初试Android高性能编程OpenCL
OpenCL支持API 21以上的某些Android设备,具体支持得看芯片厂商爸爸给不给力了,不仅仅如此,OpenCL在X86体系基本都有集成,不仅仅是Mac、Ubuntu、Windows、Android等os。详细的网站页可以参考:
https://software.intel.com/en-us/iocl-tec-opg-opencl-standard
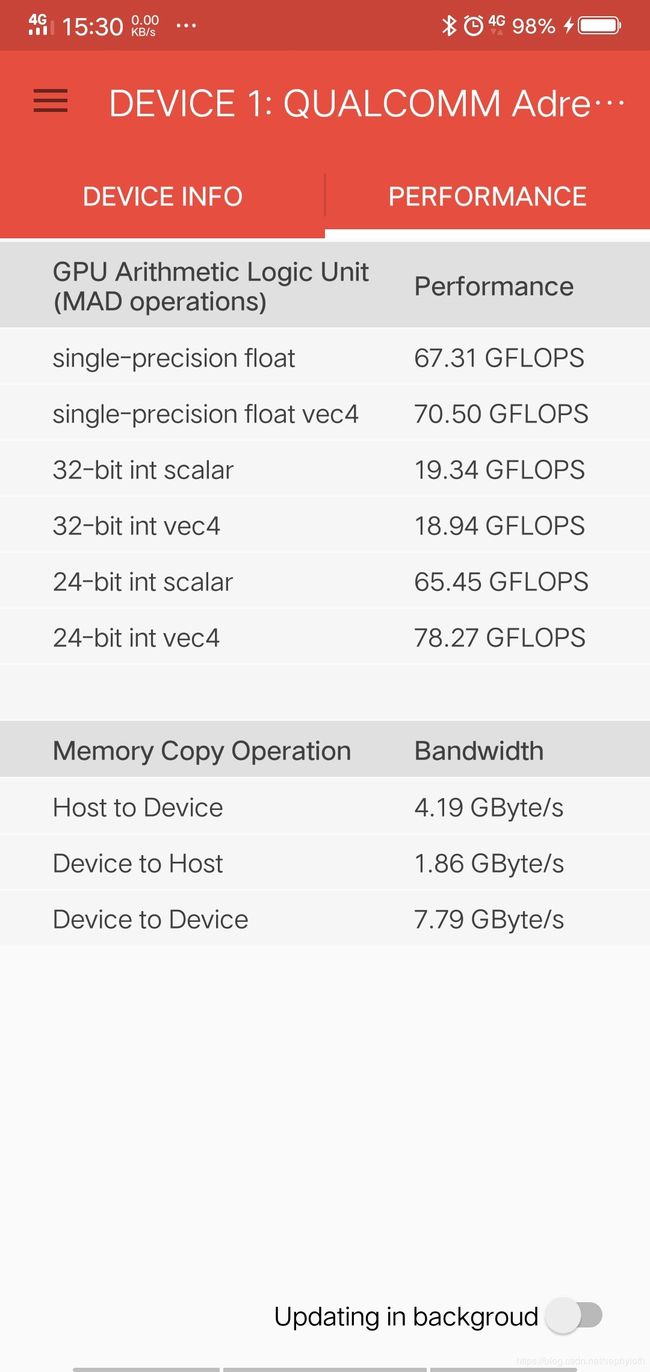
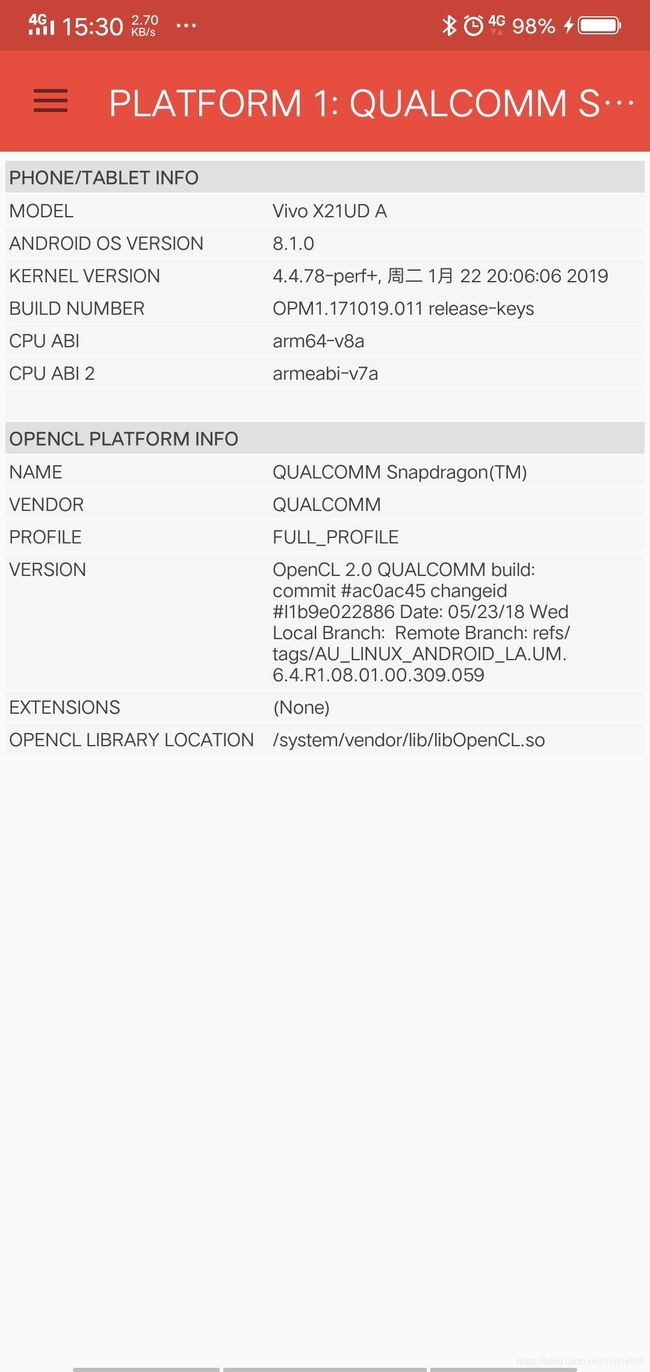
对应的官方文档中,都有详细的介绍,如果是Android,想要查看是否支持OpenCL GPU运算。可以用一个GPU测试工具OpenCL-Z工具去查看,可以显示当前手机GPU的型号和厂商信息。包括有几个GPU核心都可以看到。
笔者使用的是某国产手机,就是性价比极低,总喜欢用低价的硬件卖优化的某厂出品。但是凑活着能用。
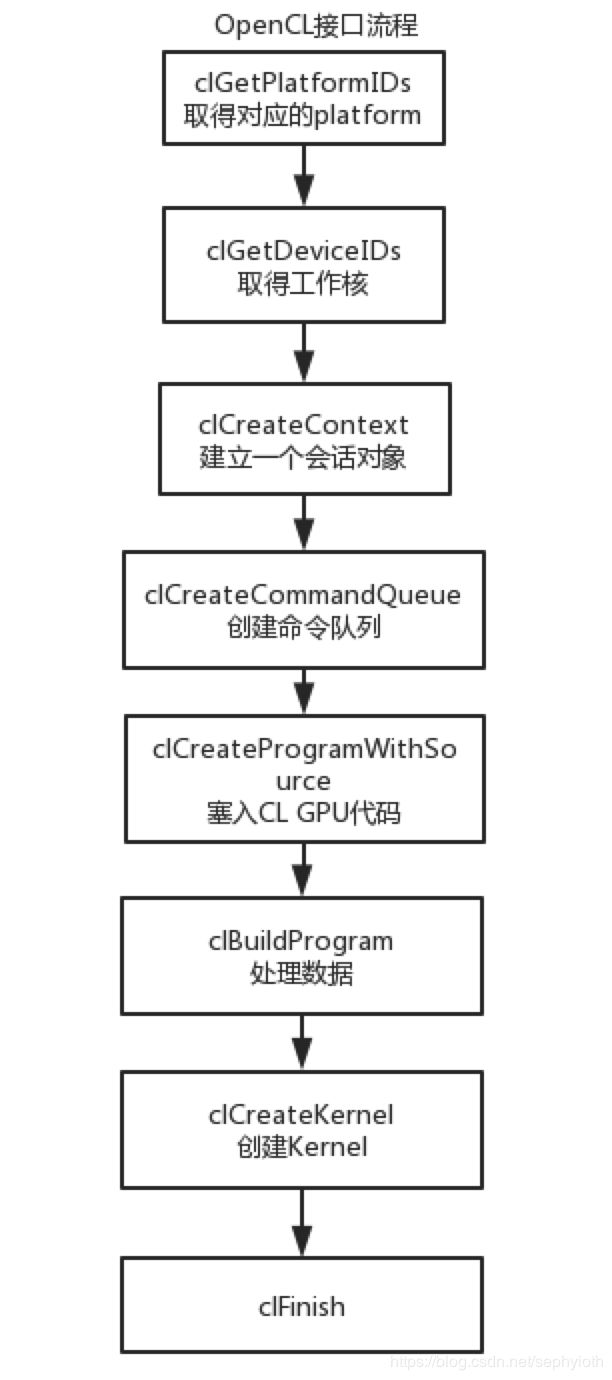
看完Inter关于OpenCL的介绍,我们大致上可以了解到一些关于openCL是什么,他本身就是GPU开放给第三方应用的FPGA接口API的形式。撸了一遍源码,发现了一个大致的使用流程如下:
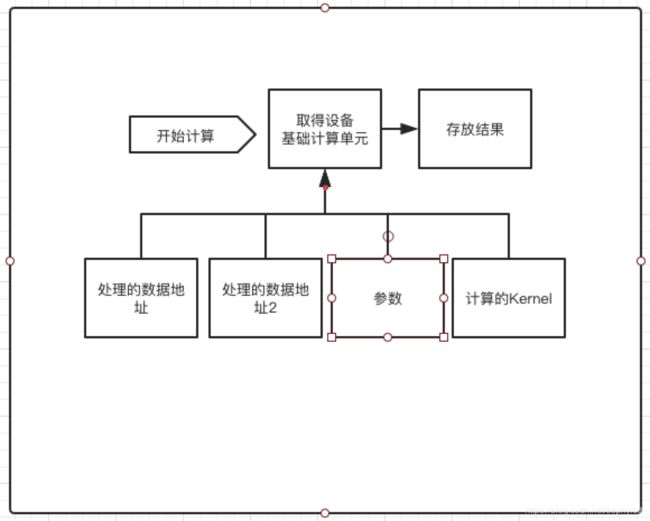
当中在塞入GPU代码段方面,还有配置参数、设置输入数据和输出数据地址方面的动作,具体视业务模块变化而变化。可能熟悉FPGA的同学都明白FPGA是一种可编程的硬件模块,并且运算效率算是比较高的。FPGA可以模拟任何的数字电路元器件,可以是GPU,也可以是CPU。而CL的接口实现原理差不多也沿用了这种思维模式。首先取得一个设备,然后在这个设备计算单元中塞入数据、代码。然后控制模块计算按照建立的模型计算数据,最后,从地址中读取相应的计算结果。差不多就是这样的一个流程。
上面那个流程比较形象的说明具体的流程模式。接下来是实际的介绍如何开始第一个应用程序的编写了。首先在官网取得对应版本OpenCL的接口方法定义头文件,这里有两个方式去搞:
-
自己编写Android.mk或者新的bp,然后去引用系统的so、头文件。官方源历程也是这样编写的。(只是用了mac,而且inter介绍的英文太多,下载了studio和docker,感觉那是一堆LOT的东西,比较烦)。
-
在cmake中包含库、头文件。打包成so,和普通集成的AS环境类似。(这里可以用省力的方式,直接提取手机的libopencl.so)
-
例子(我们现在要实现的测试功能是A数组和B数组进行累加计算,并且把结果保存到result数组中)
第一种方式觉得比较麻烦,这里重点介绍一下第二种方式的实际运行过程。首先新弄一个工程叫imageDemo,然后link C++,新建一个JAVA类比如叫ImageNativeInterface.java,然后开始编写我们的Demo接口:
package com.genesis.imageNative;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
/**
* 项目名称:ImageDemo
* 类描述:
* 创建人:genesis
* 创建时间:2019/4/10 5:45 PM
* 修改人:genesis
* 修改时间:2019/4/10 5:45 PM
* 修改备注:
*/
public class ImageNativeInterface {
private static volatile ImageNativeInterface mInterface;
public static ImageNativeInterface getInstance () {
if (mInterface == null) {
mInterface = new ImageNativeInterface();
}
return mInterface;
}
private ImageNativeInterface () {
}
public int openclDemo (int[] arrayA, int[] arrayB, int[] result, String kernelCode,
float[] runningTime) {
return nOpenCLDemo(arrayA, arrayB, result, kernelCode, runningTime);
}
public int nativeAdd (int[] arrayA, int[] arrayB, int[] result) {
return nNativeAdd(arrayA, arrayB, result);
}
//fixme 接口native
private static native int nOpenCLDemo (int[] arrayA, int[] arrayB, int[] result,
String kernelCode, float[] runningTime);
