十九、数据整理(下)
作者:Chris Albon
译者:飞龙
协议:CC BY-NC-SA 4.0
连接和合并数据帧
import pandas as pd
from IPython.display import display
from IPython.display import Image
raw_data = {
'subject_id': ['1', '2', '3', '4', '5'],
'first_name': ['Alex', 'Amy', 'Allen', 'Alice', 'Ayoung'],
'last_name': ['Anderson', 'Ackerman', 'Ali', 'Aoni', 'Atiches']}
df_a = pd.DataFrame(raw_data, columns = ['subject_id', 'first_name', 'last_name'])
df_a
|
subject_id |
first_name |
last_name |
| 0 |
1 |
Alex |
Anderson |
| 1 |
2 |
Amy |
Ackerman |
| 2 |
3 |
Allen |
Ali |
| 3 |
4 |
Alice |
Aoni |
| 4 |
5 |
Ayoung |
Atiches |
raw_data = {
'subject_id': ['4', '5', '6', '7', '8'],
'first_name': ['Billy', 'Brian', 'Bran', 'Bryce', 'Betty'],
'last_name': ['Bonder', 'Black', 'Balwner', 'Brice', 'Btisan']}
df_b = pd.DataFrame(raw_data, columns = ['subject_id', 'first_name', 'last_name'])
df_b
|
subject_id |
first_name |
last_name |
| 0 |
4 |
Billy |
Bonder |
| 1 |
5 |
Brian |
Black |
| 2 |
6 |
Bran |
Balwner |
| 3 |
7 |
Bryce |
Brice |
| 4 |
8 |
Betty |
Btisan |
raw_data = {
'subject_id': ['1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '7', '8', '9', '10', '11'],
'test_id': [51, 15, 15, 61, 16, 14, 15, 1, 61, 16]}
df_n = pd.DataFrame(raw_data, columns = ['subject_id','test_id'])
df_n
|
subject_id |
test_id |
| 0 |
1 |
51 |
| 1 |
2 |
15 |
| 2 |
3 |
15 |
| 3 |
4 |
61 |
| 4 |
5 |
16 |
| 5 |
7 |
14 |
| 6 |
8 |
15 |
| 7 |
9 |
1 |
| 8 |
10 |
61 |
| 9 |
11 |
16 |
df_new = pd.concat([df_a, df_b])
df_new
|
subject_id |
first_name |
last_name |
| 0 |
1 |
Alex |
Anderson |
| 1 |
2 |
Amy |
Ackerman |
| 2 |
3 |
Allen |
Ali |
| 3 |
4 |
Alice |
Aoni |
| 4 |
5 |
Ayoung |
Atiches |
| 0 |
4 |
Billy |
Bonder |
| 1 |
5 |
Brian |
Black |
| 2 |
6 |
Bran |
Balwner |
| 3 |
7 |
Bryce |
Brice |
| 4 |
8 |
Betty |
Btisan |
pd.concat([df_a, df_b], axis=1)
|
subject_id |
first_name |
last_name |
subject_id |
first_name |
last_name |
| 0 |
1 |
Alex |
Anderson |
4 |
Billy |
Bonder |
| 1 |
2 |
Amy |
Ackerman |
5 |
Brian |
Black |
| 2 |
3 |
Allen |
Ali |
6 |
Bran |
Balwner |
| 3 |
4 |
Alice |
Aoni |
7 |
Bryce |
Brice |
| 4 |
5 |
Ayoung |
Atiches |
8 |
Betty |
Btisan |
pd.merge(df_new, df_n, on='subject_id')
|
subject_id |
first_name |
last_name |
test_id |
| 0 |
1 |
Alex |
Anderson |
51 |
| 1 |
2 |
Amy |
Ackerman |
15 |
| 2 |
3 |
Allen |
Ali |
15 |
| 3 |
4 |
Alice |
Aoni |
61 |
| 4 |
4 |
Billy |
Bonder |
61 |
| 5 |
5 |
Ayoung |
Atiches |
16 |
| 6 |
5 |
Brian |
Black |
16 |
| 7 |
7 |
Bryce |
Brice |
14 |
| 8 |
8 |
Betty |
Btisan |
15 |
pd.merge(df_new, df_n, left_on='subject_id', right_on='subject_id')
|
subject_id |
first_name |
last_name |
test_id |
| 0 |
1 |
Alex |
Anderson |
51 |
| 1 |
2 |
Amy |
Ackerman |
15 |
| 2 |
3 |
Allen |
Ali |
15 |
| 3 |
4 |
Alice |
Aoni |
61 |
| 4 |
4 |
Billy |
Bonder |
61 |
| 5 |
5 |
Ayoung |
Atiches |
16 |
| 6 |
5 |
Brian |
Black |
16 |
| 7 |
7 |
Bryce |
Brice |
14 |
| 8 |
8 |
Betty |
Btisan |
15 |
使用外连接来合并。
“全外连接产生表 A 和表 B 中所有记录的集合,带有来自两侧的匹配记录。如果没有匹配,则缺少的一侧将包含空值。” – [来源](http://blog .codinghorror.com/a-visual-explanation-of-sql-joins/)
pd.merge(df_a, df_b, on='subject_id', how='outer')
|
subject_id |
first_name_x |
last_name_x |
first_name_y |
last_name_y |
| 0 |
1 |
Alex |
Anderson |
NaN |
NaN |
| 1 |
2 |
Amy |
Ackerman |
NaN |
NaN |
| 2 |
3 |
Allen |
Ali |
NaN |
NaN |
| 3 |
4 |
Alice |
Aoni |
Billy |
Bonder |
| 4 |
5 |
Ayoung |
Atiches |
Brian |
Black |
| 5 |
6 |
NaN |
NaN |
Bran |
Balwner |
| 6 |
7 |
NaN |
NaN |
Bryce |
Brice |
| 7 |
8 |
NaN |
NaN |
Betty |
Btisan |
使用内连接来合并。
“内联接只生成匹配表 A 和表 B 的记录集。” – 来源
pd.merge(df_a, df_b, on='subject_id', how='inner')
|
subject_id |
first_name_x |
last_name_x |
first_name_y |
last_name_y |
| 0 |
4 |
Alice |
Aoni |
Billy |
Bonder |
| 1 |
5 |
Ayoung |
Atiches |
Brian |
Black |
pd.merge(df_a, df_b, on='subject_id', how='right')
|
subject_id |
first_name_x |
last_name_x |
first_name_y |
last_name_y |
| 0 |
4 |
Alice |
Aoni |
Billy |
Bonder |
| 1 |
5 |
Ayoung |
Atiches |
Brian |
Black |
| 2 |
6 |
NaN |
NaN |
Bran |
Balwner |
| 3 |
7 |
NaN |
NaN |
Bryce |
Brice |
| 4 |
8 |
NaN |
NaN |
Betty |
Btisan |
使用左连接来合并。
“左外连接从表 A 中生成一组完整的记录,它们在表 B 中有匹配的记录。如果没有匹配,右侧将包含空。” – 来源
pd.merge(df_a, df_b, on='subject_id', how='left')
|
subject_id |
first_name_x |
last_name_x |
first_name_y |
last_name_y |
| 0 |
1 |
Alex |
Anderson |
NaN |
NaN |
| 1 |
2 |
Amy |
Ackerman |
NaN |
NaN |
| 2 |
3 |
Allen |
Ali |
NaN |
NaN |
| 3 |
4 |
Alice |
Aoni |
Billy |
Bonder |
| 4 |
5 |
Ayoung |
Atiches |
Brian |
Black |
pd.merge(df_a, df_b, on='subject_id', how='left', suffixes=('_left', '_right'))
|
subject_id |
first_name_left |
last_name_left |
first_name_right |
last_name_right |
| 0 |
1 |
Alex |
Anderson |
NaN |
NaN |
| 1 |
2 |
Amy |
Ackerman |
NaN |
NaN |
| 2 |
3 |
Allen |
Ali |
NaN |
NaN |
| 3 |
4 |
Alice |
Aoni |
Billy |
Bonder |
| 4 |
5 |
Ayoung |
Atiches |
Brian |
Black |
pd.merge(df_a, df_b, right_index=True, left_index=True)
|
subject_id_x |
first_name_x |
last_name_x |
subject_id_y |
first_name_y |
last_name_y |
| 0 |
1 |
Alex |
Anderson |
4 |
Billy |
Bonder |
| 1 |
2 |
Amy |
Ackerman |
5 |
Brian |
Black |
| 2 |
3 |
Allen |
Ali |
6 |
Bran |
Balwner |
| 3 |
4 |
Alice |
Aoni |
7 |
Bryce |
Brice |
| 4 |
5 |
Ayoung |
Atiches |
8 |
Betty |
Btisan |
列出 pandas 列中的唯一值
特别感谢 Bob Haffner 指出了一种更好的方法。
import pandas as pd
pd.set_option('display.max_row', 1000)
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', 50)
data = {'name': ['Jason', 'Molly', 'Tina', 'Jake', 'Amy'],
'year': [2012, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2014],
'reports': [4, 24, 31, 2, 3]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index = ['Cochice', 'Pima', 'Santa Cruz', 'Maricopa', 'Yuma'])
