SaltStack远程执行模块、syndic、salt-ssh模块、api调用
一、 远程执行模块
[root@server1 ~]# mkdir /srv/salt/_modules
[root@server1 ~]# cd /srv/salt/_modules
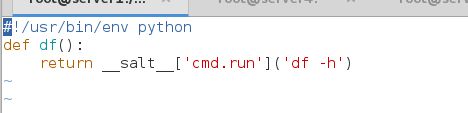
[root@server1 _modules]# vim my_disk.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
def df():
return __salt__['cmd.run']('df -h')刷新:
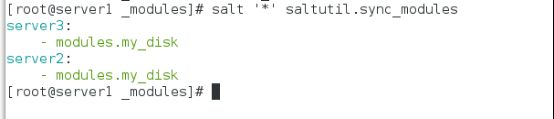
[root@server1 _modules]# salt '*' saltutil.sync_modules
调用函数:
[root@server1 _modules]# salt server2 my_disk.df
server2:
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/rhel-root 17G 1.2G 16G 8% /
devtmpfs 486M 0 486M 0% /dev
tmpfs 497M 12K 497M 1% /dev/shm
tmpfs 497M 13M 484M 3% /run
tmpfs 497M 0 497M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda1 1014M 139M 876M 14% /boot
tmpfs 100M 0 100M 0% /run/user/0
server2查看:
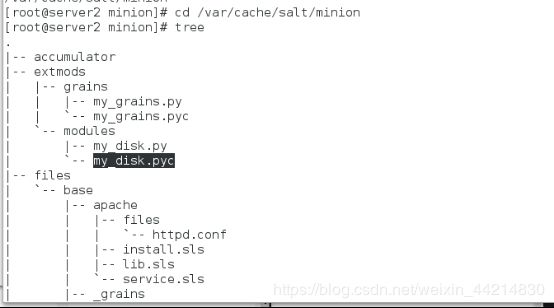
[root@server2 minion]# cd /var/cache/salt/minion
[root@server2 minion]# tree #pyc编译后的文件
二、salt-syndic(多个master)
topmsater通过syndic 和master通信,syndic是master上的一个服务,没有配置文件 syndic必须和master在同一主机上,master把任务布置给minion,minion反馈给master的syndic,再通过syndic反馈给topmoster。
1.打开一个新的虚拟机,配置好yum源,安装并开启salt-master
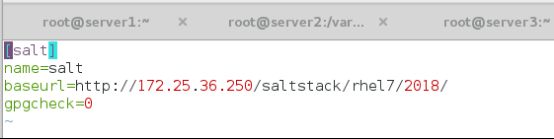
[root@server4 ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/salt.repo
[salt]
name=salt
baseurl=http://172.25.36.250/saltstack/rhel7/2018/
gpgcheck=0
[root@server4 ~]# yum install -y salt-master.service
[root@server4 ~]# systemctl start salt-master.service
[root@server4 ~]# systemctl enable salt-master.service
2 .更改master文件
[root@server4 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master
1054 order_masters: true
674 file_roots:
675 base:
676 - /srv/salt
[root@server4 ~]# systemctl restart salt-master.service
3安装并开启syndic服务
[root@server1 ~]# yum install -y salt-syndic
[root@server1 ~]# systemctl start salt-syndic4.编辑主配置文件
[root@server1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master
1058 syndic_master: 172.25.36.4
[root@server1 ~]# systemctl restart salt-master.service
5.发钥匙
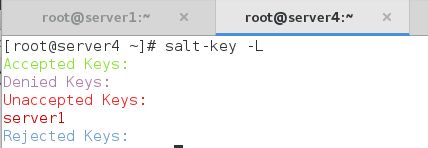
[root@server4 ~]# salt-key -L
Accepted Keys:
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
server1
Rejected Keys:
[root@server4 ~]# salt-key -A
The following keys are going to be accepted:
Unaccepted Keys:
server1
Proceed? [n/Y] y
Key for minion server1 accepted.