//fixme 本地C++ CPU计算数组
private static native int nNativeAdd(int[] arrayA, int[] arrayB, int[] result);
static {
try {
System.loadLibrary("gimage");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("LoadLib error");
}
}
}接着编写相关C++的代码实现部分:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "CL/cl.h"
#define EXIT_FAILURE 1
#define EXIT_SUCCESS 0
#define RAND_MAX 0x7fffffff
#define LOG_TAG "libGenesisBitmap"
#define LOGI(...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_INFO,LOG_TAG,__VA_ARGS__)
#define LOGE(...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_ERROR,LOG_TAG,__VA_ARGS__)
#define MAX_PLATFORMS_COUNT 16
#define CL_SUCCEEDED(clErr) CL_SUCCESS==clErr
#define CL_FAILED(clErr) CL_SUCCESS!=clErr
void addArrays(const int* arrayA, const int* arrayB, const int* Result, int length,
const char* kernelCode, float* runTime)
{
cl_platform_id platform = 0;
cl_device_type clDEviceType = CL_DEVICE_TYPE_CPU; // default
cl_kernel kernel = 0;
cl_command_queue cmd_queue = 0;
cl_context context = 0;
cl_mem memobjs[3];
cl_program program = 0;
cl_int clErr;
unsigned long long startTime = 0, endTime = 0;
// get current platform id, assuming there are no more than 16 platforms in the system
cl_platform_id pPlatforms[MAX_PLATFORMS_COUNT] = {0};
cl_uint uiPlatformsCount = 0;
clErr = clGetPlatformIDs(MAX_PLATFORMS_COUNT, pPlatforms, &uiPlatformsCount);
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, "clErr: %d uiPlatformsCount: %d", clErr,
uiPlatformsCount);
if (CL_FAILED(clErr) || 0 == uiPlatformsCount)
{
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, "ERROR: Failed to find any platform.");
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, "clErr: %d uiPlatformsCount: %d", clErr,
uiPlatformsCount);
return;
}
// go through the available platform and select our (vendor = "Intel Corporation")
cl_uint num_device;
cl_uint num_platform;
cl_platform_id* platformtag;
cl_device_id * devices;
clErr = clGetPlatformIDs(0, 0, &num_platform);
platformtag = (cl_platform_id*) malloc(sizeof(cl_platform_id) * num_platform);
clErr = clGetPlatformIDs(num_platform, platformtag, NULL);
clErr = clGetDeviceIDs(platformtag[0], CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU, 0, NULL, &num_device);
