: DB_PORT
value: "5432"
- name: DB_USER
value: gitlab
- name: DB_PASS
value: passw0rd
- name: DB_NAME
value: gitlab_production
- name: REDIS_HOST
value: redis
- name: REDIS_PORT
value: "6379"
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
- name: ssh
containerPort: 22
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /home/git/data
name: data
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /
port: 80
initialDelaySeconds: 180
timeoutSeconds: 5
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /
port: 80
initialDelaySeconds: 5
timeoutSeconds: 1
volumes:
- name: data
hostPath:
path: /data1/docker/xinsrv/gitlab
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: gitlab
namespace: k8s-ops
labels:
name: gitlab
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
nodePort: 30088
- name: ssh
port: 22
targetPort: ssh
nodePort: 30022
type: NodePort
selector:
name: gitlab
---
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: gitlab
namespace: k8s-ops
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: traefik
spec:
rules:
- host: gitlab.binghe.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: gitlab
servicePort: http
注意:在配置GitLab时,监听主机时,不能使用IP地址,需要使用主机名或者域名,上述配置中,我使用的是gitlab.binghe.com主机名。
在命令行执行如下命令创建/data1/docker/xinsrv/gitlab目录。
mkdir -p /data1/docker/xinsrv/gitlab
安装GitLab,如下所示。
kubectl apply -f gitlab.yaml
5.安装完成
查看k8s-ops命名空间部署情况,如下所示。
[root@binghe101 k8s]# kubectl get pod -n k8s-ops
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
gitlab-7b459db47c-5vk6t 0/1 Running 0 11s
postgresql-79567459d7-x52vx 1/1 Running 0 30m
redis-67f4cdc96c-h5ckz 1/1 Running 1 10h
也可以使用如下命令查看。
[root@binghe101 k8s]# kubectl get pod --namespace=k8s-ops
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
gitlab-7b459db47c-5vk6t 0/1 Running 0 36s
postgresql-79567459d7-x52vx 1/1 Running 0 30m
redis-67f4cdc96c-h5ckz 1/1 Running 1 10h
二者效果一样。
接下来,查看GitLab的端口映射,如下所示。
[root@binghe101 k8s]# kubectl get svc -n k8s-ops
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
gitlab NodePort 10.96.153.100 80:30088/TCP,22:30022/TCP 2m42s
postgresql ClusterIP 10.96.203.119 5432/TCP 32m
redis ClusterIP 10.96.107.150 6379/TCP 10h
此时,可以看到,可以通过Master节点(binghe101)的主机名gitlab.binghe.com和端口30088就能够访问GitLab。由于我这里使用的是虚拟机来搭建相关的环境,在本机访问虚拟机映射的gitlab.binghe.com时,需要配置本机的hosts文件,在本机的hosts文件中加入如下配置项。
192.168.175.101 gitlab.binghe.com
注意:在Windows操作系统中,hosts文件所在的目录如下。
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc
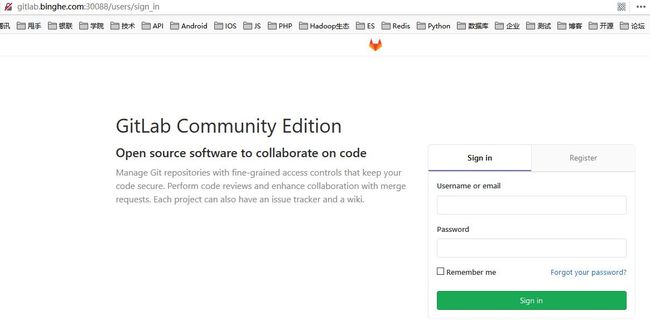
接下来,就可以在浏览器中通过链接:http://gitlab.binghe.com:30088 来访问GitLab了,如下所示。
此时,可以通过用户名root和密码admin.1231来登录GitLab了。
注意:这里的用户名是root而不是admin,因为root是GitLab默认的超级用户。
登录后的界面如下所示。
到此,K8S安装gitlab完成。
安装Harbor私有仓库
注意:这里将Harbor私有仓库安装在Master节点(binghe101服务器)上,实际生产环境中建议安装在其他服务器。
1.下载Harbor的离线安装版本
wget https://github.com/goharbor/harbor/releases/download/v1.10.2/harbor-offline-installer-v1.10.2.tgz
2.解压Harbor的安装包
tar -zxvf harbor-offline-installer-v1.10.2.tgz