6.master端测试:
[root@server4 ~]# salt '*' test.ping
server2:
True
server3:
True
三、salt-ssh
关闭server2/3上的minion,如果没有这一步不用做
[root@server2 minion]# systemctl stop salt-minion.service
[root@server3 minion]# systemctl stop salt-minion.service
1.安装salt-ssh
[root@server1 ~]# yum install -y salt-ssh2.编辑配置文件
[root@server1 ~]# cd /etc/salt/
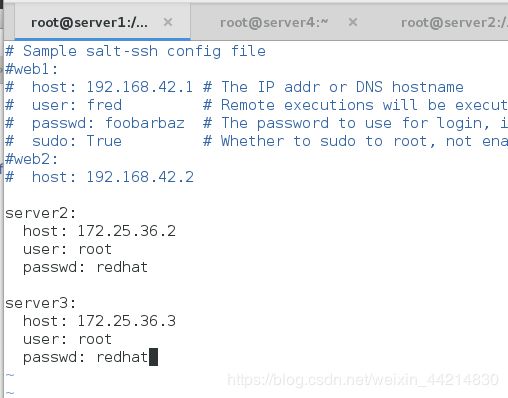
[root@server1 salt]# vim roster
server2:
host: 172.25.36.2
user: root
passwd: redhat
server3:
host: 172.25.36.3
user: root
passwd: redhat
3.测试:
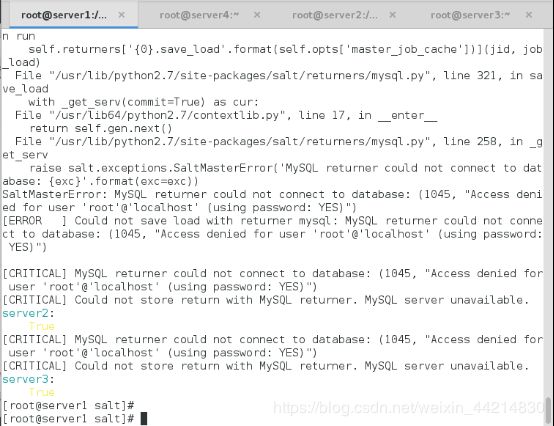
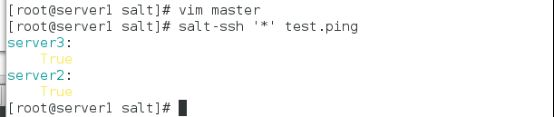
[root@server1 salt]# salt-ssh '*' test.ping
这个情况是mysql 没注释,但是成功
#注释mysql
[root@server1 salt]# vim master
#master_job_cache: mysql
#mysql.host: 'localhost'
#mysql.user: 'salt'
#mysql.pass: 'westos'
#mysql.db: 'salt'
#mysql.port: 3306
[root@server1 salt]# salt-ssh '*' test.ping
server3:
True
server2:
True
server2/3的minion服务已经关闭了,所以返回是通过ssh连接的
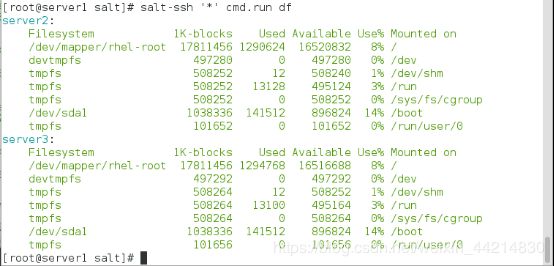
[root@server1 salt]# salt-ssh '*' cmd.run df
四、API模块
1.安装salt-api模块
[root@server1 ~]# yum install -y salt-api
2.加密
[root@server1 ~]# cd /etc/pki/tls/
[root@server1 private]# openssl genrsa 1024 > localhost.key
Generating RSA private key, 1024 bit long modulus
.............++++++
........++++++
e is 65537 (0x10001)
[root@server1 private]# cd ../certs/
[root@server1 certs]# ls
ca-bundle.crt ca-bundle.trust.crt make-dummy-cert Makefile renew-dummy-cert
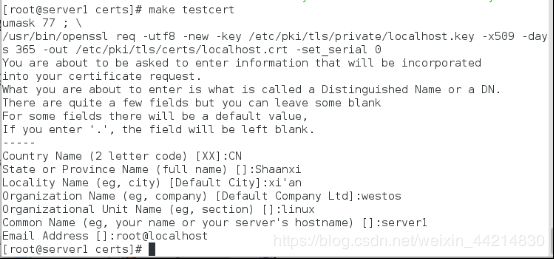
3.认证
[root@server1 certs]# make testcert
umask 77 ; \
/usr/bin/openssl req -utf8 -new -key /etc/pki/tls/private/localhost.key -x509 -days 365 -out /etc/pki/tls/certs/localhost.crt -set_serial 0
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:CN
State or Province Name (full name) []:Shaanxi
Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:xi'an
Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:westos
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:linux
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:server1
Email Address []:root@localhost
4.编辑配置文件
[root@server1 certs]# cd /etc/salt/master.d/
[root@server1 master.d]# ls
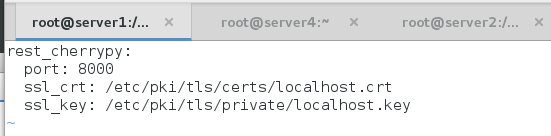
[root@server1 master.d]# vim api.conf
rest_cherrypy:
port: 8000
ssl_crt: /etc/pki/tls/certs/localhost.crt
ssl_key: /etc/pki/tls/private/localhost.key
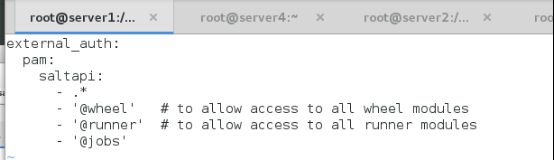
[root@server1 master.d]# vim auto.conf
external_auth:
pam:
saltapi:
- .* #权限也复制
- '@wheel' # to allow access to all wheel modules
- '@runner' # to allow access to all runner modules
- '@jobs'
