java-nio-缓冲区ByteBuffer、Netty的ByteBuf和MappedByteBuffer的使用
java-nio-缓冲区ByteBuffer、Netty的ByteBuf和MappedByteBuffer的使用
文章目录
- java-nio-缓冲区ByteBuffer、Netty的ByteBuf和MappedByteBuffer的使用
- 1.ByteBuffer
- 2.MappedByteBuffer
- 3 Netty的ByteBuf
- 4.测试
环境
idea2018,jdk1.8
记录一下缓冲区ByteBuffer、Netty的ByteBuf和MappedByteBuffer的使用笔记,参考文献:
ByteBuffer:《Java NIO》
Netty的ByteBuf:https://www.cnblogs.com/duanxz/p/3724448.html
MappedByteBuffer:https://www.cnblogs.com/ironPhoenix/p/4204472.html
1.ByteBuffer
1)ByteBuffer
mark的作用:
为某一读过的位置做标记,便于某些时候回退到该位置。
2)ByteBuffer directBuffer=ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(10);
直接内存的读写操作比普通Buffer快,但它的创建、销毁比普Buffer慢。因此直接内存使用于需要大内存空间且频繁访问的场合,不适用于频繁申请释放内存的场合
ByteBuffer使用示例:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("----------Test allocate--------");
//堆内内存是由JVM进程内存
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10240000);
System.out.println("buffer = " + buffer);
// 这部分直接用的系统内存,所以对JVM的内存没有影响
ByteBuffer directBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(10240000);
System.out.println("directBuffer = " + directBuffer);
System.out.println("----------Test wrap--------");
byte[] bytes = new byte[32];
buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(bytes);
System.out.println(buffer);
buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(bytes, 10, 22);
System.out.println(buffer);
}
/**
* @Description: ByteBuffer的操作:
* 1)NIO ByteBuffer只有一个标识位置的指针position,读写的时候需要手工调用flip()和rewind()等方法
* 2)直接内存的读写操作比普通Buffer快,但它的创建、销毁比普通Buffer慢。
* 因此直接内存使用于需要大内存空间且频繁访问的场合,不适用于频繁申请释放内存的场合。
*/
public class TestByteBufferMethod {
public static ByteBuffer getByteBuffer(String str) {
return ByteBuffer.wrap(str.getBytes());
}
public static String getString(ByteBuffer buffer) {
buffer.flip();
Charset charset = null;
CharsetDecoder decoder = null;
CharBuffer charBuffer = null;
try {
charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
decoder = charset.newDecoder();
// charBuffer = decoder.decode(buffer);//用这个的话,只能输出来一次结果,第二次显示为空
charBuffer = decoder.decode(buffer.asReadOnlyBuffer());
return charBuffer.toString();
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
return "";
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("--------Test reset----------");
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(32);
//一般在把数据写入Buffer前调用
buffer.clear();
//设置position位置
buffer.position(5);
//调用mark()会将mark设为当前的position的值,以后调用reset()会将position属性设置为mark的值
buffer.mark();
buffer.position(10);
System.out.println("before reset:" + buffer);
buffer.reset();
System.out.println("after reset:" + buffer);
System.out.println("--------Test rewind--------");
buffer.clear();
buffer.position(10);
buffer.limit(15);
System.out.println("before rewind:" + buffer);
//把position设为0,limit不变,取消mark,一般在把数据重写入Buffer前调用
buffer.rewind();
System.out.println("before rewind:" + buffer);
System.out.println("--------Test compact--------");
buffer.clear();
buffer.put("abcd".getBytes());
System.out.println("before compact:" + buffer);
System.out.println(new String(buffer.array()));
buffer.flip();
System.out.println("after flip:" + buffer);
System.out.println((char) buffer.get());
System.out.println((char) buffer.get());
System.out.println("after 2 gets:" + buffer);
//compact()方法将所有未读的数据拷贝到Buffer起始处。然后将position设到最后一个未读元素正后面
buffer.compact();
System.out.println("after compact:" + buffer);
System.out.println("\t" + new String(buffer.array()));
System.out.println("------Test get-------------");
buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(32);
String s = "123456";
buffer.put(s.getBytes());
System.out.println("before flip()" + buffer);
// 转换为读取模式,flip才能从position(置为0)开始读取到limit的数据
buffer.flip();
System.out.println("after flip():" + buffer);
//相对读,从position位置读取一个byte,并将position+1,为下次读写作准备
System.out.println((char) buffer.get());
System.out.println("after get():" + buffer);
//绝对读,读取byteBuffer底层的bytes中下标为index的byte,不改变position