解压成功后,会在服务器当前目录生成一个harbor目录。
3.配置Harbor
注意:这里,我将Harbor的端口修改成了1180,如果不修改Harbor的端口,默认的端口是80。
(1)修改harbor.yml文件
cd harbor
vim harbor.yml
修改的配置项如下所示。
hostname: 192.168.175.101
http:
port: 1180
harbor_admin_password: binghe123
###并把https注释掉,不然在安装的时候会报错:ERROR:root:Error: The protocol is https but attribute ssl_cert is not set
#https:
#port: 443
#certificate: /your/certificate/path
#private_key: /your/private/key/path
(2)修改daemon.json文件
修改/etc/docker/daemon.json文件,没有的话就创建,在/etc/docker/daemon.json文件中添加如下内容。
[root@binghe~]# cat /etc/docker/daemon.json
{
"registry-mirrors": ["https://zz3sblpi.mirror.aliyuncs.com"],
"insecure-registries":["192.168.175.101:1180"]
}
也可以在服务器上使用 ip addr 命令查看本机所有的IP地址段,将其配置到/etc/docker/daemon.json文件中。这里,我配置后的文件内容如下所示。
{
"registry-mirrors": ["https://zz3sblpi.mirror.aliyuncs.com"],
"insecure-registries":["192.168.175.0/16","172.17.0.0/16", "172.18.0.0/16", "172.16.29.0/16", "192.168.175.101:1180"]
}
4.安装并启动harbor
配置完成后,输入如下命令即可安装并启动Harbor
[root@binghe harbor]# ./install.sh
5.登录Harbor并添加账户
安装成功后,在浏览器地址栏输入http://192.168.175.101:1180打开链接,如下图所示。
输入用户名admin和密码binghe123,登录系统,如下图所示
接下来,我们选择用户管理,添加一个管理员账户,为后续打包Docker镜像和上传Docker镜像做准备。添加账户的步骤如下所示。
此处填写的密码为Binghe123。
此时,账户binghe还不是管理员,此时选中binghe账户,点击“设置为管理员”。
此时,binghe账户就被设置为管理员了。到此,Harbor的安装就完成了。
6.修改Harbor端口
如果安装Harbor后,大家需要修改Harbor的端口,可以按照如下步骤修改Harbor的端口,这里,我以将80端口修改为1180端口为例
(1)修改harbor.yml文件
cd harbor
vim harbor.yml
修改的配置项如下所示。
hostname: 192.168.175.101
http:
port: 1180
harbor_admin_password: binghe123
###并把https注释掉,不然在安装的时候会报错:ERROR:root:Error: The protocol is https but attribute ssl_cert is not set
#https:
#port: 443
#certificate: /your/certificate/path
#private_key: /your/private/key/path
(2)修改docker-compose.yml文件
vim docker-compose.yml
修改的配置项如下所示。
ports:
- 1180:80
(3)修改config.yml文件
cd common/config/registry
vim config.yml
修改的配置项如下所示。
realm: http://192.168.175.101:1180/service/token
(4)重启Docker
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart docker.service
(5)重启Harbor
[root@binghe harbor]# docker-compose down
Stopping harbor-log ... done
Removing nginx ... done
Removing harbor-portal ... done
Removing harbor-jobservice ... done
Removing harbor-core ... done
Removing redis ... done
Removing registry ... done
Removing registryctl ... done
Removing harbor-db ... done
Removing harbor-log ... done
Removing network harbor_harbor
[root@binghe harbor]# ./prepare
prepare base dir is set to /mnt/harbor
Clearing the configuration file: /config/log/logrotate.conf
Clearing the configuration file: /config/nginx/nginx.conf
Clearing the configuration file: /config/core/env
Clearing the configuration file: /config/core/app.conf
Clearing the configuration file: /config/registry/root.crt
Clearing the configuration file: /config/registry/config.yml
Clearing the configuration file: /config/registryctl/env
Clearing the configuration file: /config/registryctl/config.yml
Clearing the configuration file: /config/db/env