5.建立saltapi用户
[root@server1 master.d]# useradd saltapi
[root@server1 master.d]# passwd saltapi
6.开启api
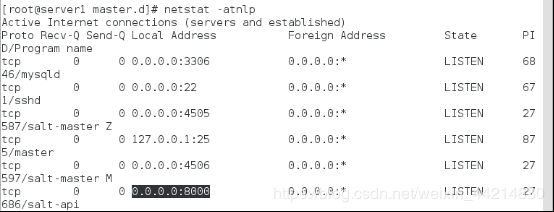
[root@server1 master.d]# systemctl restart salt-master
[root@server1 master.d]# systemctl start salt-api
[root@server1 master.d]# netstat -atnlp
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:8000 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 27686/salt-api
7.测试(在真机上)
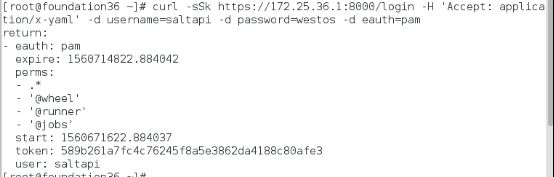
[root@foundation36 ~]# curl -sSk https://172.25.36.1:8000/login -H 'Accept: application/x-yaml' -d username=saltapi -d password=westos -d eauth=pam
return:
- eauth: pam
expire: 1560714822.884042
perms:
- .*
- '@wheel'
- '@runner'
- '@jobs'
start: 1560671622.884037
token: 589b261a7fc4c76245f8a5e3862da4188c80afe3
user: saltapi
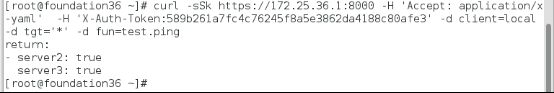
[root@foundation36 ~]# curl -sSk https://172.25.36.1:8000 -H 'Accept: application/x-yaml' -H 'X-Auth-Token:589b261a7fc4c76245f8a5e3862da4188c80afe3' -d client=local -d tgt='*' -d fun=test.ping
return:
- server2: true
server3: true
编辑python文件(真机),打印已有key的主机名
[root@foundation36 ~]# vim saltapi.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import urllib2,urllib
import time
try:
import json
except ImportError:
import simplejson as json
class SaltAPI(object):
__token_id = ''
def __init__(self,url,username,password):
self.__url = url.rstrip('/')
self.__user = username
self.__password = password
def token_id(self):
''' user login and get token id '''
params = {'eauth': 'pam', 'username': self.__user, 'password': self.__password}
encode = urllib.urlencode(params)
obj = urllib.unquote(encode)
content = self.postRequest(obj,prefix='/login')
try:
self.__token_id = content['return'][0]['token']
except KeyError:
raise KeyError
def postRequest(self,obj,prefix='/'):
url = self.__url + prefix
headers = {'X-Auth-Token' : self.__token_id}
req = urllib2.Request(url, obj, headers)
opener = urllib2.urlopen(req)
content = json.loads(opener.read())
return content
def list_all_key(self):
params = {'client': 'wheel', 'fun': 'key.list_all'}
obj = urllib.urlencode(params)
self.token_id()
content = self.postRequest(obj)
minions = content['return'][0]['data']['return']['minions']
minions_pre = content['return'][0]['data']['return']['minions_pre']
return minions,minions_pre
def delete_key(self,node_name):
params = {'client': 'wheel', 'fun': 'key.delete', 'match': node_name}
obj = urllib.urlencode(params)
self.token_id()
content = self.postRequest(obj)
ret = content['return'][0]['data']['success']
return ret