devices = (cl_device_id*) malloc(sizeof(cl_device_id) * num_device);
clErr = clGetDeviceIDs(platformtag[0], CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU, num_device, devices, NULL);
//create context
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, "create context");
cl_context_properties properties[] = {CL_CONTEXT_PLATFORM, (cl_context_properties) platform,
(cl_context_properties) NULL};
context = clCreateContext(NULL, num_device, devices, NULL, NULL, &clErr);;
if (0 == context)
{
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, "clErr: %d - Failed to create context",
clErr);
return;
}
// get context's devices
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, "get context's devices");
cl_device_id device = 0;
clErr = clGetContextInfo(context, CL_CONTEXT_DEVICES, sizeof(cl_device_id), &device, NULL);
if (CL_FAILED(clErr) || 0 == device)
{
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, "clErr: %d - Failed to get context info",
clErr);
clReleaseContext(context);
return;
}
// create a command-queue
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, "create a command-queue");
cmd_queue = clCreateCommandQueue(context, device, 0, NULL);
if (cmd_queue == (cl_command_queue) 0)
{
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG,
"clErr: %d - Failed to create command queue", clErr);
goto release_context;
}
size_t global_work_size[1];
size_t local_work_size[1];
// allocate the buffer memory objects
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, "allocate the buffer memory objects");
memobjs[0] = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY | CL_MEM_USE_HOST_PTR,
sizeof(int) * length, (void*) arrayA, NULL);
if (memobjs[0] == (cl_mem) 0)
{
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, "Failed to create memobjs[0]");
goto release_queue;
}
memobjs[1] = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY | CL_MEM_USE_HOST_PTR,
sizeof(int) * length, (void*) arrayB, NULL);
if (memobjs[1] == (cl_mem) 0)
{
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, "Failed to create memobjs[1]");
goto release_mem0;
}