Clearing the configuration file: /config/jobservice/env
Clearing the configuration file: /config/jobservice/config.yml
Generated configuration file: /config/log/logrotate.conf
Generated configuration file: /config/nginx/nginx.conf
Generated configuration file: /config/core/env
Generated configuration file: /config/core/app.conf
Generated configuration file: /config/registry/config.yml
Generated configuration file: /config/registryctl/env
Generated configuration file: /config/db/env
Generated configuration file: /config/jobservice/env
Generated configuration file: /config/jobservice/config.yml
loaded secret from file: /secret/keys/secretkey
Generated configuration file: /compose_location/docker-compose.yml
Clean up the input dir
[root@binghe harbor]# docker-compose up -d
Creating network "harbor_harbor" with the default driver
Creating harbor-log ... done
Creating harbor-db ... done
Creating redis ... done
Creating registry ... done
Creating registryctl ... done
Creating harbor-core ... done
Creating harbor-jobservice ... done
Creating harbor-portal ... done
Creating nginx ... done
[root@binghe harbor]# docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS
安装Jenkins(一般的做法)
1.安装nfs(之前安装过的话,可以省略此步)
使用 nfs 最大的问题就是写权限,可以使用 kubernetes 的 securityContext/runAsUser 指定 jenkins 容器中运行 jenkins 的用户 uid,以此来指定 nfs 目录的权限,让 jenkins 容器可写;也可以不限制,让所有用户都可以写。这里为了简单,就让所有用户可写了。
如果之前已经安装过nfs,则这一步可以省略。找一台主机,安装 nfs,这里,我以在Master节点(binghe101服务器)上安装nfs为例。
在命令行输入如下命令安装并启动nfs。
yum install nfs-utils -y
systemctl start nfs-server
systemctl enable nfs-server
2.创建nfs共享目录
在Master节点(binghe101服务器)上创建 /opt/nfs/jenkins-data目录作为nfs的共享目录,如下所示。
mkdir -p /opt/nfs/jenkins-data
接下来,编辑/etc/exports文件,如下所示。
vim /etc/exports
在/etc/exports文件文件中添加如下一行配置。
/opt/nfs/jenkins-data 192.168.175.0/24(rw,all_squash)
这里的 ip 使用 kubernetes node 节点的 ip 范围,后面的 all_squash 选项会将所有访问的用户都映射成 nfsnobody 用户,不管你是什么用户访问,最终都会压缩成 nfsnobody,所以只要将 /opt/nfs/jenkins-data 的属主改为 nfsnobody,那么无论什么用户来访问都具有写权限。
这个选项在很多机器上由于用户 uid 不规范导致启动进程的用户不同,但是同时要对一个共享目录具有写权限时很有效。
接下来,为 /opt/nfs/jenkins-data目录授权,并重新加载nfs,如下所示。
chown -R 1000 /opt/nfs/jenkins-data/
systemctl reload nfs-server
在K8S集群中任意一个节点上使用如下命令进行验证:
showmount -e NFS_IP
如果能够看到 /opt/nfs/jenkins-data 就表示 ok 了。
具体如下所示。
[root@binghe101 ~]# showmount -e 192.168.175.101
Export list for 192.168.175.101:
/opt/nfs/jenkins-data 192.168.175.0/24
[root@binghe102 ~]# showmount -e 192.168.175.101
Export list for 192.168.175.101:
/opt/nfs/jenkins-data 192.168.175.0/24
3.创建PV
Jenkins 其实只要加载对应的目录就可以读取之前的数据,但是由于 deployment 无法定义存储卷,因此我们只能使用 StatefulSet。
首先创建 pv,pv 是给 StatefulSet 使用的,每次 StatefulSet 启动都会通过 volumeClaimTemplates 这个模板去创建 pvc,因此必须得有 pv,才能供 pvc 绑定。
创建jenkins-pv.yaml文件,文件内容如下所示。
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: jenkins
spec:
nfs:
path: /opt/nfs/jenkins-data
server: 192.168.175.101
accessModes: ["ReadWriteOnce"]
capacity:
storage: 1Ti
我这里给了 1T存储空间,可以根据实际配置。
