Leetcode85 最大矩形 C++,Java,Python
Leetcode85 最大矩形
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximal-rectangle/
博主Github:https://github.com/GDUT-Rp/LeetCode
![]()
题目:
给定一个仅包含 0 和 1 的二维二进制矩阵,找出只包含 1 的最大矩形,并返回其面积。
示例 1:
输入:
[
["1","0","1","0","0"],
["1","0","1","1","1"],
["1","1","1","1","1"],
["1","0","0","1","0"]
]
输出: 6
解题思路:
方法一:暴力
直观想法
最原始地,我们可以列举每个可能的矩形。这可以通过遍历所有的(x1, y1) (x2, y2) 坐标,并以它们为对角顶点来完成。该方法过慢,不足以通过所有测试用例。
复杂性分析
- 时间复杂度: O ( N 3 M 3 ) O(N^3M^3) O(N3M3)。其中
N为行数,M为列数。- 遍历全部坐标的复杂度是 O ( N 2 M 2 ) O(N^2M^2) O(N2M2), 遍历以该两点为对角顶点的矩形又会耗费 O ( N M ) O(NM) O(NM)。故总体复杂度为 O ( N M ) ∗ O ( N 2 M 2 ) = O ( N 3 M 3 ) O(NM) * O(N^2M^2) = O(N^3M^3) O(NM)∗O(N2M2)=O(N3M3)
- 空间复杂度 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1) 的额外空间。
方法二:动态规划 - 使用柱形图的优化暴力方法
算法
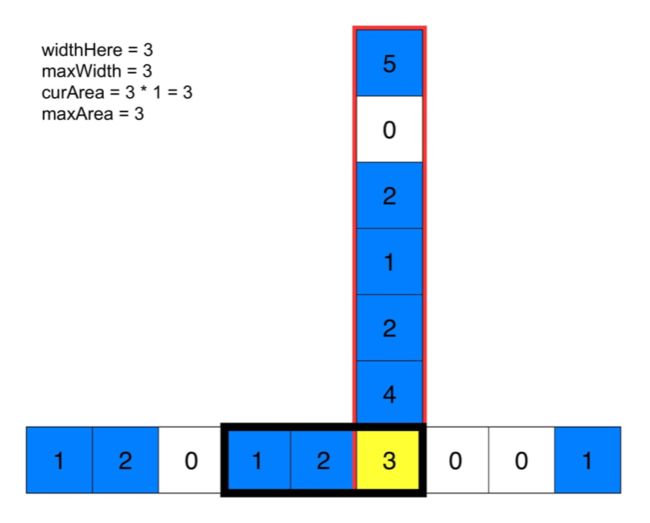
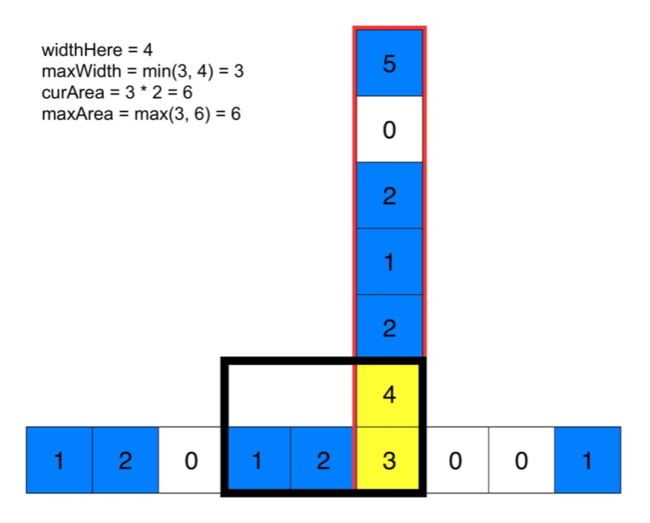
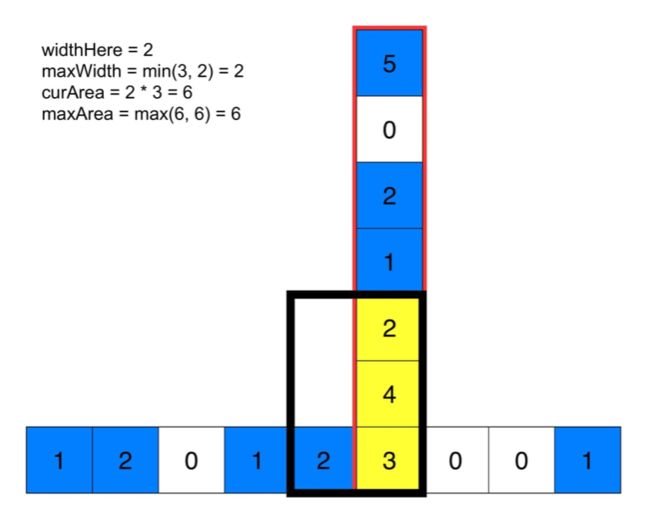
我们可以以常数时间计算出在给定的坐标结束的矩形的最大宽度。我们可以通过记录每一行中每一个方块连续的“1”的数量来实现这一点。每遍历完一行,就更新该点的最大可能宽度。通过以下代码即可实现。 row[i] = row[i - 1] + 1 if row[i] == '1'.