memobjs[2] = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_WRITE, sizeof(int) * length, NULL, NULL);
if (memobjs[1] == (cl_mem) 0)
{
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, "Failed to create memobjs[2]");
goto release_mem1;
}
// create program
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, "create program");
program = clCreateProgramWithSource(context, 1, (const char**) &kernelCode, NULL, &clErr);
if (CL_FAILED(clErr) || 0 == program)
{
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, "clErr: %d - Failed to create program",
clErr);
goto release_mem2;
}
// build program
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, "build program");
clErr = clBuildProgram(program, 1, &device, NULL, NULL, NULL);
if (CL_FAILED(clErr))
{
size_t len;
char buffer[2048];
clGetProgramBuildInfo(program, device, CL_PROGRAM_BUILD_LOG, sizeof(buffer), buffer, &len);
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG,
"clErr: %d - Failed to build program\n Log: %s", clErr, buffer);
goto release_program;
}
// create the kernel
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, "create kernel");
kernel = clCreateKernel(program, "vadd", NULL);
if (kernel == (cl_kernel) 0)
{
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, "clErr: %d - Failed to create kernel",
clErr);
goto release_program;
}
// set the args values
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, "set the args values");
clErr = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 0, sizeof(cl_mem), (void*) &memobjs[0]);
clErr |= clSetKernelArg(kernel, 1, sizeof(cl_mem), (void*) &memobjs[1]);
clErr |= clSetKernelArg(kernel, 2, sizeof(cl_mem), (void*) &memobjs[2]);
if (CL_FAILED(clErr))
{
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG,
"clErr: %d - Failed to set kernel arguments", clErr);
goto release_all;
}
// set work-item dimensions
global_work_size[0] = length;
local_work_size[0] = 512;
// execute kernel
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, "execute kernel");
struct timespec tp;
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &tp);
startTime = (unsigned long long) (tp.tv_sec * 1000000000 + tp.tv_nsec);
clErr = clEnqueueNDRangeKernel(cmd_queue, kernel, 1, NULL, global_work_size,