执行如下命令创建pv。
kubectl apply -f jenkins-pv.yaml
4.创建serviceAccount
创建service account,因为 jenkins 后面需要能够动态创建 slave,因此它必须具备一些权限。
创建jenkins-service-account.yaml文件,文件内容如下所示。
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: jenkins
---
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: jenkins
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "get", "list", "patch", "update", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods/exec"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "get", "list", "patch", "update", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods/log"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["secrets"]
verbs: ["get"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: jenkins
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: jenkins
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: jenkins
上述配置中,创建了一个 RoleBinding 和一个 ServiceAccount,并且将 RoleBinding 的权限绑定到这个用户上。所以,jenkins 容器必须使用这个 ServiceAccount 运行才行,不然 RoleBinding 的权限它将不具备。
RoleBinding 的权限很容易就看懂了,因为 jenkins 需要创建和删除 slave,所以才需要上面这些权限。至于 secrets 权限,则是 https 证书。
执行如下命令创建serviceAccount。
kubectl apply -f jenkins-service-account.yaml
5.安装Jenkins
创建jenkins-statefulset.yaml文件,文件内容如下所示。
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: jenkins
labels:
name: jenkins
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: jenkins
serviceName: jenkins
replicas: 1
updateStrategy:
type: RollingUpdate
template:
metadata:
name: jenkins
labels:
name: jenkins
spec:
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 10
serviceAccountName: jenkins
containers:
- name: jenkins
image: docker.io/jenkins/jenkins:lts
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
- containerPort: 32100
resources:
limits:
cpu: 4
memory: 4Gi
requests:
cpu: 4
memory: 4Gi
env:
- name: LIMITS_MEMORY
valueFrom:
resourceFieldRef:
resource: limits.memory
divisor: 1Mi
- name: JAVA_OPTS
# value: -XX:+UnlockExperimentalVMOptions -XX:+UseCGroupMemoryLimitForHeap -XX:MaxRAMFraction=1 -XshowSettings:vm -Dhudson.slaves.NodeProvisioner.initialDelay=0 -Dhudson.slaves.NodeProvisioner.MARGIN=50 -Dhudson.slaves.NodeProvisioner.MARGIN0=0.85
value: -Xmx$(LIMITS_MEMORY)m -XshowSettings:vm -Dhudson.slaves.NodeProvisioner.initialDelay=0 -Dhudson.slaves.NodeProvisioner.MARGIN=50 -Dhudson.slaves.NodeProvisioner.MARGIN0=0.85
volumeMounts:
- name: jenkins-home
mountPath: /var/jenkins_home
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /login
port: 8080
initialDelaySeconds: 60
timeoutSeconds: 5
failureThreshold: 12 # ~2 minutes
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /login
port: 8080
initialDelaySeconds: 60
timeoutSeconds: 5
failureThreshold: 12 # ~2 minutes
# pvc 模板,对应之前的 pv
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: jenkins-home
spec:
accessModes: ["ReadWriteOnce"]
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Ti
jenkins 部署时需要注意它的副本数,你的副本数有多少就要有多少个 pv,同样,存储会有多倍消耗。这里我只使用了一个副本,因此前面也只创建了一个 pv。