System.out.println((char) buffer.get(2));
System.out.println("after get(index):" + buffer);
byte[] dst = new byte[5];
//从position位置开始相对读,读length个byte,并写入dst下标从offset到offset+length的区域
buffer.get(dst, 3, 1);
System.out.println("after get(dst, 3, 2):" + buffer);
for (int i = 0; i < dst.length; i++) {
System.out.println("dst[i]:" + dst[i]);
}
System.out.println("buffer now is:" + buffer);
System.out.println("--------Test put-------");
ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocate(32);
System.out.println("before put(byte):" + bb);
//相对写,向position的位置写入一个byte,并将postion+1,为下次读写作准备
bb.put((byte) 'z');
System.out.println("after put(byte):" + bb);
//绝对写,向byteBuffer底层的bytes中下标为index的位置插入byte b,不改变position
bb.put(5, (byte) 'c');
System.out.println("after put(5,(byte) 'c'):" + bb);
// 这里的buffer是 abcdef[pos=3 lim=6 cap=32]
bb.put(buffer);
System.out.println("after put(buffer):" + bb);
byte[] bytes = new byte[4];
ByteBuffer buffer2 = ByteBuffer.wrap(bytes);
bb.put(bytes, 0, bytes.length);
System.out.println("after put(bytes):" + bb);
/////
ByteBuffer directBuffer=ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(10);
}
}
2.MappedByteBuffer
MappedByteBuffer文件内存映射,常用于操作读写大文件。
public class TestMappedByteBuffer {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
int length = 0x00006;//一个Byte占1B
try (FileChannel channel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("D:\\test\\2\\TestMappedByteBuffer.txt"),
StandardOpenOption.READ, StandardOpenOption.WRITE);) {
MappedByteBuffer mapBuffer = channel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, length);
for(int i=0;i3 Netty的ByteBuf
Netty的 Zero-coyp 完全是在用户态(Java 层面)的,在操作数据时,
不需要将数据 buffer 从一个内存区域拷贝到另一个内存区域. 少了一次内存的拷贝
Netty 的 Zero-copy 体现在如下几个个方面:
*
- Netty 提供了 CompositeByteBuf 类, 它可以将多个 ByteBuf 合并为一个逻辑上的 ByteBuf, 避免了各个 ByteBuf 之间的拷贝.
*- 通过 wrap 操作, 我们可以将 byte[] 数组、ByteBuf、ByteBuffer等包装成一个 Netty ByteBuf 对象, 进而避免了拷贝操作.
*- ByteBuf 支持 slice 操作, 因此可以将 ByteBuf 分解为多个共享同一个存储区域的 ByteBuf, 避免了内存的拷贝.
*- 通过 FileRegion 包装的FileChannel.tranferTo 实现文件传输, 可以直接将文件缓冲区的数据发送到目标 Channel, 避免了传统通过循环 write 方式导致的内存拷贝问题.
public class TestByteBuf {
public static String convertByteBufToString(ByteBuf buf) {
String str;
if (buf.hasArray()) {
// 处理堆缓冲区
str = new String(buf.array(), buf.arrayOffset() + buf.readerIndex(), buf.readableBytes());
} else { // 处理直接缓冲区以及复合缓冲区
byte[] bytes = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];
buf.getBytes(buf.readerIndex(), bytes);
str = new String(bytes, 0, buf.readableBytes());
}
return str;
}
public static ByteBuf convertStringToByteBuf(String str) {
return Unpooled.wrappedBuffer("abcdef".getBytes());
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//默认是创建heap buffer
System.out.print("\n-------test heapBuf----\n");
ByteBuf byteBuf1 = Unpooled.buffer(5);
//写数据
byteBuf1.writeBytes("abcdefgh".getBytes("utf-8"));
byteBuf1.setByte(0,(byte)'1');
//读数据
for (int i = 0; i < byteBuf1.capacity(); i++) {
System.out.print("\n-------test heapBuf----buf.getByte:" + (byteBuf1.getByte(i)));
}
System.out.printf("\n-------test heapBuf's capcity:" +byteBuf1.capacity());
System.out.printf("\n-------test heapBuf's ----convertByteBufToString(byteBuf1):" + convertByteBufToString(byteBuf1));
/**
* 通过 CompositeByteBuf 实现零拷贝,添加ByteBuf到CompositeByteBuf
* CompositeByteBuf 类, 它可以将多个 ByteBuf 合并为一个逻辑上的 ByteBuf, 避免了各个 ByteBuf 之间的拷贝
* CompositeByteBuf和添加的ByteBuf共用存储空间
*/
System.out.print("\n-------test CompositeByteBuf----\n");
//组合缓冲区
CompositeByteBuf compBuf = Unpooled.compositeBuffer();
//堆缓冲区
ByteBuf heapBuf = Unpooled.buffer(4);
//直接缓冲区
ByteBuf directBuf = Unpooled.directBuffer(4);
heapBuf.writeBytes("a".getBytes());
directBuf.writeBytes("ef".getBytes());
compBuf.addComponents(true, heapBuf, directBuf);
compBuf.writeBytes("cdgh".getBytes());
compBuf.setByte(0,(byte)'g');
System.out.printf("\n-------test CompositeByteBuf:" + heapBuf);