df
|
name |
reports |
year |
| Cochice |
Jason |
4 |
2012 |
| Pima |
Molly |
24 |
2012 |
| Santa Cruz |
Tina |
31 |
2013 |
| Maricopa |
Jake |
2 |
2014 |
| Yuma |
Amy |
3 |
2014 |
df.name.unique()
加载 JSON 文件
import pandas as pd
url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/chrisalbon/simulated_datasets/master/data.json'
df = pd.read_json(url, orient='columns')
df.head(10)
|
category |
datetime |
integer |
| 0 |
0 |
2015-01-01 00:00:00 |
5 |
| 1 |
0 |
2015-01-01 00:00:01 |
5 |
| 10 |
0 |
2015-01-01 00:00:10 |
5 |
| 11 |
0 |
2015-01-01 00:00:11 |
5 |
| 12 |
0 |
2015-01-01 00:00:12 |
8 |
| 13 |
0 |
2015-01-01 00:00:13 |
9 |
| 14 |
0 |
2015-01-01 00:00:14 |
8 |
| 15 |
0 |
2015-01-01 00:00:15 |
8 |
| 16 |
0 |
2015-01-01 00:00:16 |
2 |
| 17 |
0 |
2015-01-01 00:00:17 |
1 |
加载 Excel 文件
import pandas as pd
url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/chrisalbon/simulated_datasets/master/data.xlsx'
df = pd.read_excel(url, sheetname=0, header=1)
df.head(10)
|
5 |
2015-01-01 00:00:00 |
0 |
| 0 |
5 |
2015-01-01 00:00:01 |
0 |
| 1 |
9 |
2015-01-01 00:00:02 |
0 |
| 2 |
6 |
2015-01-01 00:00:03 |
0 |
| 3 |
6 |
2015-01-01 00:00:04 |
0 |
| 4 |
9 |
2015-01-01 00:00:05 |
0 |
| 5 |
7 |
2015-01-01 00:00:06 |
0 |
| 6 |
1 |
2015-01-01 00:00:07 |
0 |
| 7 |
6 |
2015-01-01 00:00:08 |
0 |
| 8 |
9 |
2015-01-01 00:00:09 |
0 |
| 9 |
5 |
2015-01-01 00:00:10 |
0 |
将 Excel 表格加载为数据帧
import pandas as pd
xls_file = pd.ExcelFile('../data/example.xls')
xls_file
xls_file.sheet_names
df = xls_file.parse('Sheet1')
df
|
year |
deaths_attacker |
deaths_defender |
soldiers_attacker |
soldiers_defender |
wounded_attacker |
wounded_defender |
| 0 |
1945 |
425 |
423 |
2532 |
37235 |
41 |
14 |
| 1 |
1956 |
242 |
264 |
6346 |
2523 |
214 |
1424 |
| 2 |
1964 |
323 |
1231 |
3341 |
2133 |
131 |
131 |
| 3 |
1969 |
223 |
23 |
6732 |
1245 |
12 |
12 |
| 4 |
1971 |
783 |
23 |
12563 |
2671 |
123 |
34 |
| 5 |
1981 |
436 |
42 |
2356 |
7832 |
124 |
124 |
| 6 |
1982 |
324 |
124 |
253 |
2622 |
264 |
1124 |
| 7 |
1992 |
3321 |
631 |
5277 |
3331 |
311 |
1431 |
| 8 |
1999 |
262 |
232 |
2732 |
2522 |
132 |
122 |
| 9 |
2004 |
843 |
213 |
6278 |
26773 |
623 |
2563 |
加载 CSV
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
raw_data = {'first_name': ['Jason', 'Molly', 'Tina', 'Jake', 'Amy'],
'last_name': ['Miller', 'Jacobson', ".", 'Milner', 'Cooze'],
'age': [42, 52, 36, 24, 73],
'preTestScore': [4, 24, 31, ".", "."],
'postTestScore': ["25,000", "94,000", 57, 62, 70]}
df = pd.DataFrame(raw_data, columns = ['first_name', 'last_name', 'age', 'preTestScore', 'postTestScore'])
df
|
first_name |
last_name |
age |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
| 0 |
Jason |
Miller |
42 |
4 |
25,000 |
| 1 |
Molly |
Jacobson |
52 |
24 |
94,000 |
| 2 |
Tina |
. |
36 |
31 |
57 |
| 3 |
Jake |
Milner |
24 |
. |
62 |
| 4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73 |
. |
70 |
df.to_csv('pandas_dataframe_importing_csv/example.csv')
df = pd.read_csv('pandas_dataframe_importing_csv/example.csv')
df
|
Unnamed: 0 |
first_name |
last_name |
age |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
| 0 |
0 |
Jason |
Miller |
42 |
4 |
25,000 |
| 1 |
1 |
Molly |
Jacobson |
52 |
24 |
94,000 |
| 2 |
2 |
Tina |
. |
36 |
31 |
57 |
| 3 |
3 |
Jake |
Milner |
24 |
. |
62 |
| 4 |
4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73 |
. |
70 |
df = pd.read_csv('pandas_dataframe_importing_csv/example.csv', header=None)
df
|
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
| 0 |
NaN |
first_name |
last_name |
age |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
| 1 |
0.0 |
Jason |
Miller |
42 |
4 |
25,000 |
| 2 |
1.0 |
Molly |
Jacobson |
52 |
24 |
94,000 |
| 3 |
2.0 |
Tina |
. |
36 |
31 |
57 |
| 4 |
3.0 |
Jake |
Milner |
24 |
. |
62 |
| 5 |
4.0 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73 |
. |
70 |
df = pd.read_csv('pandas_dataframe_importing_csv/example.csv', names=['UID', 'First Name', 'Last Name', 'Age', 'Pre-Test Score', 'Post-Test Score'])
df
|
UID |
First Name |
Last Name |
Age |
Pre-Test Score |
Post-Test Score |
| 0 |
NaN |
first_name |
last_name |
age |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
| 1 |
0.0 |
Jason |
Miller |
42 |
4 |
25,000 |
| 2 |
1.0 |
Molly |
Jacobson |
52 |
24 |
94,000 |
| 3 |
2.0 |
Tina |
. |
36 |
31 |
57 |
| 4 |
3.0 |
Jake |
Milner |
24 |
. |
62 |
| 5 |
4.0 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73 |
. |
70 |
df = pd.read_csv('pandas_dataframe_importing_csv/example.csv', index_col='UID', names=['UID', 'First Name', 'Last Name', 'Age', 'Pre-Test Score', 'Post-Test Score'])
df
|
First Name |
Last Name |
Age |
Pre-Test Score |
Post-Test Score |
| UID |
|
|
|
|
|
| NaN |
first_name |
last_name |
age |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
| 0.0 |
Jason |
Miller |
42 |
4 |
25,000 |
| 1.0 |
Molly |
Jacobson |
52 |
24 |
94,000 |
| 2.0 |
Tina |
. |
36 |
31 |
57 |
| 3.0 |
Jake |
Milner |
24 |
. |
62 |
| 4.0 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73 |
. |
70 |
df = pd.read_csv('pandas_dataframe_importing_csv/example.csv', index_col=['First Name', 'Last Name'], names=['UID', 'First Name', 'Last Name', 'Age', 'Pre-Test Score', 'Post-Test Score'])
df
|
|
UID |
Age |
Pre-Test Score |
Post-Test Score |
| First Name |
Last Name |
|
|
|
|
| first_name |
last_name |
NaN |
age |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
| Jason |
Miller |
0.0 |
42 |
4 |
25,000 |
| Molly |
Jacobson |
1.0 |
52 |
24 |
94,000 |
| Tina |
. |
2.0 |
36 |
31 |
57 |
| Jake |
Milner |
3.0 |
24 |
. |
62 |
| Amy |
Cooze |
4.0 |
73 |
. |
70 |
df = pd.read_csv('pandas_dataframe_importing_csv/example.csv', na_values=['.'])