使用如下命令安装Jenkins。
kubectl apply -f jenkins-statefulset.yaml
6.创建Service
创建jenkins-service.yaml文件,文件内容如下所示。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: jenkins
spec:
# type: LoadBalancer
selector:
name: jenkins
# ensure the client ip is propagated to avoid the invalid crumb issue when using LoadBalancer (k8s >=1.7)
#externalTrafficPolicy: Local
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
nodePort: 31888
targetPort: 8080
protocol: TCP
- name: jenkins-agent
port: 32100
nodePort: 32100
targetPort: 32100
protocol: TCP
type: NodePort
使用如下命令安装Service。
kubectl apply -f jenkins-service.yaml
7.安装 ingress
jenkins 的 web 界面需要从集群外访问,这里我们选择的是使用 ingress。创建jenkins-ingress.yaml文件,文件内容如下所示。
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: jenkins
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: jenkins
servicePort: 31888
host: jekins.binghe.com
这里,需要注意的是host必须配置为域名或者主机名,否则会报错,如下所示。
The Ingress "jenkins" is invalid: spec.rules[0].host: Invalid value: "192.168.175.101": must be a DNS name, not an IP address
使用如下命令安装ingress。
kubectl apply -f jenkins-ingress.yaml
最后,由于我这里使用的是虚拟机来搭建相关的环境,在本机访问虚拟机映射的jekins.binghe.com时,需要配置本机的hosts文件,在本机的hosts文件中加入如下配置项。
192.168.175.101 jekins.binghe.com
注意:在Windows操作系统中,hosts文件所在的目录如下。
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc
接下来,就可以在浏览器中通过链接:http://jekins.binghe.com:31888 来访问Jekins了。
物理机安装SVN
这里,以在Master节点(binghe101服务器)上安装SVN为例。
1.使用yum安装SVN
在命令行执行如下命令安装SVN。
yum -y install subversion
2.创建SVN库
依次执行如下命令。
#创建/data/svn
mkdir -p /data/svn
#初始化svn
svnserve -d -r /data/svn
#创建代码仓库
svnadmin create /data/svn/test
3.配置SVN
mkdir /data/svn/conf
cp /data/svn/test/conf/* /data/svn/conf/
cd /data/svn/conf/
[root@binghe101 conf]# ll
总用量 20
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1080 5月 12 02:17 authz
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 885 5月 12 02:17 hooks-env.tmpl
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 309 5月 12 02:17 passwd
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4375 5月 12 02:17 svnserve.conf
- 配置authz文件,
vim authz
配置后的内容如下所示。
[aliases]
# joe = /C=XZ/ST=Dessert/L=Snake City/O=Snake Oil, Ltd./OU=Research Institute/CN=Joe Average
[groups]
# harry_and_sally = harry,sally
# harry_sally_and_joe = harry,sally,&joe
SuperAdmin = admin
binghe = admin,binghe
# [/foo/bar]
# harry = rw
# &joe = r
# * =
# [repository:/baz/fuz]
# @harry_and_sally = rw
# * = r
[test:/]
@SuperAdmin=rw
@binghe=rw
- 配置passwd文件
vim passwd
配置后的内容如下所示。
[users]
# harry = harryssecret
# sally = sallyssecret
admin = admin123
binghe = binghe123
- 配置 svnserve.conf
vim svnserve.conf
配置后的文件如下所示。
### This file controls the configuration of the svnserve daemon, if you
### use it to allow access to this repository. (If you only allow
### access through http: and/or file: URLs, then this file is
### irrelevant.)
### Visit http://subversion.apache.org/ for more information.
[general]