local_work_size, 0, NULL, NULL);
if (CL_FAILED(clErr))
{
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, "clErr: %d - Failed to execute kernel",
clErr);
goto release_all;
}
clErr = clFinish(cmd_queue);
if (CL_FAILED(clErr))
{
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, "clErr: %d - Failed to finish queue",
clErr);
goto release_all;
}
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &tp);
endTime = (unsigned long long) (tp.tv_sec * 1000000000 + tp.tv_nsec);
*runTime = (endTime - startTime) / 1000000.0f;
// read output Buffer
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, "read output Buffer");
clErr = clEnqueueReadBuffer(cmd_queue, memobjs[2], CL_TRUE, 0, length * sizeof(int),
(void*) Result, 0, NULL, NULL);
if (CL_FAILED(clErr))
{
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, "clErr: %d - Failed to read output Buffer",
clErr);
goto release_all;
}
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "Done!");
//release kernel, program, and memory objects
release_all:
clReleaseKernel(kernel);
release_program:
clReleaseProgram(program);
release_mem2:
clReleaseMemObject(memobjs[2]);
release_mem1:
clReleaseMemObject(memobjs[1]);
release_mem0:
clReleaseMemObject(memobjs[0]);
release_queue:
clReleaseCommandQueue(cmd_queue);
release_context:
clReleaseContext(context);
return;
}
extern "C"
JNIEXPORT jint
JNICALL
Java_com_genesis_imageNative_ImageNativeInterface_nOpenCLDemo(JNIEnv* env, jclass type,
jintArray arrayA_, jintArray arrayB_,
jintArray result_,
jstring kernelCode_,
jfloatArray runningTime)
{
int * c_arrayA = env->GetIntArrayElements(arrayA_, NULL);
int * c_arrayB = env->GetIntArrayElements(arrayB_, NULL);
int * c_Result = env->GetIntArrayElements(result_, NULL);
float* c_runTime = env->GetFloatArrayElements(runningTime, NULL);
int length = env->GetArrayLength(arrayA_);
const char* nativeKernelCode = env->GetStringUTFChars(kernelCode_, 0);
addArrays(c_arrayA, c_arrayB, c_Result, length, nativeKernelCode, c_runTime);
env->ReleaseIntArrayElements(arrayA_, c_arrayA, 0);
env->ReleaseIntArrayElements(arrayB_, c_arrayB, 0);
env->ReleaseIntArrayElements(result_, c_Result, 0);
env->ReleaseFloatArrayElements(runningTime, c_runTime, 0);