一旦我们知道了每个点对应的最大宽度,我们就可以在线性时间内计算出以该点为右下角的最大矩形。当我们遍历列时,可知从初始点到当前点矩形的最大宽度,就是我们遇到的每个最大宽度的最小值。 我们定义:
m a x W i d t h = m i n ( m a x W i d t h , w i d t h H e r e ) maxWidth=min(maxWidth,widthHere) maxWidth=min(maxWidth,widthHere)
c u r A r e a = m a x W i d t h ∗ ( c u r r e ∗ ∗ ∗ o w − o r i g i n a l R o w + 1 ) curArea = maxWidth * (curre***ow - originalRow + 1) curArea=maxWidth∗(curre∗∗∗ow−originalRow+1)
m a x A r e a = m a x ( m a x A r e a , c u r A r e a ) maxArea=max(maxArea,curArea) maxArea=max(maxArea,curArea)
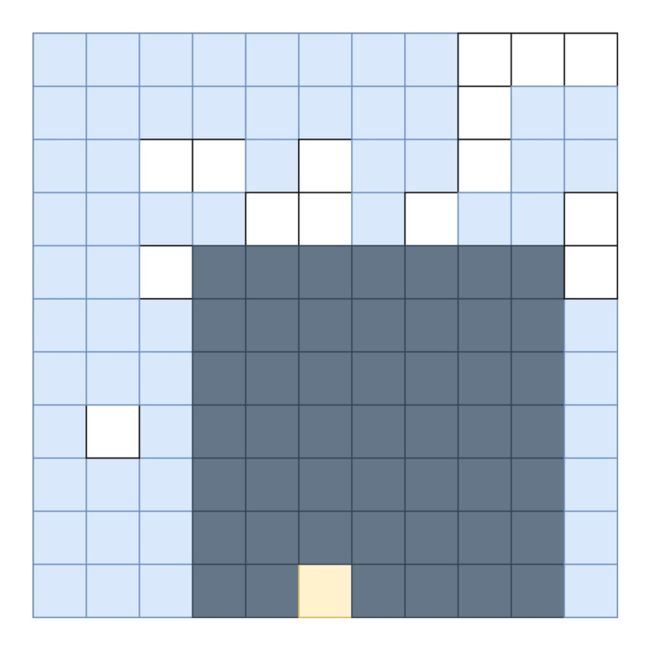
下面的动画有助于理解。给定每个点的最大宽度,可计算出底端黄色方块的最大矩形面积。
对每个点重复这一过程,就可以得到全局最大。
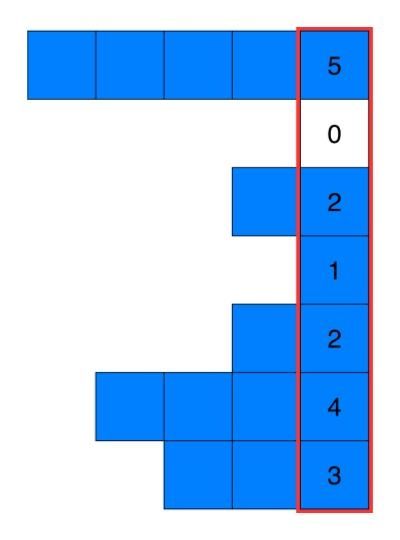
注意,我们预计算最大宽度的方法事实上将输入转化成了一系列的柱状图,每一栏是一个新的柱状图。我们在针对每个柱状图计算最大面积。
C++:
class Solution {
public:
int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>> &matrix) {
if (matrix.size() == 0) {
return 0;
}
int maxarea = 0;
int dp[matrix.size()][matrix[0].size()];
memset(dp, 0, sizeof(dp)); // 初始化为0
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.size(); ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < matrix[0].size(); ++j) {
if (matrix[i][j] == '1') {
dp[i][j] = j == 0 ? 1 : dp[i][j - 1] + 1; // dp,计算宽度
int width = dp[i][j];
for (int k = i; k >= 0; k--) {
width = min(width, dp[k][j]); // 向上每次取该行向下最短宽
maxarea = max(maxarea, width * (i - k + 1)); // 最短宽 * 高度
}
}
}
}
return maxarea;
}
};
Java:
class Solution {
public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {
if (matrix.length == 0) return 0;
int maxarea = 0;
int[][] dp = new int[matrix.length][matrix[0].length];
for(int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < matrix[0].length; j++){
if (matrix[i][j] == '1'){
// compute the maximum width and update dp with it
dp[i][j] = j == 0? 1 : dp[i][j-1] + 1;
int width = dp[i][j];
// compute the maximum area rectangle with a lower right corner at [i, j]
for(int k = i; k >= 0; k--){
width = Math.min(width, dp[k][j]);
maxarea = Math.max(maxarea, width * (i - k + 1));
}
}
}
} return maxarea;
}
}
Python:
class Solution:
def maximalRectangle(self, matrix: List[List[str]]) -> int:
maxarea = 0
dp = [[0] * len(matrix[0]) for _ in range(len(matrix))]
for i in range(len(matrix)):
for j in range(len(matrix[0])):
if matrix[i][j] == '0': continue
# compute the maximum width and update dp with it
width = dp[i][j] = dp[i][j-1] + 1 if j else 1