### The anon-access and auth-access options control access to the
### repository for unauthenticated (a.k.a. anonymous) users and
### authenticated users, respectively.
### Valid values are "write", "read", and "none".
### Setting the value to "none" prohibits both reading and writing;
### "read" allows read-only access, and "write" allows complete
### read/write access to the repository.
### The sample settings below are the defaults and specify that anonymous
### users have read-only access to the repository, while authenticated
### users have read and write access to the repository.
anon-access = none
auth-access = write
### The password-db option controls the location of the password
### database file. Unless you specify a path starting with a /,
### the file's location is relative to the directory containing
### this configuration file.
### If SASL is enabled (see below), this file will NOT be used.
### Uncomment the line below to use the default password file.
password-db = /data/svn/conf/passwd
### The authz-db option controls the location of the authorization
### rules for path-based access control. Unless you specify a path
### starting with a /, the file's location is relative to the
### directory containing this file. The specified path may be a
### repository relative URL (^/) or an absolute file:// URL to a text
### file in a Subversion repository. If you don't specify an authz-db,
### no path-based access control is done.
### Uncomment the line below to use the default authorization file.
authz-db = /data/svn/conf/authz
### The groups-db option controls the location of the file with the
### group definitions and allows maintaining groups separately from the
### authorization rules. The groups-db file is of the same format as the
### authz-db file and should contain a single [groups] section with the
### group definitions. If the option is enabled, the authz-db file cannot
### contain a [groups] section. Unless you specify a path starting with
### a /, the file's location is relative to the directory containing this
### file. The specified path may be a repository relative URL (^/) or an
### absolute file:// URL to a text file in a Subversion repository.
### This option is not being used by default.
# groups-db = groups
### This option specifies the authentication realm of the repository.
### If two repositories have the same authentication realm, they should
### have the same password database, and vice versa. The default realm
### is repository's uuid.
realm = svn
### The force-username-case option causes svnserve to case-normalize
### usernames before comparing them against the authorization rules in the
### authz-db file configured above. Valid values are "upper" (to upper-
### case the usernames), "lower" (to lowercase the usernames), and
### "none" (to compare usernames as-is without case conversion, which
### is the default behavior).
# force-username-case = none
### The hooks-env options specifies a path to the hook script environment
### configuration file. This option overrides the per-repository default
### and can be used to configure the hook script environment for multiple
### repositories in a single file, if an absolute path is specified.
### Unless you specify an absolute path, the file's location is relative
### to the directory containing this file.
# hooks-env = hooks-env
[sasl]
### This option specifies whether you want to use the Cyrus SASL
### library for authentication. Default is false.
### Enabling this option requires svnserve to have been built with Cyrus
### SASL support; to check, run 'svnserve --version' and look for a line
### reading 'Cyrus SASL authentication is available.'
# use-sasl = true
### These options specify the desired strength of the security layer
### that you want SASL to provide. 0 means no encryption, 1 means
### integrity-checking only, values larger than 1 are correlated
### to the effective key length for encryption (e.g. 128 means 128-bit
### encryption). The values below are the defaults.
# min-encryption = 0
# max-encryption = 256
接下来,将/data/svn/conf目录下的svnserve.conf文件复制到/data/svn/test/conf/目录下。如下所示。
[root@binghe101 conf]# cp /data/svn/conf/svnserve.conf /data/svn/test/conf/
cp:是否覆盖'/data/svn/test/conf/svnserve.conf'? y
4.启动SVN服务
(1)创建svnserve.service服务
创建svnserve.service文件
vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/svnserve.service
文件的内容如下所示。
[Unit]
Description=Subversion protocol daemon
After=syslog.target network.target
Documentation=man:svnserve(8)
[Service]
Type=forking
EnvironmentFile=/etc/sysconfig/svnserve
#ExecStart=/usr/bin/svnserve --daemon --pid-file=/run/svnserve/svnserve.pid $OPTIONS