pd.isnull(df)
|
Unnamed: 0 |
first_name |
last_name |
age |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
| 0 |
False |
False |
False |
False |
False |
False |
| 1 |
False |
False |
False |
False |
False |
False |
| 2 |
False |
False |
True |
False |
False |
False |
| 3 |
False |
False |
False |
False |
True |
False |
| 4 |
False |
False |
False |
False |
True |
False |
sentinels = {'Last Name': ['.', 'NA'], 'Pre-Test Score': ['.']}
df = pd.read_csv('pandas_dataframe_importing_csv/example.csv', na_values=sentinels)
df
|
Unnamed: 0 |
first_name |
last_name |
age |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
| 0 |
0 |
Jason |
Miller |
42 |
4 |
25,000 |
| 1 |
1 |
Molly |
Jacobson |
52 |
24 |
94,000 |
| 2 |
2 |
Tina |
. |
36 |
31 |
57 |
| 3 |
3 |
Jake |
Milner |
24 |
. |
62 |
| 4 |
4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73 |
. |
70 |
df = pd.read_csv('pandas_dataframe_importing_csv/example.csv', na_values=sentinels, skiprows=3)
df
|
2 |
Tina |
. |
36 |
31 |
57 |
| 0 |
3 |
Jake |
Milner |
24 |
. |
62 |
| 1 |
4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73 |
. |
70 |
df = pd.read_csv('pandas_dataframe_importing_csv/example.csv', thousands=',')
df
|
Unnamed: 0 |
first_name |
last_name |
age |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
| 0 |
0 |
Jason |
Miller |
42 |
4 |
25000 |
| 1 |
1 |
Molly |
Jacobson |
52 |
24 |
94000 |
| 2 |
2 |
Tina |
. |
36 |
31 |
57 |
| 3 |
3 |
Jake |
Milner |
24 |
. |
62 |
| 4 |
4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73 |
. |
70 |
长到宽的格式
import pandas as pd
raw_data = {'patient': [1, 1, 1, 2, 2],
'obs': [1, 2, 3, 1, 2],
'treatment': [0, 1, 0, 1, 0],
'score': [6252, 24243, 2345, 2342, 23525]}
df = pd.DataFrame(raw_data, columns = ['patient', 'obs', 'treatment', 'score'])
df
|
patient |
obs |
treatment |
score |
| 0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
6252 |
| 1 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
24243 |
| 2 |
1 |
3 |
0 |
2345 |
| 3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
2342 |
| 4 |
2 |
2 |
0 |
23525 |
制作“宽的”数据。
现在,我们将创建一个“宽的”数据帧,其中行数按患者编号,列按观测编号,单元格值为得分值。
df.pivot(index='patient', columns='obs', values='score')
| obs |
1 |
2 |
3 |
| patient |
|
|
|
| 1 |
6252.0 |
24243.0 |
2345.0 |
| 2 |
2342.0 |
23525.0 |
NaN |
在数据帧中小写列名
import pandas as pd
pd.set_option('display.max_row', 1000)
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', 50)
data = {'NAME': ['Jason', 'Molly', 'Tina', 'Jake', 'Amy'],
'YEAR': [2012, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2014],
'REPORTS': [4, 24, 31, 2, 3]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index = ['Cochice', 'Pima', 'Santa Cruz', 'Maricopa', 'Yuma'])
df
|
NAME |
REPORTS |
YEAR |
| Cochice |
Jason |
4 |
2012 |
| Pima |
Molly |
24 |
2012 |
| Santa Cruz |
Tina |
31 |
2013 |
| Maricopa |
Jake |
2 |
2014 |
| Yuma |
Amy |
3 |
2014 |
df.columns = map(str.lower, df.columns)
df
|
name |
reports |
year |
| Cochice |
Jason |
4 |
2012 |
| Pima |
Molly |
24 |
2012 |
| Santa Cruz |
Tina |
31 |
2013 |
| Maricopa |
Jake |
2 |
2014 |
| Yuma |
Amy |
3 |
2014 |
使用函数创建新列
import pandas as pd
raw_data = {'regiment': ['Nighthawks', 'Nighthawks', 'Nighthawks', 'Nighthawks', 'Dragoons', 'Dragoons', 'Dragoons', 'Dragoons', 'Scouts', 'Scouts', 'Scouts', 'Scouts'],
'company': ['1st', '1st', '2nd', '2nd', '1st', '1st', '2nd', '2nd','1st', '1st', '2nd', '2nd'],
'name': ['Miller', 'Jacobson', 'Ali', 'Milner', 'Cooze', 'Jacon', 'Ryaner', 'Sone', 'Sloan', 'Piger', 'Riani', 'Ali'],
'preTestScore': [4, 24, 31, 2, 3, 4, 24, 31, 2, 3, 2, 3],
'postTestScore': [25, 94, 57, 62, 70, 25, 94, 57, 62, 70, 62, 70]}
df = pd.DataFrame(raw_data, columns = ['regiment', 'company', 'name', 'preTestScore', 'postTestScore'])
df
|
regiment |
company |
name |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
| 0 |
Nighthawks |
1st |
Miller |
4 |
25 |
| 1 |
Nighthawks |
1st |
Jacobson |
24 |
94 |
| 2 |
Nighthawks |
2nd |
Ali |
31 |
57 |
| 3 |
Nighthawks |
2nd |
Milner |
2 |
62 |
| 4 |
Dragoons |
1st |
Cooze |
3 |
70 |
| 5 |
Dragoons |
1st |
Jacon |
4 |
25 |
| 6 |
Dragoons |
2nd |
Ryaner |
24 |
94 |
| 7 |
Dragoons |
2nd |
Sone |
31 |
57 |
| 8 |
Scouts |
1st |
Sloan |
2 |
62 |
| 9 |
Scouts |
1st |
Piger |
3 |
70 |
| 10 |
Scouts |
2nd |
Riani |
2 |
62 |
| 11 |
Scouts |
2nd |
Ali |
3 |
70 |
def pre_post_difference(pre, post):
return post - pre
df['score_change'] = pre_post_difference(df['preTestScore'], df['postTestScore'])
df
|
regiment |
company |
name |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
score_change |
| 0 |
Nighthawks |
1st |
Miller |
4 |
25 |
21 |
| 1 |
Nighthawks |
1st |
Jacobson |
24 |
94 |
70 |
| 2 |
Nighthawks |
2nd |
Ali |
31 |
57 |
26 |
| 3 |
Nighthawks |
2nd |
Milner |
2 |
62 |
60 |
| 4 |
Dragoons |
1st |
Cooze |
3 |
70 |
67 |
| 5 |
Dragoons |
1st |
Jacon |
4 |
25 |
21 |
| 6 |
Dragoons |
2nd |
Ryaner |
24 |
94 |
70 |
| 7 |
Dragoons |
2nd |
Sone |
31 |
57 |
26 |
| 8 |
Scouts |
1st |
Sloan |
2 |
62 |
60 |
| 9 |
Scouts |
1st |
Piger |
3 |
70 |
67 |
| 10 |
Scouts |
2nd |
Riani |
2 |
62 |
60 |
| 11 |
Scouts |
2nd |
Ali |
3 |
70 |
67 |
def score_multipler_2x_and_3x(x):
return x*2, x*3
df['post_score_x2'], df['post_score_x3'] = zip(*df['postTestScore'].map(score_multipler_2x_and_3x))
df
|
regiment |
company |
name |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
score_change |
post_score_x2 |
post_score_x3 |
| 0 |
Nighthawks |
1st |
Miller |
4 |
25 |
21 |
50 |
75 |
| 1 |
Nighthawks |
1st |
Jacobson |
24 |
94 |
70 |
188 |
282 |
| 2 |
Nighthawks |
2nd |
Ali |
31 |
57 |
26 |
114 |
171 |
| 3 |
Nighthawks |
2nd |
Milner |
2 |
62 |
60 |
124 |
186 |
| 4 |
Dragoons |
1st |
Cooze |
3 |
70 |
67 |
140 |
210 |
| 5 |
Dragoons |
1st |
Jacon |
4 |
25 |
21 |
50 |
75 |
| 6 |
Dragoons |
2nd |
Ryaner |
24 |
94 |
70 |
188 |
282 |
| 7 |
Dragoons |
2nd |
Sone |
31 |
57 |
26 |
114 |
171 |
| 8 |
Scouts |
1st |
Sloan |
2 |
62 |
60 |
124 |
186 |
| 9 |
Scouts |
1st |
Piger |
3 |
70 |
67 |
140 |
210 |
| 10 |
Scouts |
2nd |
Riani |
2 |
62 |
60 |
124 |
186 |
| 11 |
Scouts |
2nd |
Ali |
3 |
70 |
67 |
140 |
210 |
将外部值映射为数据帧的值
import pandas as pd
raw_data = {'first_name': ['Jason', 'Molly', 'Tina', 'Jake', 'Amy'],
'last_name': ['Miller', 'Jacobson', 'Ali', 'Milner', 'Cooze'],
'age': [42, 52, 36, 24, 73],
'city': ['San Francisco', 'Baltimore', 'Miami', 'Douglas', 'Boston']}
df = pd.DataFrame(raw_data, columns = ['first_name', 'last_name', 'age', 'city'])
df
|
first_name |
last_name |
age |
city |
| 0 |
Jason |
Miller |
42 |
San Francisco |
| 1 |
Molly |
Jacobson |
52 |
Baltimore |
| 2 |
Tina |
Ali |
36 |
Miami |
| 3 |
Jake |
Milner |
24 |
Douglas |
| 4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73 |
Boston |
city_to_state = { 'San Francisco' : 'California',
'Baltimore' : 'Maryland',
'Miami' : 'Florida',
'Douglas' : 'Arizona',
'Boston' : 'Massachusetts'}
df['state'] = df['city'].map(city_to_state)
df
|
first_name |
last_name |
age |
city |
state |
| 0 |
Jason |
Miller |
42 |
San Francisco |
California |
| 1 |
Molly |
Jacobson |
52 |
Baltimore |
Maryland |
| 2 |
Tina |
Ali |
36 |
Miami |
Florida |
| 3 |
Jake |
Milner |
24 |
Douglas |
Arizona |
| 4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73 |
Boston |
Massachusetts |
数据帧中的缺失数据
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
raw_data = {'first_name': ['Jason', np.nan, 'Tina', 'Jake', 'Amy'],
'last_name': ['Miller', np.nan, 'Ali', 'Milner', 'Cooze'],
'age': [42, np.nan, 36, 24, 73],
'sex': ['m', np.nan, 'f', 'm', 'f'],
'preTestScore': [4, np.nan, np.nan, 2, 3],
'postTestScore': [25, np.nan, np.nan, 62, 70]}
df = pd.DataFrame(raw_data, columns = ['first_name', 'last_name', 'age', 'sex', 'preTestScore', 'postTestScore'])
df
|
first_name |
last_name |
age |
sex |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
| 0 |
Jason |
Miller |
42.0 |
m |
4.0 |
25.0 |
| 1 |
NaN |
NaN |
NaN |
NaN |
NaN |
NaN |
| 2 |
Tina |
Ali |
36.0 |
f |
NaN |
NaN |
| 3 |
Jake |
Milner |
24.0 |
m |
2.0 |
62.0 |
| 4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73.0 |
f |
3.0 |
70.0 |
df_no_missing = df.dropna()
df_no_missing
|
first_name |
last_name |
age |
sex |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
| 0 |
Jason |
Miller |
42.0 |
m |
4.0 |
25.0 |
| 3 |
Jake |
Milner |
24.0 |
m |
2.0 |
62.0 |
| 4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73.0 |
f |
3.0 |
70.0 |
df_cleaned = df.dropna(how='all')
df_cleaned