return 1;
}
extern "C"
JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL
Java_com_genesis_imageNative_ImageNativeInterface_nNativeAdd(JNIEnv* env, jclass type,
jintArray arrayA_, jintArray arrayB_,
jintArray result_)
{
jint* arrayA = env->GetIntArrayElements(arrayA_, NULL);
jint* arrayB = env->GetIntArrayElements(arrayB_, NULL);
jint* result = env->GetIntArrayElements(result_, NULL);
int length = env->GetArrayLength(arrayA_);
for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i)
{
result[i] = arrayA[i] + arrayB[i];
}
env->ReleaseIntArrayElements(arrayA_, arrayA, 0);
env->ReleaseIntArrayElements(arrayB_, arrayB, 0);
env->ReleaseIntArrayElements(result_, result, 0);
return 1;
} 那么问题来了,对应的CL接口代码是什么呢?接下来的这段字符文件即可:
__kernel void vadd(__global const int *a, __global const int *b, __global int *c)
{
int gid = get_global_id(0);
c[gid] = a[gid] + b[gid];
}关联OpenCL头文件和so.
# For more information about using CMake with Android Studio, read the
# documentation: https://d.android.com/studio/projects/add-native-code.html
# Sets the minimum version of CMake required to build the native library
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.4.1)
# Creates and names a library, sets it as either STATIC
# or SHARED, and provides the relative paths to its source code.
# You can define multiple libraries, and CMake builds them for you.
# Gradle automatically packages shared libraries with your APK.
include_directories(${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/src/main/cpp/include)
#add_library(libOpenCL SHARED IMPORTED)
#set_target_properties(libOpenCL PROPERTIES IMPORTED_LOCATION
# ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/src/main/jniLibs/opencl/${ANDROID_ABI}/libOpenCL.so)
add_library( # Sets the name of the library.
gimage
# Sets the library as a shared library.
SHARED
# Provides a relative path to your source file(s).
src/main/cpp/native-lib.cpp)
# Specifies libraries CMake should link to your target library. You
# can link multiple libraries, such as libraries you define in this
# build script, prebuilt third-party libraries, or system libraries.
target_link_libraries( # Specifies the target library.