# compute the maximum area rectangle with a lower right corner at [i, j]
for k in range(i, -1, -1):
width = min(width, dp[k][j])
maxarea = max(maxarea, width * (i-k+1))
return maxarea
复杂性分析
- 时间复杂度: O ( N 2 M ) O(N^2M) O(N2M)。由于需要遍历同一列中的值,计算每个点对应最大面积需要 O ( N ) O(N) O(N)。对全部 N ∗ M N * M N∗M个点都要计算,因此总共 O ( N ) ∗ O ( N M ) = O ( N 2 M ) O(N) * O(NM) = O(N^2M) O(N)∗O(NM)=O(N2M)。
- 空间复杂度 O ( N M ) O(NM) O(NM) 的额外空间。 我们分配了一个等大的数组,用于存储每个点的最大宽度。
方法三:动态规划 - 每个点的最大高度
算法
想象一个算法,对于每个点我们会通过以下步骤计算一个矩形:
不断向上方遍历,直到遇到“0”,以此找到矩形的最大高度。
向左右两边扩展,直到无法容纳矩形最大高度。
例如,找到黄色点对应的矩形:
给定一个最大矩形,其高为 h, 左边界 l,右边界 r,在矩形的底边,区间 [l, r] 内必然存在一点,其上连续1的个数(高度)<=h。若该点存在,则由于边界内的高度必能容纳 h,以上述方法定义的矩形会向上延伸到高度h,再左右扩展到边界 [l, r] ,于是该矩形就是最大矩形。
若不存在这样的点,则由于 [l, r]内所有的高度均大于 h,可以通过延伸高度来生成更大的矩形,因此该矩形不可能最大。
综上,对于每个点,只需要计算h,l,和 r - 矩形的高,左边界和右边界。
使用动态规划,我们可以在线性时间内用上一行每个点的 h,l,和 r 计算出下一行每个点的的h,l,和r。
算法
给定一行 matrix[i],我们通过定义三个数组height,left,和 right来记录每个点的h,l,和 r。height[j] 对应matrix[i][j]的高,以此类推。
问题转化为如何更新每个数组。
Height:
这个比较容易。 h 的定义是从该点出发连续的1的个数。我们从方法二中已经学会了在一行中计算的方法:
row[j] = row[j - 1] + 1 if row[j] == '1'
只需要一点改动即可:
new_height[j] = old_height[j] + 1 if row[j] == '1' else 0
Left:
考虑哪些因素会导致矩形左边界的改变。由于当前行之上的全部0已经考虑在当前版本的left中,唯一能影响left就是在当前行遇到0。
因此我们可以定义:
new_left[j] = max(old_left[j], cur_left)
cur_left是我们遇到的最右边的0的序号加1。当我们将矩形向左 “扩展” ,我们知道,不能超过该点,否则会遇到0。
Right:
我们可以沿用 left 的思路,定义:
new_right[j] = min(old_right[j], cur_right)
cur_right 是我们遇到的最左边的0的序号。简便起见,我们不把 cur_right 减去1 (就像我们给cur_left加上1那样) ,这样我们就可以用height[j] * (right[j] - left[j]) 而非height[j] * (right[j] + 1 - left[j])来计算矩形面积。
这意味着, 严格地说 ,矩形的底边由半开半闭区间[l, r) 决定,而非闭区间 [l, r],且 right比右边界大1。尽管不这样做算法也可以正确运行,但这样会让计算看起来更简洁。
注意,为了正确的记录 cur_right,我们需要从右向左迭代。因此,更新right时需要从右向左。
一旦left,right,和 height数组能够正确更新,我们就只需要计算每个矩形的面积。
由于我们知道矩形 j的边界和高,可以简单地用height[j] * (right[j] - left[j])来计算面积,若j的面积 大于max_area,则更新之。
.
C++:
int maximalRectangle_stack(vector<vector<char>> &matrix) {
if (matrix.size() == 0) {
return 0;
}
int m = matrix.size();
int n = matrix[0].size();
int left[n];
int right[n];
int height[n];
memset(right, n, sizeof(right));
memset(left, n, sizeof(left));
memset(height, n, sizeof(height));
int maxarea = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
int cur_left = 0, cur_right = n;
// update height
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (matrix[i][j] == '1') {
height[j]++;
} else {
height[j] = 0;
}
}
// update left
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (matrix[i][j] == '1') {