|
first_name |
last_name |
age |
sex |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
| 0 |
Jason |
Miller |
42.0 |
m |
4.0 |
25.0 |
| 2 |
Tina |
Ali |
36.0 |
f |
NaN |
NaN |
| 3 |
Jake |
Milner |
24.0 |
m |
2.0 |
62.0 |
| 4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73.0 |
f |
3.0 |
70.0 |
df['location'] = np.nan
df
|
first_name |
last_name |
age |
sex |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
location |
| 0 |
Jason |
Miller |
42.0 |
m |
4.0 |
25.0 |
NaN |
| 1 |
NaN |
NaN |
NaN |
NaN |
NaN |
NaN |
NaN |
| 2 |
Tina |
Ali |
36.0 |
f |
NaN |
NaN |
NaN |
| 3 |
Jake |
Milner |
24.0 |
m |
2.0 |
62.0 |
NaN |
| 4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73.0 |
f |
3.0 |
70.0 |
NaN |
df.dropna(axis=1, how='all')
|
first_name |
last_name |
age |
sex |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
| 0 |
Jason |
Miller |
42.0 |
m |
4.0 |
25.0 |
| 1 |
NaN |
NaN |
NaN |
NaN |
NaN |
NaN |
| 2 |
Tina |
Ali |
36.0 |
f |
NaN |
NaN |
| 3 |
Jake |
Milner |
24.0 |
m |
2.0 |
62.0 |
| 4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73.0 |
f |
3.0 |
70.0 |
df.dropna(thresh=5)
|
first_name |
last_name |
age |
sex |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
location |
| 0 |
Jason |
Miller |
42.0 |
m |
4.0 |
25.0 |
NaN |
| 3 |
Jake |
Milner |
24.0 |
m |
2.0 |
62.0 |
NaN |
| 4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73.0 |
f |
3.0 |
70.0 |
NaN |
df.fillna(0)
|
first_name |
last_name |
age |
sex |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
location |
| 0 |
Jason |
Miller |
42.0 |
m |
4.0 |
25.0 |
0.0 |
| 1 |
0 |
0 |
0.0 |
0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
| 2 |
Tina |
Ali |
36.0 |
f |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
| 3 |
Jake |
Milner |
24.0 |
m |
2.0 |
62.0 |
0.0 |
| 4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73.0 |
f |
3.0 |
70.0 |
0.0 |
df["preTestScore"].fillna(df["preTestScore"].mean(), inplace=True)
df
|
first_name |
last_name |
age |
sex |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
location |
| 0 |
Jason |
Miller |
42.0 |
m |
4.0 |
25.0 |
NaN |
| 1 |
NaN |
NaN |
NaN |
NaN |
3.0 |
NaN |
NaN |
| 2 |
Tina |
Ali |
36.0 |
f |
3.0 |
NaN |
NaN |
| 3 |
Jake |
Milner |
24.0 |
m |
2.0 |
62.0 |
NaN |
| 4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73.0 |
f |
3.0 |
70.0 |
NaN |
df["postTestScore"].fillna(df.groupby("sex")["postTestScore"].transform("mean"), inplace=True)
df
|
first_name |
last_name |
age |
sex |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
location |
| 0 |
Jason |
Miller |
42.0 |
m |
4.0 |
25.0 |
NaN |
| 1 |
NaN |
NaN |
NaN |
NaN |
3.0 |
NaN |
NaN |
| 2 |
Tina |
Ali |
36.0 |
f |
3.0 |
70.0 |
NaN |
| 3 |
Jake |
Milner |
24.0 |
m |
2.0 |
62.0 |
NaN |
| 4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73.0 |
f |
3.0 |
70.0 |
NaN |
df[df['age'].notnull() & df['sex'].notnull()]
|
first_name |
last_name |
age |
sex |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
location |
| 0 |
Jason |
Miller |
42.0 |
m |
4.0 |
25.0 |
NaN |
| 2 |
Tina |
Ali |
36.0 |
f |
3.0 |
70.0 |
NaN |
| 3 |
Jake |
Milner |
24.0 |
m |
2.0 |
62.0 |
NaN |
| 4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73.0 |
f |
3.0 |
70.0 |
NaN |
pandas 中的移动平均
import pandas as pd
data = {'score': [1,1,1,2,2,2,3,3,3]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df
|
score |
| 0 |
1 |
| 1 |
1 |
| 2 |
1 |
| 3 |
2 |
| 4 |
2 |
| 5 |
2 |
| 6 |
3 |
| 7 |
3 |
| 8 |
3 |
df.rolling(window=2).mean()
|
score |
| 0 |
NaN |
| 1 |
1.0 |
| 2 |
1.0 |
| 3 |
1.5 |
| 4 |
2.0 |
| 5 |
2.0 |
| 6 |
2.5 |
| 7 |
3.0 |
| 8 |
3.0 |
规范化一列
import pandas as pd
from sklearn import preprocessing
%matplotlib inline
data = {'score': [234,24,14,27,-74,46,73,-18,59,160]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df
|
score |
| 0 |
234 |
| 1 |
24 |
| 2 |
14 |
| 3 |
27 |
| 4 |
-74 |
| 5 |
46 |
| 6 |
73 |
| 7 |
-18 |
| 8 |
59 |
| 9 |
160 |
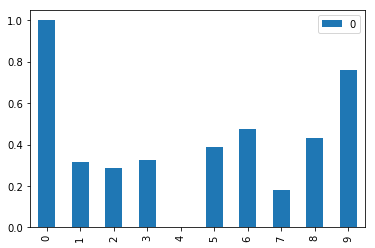
df['score'].plot(kind='bar')

x = df[['score']].values.astype(float)
min_max_scaler = preprocessing.MinMaxScaler()
x_scaled = min_max_scaler.fit_transform(x)
df_normalized = pd.DataFrame(x_scaled)
df_normalized
|
0 |
| 0 |
1.000000 |
| 1 |
0.318182 |
| 2 |
0.285714 |
| 3 |
0.327922 |
| 4 |
0.000000 |
| 5 |
0.389610 |
| 6 |
0.477273 |
| 7 |
0.181818 |
| 8 |
0.431818 |
| 9 |
0.759740 |
df_normalized.plot(kind='bar')
Pandas 中的级联表
import pandas as pd
raw_data = {'regiment': ['Nighthawks', 'Nighthawks', 'Nighthawks', 'Nighthawks', 'Dragoons', 'Dragoons', 'Dragoons', 'Dragoons', 'Scouts', 'Scouts', 'Scouts', 'Scouts'],
'company': ['1st', '1st', '2nd', '2nd', '1st', '1st', '2nd', '2nd','1st', '1st', '2nd', '2nd'],
'TestScore': [4, 24, 31, 2, 3, 4, 24, 31, 2, 3, 2, 3]}
df = pd.DataFrame(raw_data, columns = ['regiment', 'company', 'TestScore'])
df
|
regiment |
company |
TestScore |
| 0 |
Nighthawks |
1st |
4 |
| 1 |
Nighthawks |
1st |
24 |
| 2 |
Nighthawks |
2nd |
31 |
| 3 |
Nighthawks |
2nd |
2 |
| 4 |
Dragoons |
1st |
3 |
| 5 |
Dragoons |
1st |
4 |
| 6 |
Dragoons |
2nd |
24 |
| 7 |
Dragoons |
2nd |
31 |
| 8 |
Scouts |
1st |
2 |
| 9 |
Scouts |
1st |
3 |
| 10 |
Scouts |
2nd |
2 |
| 11 |
Scouts |
2nd |
3 |
pd.pivot_table(df, index=['regiment','company'], aggfunc='mean')
|
|
TestScore |
| regiment |
company |
|
| Dragoons |
1st |
3.5 |
|
2nd |
27.5 |
| Nighthawks |
1st |
14.0 |
|
2nd |
16.5 |
| Scouts |
1st |
2.5 |
|
2nd |
2.5 |
df.pivot_table(index=['regiment','company'], aggfunc='count')
|
|
TestScore |
| regiment |
company |
|
| Dragoons |
1st |
2 |
|
2nd |
2 |
| Nighthawks |
1st |
2 |
|
2nd |
2 |
| Scouts |
1st |
2 |
|
2nd |
2 |
在 Pandas 中快速修改字符串列
我经常需要或想要改变一串字符串中所有项目的大小写(例如BRAZIL到Brazil等)。 有很多方法可以实现这一目标,但我已经确定这是最容易和最快的方法。
import pandas as pd
first_names = pd.Series(['Steve Murrey', 'Jane Fonda', 'Sara McGully', 'Mary Jane'])
first_names
'''
0 Steve Murrey
1 Jane Fonda
2 Sara McGully
3 Mary Jane
dtype: object
'''
first_names.str.lower()
'''
0 steve murrey
1 jane fonda
2 sara mcgully
3 mary jane
dtype: object
'''
first_names.str.upper()
'''
0 STEVE MURREY
1 JANE FONDA
2 SARA MCGULLY
3 MARY JANE
dtype: object
'''
first_names.str.title()
'''
0 Steve Murrey
1 Jane Fonda
2 Sara Mcgully
3 Mary Jane
dtype: object
'''
first_names.str.split(" ")
'''
0 [Steve, Murrey]
1 [Jane, Fonda]
2 [Sara, McGully]
3 [Mary, Jane]
dtype: object
'''
first_names.str.capitalize()
'''
0 Steve murrey
1 Jane fonda
2 Sara mcgully
3 Mary jane
dtype: object
'''
明白了吧。更多字符串方法在这里。
随机抽样数据帧
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
raw_data = {'first_name': ['Jason', 'Molly', 'Tina', 'Jake', 'Amy'],
'last_name': ['Miller', 'Jacobson', 'Ali', 'Milner', 'Cooze'],
'age': [42, 52, 36, 24, 73],
'preTestScore': [4, 24, 31, 2, 3],
'postTestScore': [25, 94, 57, 62, 70]}
df = pd.DataFrame(raw_data, columns = ['first_name', 'last_name', 'age', 'preTestScore', 'postTestScore'])
df
|
first_name |
last_name |
age |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
| 0 |
Jason |
Miller |
42 |
4 |
25 |
| 1 |
Molly |
Jacobson |
52 |
24 |
94 |
| 2 |
Tina |
Ali |
36 |
31 |
57 |
| 3 |
Jake |
Milner |
24 |
2 |
62 |
| 4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73 |
3 |
70 |
df.take(np.random.permutation(len(df))[:2])
|
first_name |
last_name |
age |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
| 1 |
Molly |
Jacobson |
52 |
24 |
94 |
| 4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73 |
3 |
70 |
对数据帧的行排名
import pandas as pd
data = {'name': ['Jason', 'Molly', 'Tina', 'Jake', 'Amy'],
'year': [2012, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2014],
'reports': [4, 24, 31, 2, 3],
'coverage': [25, 94, 57, 62, 70]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index = ['Cochice', 'Pima', 'Santa Cruz', 'Maricopa', 'Yuma'])
df
|
coverage |
name |
reports |
year |
| Cochice |
25 |
Jason |
4 |
2012 |
| Pima |
94 |
Molly |
24 |
2012 |
| Santa Cruz |
57 |
Tina |
31 |
2013 |
| Maricopa |
62 |
Jake |
2 |
2014 |
| Yuma |
70 |
Amy |
3 |
2014 |
5 rows × 4 columns
df['coverageRanked'] = df['coverage'].rank(ascending=1)
df
|
coverage |
name |
reports |
year |
coverageRanked |
| Cochice |
25 |
Jason |
4 |
2012 |
1 |
| Pima |
94 |
Molly |
24 |
2012 |
5 |
| Santa Cruz |
57 |
Tina |
31 |
2013 |
2 |
| Maricopa |
62 |
Jake |
2 |
2014 |
3 |
| Yuma |
70 |
Amy |
3 |
2014 |
4 |
5 rows × 5 columns
正则表达式基础
import re
import sys
text = 'The quick brown fox jumped over the lazy black bear.'