gimage
-ljnigraphics
-lOpenCL
log
# Links the target library to the log library
# included in the NDK.
${log-lib})如上,我们就基本就实现了a数组和b数组进行叠加存入c数组的操作咯。OpenCL接口功能很强大,也具有一套自己的语法编辑规则。后面会举例其他例子。这里在贴下上层Java的代码段:
private static final int ARRAY_SIZE = 262144;
public void calcVectors (View view) {
int[] arrayA = new int[ARRAY_SIZE];
int[] arrayB = new int[ARRAY_SIZE];
int[] arrayC = new int[ARRAY_SIZE];
float[] execTime = new float[1];
execTime[0] = 0;
AssetManager am = getAssets();
try {
initArrays(arrayA, arrayB, arrayC, ARRAY_SIZE);
InputStream is = am.open("OpenCLFirstApp_kernel.cl");
String kernelCode = convertInputStreamToString(is);
ImageNativeInterface.getInstance().openclDemo(arrayA, arrayB, arrayC, kernelCode,
execTime);
//fixme 调用其他函数得到计算数据
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.d("oclDebug", e.toString());
}
String print = String.valueOf(execTime[0]);
print += " (ms)";
TextView myTextField = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv1);
myTextField.setText(print);
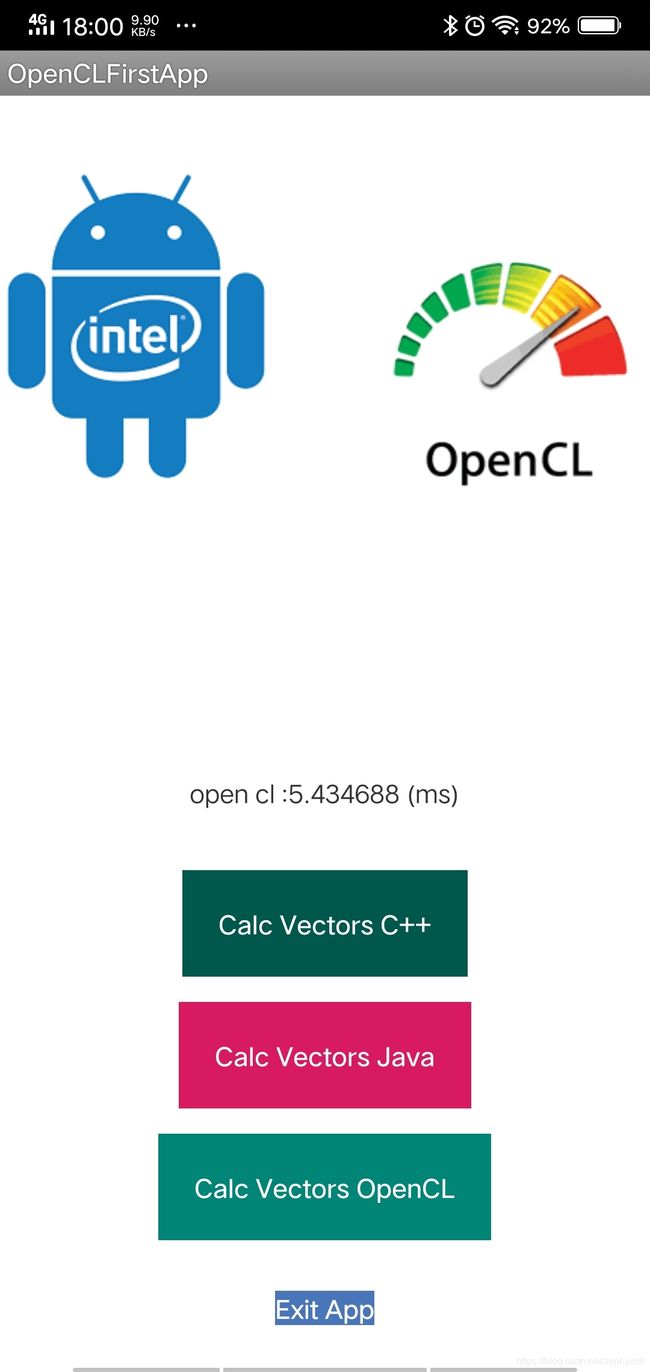
}调用这段方法就可以在OpenCL当中在GPU计算262144个数组累加的计算了。
运算结果对比:
OpenCL的算法编写是以字符的形式传入,我们这里也可以说说其他的代码,如果需要实际例子,可以参考openCV的相关kernel代码,有很多类比如高斯模糊,卷积都用了这类OpenCL接口。
-
总结
以上仅对Android 单纯单核心运算做了介绍,事实上,在Android 8.0之后的版本中,存在对AIT的优化,特别是循环运算、浮点数运算等等做了优化,实际上跑大容量固定值算法的时间周期在第一次可能会比较慢,但是在第二次启动同一段JAVA算法段,AIT会对相应的代码做优化处理。结果就会直接反应在性能上。8.0指令优化的点包括:
-
消除边界检查
-
静态:在编译时证明范围位于边界内
-
动态:运行时测试确保循环始终位于边界内(否则不进行优化)
-
-
消除归纳变量
-
移除无用归纳
-
用封闭式表达式替换仅在循环后使用的归纳
-
-
消除循环主体内的无用代码,移除整个死循环
-
强度降低
-
循环转换:逆转、交换、拆分、展开、单模等
-
SIMDization(也称为矢量化)