ExecStart=/usr/bin/svnserve --daemon $OPTIONS
PrivateTmp=yes
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
接下来执行如下命令使配置生效。
systemctl daemon-reload
命令执行成功后,修改 /etc/sysconfig/svnserve 文件。
vim /etc/sysconfig/svnserve
修改后的文件内容如下所示。
# OPTIONS is used to pass command-line arguments to svnserve.
#
# Specify the repository location in -r parameter:
OPTIONS="-r /data/svn"
(2)启动SVN
首先查看SVN状态,如下所示。
[root@itence10 conf]# systemctl status svnserve.service
● svnserve.service - Subversion protocol daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/svnserve.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: inactive (dead)
Docs: man:svnserve(8)
可以看到,此时SVN并没有启动,接下来,需要启动SVN。
systemctl start svnserve.service
设置SVN服务开机自启动。
systemctl enable svnserve.service
接下来,就可以下载安装TortoiseSVN,输入链接svn://192.168.0.10/test 并输入用户名binghe,密码binghe123来连接SVN了。
物理机安装Jenkins
注意:安装Jenkins之前需要安装JDK和Maven,我这里同样将Jenkins安装在Master节点(binghe101服务器)。
1.启用Jenkins库
运行以下命令以下载repo文件并导入GPG密钥:
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/jenkins.repo http://pkg.jenkins-ci.org/redhat-stable/jenkins.repo
rpm --import https://jenkins-ci.org/redhat/jenkins-ci.org.key
2.安装Jenkins
执行如下命令安装Jenkis。
yum install jenkins
接下来,修改Jenkins默认端口,如下所示。
vim /etc/sysconfig/jenkins
修改后的两项配置如下所示。
JENKINS_JAVA_CMD="/usr/local/jdk1.8.0_212/bin/java"
JENKINS_PORT="18080"
此时,已经将Jenkins的端口由8080修改为18080
3.启动Jenkins
在命令行输入如下命令启动Jenkins。
systemctl start jenkins
配置Jenkins开机自启动。
systemctl enable jenkins
查看Jenkins的运行状态。
[root@itence10 ~]# systemctl status jenkins
● jenkins.service - LSB: Jenkins Automation Server