three_letter_word = '\w{3}'
pattern_re = re.compile(three_letter_word); pattern_re
re.compile(r'\w{3}', re.UNICODE)
re_search = re.search('..own', text)
if re_search:
print(re_search.group())
re.match
re.match()仅用于匹配字符串的开头或整个字符串。对于其他任何内容,请使用re.search。
Match all three letter words in text
re_match = re.match('..own', text)
if re_match:
print(re_match.group())
else:
print('No matches')
re.split
re_split = re.split('e', text); re_split
re.sub
用其他东西替换正则表达式模式串。3表示要进行的最大替换次数。
re_sub = re.sub('e', 'E', text, 3); print(re_sub)
正则表达式示例
import re
text = 'A flock of 120 quick brown foxes jumped over 30 lazy brown, bears.'
re.findall('^A', text)
re.findall('bears.$', text)
re.findall('f..es', text)
re.findall('[aeiou]', text)
re.findall('[^aeiou]', text)
'''
['A',
' ',
'f',
'l',
'c',
'k',
' ',
'f',
' ',
'1',
'2',
'0',
' ',
'q',
'c',
'k',
' ',
'b',
'r',
'w',
'n',
' ',
'f',
'x',
's',
' ',
'j',
'm',
'p',
'd',
' ',
'v',
'r',
' ',
'3',
'0',
' ',
'l',
'z',
'y',
' ',
'b',
'r',
'w',
'n',
',',
' ',
'b',
'r',
's',
'.']
'''
re.findall('a|A', text)
re.findall('(foxes)', text)
re.findall('\w\w\w\w\w', text)
re.findall('\W\W', text)
re.findall('\s', text)
re.findall('\S\S', text)
'''
['fl',
'oc',
'of',
'12',
'qu',
'ic',
'br',
'ow',
'fo',
'xe',
'ju',
'mp',
'ed',
'ov',
'er',
'30',
'la',
'zy',
'br',
'ow',
'n,',
'be',
'ar',
's.']
'''
re.findall('\d\d\d', text)
re.findall('\D\D\D\D\D', text)
'''
['A flo',
'ck of',
' quic',
'k bro',
'wn fo',
'xes j',
'umped',
' over',
' lazy',
' brow',
'n, be']
'''
re.findall('\AA', text)
re.findall('bears.\Z', text)
re.findall('\b[foxes]', text)
re.findall('\n', text)
re.findall('[Ff]oxes', 'foxes Foxes Doxes')
re.findall('[Ff]oxes', 'foxes Foxes Doxes')
re.findall('[a-z]', 'foxes Foxes')
re.findall('[A-Z]', 'foxes Foxes')
re.findall('[a-zA-Z0-9]', 'foxes Foxes')
re.findall('[^aeiou]', 'foxes Foxes')
re.findall('[^0-9]', 'foxes Foxes')
re.findall('foxes?', 'foxes Foxes')
re.findall('ox*', 'foxes Foxes')
re.findall('ox+', 'foxes Foxes')
re.findall('\d{3}', text)
re.findall('\d{2,}', text)
re.findall('\d{2,3}', text)
re.findall('^A', text)
re.findall('bears.$', text)
re.findall('\AA', text)
re.findall('bears.\Z', text)
re.findall('bears(?=.)', text)
re.findall('foxes(?!!)', 'foxes foxes!')
re.findall('foxes|foxes!', 'foxes foxes!')
re.findall('fox(es!)', 'foxes foxes!')
re.findall('foxes(!)', 'foxes foxes!')
重索引序列和数据帧
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
brushFireRisk = pd.Series([34, 23, 12, 23], index = ['Bisbee', 'Douglas', 'Sierra Vista', 'Tombstone'])
brushFireRisk
'''
Bisbee 34
Douglas 23
Sierra Vista 12
Tombstone 23
dtype: int64
'''
brushFireRiskReindexed = brushFireRisk.reindex(['Tombstone', 'Douglas', 'Bisbee', 'Sierra Vista', 'Barley', 'Tucson'])
brushFireRiskReindexed
'''
Tombstone 23.0
Douglas 23.0
Bisbee 34.0
Sierra Vista 12.0
Barley NaN
Tucson NaN
dtype: float64
'''
brushFireRiskReindexed = brushFireRisk.reindex(['Tombstone', 'Douglas', 'Bisbee', 'Sierra Vista', 'Barley', 'Tucson'], fill_value = 0)
brushFireRiskReindexed
'''
Tombstone 23
Douglas 23
Bisbee 34
Sierra Vista 12
Barley 0
Tucson 0
dtype: int64
'''
data = {'county': ['Cochice', 'Pima', 'Santa Cruz', 'Maricopa', 'Yuma'],
'year': [2012, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2014],
'reports': [4, 24, 31, 2, 3]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df
|
county |
reports |
year |
| 0 |
Cochice |
4 |
2012 |
| 1 |
Pima |
24 |
2012 |
| 2 |
Santa Cruz |
31 |
2013 |
| 3 |
Maricopa |
2 |
2014 |
| 4 |
Yuma |
3 |
2014 |
df.reindex([4, 3, 2, 1, 0])
|
county |
reports |
year |
| 4 |
Yuma |
3 |
2014 |
| 3 |
Maricopa |
2 |
2014 |
| 2 |
Santa Cruz |
31 |
2013 |
| 1 |
Pima |
24 |
2012 |
| 0 |
Cochice |
4 |
2012 |
columnsTitles = ['year', 'reports', 'county']
df.reindex(columns=columnsTitles)
|
year |
reports |
county |
| 0 |
2012 |
4 |
Cochice |
| 1 |
2012 |
24 |
Pima |
| 2 |
2013 |
31 |
Santa Cruz |
| 3 |
2014 |
2 |
Maricopa |
| 4 |
2014 |
3 |
Yuma |
重命名列标题
来自 StackOverflow 上的 rgalbo。
import pandas as pd
raw_data = {'0': ['first_name', 'Molly', 'Tina', 'Jake', 'Amy'],
'1': ['last_name', 'Jacobson', 'Ali', 'Milner', 'Cooze'],
'2': ['age', 52, 36, 24, 73],
'3': ['preTestScore', 24, 31, 2, 3]}
df = pd.DataFrame(raw_data)
df
|
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
| 0 |
first_name |
last_name |
age |
preTestScore |
| 1 |
Molly |
Jacobson |
52 |
24 |
| 2 |
Tina |
Ali |
36 |
31 |
| 3 |
Jake |
Milner |
24 |
2 |
| 4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73 |
3 |
header = df.iloc[0]
'''
0 first_name
1 last_name
2 age
3 preTestScore
Name: 0, dtype: object
'''
df = df[1:]
df.rename(columns = header)
|
first_name |
last_name |
age |
preTestScore |
| 1 |
Molly |
Jacobson |
52 |
24 |
| — |
— |
— |
— |
— |
| 2 |
Tina |
Ali |
36 |
31 |
| — |
— |
— |
— |
— |
| 3 |
Jake |
Milner |
24 |
2 |
| — |
— |
— |
— |
— |
| 4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73 |
3 |
| — |
— |
— |
— |
— |
重命名多个数据帧的列名
import pandas as pd
pd.set_option('display.max_row', 1000)
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', 50)
data = {'Commander': ['Jason', 'Molly', 'Tina', 'Jake', 'Amy'],
'Date': ['2012, 02, 08', '2012, 02, 08', '2012, 02, 08', '2012, 02, 08', '2012, 02, 08'],
'Score': [4, 24, 31, 2, 3]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index = ['Cochice', 'Pima', 'Santa Cruz', 'Maricopa', 'Yuma'])
df
|
Commander |
Date |
Score |
| Cochice |
Jason |
2012, 02, 08 |
4 |
| Pima |
Molly |
2012, 02, 08 |
24 |
| Santa Cruz |
Tina |
2012, 02, 08 |
31 |
| Maricopa |
Jake |
2012, 02, 08 |
2 |
| Yuma |
Amy |
2012, 02, 08 |
3 |
df.columns = ['Leader', 'Time', 'Score']
df
|
Leader |
Time |
Score |
| Cochice |
Jason |
2012, 02, 08 |
4 |
| Pima |
Molly |
2012, 02, 08 |
24 |
| Santa Cruz |
Tina |
2012, 02, 08 |
31 |
| Maricopa |
Jake |
2012, 02, 08 |
2 |
| Yuma |
Amy |
2012, 02, 08 |
3 |
df.rename(columns={'Leader': 'Commander'}, inplace=True)
df
|
Commander |
Time |
Score |
| Cochice |
Jason |
2012, 02, 08 |
4 |
| Pima |
Molly |
2012, 02, 08 |
24 |
| Santa Cruz |
Tina |
2012, 02, 08 |
31 |
| Maricopa |
Jake |
2012, 02, 08 |
2 |
| Yuma |
Amy |
2012, 02, 08 |
3 |
替换值
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
raw_data = {'first_name': ['Jason', 'Molly', 'Tina', 'Jake', 'Amy'],
'last_name': ['Miller', 'Jacobson', 'Ali', 'Milner', 'Cooze'],
'age': [42, 52, 36, 24, 73],