System.out.printf("\n-------test CompositeByteBuf:" + directBuf);
System.out.printf("\n-------test CompositeByteBuf:" + compBuf);
System.out.printf("\n-------test CompositeByteBuf heapBuf:" + convertByteBufToString(heapBuf));
System.out.printf("\n-------test CompositeByteBuf directBuf:" + convertByteBufToString(directBuf));
System.out.printf("\n-------test CompositeByteBuf compBuf:" + convertByteBufToString(compBuf));
//查看内存地址
AddressPrint addressPrint=new AddressPrint();
System.out.printf("\n-------test CompositeByteBuf heapBuf address:%s;directBuf address:%s;compBuf address:%s;",addressPrint.addressOf(heapBuf.getByte(0)),addressPrint.addressOf(directBuf.getByte(0)),addressPrint.addressOf(compBuf.getByte(0)));
/**
* 额外的拷贝将byte 数组拷贝到 ByteBuf
*/
/*ByteBuf byteBuf = Unpooled.buffer();
byteBuf.writeBytes(bytes2);*/
/**
* 通过 wrap 操作, 可以将 byte[] 数组、ByteBuf、ByteBuffer等包装成一个 Netty ByteBuf 对象, 进而避免了拷贝操作
* ByteBuf 对象是和 bytes 数组共用了同一个存储空间, 对 bytes 的修改也会反映到 ByteBuf 对象中
*/
ByteBuf byteBuf = Unpooled.wrappedBuffer("abcdef".getBytes());
/**
* 通过 slice 操作,slice 操作可以将一个 ByteBuf 切片 为多个共享一个存储区域的 ByteBuf 对象
*/
ByteBuf byteBuf3 = Unpooled.buffer(16);
byteBuf3.writeBytes("abcdef".getBytes());
ByteBuf header = byteBuf3.slice(0, 5);
ByteBuf body = byteBuf3.slice(5, 10);
System.out.printf("\n-------test wrap,slice----byteBuf3:" + byteBuf3);
System.out.printf("\n-------test wrap,slice----header:" + header);
System.out.printf("\n-------test wrap,slice----body:" + body);
System.out.printf("\n-------test wrap,slice----byteBuf3 address:%s;header address:%s;body address:%s;",addressPrint.addressOf(byteBuf3.getByte(0)),addressPrint.addressOf(header.getByte(0)),addressPrint.addressOf(body.getByte(0)));
/**
*
*/
ByteBuf buf1 = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Netty in Action test!", CharsetUtil.UTF_8);
//复制ByteBuf 0-14位置的内容
ByteBuf copy = buf1.copy(0, 14);
//同样修改内容
buf1.setByte(0, (byte) 'J');
//复制缓冲和原始缓冲并没有共享数据
System.out.print("\nbuf1.getByte(0)" + (char) buf1.getByte(0));
System.out.print("\ncopy.getByte(0)" + (char) copy.getByte(0));
////////////netty池化的内存分配:PooledByteBufAllocator采用了jemalloc内存分配算法///////////
ByteBuf poolBuf = PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer(5);
poolBuf.writeBytes("abc".getBytes());
}
public static class AddressPrint {
private Unsafe unsafe;
{
try
{
Field field = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
field.setAccessible(true);
unsafe = (Unsafe)field.get(null);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public String addressOf(Object o)
throws Exception
{
Object[] array = new Object[] {o};
long baseOffset = unsafe.arrayBaseOffset(Object[].class);
int addressSize = unsafe.addressSize();
long objectAddress;
switch (addressSize)
{
case 4:
objectAddress = unsafe.getInt(array, baseOffset);
break;
case 8:
objectAddress = unsafe.getLong(array, baseOffset);
break;
default:
throw new Error("unsupported address size: " + addressSize);
}
return(Long.toHexString(objectAddress));
}
public void printBytes(long objectAddress, int num)
{
for (long i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
int cur = unsafe.getByte(objectAddress + i);
System.out.print((char)cur);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
4.测试
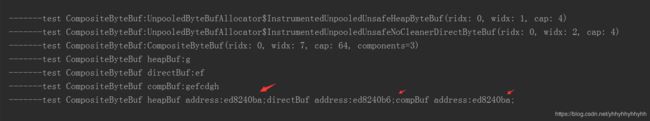
1)CompositeByteBuf组合缓存区的首字节内存地址和添加的ByteBuf的首字节内存地址关系:
//组合缓冲区
CompositeByteBuf compBuf = Unpooled.compositeBuffer();
//堆缓冲区
ByteBuf heapBuf = Unpooled.buffer(4);
//直接缓冲区
ByteBuf directBuf = Unpooled.directBuffer(4);
heapBuf.writeBytes("a".getBytes());
directBuf.writeBytes("ef".getBytes());
compBuf.addComponents(true, heapBuf, directBuf);
compBuf.writeBytes("cdgh".getBytes());
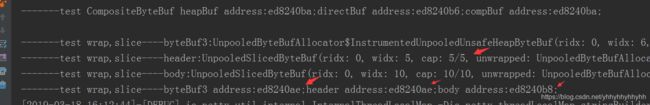
2)slice后各ByteBuf的首字节内存地址关系:
ByteBuf byteBuf3 = Unpooled.buffer(16);
byteBuf3.writeBytes("abcdef".getBytes());
ByteBuf header = byteBuf3.slice(0, 5);
ByteBuf body = byteBuf3.slice(5, 10);