def accept_key(self,node_name):
params = {'client': 'wheel', 'fun': 'key.accept', 'match': node_name}
obj = urllib.urlencode(params)
self.token_id()
content = self.postRequest(obj)
ret = content['return'][0]['data']['success']
return ret
def remote_noarg_execution(self,tgt,fun):
''' Execute commands without parameters '''
params = {'client': 'local', 'tgt': tgt, 'fun': fun}
obj = urllib.urlencode(params)
self.token_id()
content = self.postRequest(obj)
ret = content['return'][0][tgt]
return ret
def remote_execution(self,tgt,fun,arg):
''' Command execution with parameters '''
params = {'client': 'local', 'tgt': tgt, 'fun': fun, 'arg': arg}
obj = urllib.urlencode(params)
self.token_id()
content = self.postRequest(obj)
ret = content['return'][0][tgt]
return ret
def target_remote_execution(self,tgt,fun,arg):
''' Use targeting for remote execution '''
params = {'client': 'local', 'tgt': tgt, 'fun': fun, 'arg': arg, 'expr_form': 'nodegroup'}
obj = urllib.urlencode(params)
self.token_id()
content = self.postRequest(obj)
jid = content['return'][0]['jid']
return jid
def deploy(self,tgt,arg):
''' Module deployment '''
params = {'client': 'local', 'tgt': tgt, 'fun': 'state.sls', 'arg': arg}
obj = urllib.urlencode(params)
self.token_id()
content = self.postRequest(obj)
return content
def async_deploy(self,tgt,arg):
''' Asynchronously send a command to connected minions '''
params = {'client': 'local_async', 'tgt': tgt, 'fun': 'state.sls', 'arg': arg}
obj = urllib.urlencode(params)
self.token_id()
content = self.postRequest(obj)
jid = content['return'][0]['jid']
return jid
def target_deploy(self,tgt,arg):
''' Based on the node group forms deployment '''
params = {'client': 'local_async', 'tgt': tgt, 'fun': 'state.sls', 'arg': arg, 'expr_form': 'nodegroup'}
obj = urllib.urlencode(params)
self.token_id()
content = self.postRequest(obj)
jid = content['return'][0]['jid']
return jid
def main():
sapi = SaltAPI(url="https://172.25.36.1:8000",username="saltapi",password="westos")
#sapi.token_id()
print sapi.list_all_key()
#sapi.delete_key('test-01')
#sapi.accept_key('test-01')
#sapi.deploy('test-01','nginx')
#print sapi.remote_noarg_execution('test-01','grains.items')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
[root@foundation36 ~]# python saltapi.py
([u'server2', u'server3'], [])
执行python脚本开启nginx:
[root@foundation36 ~]# vim saltapi.py #更改main函数
sapi.deploy('server3','nginx.service')
关闭server3上的nginx,执行python脚本,server3上的nginx会自动开启
[root@foundation36 ~]# python saltapi.py
- 关闭server3上的nginx,curl localhost #访问被拒绝
- 执行脚本后: curl localhost #访问成功