'preTestScore': [-999, -999, -999, 2, 1],
'postTestScore': [2, 2, -999, 2, -999]}
df = pd.DataFrame(raw_data, columns = ['first_name', 'last_name', 'age', 'preTestScore', 'postTestScore'])
df
|
first_name |
last_name |
age |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
| 0 |
Jason |
Miller |
42 |
-999 |
2 |
| 1 |
Molly |
Jacobson |
52 |
-999 |
2 |
| 2 |
Tina |
Ali |
36 |
-999 |
-999 |
| 3 |
Jake |
Milner |
24 |
2 |
2 |
| 4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73 |
1 |
-999 |
df.replace(-999, np.nan)
|
first_name |
last_name |
age |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
| 0 |
Jason |
Miller |
42 |
NaN |
2.0 |
| 1 |
Molly |
Jacobson |
52 |
NaN |
2.0 |
| 2 |
Tina |
Ali |
36 |
NaN |
NaN |
| 3 |
Jake |
Milner |
24 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
| 4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73 |
1.0 |
NaN |
将数据帧保存为 CSV
import pandas as pd
raw_data = {'first_name': ['Jason', 'Molly', 'Tina', 'Jake', 'Amy'],
'last_name': ['Miller', 'Jacobson', 'Ali', 'Milner', 'Cooze'],
'age': [42, 52, 36, 24, 73],
'preTestScore': [4, 24, 31, 2, 3],
'postTestScore': [25, 94, 57, 62, 70]}
df = pd.DataFrame(raw_data, columns = ['first_name', 'last_name', 'age', 'preTestScore', 'postTestScore'])
df
|
first_name |
last_name |
age |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
| 0 |
Jason |
Miller |
42 |
4 |
25 |
| 1 |
Molly |
Jacobson |
52 |
24 |
94 |
| 2 |
Tina |
Ali |
36 |
31 |
57 |
| 3 |
Jake |
Milner |
24 |
2 |
62 |
| 4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73 |
3 |
70 |
将名为df的数据帧保存为 csv。
df.to_csv('example.csv')
在列中搜索某个值
import pandas as pd
raw_data = {'first_name': ['Jason', 'Jason', 'Tina', 'Jake', 'Amy'],
'last_name': ['Miller', 'Miller', 'Ali', 'Milner', 'Cooze'],
'age': [42, 42, 36, 24, 73],
'preTestScore': [4, 4, 31, 2, 3],
'postTestScore': [25, 25, 57, 62, 70]}
df = pd.DataFrame(raw_data, columns = ['first_name', 'last_name', 'age', 'preTestScore', 'postTestScore'])
df
|
first_name |
last_name |
age |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
| 0 |
Jason |
Miller |
42 |
4 |
25 |
| 1 |
Jason |
Miller |
42 |
4 |
25 |
| 2 |
Tina |
Ali |
36 |
31 |
57 |
| 3 |
Jake |
Milner |
24 |
2 |
62 |
| 4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73 |
3 |
70 |
df['preTestScore'].where(df['postTestScore'] > 50)
'''
0 NaN
1 NaN
2 31.0
3 2.0
4 3.0
Name: preTestScore, dtype: float64
'''
选择包含特定值的行和列
import pandas as pd
pd.set_option('display.max_row', 1000)
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', 50)
data = {'name': ['Jason', 'Molly', 'Tina', 'Jake', 'Amy'],
'year': [2012, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2014],
'reports': [4, 24, 31, 2, 3]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index = ['Cochice', 'Pima', 'Santa Cruz', 'Maricopa', 'Yuma'])
df
|
name |
reports |
year |
| Cochice |
Jason |
4 |
2012 |
| Pima |
Molly |
24 |
2012 |
| Santa Cruz |
Tina |
31 |
2013 |
| Maricopa |
Jake |
2 |
2014 |
| Yuma |
Amy |
3 |
2014 |
value_list = ['Tina', 'Molly', 'Jason']
df[df.name.isin(value_list)]
|
name |
reports |
year |
| Cochice |
Jason |
4 |
2012 |
| Pima |
Molly |
24 |
2012 |
| Santa Cruz |
Tina |
31 |
2013 |
df[~df.name.isin(value_list)]
|
name |
reports |
year |
| Maricopa |
Jake |
2 |
2014 |
| Yuma |
Amy |
3 |
2014 |
选择具有特定值的行
import pandas as pd
data = {'name': ['Jason', 'Molly'],
'country': [['Syria', 'Lebanon'],['Spain', 'Morocco']]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df
|
country |
name |
| 0 |
[Syria, Lebanon] |
Jason |
| 1 |
[Spain, Morocco] |
Molly |
df[df['country'].map(lambda country: 'Syria' in country)]
|
country |
name |
| 0 |
[Syria, Lebanon] |
Jason |
使用多个过滤器选择行
import pandas as pd
data = {'name': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E'],
'score': [1,2,3,4,5]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df
|
name |
score |
| 0 |
A |
1 |
| 1 |
B |
2 |
| 2 |
C |
3 |
| 3 |
D |
4 |
| 4 |
E |
5 |
df[(df['score'] > 1) & (df['score'] < 5)]
|
name |
score |
| 1 |
B |
2 |
| 2 |
C |
3 |
| 3 |
D |
4 |
根据条件选择数据帧的行
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
raw_data = {'first_name': ['Jason', 'Molly', np.nan, np.nan, np.nan],
'nationality': ['USA', 'USA', 'France', 'UK', 'UK'],
'age': [42, 52, 36, 24, 70]}
df = pd.DataFrame(raw_data, columns = ['first_name', 'nationality', 'age'])
df
|
first_name |
nationality |
age |
| 0 |
Jason |
USA |
42 |
| 1 |
Molly |
USA |
52 |
| 2 |
NaN |
France |
36 |
| 3 |
NaN |
UK |
24 |
| 4 |
NaN |
UK |
70 |
american = df['nationality'] == "USA"
elderly = df['age'] > 50
df[american & elderly]
|
first_name |
nationality |
age |
| 1 |
Molly |
USA |
52 |
df[df['first_name'].notnull() & (df['nationality'] == "USA")]
|
first_name |
nationality |
age |
| 0 |
Jason |
USA |
42 |
| 1 |
Molly |
USA |
52 |
数据帧简单示例
import pandas as pd
raw_data = {'first_name': ['Jason', 'Molly', 'Tina', 'Jake', 'Amy'],
'last_name': ['Miller', 'Jacobson', 'Ali', 'Milner', 'Cooze'],
'age': [42, 52, 36, 24, 73],
'preTestScore': [4, 24, 31, 2, 3],
'postTestScore': [25, 94, 57, 62, 70]}
df = pd.DataFrame(raw_data, columns = ['first_name', 'last_name', 'age', 'preTestScore', 'postTestScore'])
df
|
first_name |
last_name |
age |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
| 0 |
Jason |
Miller |
42 |
4 |
25 |
| 1 |
Molly |
Jacobson |
52 |
24 |
94 |
| 2 |
Tina |
Ali |
36 |
31 |
57 |
| 3 |
Jake |
Milner |
24 |
2 |
62 |
| 4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
73 |
3 |
70 |
raw_data_2 = {'first_name': ['Sarah', 'Gueniva', 'Know', 'Sara', 'Cat'],
'last_name': ['Mornig', 'Jaker', 'Alom', 'Ormon', 'Koozer'],
'age': [53, 26, 72, 73, 24],
'preTestScore': [13, 52, 72, 26, 26],
'postTestScore': [82, 52, 56, 234, 254]}
df_2 = pd.DataFrame(raw_data_2, columns = ['first_name', 'last_name', 'age', 'preTestScore', 'postTestScore'])
df_2
|
first_name |
last_name |
age |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
| 0 |
Sarah |
Mornig |
53 |
13 |
82 |
| 1 |
Gueniva |
Jaker |
26 |
52 |
52 |
| 2 |
Know |
Alom |
72 |
72 |
56 |
| 3 |
Sara |
Ormon |
73 |
26 |
234 |
| 4 |
Cat |
Koozer |
24 |
26 |
254 |
raw_data_3 = {'first_name': ['Sarah', 'Gueniva', 'Know', 'Sara', 'Cat'],
'last_name': ['Mornig', 'Jaker', 'Alom', 'Ormon', 'Koozer'],
'postTestScore_2': [82, 52, 56, 234, 254]}
df_3 = pd.DataFrame(raw_data_3, columns = ['first_name', 'last_name', 'postTestScore_2'])