left[j] = max(left[j], cur_left);
} else {
left[j] = 0, cur_left = j + 1;
}
}
// update right
for (int j = n - 1; j >= 0; --j) {
if (matrix[i][j] == '1') {
right[j] = min(right[j], cur_right);
} else {
right[j] = n;
cur_right = j;
}
}
// update area
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
maxarea = max(maxarea, (right[j] - left[j]) * height[j]);
}
}
return maxarea;
}
Java:
class Solution {
public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {
if(matrix.length == 0) return 0;
int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
int[] left = new int[n]; // initialize left as the leftmost boundary possible
int[] right = new int[n];
int[] height = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(right, n); // initialize right as the rightmost boundary possible
int maxarea = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int cur_left = 0, cur_right = n;
// update height
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(matrix[i][j] == '1') height[j]++;
else height[j] = 0;
}
// update left
for(int j=0; j<n; j++) {
if(matrix[i][j]=='1') left[j]=Math.max(left[j],cur_left);
else {left[j]=0; cur_left=j+1;}
}
// update right
for(int j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if(matrix[i][j] == '1') right[j] = Math.min(right[j], cur_right);
else {right[j] = n; cur_right = j;}
}
// update area
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
maxarea = Math.max(maxarea, (right[j] - left[j]) * height[j]);
}
return maxarea;
}
}
Python:
class Solution:
def maximalRectangle(self, matrix: List[List[str]]) -> int:
if not matrix: return 0
m = len(matrix)
n = len(matrix[0])
left = [0] * n # initialize left as the leftmost boundary possible
right = [n] * n # initialize right as the rightmost boundary possible
height = [0] * n
maxarea = 0
for i in range(m):
cur_left, cur_right = 0, n
# update height
for j in range(n):
if matrix[i][j] == '1': height[j] += 1
else: height[j] = 0
# update left
for j in range(n):
if matrix[i][j] == '1': left[j] = max(left[j], cur_left)
else:
left[j] = 0
cur_left = j + 1
# update right
for j in range(n-1, -1, -1):
if matrix[i][j] == '1': right[j] = min(right[j], cur_right)
else:
right[j] = n
cur_right = j
# update the area
for j in range(n):
maxarea = max(maxarea, height[j] * (right[j] - left[j]))
return maxarea
复杂性分析
- 时间复杂度: O ( N M ) O(NM) O(NM)。每次对于
N的迭代我们会对M迭代常数次。