Loaded: loaded (/etc/rc.d/init.d/jenkins; generated)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2020-05-12 04:33:40 EDT; 28s ago
Docs: man:systemd-sysv-generator(8)
Tasks: 71 (limit: 26213)
Memory: 550.8M
说明,Jenkins启动成功。
配置Jenkins运行环境
1.登录Jenkins
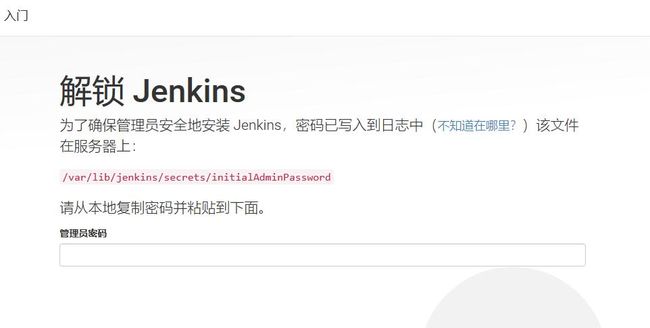
首次安装后,需要配置Jenkins的运行环境。首先,在浏览器地址栏访问链接http://192.168.0.10:18080,打开Jenkins界面。
根据提示使用如下命令到服务器上找密码值,如下所示。
[root@binghe101 ~]# cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword
71af861c2ab948a1b6efc9f7dde90776
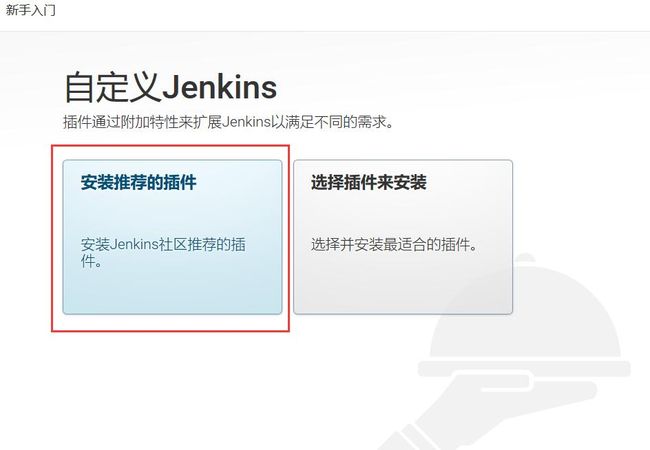
将密码71af861c2ab948a1b6efc9f7dde90776复制到文本框,点击继续。会跳转到自定义Jenkins页面,如下所示。
这里,可以直接选择“安装推荐的插件”。之后会跳转到一个安装插件的页面,如下所示。
此步骤可能有下载失败的情况,可直接忽略。
2.安装插件
需要安装的插件
-
Kubernetes Cli Plugin:该插件可直接在Jenkins中使用kubernetes命令行进行操作。
-
Kubernetes plugin: 使用kubernetes则需要安装该插件
-
Kubernetes Continuous Deploy Plugin:kubernetes部署插件,可根据需要使用
还有更多的插件可供选择,可点击 系统管理->管理插件进行管理和添加,安装相应的Docker插件、SSH插件、Maven插件。其他的插件可以根据需要进行安装。如下图所示。
3.配置Jenkins
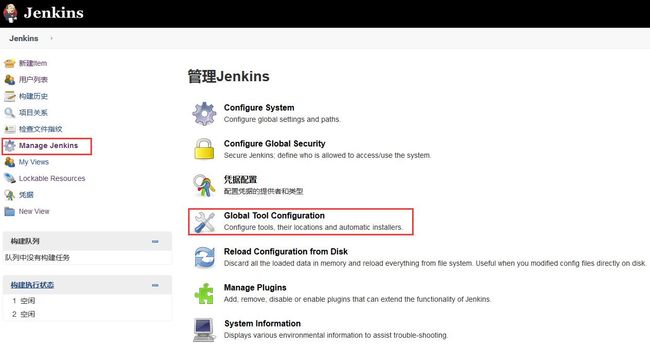
(1)配置JDK和Maven
在Global Tool Configuration中配置JDK和Maven,如下所示,打开Global Tool Configuration界面。
接下来就开始配置JDK和Maven了。
由于我在服务器上将Maven安装在/usr/local/maven-3.6.3目录下,所以,需要在“Maven 配置”中进行配置,如下图所示。

接下来,配置JDK,如下所示。
注意:不要勾选“Install automatically”
接下来,配置Maven,如下所示。
注意:不要勾选“Install automatically”
(2)配置SSH
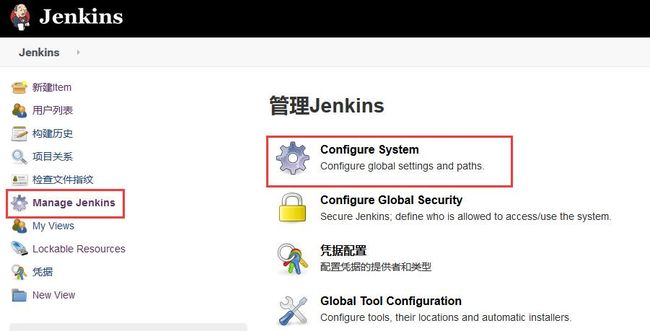
进入Jenkins的Configure System界面配置SSH,如下所示。
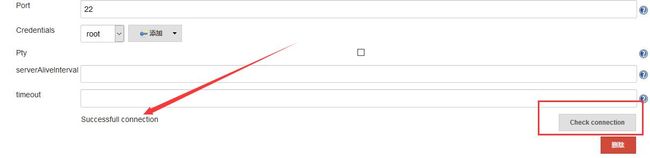
找到 SSH remote hosts 进行配置。
配置完成后,点击Check connection按钮,会显示 Successfull connection。如下所示。
至此,Jenkins的基本配置就完成了。
写在最后
如果觉得文章对你有点帮助,请微信搜索并关注「 冰河技术 」微信公众号,跟冰河学习各种编程技术。
最后附上K8S最全知识图谱链接:
https://www.processon.com/view/link/5ac64532e4b00dc8a02f05eb?spm=a2c4e.10696291.0.0.6ec019a4bYSFIw#map
祝大家在学习K8S时,少走弯路。