df_3
|
first_name |
last_name |
postTestScore_2 |
| 0 |
Sarah |
Mornig |
82 |
| 1 |
Gueniva |
Jaker |
52 |
| 2 |
Know |
Alom |
56 |
| 3 |
Sara |
Ormon |
234 |
| 4 |
Cat |
Koozer |
254 |
排序数据帧的行
import pandas as pd
data = {'name': ['Jason', 'Molly', 'Tina', 'Jake', 'Amy'],
'year': [2012, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2014],
'reports': [1, 2, 1, 2, 3],
'coverage': [2, 2, 3, 3, 3]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index = ['Cochice', 'Pima', 'Santa Cruz', 'Maricopa', 'Yuma'])
df
|
coverage |
name |
reports |
year |
| Cochice |
2 |
Jason |
1 |
2012 |
| Pima |
2 |
Molly |
2 |
2012 |
| Santa Cruz |
3 |
Tina |
1 |
2013 |
| Maricopa |
3 |
Jake |
2 |
2014 |
| Yuma |
3 |
Amy |
3 |
2014 |
df.sort_values(by='reports', ascending=0)
|
coverage |
name |
reports |
year |
| Yuma |
3 |
Amy |
3 |
2014 |
| Pima |
2 |
Molly |
2 |
2012 |
| Maricopa |
3 |
Jake |
2 |
2014 |
| Cochice |
2 |
Jason |
1 |
2012 |
| Santa Cruz |
3 |
Tina |
1 |
2013 |
df.sort_values(by=['coverage', 'reports'])
|
coverage |
name |
reports |
year |
| Cochice |
2 |
Jason |
1 |
2012 |
| Pima |
2 |
Molly |
2 |
2012 |
| Santa Cruz |
3 |
Tina |
1 |
2013 |
| Maricopa |
3 |
Jake |
2 |
2014 |
| Yuma |
3 |
Amy |
3 |
2014 |
将经纬度坐标变量拆分为单独的变量
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
raw_data = {'geo': ['40.0024, -105.4102', '40.0068, -105.266', '39.9318, -105.2813', np.nan]}
df = pd.DataFrame(raw_data, columns = ['geo'])
df
|
geo |
| 0 |
40.0024, -105.4102 |
| 1 |
40.0068, -105.266 |
| 2 |
39.9318, -105.2813 |
| 3 |
NaN |
| — |
— |
lat = []
lon = []
for row in df['geo']:
try:
lat.append(row.split(',')[0])
lon.append(row.split(',')[1])
except:
lat.append(np.NaN)
lon.append(np.NaN)
df['latitude'] = lat
df['longitude'] = lon
df
|
geo |
latitude |
longitude |
| 0 |
40.0024, -105.4102 |
40.0024 |
-105.4102 |
| 1 |
40.0068, -105.266 |
40.0068 |
-105.266 |
| 2 |
39.9318, -105.2813 |
39.9318 |
-105.2813 |
| 3 |
NaN |
NaN |
NaN |
数据流水线
raw_data = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
def add_6(numbers):
for x in numbers:
output = x+6
yield output
def subtract_2(numbers):
for x in numbers:
output = x-2
yield output
def multiply_by_100(numbers):
for x in numbers:
output = x*100
yield output
step1 = add_6(raw_data)
step2 = subtract_2(step1)
pipeline = multiply_by_100(step2)
next(pipeline)
next(pipeline)
for raw_data in pipeline:
print(raw_data)
'''
700
800
900
1000
1100
1200
1300
1400
'''
数据帧中的字符串整理
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import re as re
raw_data = {'first_name': ['Jason', 'Molly', 'Tina', 'Jake', 'Amy'],
'last_name': ['Miller', 'Jacobson', 'Ali', 'Milner', 'Cooze'],
'email': ['[[email protected]](/cdn-cgi/l/email-protection)', '[[email protected]](/cdn-cgi/l/email-protection)', np.NAN, '[[email protected]](/cdn-cgi/l/email-protection)', '[[email protected]](/cdn-cgi/l/email-protection)'],
'preTestScore': [4, 24, 31, 2, 3],
'postTestScore': [25, 94, 57, 62, 70]}
df = pd.DataFrame(raw_data, columns = ['first_name', 'last_name', 'email', 'preTestScore', 'postTestScore'])
df
|
first_name |
last_name |
email |
preTestScore |
postTestScore |
| 0 |
Jason |
Miller |
[email protected] |
4 |
25 |
| 1 |
Molly |
Jacobson |
[email protected] |
24 |
94 |
| 2 |
Tina |
Ali |
NaN |
31 |
57 |
| 3 |
Jake |
Milner |
[email protected] |
2 |
62 |
| 4 |
Amy |
Cooze |
[email protected] |
3 |
70 |
df['email'].str.contains('gmail')
'''
0 True
1 True
2 NaN
3 False
4 False
Name: email, dtype: object
'''
pattern = '([A-Z0-9._%+-]+)@([A-Z0-9.-]+)\\.([A-Z]{2,4})'
df['email'].str.findall(pattern, flags=re.IGNORECASE)
'''
0 [(jas203, gmail, com)]
1 [(momomolly, gmail, com)]
2 NaN
3 [(battler, milner, com)]
4 [(Ames1234, yahoo, com)]
Name: email, dtype: object
'''
matches = df['email'].str.match(pattern, flags=re.IGNORECASE)
matches
'''
/Users/chrisralbon/anaconda/lib/python3.5/site-packages/ipykernel/__main__.py:1: FutureWarning: In future versions of pandas, match will change to always return a bool indexer.
if __name__ == '__main__':
0 (jas203, gmail, com)
1 (momomolly, gmail, com)
2 NaN
3 (battler, milner, com)
4 (Ames1234, yahoo, com)
Name: email, dtype: object
'''
matches.str[1]
'''
0 gmail
1 gmail
2 NaN
3 milner
4 yahoo
Name: email, dtype: object
'''
和 Pandas 一起使用列表推导式
import pandas as pd
pd.set_option('display.max_row', 1000)
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', 50)
data = {'name': ['Jason', 'Molly', 'Tina', 'Jake', 'Amy'],
'year': [2012, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2014],
'reports': [4, 24, 31, 2, 3]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index = ['Cochice', 'Pima', 'Santa Cruz', 'Maricopa', 'Yuma'])
df
|
name |
reports |
year |
| Cochice |
Jason |
4 |
2012 |
| Pima |
Molly |
24 |
2012 |
| Santa Cruz |
Tina |
31 |
2013 |
| Maricopa |
Jake |
2 |
2014 |
| Yuma |
Amy |
3 |
2014 |
作为循环的列表推导式。
next_year = []
for row in df['year']:
next_year.append(row + 1)
df['next_year'] = next_year
df
|
name |
reports |
year |
next_year |
| Cochice |
Jason |
4 |
2012 |
2013 |
| Pima |
Molly |
24 |
2012 |
2013 |
| Santa Cruz |
Tina |
31 |
2013 |
2014 |
| Maricopa |
Jake |
2 |
2014 |
2015 |
| Yuma |
Amy |
3 |
2014 |
2015 |
作为列表推导式。
df['previous_year'] = [row-1 for row in df['year']]
df
|
name |
reports |
year |
next_year |
previous_year |
| Cochice |
Jason |
4 |
2012 |
2013 |
2011 |
| Pima |
Molly |
24 |
2012 |
2013 |
2011 |
| Santa Cruz |
Tina |
31 |
2013 |
2014 |
2012 |
| Maricopa |
Jake |
2 |
2014 |
2015 |
2013 |
| Yuma |
Amy |
3 |
2014 |
2015 |
2013 |
使用 Seaborn 来可视化数据帧
import pandas as pd
%matplotlib inline
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
df = pd.DataFrame()
df['x'] = random.sample(range(1, 100), 25)
df['y'] = random.sample(range(1, 100), 25)
df.head()
|
x |
y |
| 0 |
18 |
25 |
| 1 |
42 |
67 |
| 2 |
52 |
77 |
| 3 |
4 |
34 |
| 4 |
14 |
69 |
sns.lmplot('x', 'y', data=df, fit_reg=False)
sns.kdeplot(df.y)

sns.kdeplot(df.y, df.x)
sns.distplot(df.x)
plt.hist(df.x, alpha=.3)
sns.rugplot(df.x);
sns.boxplot([df.y, df.x])

sns.violinplot([df.y, df.x])
sns.heatmap([df.y, df.x], annot=True, fmt="d")

sns.clustermap(df)

Pandas 数据结构
import pandas as pd
序列 101
序列是一维数组(类似 R 的向量)。
floodingReports = pd.Series([5, 6, 2, 9, 12])
floodingReports
'''
0 5
1 6
2 2
3 9
4 12
dtype: int64
'''
请注意,第一列数字(0 到 4)是索引。
floodingReports = pd.Series([5, 6, 2, 9, 12], index=['Cochise County', 'Pima County', 'Santa Cruz County', 'Maricopa County', 'Yuma County'])
floodingReports
'''
Cochise County 5
Pima County 6
Santa Cruz County 2
Maricopa County 9
Yuma County 12
dtype: int64
'''
floodingReports['Cochise County']
floodingReports[floodingReports > 6]
'''
Maricopa County 9
Yuma County 12
dtype: int64
'''
从字典中创建 Pandas 序列。
注意:执行此操作时,字典的键将成为序列索引。
fireReports_dict = {'Cochise County': 12, 'Pima County': 342, 'Santa Cruz County': 13, 'Maricopa County': 42, 'Yuma County' : 52}
fireReports = pd.Series(fireReports_dict); fireReports
'''
Cochise County 12
Maricopa County 42
Pima County 342
Santa Cruz County 13
Yuma County 52
dtype: int64
'''
fireReports.index = ["Cochice", "Pima", "Santa Cruz", "Maricopa", "Yuma"]
fireReports
'''
Cochice 12
Pima 42
Santa Cruz 342
Maricopa 13
Yuma 52
dtype: int64
'''
数据帧 101
数据帧就像 R 的数据帧。
data = {'county': ['Cochice', 'Pima', 'Santa Cruz', 'Maricopa', 'Yuma'],
'year': [2012, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2014],
'reports': [4, 24, 31, 2, 3]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df
|
county |
reports |
year |
| 0 |
Cochice |
4 |
2012 |
| 1 |
Pima |
24 |
2012 |
| 2 |
Santa Cruz |
31 |
2013 |
| 3 |
Maricopa |
2 |
2014 |
| 4 |
Yuma |
3 |
2014 |
dfColumnOrdered = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=['county', 'year', 'reports'])
dfColumnOrdered
|
county |
year |
reports |
| 0 |
Cochice |
2012 |
4 |
| 1 |
Pima |
2012 |
24 |
| 2 |
Santa Cruz |
2013 |
31 |
| 3 |
Maricopa |
2014 |
2 |
| 4 |
Yuma |
2014 |
3 |
dfColumnOrdered['newsCoverage'] = pd.Series([42.3, 92.1, 12.2, 39.3, 30.2])
dfColumnOrdered
|
county |
year |
reports |
newsCoverage |
| 0 |
Cochice |
2012 |
4 |
42.3 |
| 1 |
Pima |
2012 |
24 |
92.1 |
| 2 |
Santa Cruz |
2013 |
31 |
12.2 |
| 3 |
Maricopa |
2014 |
2 |
39.3 |
| 4 |
Yuma |
2014 |
3 |
30.2 |
del dfColumnOrdered['newsCoverage']
dfColumnOrdered
|
county |
year |
reports |
| 0 |
Cochice |
2012 |
4 |
| 1 |
Pima |
2012 |
24 |
| 2 |
Santa Cruz |
2013 |
31 |
| 3 |
Maricopa |
2014 |
2 |
| 4 |
Yuma |
2014 |
3 |
dfColumnOrdered.T
|
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
| county |
Cochice |
Pima |
Santa Cruz |
Maricopa |
Yuma |
| year |
2012 |
2012 |
2013 |
2014 |
2014 |
| reports |
4 |
24 |
31 |
2 |
3 |
Pandas 时间序列基础
from datetime import datetime
import pandas as pd
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as pyplot
data = {'date': ['2014-05-01 18:47:05.069722', '2014-05-01 18:47:05.119994', '2014-05-02 18:47:05.178768', '2014-05-02 18:47:05.230071', '2014-05-02 18:47:05.230071', '2014-05-02 18:47:05.280592', '2014-05-03 18:47:05.332662', '2014-05-03 18:47:05.385109', '2014-05-04 18:47:05.436523', '2014-05-04 18:47:05.486877'],
'battle_deaths': [34, 25, 26, 15, 15, 14, 26, 25, 62, 41]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns = ['date', 'battle_deaths'])
print(df)
'''
date battle_deaths
0 2014-05-01 18:47:05.069722 34
1 2014-05-01 18:47:05.119994 25
2 2014-05-02 18:47:05.178768 26
3 2014-05-02 18:47:05.230071 15
4 2014-05-02 18:47:05.230071 15
5 2014-05-02 18:47:05.280592 14
6 2014-05-03 18:47:05.332662 26
7 2014-05-03 18:47:05.385109 25
8 2014-05-04 18:47:05.436523 62
9 2014-05-04 18:47:05.486877 41
'''
df['date'] = pd.to_datetime(df['date'])
df.index = df['date']
del df['date']
df
|
battle_deaths |
| date |
|
| 2014-05-01 18:47:05.069722 |
34 |
| 2014-05-01 18:47:05.119994 |
25 |
| 2014-05-02 18:47:05.178768 |
26 |
| 2014-05-02 18:47:05.230071 |
15 |
| 2014-05-02 18:47:05.230071 |
15 |
| 2014-05-02 18:47:05.280592 |
14 |
| 2014-05-03 18:47:05.332662 |
26 |
| 2014-05-03 18:47:05.385109 |
25 |
| 2014-05-04 18:47:05.436523 |
62 |
| 2014-05-04 18:47:05.486877 |
41 |
df['2014']
|
battle_deaths |
| date |
|
| 2014-05-01 18:47:05.069722 |
34 |
| 2014-05-01 18:47:05.119994 |
25 |
| 2014-05-02 18:47:05.178768 |
26 |
| 2014-05-02 18:47:05.230071 |
15 |
| 2014-05-02 18:47:05.230071 |
15 |
| 2014-05-02 18:47:05.280592 |
14 |
| 2014-05-03 18:47:05.332662 |
26 |
| 2014-05-03 18:47:05.385109 |
25 |
| 2014-05-04 18:47:05.436523 |
62 |
| 2014-05-04 18:47:05.486877 |
41 |
df['2014-05']
|
battle_deaths |
| date |
|
| 2014-05-01 18:47:05.069722 |
34 |
| 2014-05-01 18:47:05.119994 |
25 |
| 2014-05-02 18:47:05.178768 |
26 |
| 2014-05-02 18:47:05.230071 |
15 |
| 2014-05-02 18:47:05.230071 |
15 |
| 2014-05-02 18:47:05.280592 |
14 |
| 2014-05-03 18:47:05.332662 |
26 |
| 2014-05-03 18:47:05.385109 |
25 |
| 2014-05-04 18:47:05.436523 |
62 |
| 2014-05-04 18:47:05.486877 |
41 |
df[datetime(2014, 5, 3):]
|
battle_deaths |
| date |
|
| 2014-05-03 18:47:05.332662 |
26 |
| 2014-05-03 18:47:05.385109 |
25 |
| 2014-05-04 18:47:05.436523 |
62 |
| 2014-05-04 18:47:05.486877 |
41 |
Observations between May 3rd and May 4th
df['5/3/2014':'5/4/2014']
|
battle_deaths |
| date |
|
| 2014-05-03 18:47:05.332662 |
26 |
| 2014-05-03 18:47:05.385109 |
25 |
| 2014-05-04 18:47:05.436523 |
62 |
| 2014-05-04 18:47:05.486877 |
41 |
df.truncate(after='5/3/2014')
|
battle_deaths |
| date |
|
| 2014-05-01 18:47:05.069722 |
34 |
| 2014-05-01 18:47:05.119994 |
25 |
| 2014-05-02 18:47:05.178768 |
26 |
| 2014-05-02 18:47:05.230071 |
15 |
| 2014-05-02 18:47:05.230071 |
15 |
| 2014-05-02 18:47:05.280592 |
14 |
df['5-2014']
|
battle_deaths |
| date |
|
| 2014-05-01 18:47:05.069722 |
34 |
| 2014-05-01 18:47:05.119994 |
25 |
| 2014-05-02 18:47:05.178768 |
26 |
| 2014-05-02 18:47:05.230071 |
15 |
| 2014-05-02 18:47:05.230071 |
15 |
| 2014-05-02 18:47:05.280592 |
14 |
| 2014-05-03 18:47:05.332662 |
26 |
| 2014-05-03 18:47:05.385109 |
25 |
| 2014-05-04 18:47:05.436523 |
62 |
| 2014-05-04 18:47:05.486877 |
41 |
df.groupby(level=0).count()
|
battle_deaths |
| date |
|
| 2014-05-01 18:47:05.069722 |
1 |
| 2014-05-01 18:47:05.119994 |
1 |
| 2014-05-02 18:47:05.178768 |
1 |
| 2014-05-02 18:47:05.230071 |
2 |
| 2014-05-02 18:47:05.280592 |
1 |
| 2014-05-03 18:47:05.332662 |
1 |
| 2014-05-03 18:47:05.385109 |
1 |
| 2014-05-04 18:47:05.436523 |
1 |
| 2014-05-04 18:47:05.486877 |
1 |
df.resample('D').mean()
|
battle_deaths |
| date |
|
| 2014-05-01 |
29.5 |
| 2014-05-02 |
17.5 |
| 2014-05-03 |
25.5 |
| 2014-05-04 |
51.5 |
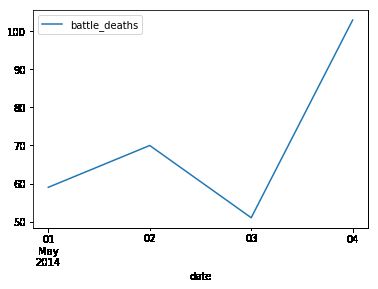
df.resample('D').sum()
|
battle_deaths |
| date |
|
| 2014-05-01 |
59 |
| 2014-05-02 |
70 |
| 2014-05-03 |
51 |
| 2014-05-04 |
103 |
df.resample('D').sum().plot()